Market Overview
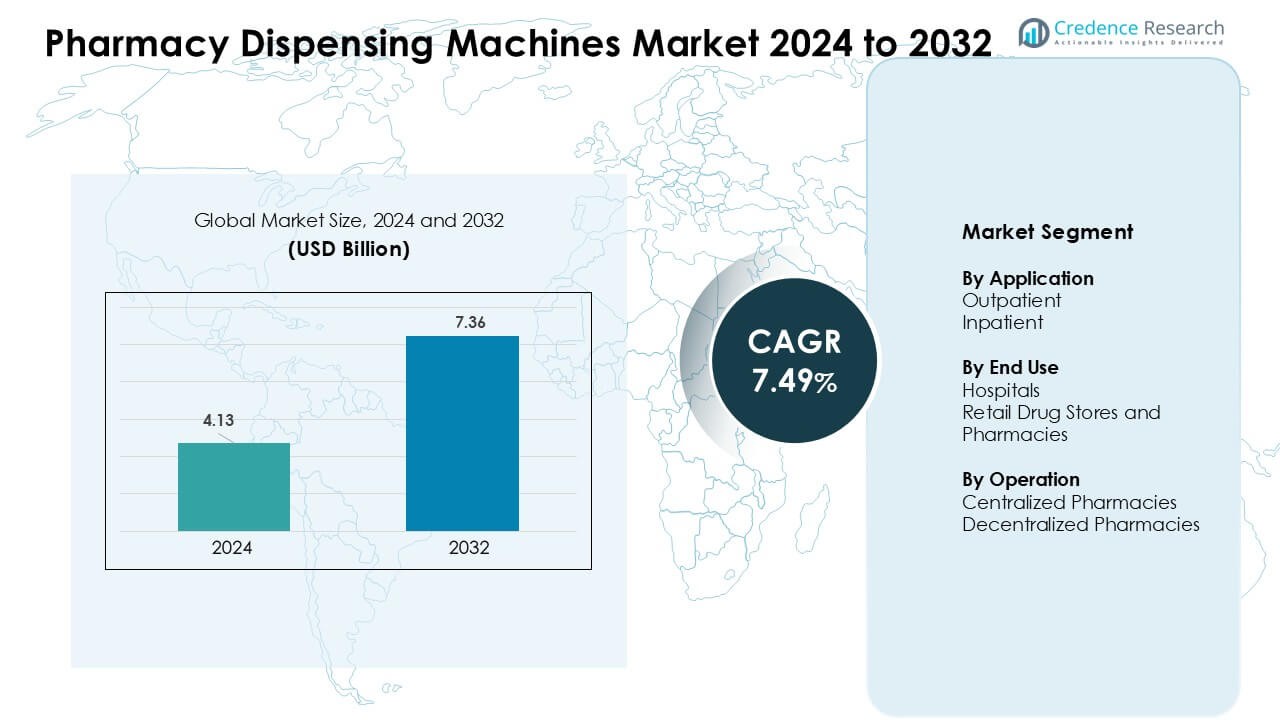
Pharmacy Dispensing Machines Market was valued at USD 4.13 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 7.36 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 7.49 % during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Pharmacy Dispensing Machines Market Size 2024 |
USD 4.13 Billion |
| Pharmacy Dispensing Machines Market, CAGR |
7.49 % |
| Pharmacy Dispensing Machines Market Size 2032 |
USD 7.36 Billion |
The Pharmacy Dispensing Machines Market is shaped by key players such as Capsa Healthcare, ScriptPro LLC, Omnicell, Inc., Baxter, Accu-Chart, BD, Avery Weigh-Tronix, and PEARSON MEDICAL TECHNOLOGIES. These companies compete by offering automated dispensing platforms that enhance medication accuracy, reduce manual workload, and support integrated digital workflows across hospitals and retail pharmacies. Vendors focus on robotics, real-time inventory control, and secure dispensing for high-risk drugs to strengthen adoption. North America led the market in 2024 with a 38% share, supported by strong healthcare digitalization, large hospital networks, and rapid uptake of advanced pharmacy automation systems.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Insights
- The Pharmacy Dispensing Machines Market was valued at USD 4.13 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 7.36 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 7.49%.
- Demand rises due to higher prescription volumes, workforce shortages, and the need for greater medication accuracy in hospitals and retail pharmacies.
