Market Overview
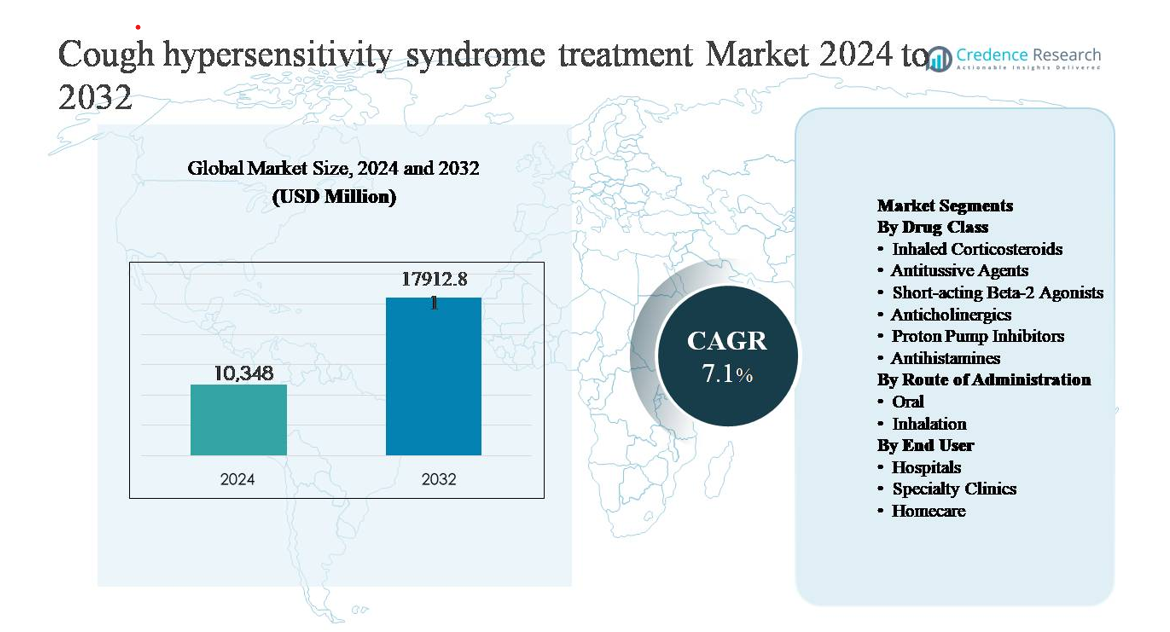
The cough hypersensitivity syndrome treatment market was valued at USD 10,348 million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 17,912.81 million by 2032, expanding at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.1% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Cough Hypersensitivity Syndrome Treatment Market Size 2024 |
USD 10,348 million |
| Cough Hypersensitivity Syndrome Treatment Market, CAGR |
7.1% |
| Cough Hypersensitivity Syndrome Treatment Market Size 2032 |
USD 17,912.81 million |
The cough hypersensitivity syndrome treatment market is led by established pharmaceutical companies with strong respiratory and specialty care portfolios, including Pfizer Inc., GlaxoSmithKline plc, Novartis AG, AstraZeneca, Sanofi, Merck & Co., Johnson & Johnson, Bayer AG, Boehringer Ingelheim, Teva Pharmaceutical Industries, Mylan, Akorn, and Prestige Consumer Healthcare. These players compete through broad antitussive and respiratory drug portfolios, global distribution networks, and continued investment in innovation for chronic cough management. North America leads the market with a 38% share, driven by high diagnosis rates, advanced specialist care, and early adoption of novel therapies. Europe follows with a 29% share, supported by strong public healthcare systems and guideline-based treatment adoption, while Asia Pacific holds 22%, reflecting rapid growth from expanding access and rising awareness.
Market Insights
- The cough hypersensitivity syndrome treatment market was valued at USD 10,348 million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 17,912.81 million by 2032, expanding at a CAGR of 7.1%, reflecting growing recognition of chronic refractory cough and expanding therapeutic adoption globally.
- Market growth is primarily driven by rising diagnosis of cough hypersensitivity syndrome, increasing prevalence of chronic cough linked to respiratory and gastrointestinal comorbidities, and expanding use of targeted antitussive agents and neuromodulators in long-term management.
- Key market trends include a shift toward mechanism-based therapies targeting sensory nerve dysfunction, increasing preference for oral formulations, and growing dominance of antitussive agents as the leading drug class segment, supported by broad clinical use and patient compliance.
- The competitive landscape is shaped by established pharmaceutical companies competing through broad respiratory portfolios, global distribution, and innovation in chronic cough therapies, with differentiation centered on efficacy, tolerability, and outpatient suitability.
