Market Overview
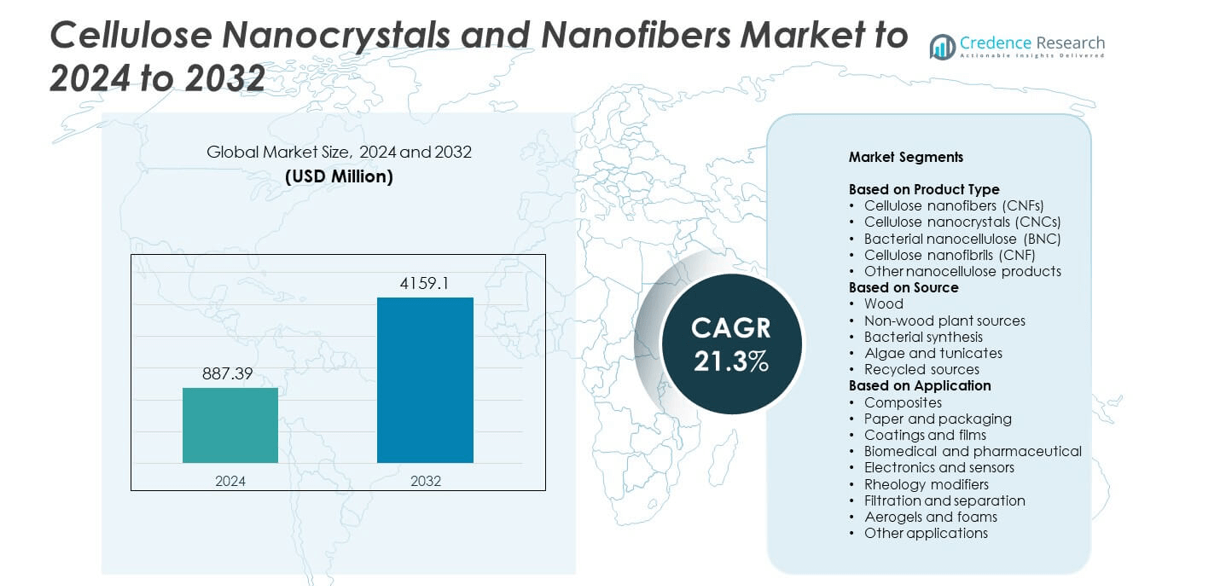
Cellulose Nanocrystals and Nanofibers Market size was valued at USD 887.39 million in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 4159.1 million by 2032, at a CAGR of 21.3% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Cellulose Nanocrystals and Nanofibers Market Size 2024 |
USD 887.39 million |
| Cellulose Nanocrystals and Nanofibers Market, CAGR |
21.3% |
| Cellulose Nanocrystals and Nanofibers Market Size 2032 |
USD 4159.1 million |
The Cellulose Nanocrystals and Nanofibers Market includes major players such as Melodea, UPM, FiberLean Technologies, Stora Enso, Kruger Inc., CelluForce, Borregaard AS, Sappi, Nippon Paper Industries, and CelluComp. These companies strengthen their presence through large-scale pulp integration, advanced refining technologies, and expansion into high-value applications such as coatings, packaging, composites, and filtration. North America leads the global market with about 37% share, supported by strong commercialization activity and steady raw material supply. Europe follows with nearly 32% share due to strict sustainability mandates and well-established pulp industries. Asia Pacific holds around 24% share, driven by expanding electronics, packaging, and advanced materials demand.
Market Insights
- The Cellulose Nanocrystals and Nanofibers Market was valued at USD 887.39 million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 4159.1 million by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 21.3%.
- Demand rises as industries shift to bio-based materials, with cellulose nanofibers holding about 42% share due to strong adoption in packaging, coatings, and composites.
- Trends include growth in plastic-free packaging, functionalized nanocellulose for electronics, and rising use in filtration and biomedical products as companies seek high-performance renewable materials.