- Trends include rapid adoption of robotics, barcode verification, AI-enabled inventory tools, and hybrid centralized–decentralized dispensing models across large healthcare networks.
- Competition intensifies among key players offering integrated systems that link with electronic prescriptions and EHR platforms, while smaller providers face restraints from high upfront costs and complex IT integration.
- North America led the market with about 38% share in 2024, while hospitals held the dominant end-use share; Asia Pacific grew fastest due to expanding healthcare infrastructure and rising digital transformation.
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Application
Outpatient dispensing held the dominant share in 2024 with about 58%. Outpatient demand rose as clinics and retail chains adopted automated systems to reduce wait time and manage rising prescription loads. These sites used machines to cut manual errors and improve pickup speed, which helped patient flow during peak hours. Growth also came from strong use of digital scripts and higher footfall at community clinics. Inpatient use expanded as hospitals focused on accuracy for high-risk drugs and tighter inventory control in wards and critical care units.
- For instance, Omnicell’s XT Automated Dispensing Cabinets use barcode-verified dispensing and real-time tracking to reduce medication selection errors and support high daily medication transaction volumes in outpatient pharmacy settings.
By End Use
Hospitals led the end-use segment in 2024 with nearly 62% share. Large hospital networks invested heavily in automated dispensing to support safe medication delivery and lower nurse workload. These systems improved tracking for controlled drugs and reduced delays in emergency units. Demand grew with the rise of integrated EMR platforms that linked machines with hospital IT systems. Retail drug stores and pharmacies also grew as chains deployed compact dispensing units to enhance speed, reduce stockouts, and manage rising chronic therapy volumes.
- For instance, Swisslog Healthcare states that its PillPick® system can dispense up to 10,000 unit doses per hour while achieving picking accuracy above 99.9%, enabling large hospitals to meet continuous inpatient medication demand
By Operation
Centralized pharmacies dominated the operation segment in 2024 with about 57% share. Central hubs allowed higher automation levels, bulk filling, and consistent quality checks, which pushed demand from major hospital systems. These centers used high-capacity robots to handle large prescription volumes and improve cost efficiency. Growth was driven by the shift toward hub-and-spoke models that supported same-day delivery and streamlined inventory planning. Decentralized pharmacies grew as smaller clinics and hospital departments adopted point-of-use systems for faster access and reduced medication turnaround time.
Key Growth Drivers
Growing Demand for Medication Accuracy and Patient Safety
Healthcare providers focus strongly on reducing medication errors as patient volumes rise. Pharmacy dispensing machines support this goal by automating counting, labeling, verification, and packaging tasks that normally rely on manual accuracy. Barcode validation, sealed unit-dose formats, and integration with electronic prescriptions help prevent dispensing mistakes. Hospitals use these systems to improve the safety of high-alert medications and maintain compliance with strict audit and reporting rules. Retail pharmacies also invest in automation to reduce misfills during peak hours. The broader movement toward quality-based care and lower adverse drug event rates drives steady adoption. As healthcare networks expand, the need for consistent, traceable, and error-free medication workflows strengthens this growth driver.
Rising Prescription Volumes and Workforce Constraints
Prescription counts increase each year due to chronic disease growth, aging populations, and expanded access to outpatient care. Pharmacies struggle with limited staffing and rising operational workloads, which makes automation essential for maintaining efficiency. Pharmacy dispensing machines reduce manual labor by automating repetitive tasks such as sorting, filling, and packaging. This shift frees pharmacists and technicians to focus on counseling, medication review, and clinical support. In hospitals, automated systems help manage heavy inpatient loads and support around-the-clock availability without expanding staff. Retail chains adopt compact machines to speed up service during high-traffic periods. These advantages align with the healthcare sector’s need for higher throughput, reduced overtime, and stable productivity under growing demand.
- For instance, ScriptPro documents that its robotic dispensing systems automate counting, labeling, and vial handling in a single workflow, enabling high-throughput prescription filling under continuous operation in retail pharmacy settings.