- Regionally, North America leads with 38% market share, followed by Europe at 29% and Asia Pacific at 22%, while hospitals remain the dominant end-user segment due to higher diagnosis rates and specialist-driven treatment initiation.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Drug Class:
The drug class segment is dominated by antitussive agents, which account for the largest market share due to their direct action on cough reflex pathways and widespread use in chronic and refractory cough management. Centrally acting and peripherally acting antitussives are increasingly prescribed as first-line symptomatic therapies, particularly in patients unresponsive to conventional treatments. Growth is further driven by rising adoption of neuromodulators and late-stage P2X3 receptor antagonists targeting sensory nerve hypersensitivity. Inhaled corticosteroids and proton pump inhibitors maintain steady demand, supported by overlapping respiratory and gastroesophageal comorbidities.
- “For instance, Merck’s peripherally actingP2X3 receptor antagonist gefapixant demonstrated clinically meaningful cough frequency reduction in the Phase 3 COUGH-1 and COUGH-2 trials, which together enrolled over 2,000 adult patients, using an optimized oral dose of 45 mg twice daily.”
By Route of Administration:
The oral route of administration represents the dominant sub-segment, holding the highest market share owing to ease of administration, better patient compliance, and the availability of a wide range of oral antitussives, neuromodulators, and adjunct therapies. Oral formulations are preferred in long-term management of chronic cough and hypersensitivity conditions, particularly in outpatient and homecare settings. Market growth is supported by ongoing development of novel oral small-molecule therapies with improved tolerability. Inhalation routes remain important for corticosteroids and bronchodilators but serve a more adjunctive role.
- For instamce, Budesonide dry-powder inhalers are routinely prescribed at a daily dose of 200–400 µg (often divided into two actuations, e.g., 200 µg twice daily or two 100 µg puffs) for airway inflammation associated with conditions like asthma, and short-acting bronchodilators such as salbutamol deliver 100 µg per inhalation.
By End User:
Hospitals constitute the dominant end-user segment, driven by higher diagnosis rates of chronic and refractory cough, access to multidisciplinary respiratory care, and use of advanced diagnostic protocols. Hospitals manage complex cases requiring specialist evaluation, drug initiation, and monitoring of emerging therapies. The segment benefits from increasing referrals for unexplained chronic cough and participation in clinical trials for novel treatments. Specialty clinics are expanding rapidly due to focused cough management programs, while homecare adoption grows steadily with long-term oral therapy use and telemedicine-supported follow-ups.
Key Growth Drivers
Rising Prevalence and Improved Clinical Recognition of Chronic Cough Disorders
Growing awareness of cough hypersensitivity syndrome as a distinct clinical entity is a major driver of market expansion. Historically underdiagnosed, the condition is now increasingly recognized in patients with refractory and unexplained chronic cough, supported by updated clinical guidelines and specialist consensus. Pulmonologists and otolaryngologists are adopting structured diagnostic algorithms to differentiate hypersensitivity-driven cough from asthma, GERD, or postnasal drip. This improved recognition expands the treatable patient pool and drives demand for targeted pharmacological therapies. Aging populations, higher exposure to environmental irritants, and rising prevalence of comorbid respiratory and gastrointestinal conditions further contribute to sustained growth in treatment adoption across developed and emerging healthcare systems.
- For instance, the European Respiratory Society (ERS) clinical task force formalized chronic cough as a cough hypersensitivity syndrome (CHS) concept, drawing on existing literature and expert opinion to directly influence diagnostic and treatment approaches in specialist respiratory clinics.”
Advancements in Targeted Pharmacological Therapies
The development of novel therapies that directly target sensory nerve dysfunction is significantly accelerating market growth. Traditional symptomatic treatments are increasingly complemented by neuromodulators and next-generation antitussive agents designed to suppress aberrant cough reflex sensitivity. Late-stage clinical development of P2X3 receptor antagonists has reshaped therapeutic expectations by addressing underlying neurogenic mechanisms rather than only symptomatic relief. Improved efficacy profiles, better tolerability, and oral administration formats are supporting broader physician acceptance and long-term patient adherence. These innovations are expanding treatment options for patients who fail standard therapies, strengthening clinical confidence and driving prescription volumes in specialized respiratory care settings.
- For instance, investigator-initiated clinical studies evaluating gabapentin in refractory chronic cough applied titrated oral doses up to 1,800 mg per day, documenting measurable reductions in objective cough counts and symptom severity scores.