- Competition strengthens as global producers expand refining capacity, improve surface modification, and partner with packaging, automotive, and electronics sectors to scale commercial use.
- North America leads with about 37% share, followed by Europe at 32% and Asia Pacific at 24%, while paper and packaging remain the largest application segment with nearly 38% share across global markets.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Product Type
Cellulose nanofibers lead this segment with about 42% share due to broad use in packaging, coatings, and strength-improving composites. CNFs offer high tensile strength, low density, and strong barrier properties, which drive adoption across sustainable material projects. Growth rises as manufacturers shift to bio-based reinforcements to replace petroleum materials. CNCs grow steadily because they support electronics and biomedical films, while bacterial nanocellulose gains traction in wound care. Other nanocellulose products expand in niche areas such as specialty foams and filtration aids.
- For instance, Nippon Paper Industries runs a TEMPO-oxidized cellulose nanofiber plant in Ishinomaki. The facility has production capacity of 500 tons per year.
By Source
Wood dominates the source segment with nearly 63% share because wood pulp offers reliable supply, low cost, and large-scale processing efficiency. The pulp industry provides established refining systems that help meet rising nanocellulose demand for packaging and composite applications. Non-wood plants grow at a fast rate due to agricultural residue use, while bacterial synthesis supports high-purity medical grades. Algae and tunicates remain limited but valuable for specialty nano-reinforcements. Recycled sources gain attention as brands adopt circular material strategies.
- For instance, CelluForce in Canada operates what is described as the world’s largest cellulose nanocrystal plant. The facility can produce 300 tonnes of sulfated CNC per year from wood pulp.
By Application
Paper and packaging lead this segment with around 38% share because nanocellulose improves strength, printability, and barrier performance in lightweight packaging. The shift toward plastic-free packaging boosts this category as converters adopt CNF coatings and CNC films to replace synthetic layers. Composites gain steady demand from automotive and construction due to weight reduction efforts. Coatings, electronics, and rheology modifiers rise with growth in advanced materials. Biomedical, filtration, and aerogel applications expand as firms explore high-value specialty uses.
Key Growth Drivers
Rising Demand for Sustainable Materials
Global industries shift toward low-carbon materials, which increases the use of nanocellulose in packaging, coatings, and composites. Cellulose nanocrystals and nanofibers replace petroleum materials due to strong mechanical strength and biodegradability. Brands in food, cosmetics, and consumer goods adopt these bio-based reinforcements to meet stricter waste rules. Growing investment in renewable materials strengthens commercial scale-up across major regions.
- For instance, Stora Enso’s rebuilt consumer packaging board line at its Oulu mill is designed for annual capacity of 750,000 tonnes of folding boxboard and coated unbleached kraft.
Expansion of Advanced Composites
Lightweight composite demand rises in automotive, aerospace, and construction, boosting nanocellulose adoption. Nanocellulose improves stiffness, fatigue resistance, and bonding strength, helping manufacturers reduce weight without losing performance. Countries promote green mobility and low-emission construction, which accelerates composite innovation. New hybrid composites with CNCs and CNFs support wider structural applications.
- For instance, Borregaard’s Exilva plant in Norway can supply microfibrillated cellulose equivalent to about 1,000 tons of dry fibrils each year.
Growth in High-Value Applications
Biomedical, electronics, and filtration sectors expand their nanocellulose use due to high purity, tunable surface chemistry, and strong biocompatibility. Demand rises for wound dressings, implant coatings, sensors, and membrane systems. Companies explore high-margin uses where nanocellulose enables conductivity control, moisture regulation, and selective filtration. Advancements in nano-engineered films improve commercialization in premium applications.
Key Trends and Opportunities
Shift Toward Plastic-Free Packaging
Brands accelerate the move away from single-use plastics, creating strong interest in CNF-based barrier coatings and CNC films. Nanocellulose enhances water resistance, oxygen blocking, and print quality, supporting recyclable packaging lines. Countries enforcing stricter plastic bans raise demand for bio-barrier solutions. Packaging converters invest in scalable nanocellulose formulations for cups, flexible packs, and cartons.
- For instance, Tetra Pak reported producing 179 billion paper-based carton packages in 2023, and its large-scale validation of an aseptic package with a paper-based barrier with Lactogal has involved 25 million packages since 2023, demonstrating an industry-scale move away from plastic-intensive formats.
Advances in Nanocellulose Functionalization
Surface modification techniques improve compatibility of nanocellulose with polymers, resins, and hybrid materials. This trend supports growth in electronics, specialty coatings, and energy storage products. Functionalized CNCs offer improved conductivity and thermal stability, enabling new sensor and display applications. Opportunities rise as companies invest in tailored chemistries for sector-specific needs.
- For instance, Betulium in Finland supplies phosphorylated cellulose nanofibers where the phosphate group content is specified at about 0.66 and 1 millimole per gram for different grades.
Growing Use in Filtration and Water Treatment
Nanocellulose gains attention in membranes due to high surface area and strong contaminant-binding ability. Demand increases for sustainable filtration systems in industrial wastewater, desalination, and air purification. CNF-based membranes improve durability and selectivity, which helps reduce reliance on synthetic polymers. Emerging markets adopt eco-friendly solutions for growing water scarcity.
Key Challenges
High Production and Processing Costs
Nanocellulose extraction, drying, and surface modification require energy-intensive steps and advanced equipment, which raises production cost. Scale limitations restrict supply, affecting price competitiveness against synthetic materials. Companies work to reduce cost through continuous refining, enzymatic pretreatment, and improved drying technologies. Wider industrial adoption depends on lowering processing complexity.
Limited Standardization and Performance Variability
Nanocellulose properties vary due to differences in source, extraction method, and processing conditions. This lack of consistency complicates adoption in sectors that need uniform performance. Absence of global standards affects certification and testing frameworks. Industries require strict material stability to integrate nanocellulose into long-term commercial products.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America holds about 37% share in the Cellulose Nanocrystals and Nanofibers Market in 2024. The region benefits from strong demand for sustainable packaging, advanced composites, and biomedical materials. Research institutions and startups accelerate product innovation using CNCs and CNFs for coatings, filters, and electronic films. The United States leads adoption due to active commercialization efforts and supportive environmental regulations. Canadian pulp producers contribute to stable raw material supply. Investments in pilot-scale plants help expand regional production capacity and strengthen the presence of nanocellulose in high-performance industrial applications.
Europe
Europe accounts for nearly 32% share, driven by strict sustainability laws and strong interest in renewable packaging materials. Countries such as Sweden, Finland, and Germany lead due to advanced pulp industries and higher adoption of lightweight composites. Demand rises across automotive, construction, and specialty coatings as companies replace synthetic fibers with bio-based alternatives. The region also expands medical and cosmetic applications supported by biocompatibility advantages. EU circular economy policies further encourage nanocellulose integration across industrial sectors. Collaborative projects between universities and manufacturers strengthen long-term market growth prospects.
Asia Pacific
Asia Pacific holds around 24% share and grows rapidly due to expanding paper, packaging, and electronics industries. China and Japan dominate regional production as they scale nanocellulose for films, sensors, and strength-enhanced packaging. India and South Korea adopt CNF-based coatings in food packaging to meet rising sustainability regulations. Strong pulp availability and low-cost processing also support regional growth. Increasing investment in advanced composites for vehicles and infrastructure projects strengthens long-term demand. Government-backed research programs help accelerate technology transfer from laboratories to commercial manufacturing.