Expansion of Specialist Care and Structured Treatment Pathways
The growing role of specialty cough clinics and multidisciplinary respiratory care centers is reinforcing market growth. These settings enable comprehensive assessment, accurate diagnosis, and individualized treatment plans for patients with chronic cough hypersensitivity. Increased referrals from primary care providers to pulmonology and otolaryngology specialists improve diagnosis rates and treatment initiation. Standardized care pathways and follow-up protocols support long-term therapy use, particularly for oral antitussives and neuromodulators. The expansion of hospital-based cough programs and integration of telemedicine for follow-up management further increase treatment continuity, supporting sustained demand across hospital and outpatient care environments.
Key Trends & Opportunities
Shift Toward Mechanism-Based and Precision Therapies
A key trend shaping the market is the transition from empiric symptomatic management to mechanism-driven treatment strategies. Pharmaceutical development increasingly focuses on therapies targeting specific neural pathways responsible for cough hypersensitivity, enabling more predictable outcomes. This shift creates opportunities for precision medicine approaches that tailor therapy based on cough phenotype and patient response. As diagnostic tools improve, clinicians are better positioned to match patients with appropriate treatments, enhancing clinical outcomes and reducing trial-and-error prescribing. This evolution supports premium therapy adoption and long-term treatment persistence in chronic cases.
- For instance, Bellus Health engineered BLU-5937 (camlipixant) to preferentially block P2X3 homotrimeric receptorswhile sparing P2X2/3 heterotrimers, aiming to reduce taste-related side effects. Its Phase 2 clinical program, specifically the RELIEF trial and the subsequent SOOTHE trial, evaluated twice-daily (BID) oral dosing at various levels (including 25 mg, 50 mg, 100 mg, and 200 mg).
Growing Adoption of Oral Therapies in Outpatient and Homecare Settings
The increasing use of oral formulations is expanding treatment beyond hospital environments into specialty clinics and homecare. Oral therapies offer ease of administration, improved adherence, and suitability for long-term management, making them ideal for chronic cough hypersensitivity. This trend aligns with broader healthcare shifts toward outpatient care and remote monitoring. Teleconsultations and digital symptom-tracking tools further enhance patient engagement and therapy optimization. These developments create opportunities for pharmaceutical companies to expand market reach through patient-centric treatment models and extended-duration therapy strategies.
- For instance, controlled clinical use of gabapentin for refractory chronic cough employs gradual oral titration up to 1,800 mg per day, allowing dosing adjustments to be managed through outpatient follow-up rather than inpatient monitoring.
Key Challenges
Diagnostic Complexity and Overlapping Etiologies
Accurate diagnosis of cough hypersensitivity syndrome remains a significant challenge due to symptom overlap with asthma, GERD, upper airway cough syndrome, and other chronic respiratory conditions. Lack of definitive biomarkers and reliance on exclusion-based diagnosis can delay treatment initiation and limit therapy uptake. Variability in physician awareness and access to specialist evaluation further complicates consistent diagnosis across regions. These factors constrain market growth by reducing the addressable patient population and prolonging treatment pathways, particularly in primary care settings.
Treatment Adherence and Tolerability Concerns
Long-term management of cough hypersensitivity syndrome often requires extended pharmacotherapy, raising concerns around tolerability, side effects, and patient adherence. Neuromodulators and centrally acting antitussives may cause sensory disturbances or central nervous system effects, leading to discontinuation in some patients. Inconsistent symptom improvement can also affect patient confidence in therapy. These challenges place pressure on clinicians to balance efficacy with safety and highlight the need for better-tolerated treatments, which remains a critical barrier to sustained therapy adoption.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America dominates the cough hypersensitivity syndrome treatment market with an estimated 38% share, supported by high awareness, early diagnosis, and strong specialist access. Well-established pulmonology and otolaryngology networks enable accurate identification of refractory and unexplained chronic cough. The region benefits from rapid adoption of novel antitussive agents, neuromodulators, and emerging mechanism-based therapies. Favorable reimbursement frameworks and strong clinical trial activity further reinforce treatment uptake. The United States leads regional demand, driven by advanced healthcare infrastructure, structured referral pathways, and high patient compliance with long-term oral therapies.
Europe
Europe accounts for approximately 29% of the global market, driven by robust public healthcare systems and widespread adherence to evidence-based respiratory treatment guidelines. Countries such as Germany, the UK, France, and Italy contribute significantly due to strong specialist care availability and increasing differentiation of cough hypersensitivity from asthma and GERD. Growing use of structured diagnostic pathways and rising acceptance of neuromodulators support steady market growth. Regulatory emphasis on chronic respiratory disease management and expanding access to innovative therapies continue to sustain Europe’s strong market position.