Latin America
Latin America captures about 4% share, supported by the region’s strong pulp and paper base. Brazil and Chile lead due to their large forestry industries and emerging interest in bio-based specialty materials. Packaging producers explore CNF coatings to improve recyclability and reduce plastic use. Adoption remains moderate but grows as local industries seek cost-effective renewable additives. Universities collaborate with manufacturers to develop nanocellulose applications for agriculture, construction, and water filtration. Limited large-scale production capacity slows growth, but rising sustainability targets improve long-term demand potential.
Middle East and Africa
The Middle East and Africa hold nearly 3% share, reflecting early-stage adoption and limited processing capacity. Demand grows slowly in packaging, construction additives, and filtration markets. Countries in the Gulf region explore nanocellulose for lightweight composites and water treatment membranes due to rising desalination needs. South Africa shows interest in agricultural and industrial applications using locally sourced biomass. Market expansion is constrained by high production cost and fewer research facilities. However, increasing focus on renewable materials and rising investment in green technologies gradually support regional development.
Market Segmentations:
By Product Type
- Cellulose nanofibers (CNFs)
- Cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs)
- Bacterial nanocellulose (BNC)
- Cellulose nanofibrils (CNF)
- Other nanocellulose products
By Source
- Wood
- Non-wood plant sources
- Bacterial synthesis
- Algae and tunicates
- Recycled sources
By Application
- Composites
- Paper and packaging
- Coatings and films
- Biomedical and pharmaceutical
- Electronics and sensors
- Rheology modifiers
- Filtration and separation
- Aerogels and foams
- Other applications
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
The Cellulose Nanocrystals and Nanofibers Market features key players such as Melodea, UPM, FiberLean Technologies, Stora Enso, Kruger Inc., CelluForce, Borregaard AS, Sappi, Nippon Paper Industries, and CelluComp. These companies expand their presence through scaling production capacity, improving refining technologies, and advancing high-performance nanocellulose grades for packaging, coatings, composites, and filtration applications. Market participants focus on enhancing barrier properties, mechanical strength, and compatibility with polymers to support broader industrial use. Strong investment flows into pilot plants and commercial facilities to reduce processing costs and support mass adoption. Partnerships with automotive, packaging, and electronics manufacturers help accelerate material qualification and certification. Firms also invest in surface modification, functionalized nanocellulose, and hybrid formulations to target premium applications in biomedical devices, electronics, and specialty coatings. Sustainability commitments and rising regulations on single-use plastics strengthen competition, pushing companies to deliver reliable and scalable bio-based material solutions.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
- Melodea
- UPM
- FiberLean Technologies
- Stora Enso
- Kruger Inc.
- CelluForce
- Borregaard AS
- Sappi
- Nippon Paper Industries
- CelluComp
Recent Developments
- In 2025, CelluForce continues to lead in the production of high-quality sulfated cellulose nanocrystals, branded as CelluRods®, which are biodegradable with a low carbon footprint.
- In 2025, Stora Enso heavily invests in nanocellulose within its bio-based materials strategy. Efforts center on using cellulose nanofibers in sustainable packaging and advanced fiber composites.
- In 2024, FiberLean Technologies was acquired by United Bankers’ UB FIGG fund, and continues to produce mineral-nanocellulose (microfibrillated cellulose) composites for industrial applications, particularly in the paper and packaging industries.
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Product Type, Source, Application and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- The market will grow rapidly as industries shift to bio-based materials.
- Packaging producers will adopt nanocellulose coatings to replace plastic layers.
- Advanced composites will expand use of CNCs and CNFs in automotive and construction.
- Electronics firms will explore nanocellulose films for sensors and flexible devices.
- Biomedical applications will rise due to strong biocompatibility and purity.
- Filtration systems will integrate nanocellulose membranes for cleaner water solutions.
- Production capacity will expand through pilot plants and large-scale refining units.
- Surface-modified nanocellulose will unlock new high-value applications.
- Costs will decline as processing efficiency improves across global facilities.
- Circular economy policies will push wider adoption in packaging and industrial products.