Asia Pacific
Asia Pacific holds around 22% market share and represents the fastest-growing regional segment. Growth is fueled by large patient populations, rising exposure to air pollution, and increasing prevalence of respiratory and gastrointestinal comorbidities. Improving healthcare infrastructure and expanding access to specialists in countries such as China, Japan, South Korea, and Australia are improving diagnosis rates. Increasing adoption of oral antitussives and long-term therapies in outpatient settings supports market expansion. Government healthcare investments and growing awareness of chronic cough conditions further accelerate regional growth.
Latin America
Latin America accounts for approximately 7% of the market, with Brazil and Mexico leading regional demand. Market growth is supported by gradual improvements in respiratory care access and increasing recognition of chronic cough disorders. Hospitals remain the primary treatment centers, with oral antitussives and adjunct therapies dominating prescriptions. However, variability in diagnostic practices and limited reimbursement for advanced therapies constrain faster adoption. Ongoing healthcare system modernization, rising specialist training, and improved patient awareness are expected to support steady but moderate market expansion.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region holds about 4% of the global market, reflecting limited diagnosis rates and uneven access to specialized respiratory care. Demand is concentrated in Gulf Cooperation Council countries, where higher healthcare spending and expanding specialty clinics support treatment uptake. Environmental factors such as dust exposure and smoking prevalence contribute to chronic cough incidence. However, reliance on symptomatic therapies and limited availability of advanced treatments restrict broader market growth. Gradual infrastructure development and increasing specialist availability are expected to drive incremental expansion.
Market Segmentations:
By Drug Class
- Inhaled Corticosteroids
- Antitussive Agents
- Short-acting Beta-2 Agonists
- Anticholinergics
- Proton Pump Inhibitors
- Antihistamines
By Route of Administration
By End User
- Hospitals
- Specialty Clinics
- Homecare
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape of the cough hypersensitivity syndrome treatment market is characterized by a mix of established pharmaceutical companies and emerging specialty drug developers focused on chronic cough and neurosensory disorders. Market participants compete through differentiated drug portfolios, strong respiratory franchise positioning, and investment in mechanism-based therapies that address underlying cough reflex hypersensitivity. Established players leverage broad distribution networks and physician relationships to sustain sales of conventional antitussives, inhaled therapies, and adjunct treatments. At the same time, innovation-driven companies are advancing targeted neuromodulators and next-generation antitussive agents through late-stage clinical development to capture unmet needs in refractory cough management. Strategic priorities include clinical trial expansion, regulatory approvals, and partnerships with respiratory specialists to strengthen market penetration. Competitive differentiation increasingly centers on efficacy, tolerability, oral formulation availability, and long-term patient adherence, shaping market dynamics over the forecast period.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
- Pfizer Inc. (U.S.)
- Novartis AG (Switzerland)
- GlaxoSmithKline plc (U.K.)
- AstraZeneca (U.K.)
- Sanofi (France)
- Merck & Co., Inc. (U.S.)
- Johnson & Johnson Private Limited (U.S.)
- Bayer AG (Germany)
- Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH (Germany)
- Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd. (Israel)
Recent Developments
- In October 2024, Sanofi reaffirmed its respiratory and immunology R&D focus during pipeline communications, highlighting continued research into type-2 inflammation and airway sensory signaling relevant to chronic respiratory symptoms. While Sanofi does not currently advance a dedicated P2X3 or cough-hypersensitivity specific molecule, its biologics research platforms continue to generate translational insights into neuro-immune interactions involved in persistent cough phenotypes associated with asthma and eosinophilic airway disease.
- In August 2024, Bayer highlighted progress within its cardiopulmonary and precision health research initiatives, including continued investigation of neural and inflammatory signaling pathways implicated in chronic respiratory symptoms. While Bayer does not have an active late-stage program specifically targeting cough hypersensitivity syndrome, its small-molecule research capabilities in ion channel modulation and sensory pharmacology remain relevant to long-term therapeutic opportunities in chronic cough management.
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Drug class, Route of administration, End-User and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- Growing clinical recognition of cough hypersensitivity syndrome will expand the diagnosed and treated patient population globally.
- Increased adoption of mechanism-based therapies will shift treatment approaches beyond symptomatic management.
- Continued development of targeted antitussive agents will improve efficacy in refractory and unexplained chronic cough.
- Oral formulations will gain wider acceptance due to convenience and suitability for long-term therapy.
- Specialty cough clinics will play a larger role in structured diagnosis and treatment optimization.
- Integration of digital health tools will support symptom monitoring and treatment adherence.
- Hospital-led initiation of therapy will remain critical for complex and severe cases.
- Expanding access to respiratory care in emerging markets will accelerate treatment uptake.
- Improved tolerability profiles will enhance long-term patient compliance.
- Collaboration between pharmaceutical companies and respiratory specialists will strengthen clinical adoption pathways.