Integration with Digital Health Ecosystems and Connected Pharmacy Models
Digital health adoption expands quickly, and pharmacy dispensing machines integrate smoothly with electronic health records, e-prescriptions, and real-time inventory systems. This connectivity supports more accurate dispensing, faster verification, and seamless data sharing across multiple care locations. Integrated systems also reduce stockouts, improve controlled-substance tracking, and support automated audits. As telehealth grows, centralized automated hubs process prescriptions for home delivery and remote patient management. This digital alignment improves workflow visibility, enhances regulatory compliance, and strengthens operational consistency across large hospital and retail networks. The shift toward smart, connected pharmacies reinforces this growth driver and encourages broader investment in advanced automation.
- For instance, Omnicell confirms that its automation platforms integrate with major electronic medical record systems to enable real-time inventory visibility and closed-loop medication management across inpatient and outpatient settings.
Key Trends & Opportunities
Shift Toward Hybrid Centralized–Decentralized Pharmacy Models
Hospitals and pharmacy chains increasingly adopt hybrid automation that combines centralized high-volume hubs with decentralized point-of-care dispensing units. Centralized locations handle bulk filling, packaging, and verification at scale, while decentralized stations provide rapid access to medications in emergency units, wards, and clinics. This model boosts dispensing speed, reduces delays, and strengthens inventory accuracy across multiple sites. Retail networks also use hybrid systems to improve same-day delivery and local store replenishment. Vendors respond with flexible systems that sync real-time data across all nodes, enabling better demand forecasting and supply planning. This structural shift opens significant opportunities for scalable and network-wide automation.
- For instance, Capsa Healthcare states that its central pharmacy automation integrates with decentralized medication carts and cabinets, using barcode-supported workflows to improve dispensing accuracy and medication traceability in hospital settings.
Robotics, AI, and Advanced Automation Enhancements
Next-generation dispensing machines incorporate robotics, AI-driven analytics, machine-vision inspection, and automated packaging systems. Robotics improves speed and consistency, especially in centralized hubs that handle thousands of daily prescriptions. AI enhances demand forecasting, inventory optimization, and predictive maintenance, helping providers cut costs. Machine-vision tools detect fill errors or packaging defects before medicines reach patients. Touchless dispensing and compact robotic units attract both hospitals and retail chains seeking higher hygiene and faster service. These technological upgrades create strong opportunities for innovation, system replacement cycles, and expansion into smaller pharmacy environments with limited space.
- For instance, Parata Systems documents that its pharmacy automation platforms capture real-time usage data and automate inventory counting, supporting perpetual inventory accuracy and reducing manual stock-check workloads.
Key Challenges
High Upfront Investment and Integration Complexity
The purchase, installation, and integration of pharmacy dispensing machines require significant capital. Smaller hospitals, clinics, and independent retail pharmacies face budget constraints that slow adoption. Integration with existing IT systems such as EHR platforms, inventory systems, and billing tools adds cost and technical complexity. Providers fear workflow disruptions during installation and the training period. Some organizations delay deployment due to uncertainty about return on investment. These financial and operational hurdles remain major barriers, especially in cost-sensitive regions where automation budgets are limited.
Cybersecurity Risks and Data Protection Challenges
As pharmacy dispensing machines become more connected, cybersecurity risks increase. These systems store patient data, prescription histories, and controlled-drug records that must remain secure. Ransomware, unauthorized access, and system downtime pose serious threats to dispensing operations. Providers must implement strong encryption, multi-level authentication, and detailed audit logs to maintain compliance with regulatory requirements. Cyberattacks can halt pharmacy workflows and compromise patient safety. Vendors must harden system architecture and provide ongoing security updates to protect pharmacy networks. Rising digital integration makes cybersecurity readiness a critical challenge for widespread market adoption.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America held the largest share in 2024 with about 38%. Hospitals and retail pharmacy chains invested heavily in automation to reduce dispensing errors and improve workflow speed. Strong adoption of electronic prescriptions and strict regulatory focus on medication safety supported rapid machine deployment. Large health systems expanded centralized hubs to handle rising prescription loads. Retail drug stores also upgraded dispensing infrastructure to manage high chronic-care demand. Continuous integration with digital health platforms and strong vendor presence kept North America ahead in overall market penetration.
Europe
Europe accounted for nearly 29% of the market share in 2024. The region’s mature healthcare systems encouraged steady adoption of automated dispensing to enhance patient safety and reduce operational workload. Hospitals across Germany, France, and the U.K. invested in decentralized pharmacy units to speed inpatient medication delivery. Retail pharmacies adopted compact automation to manage rising consumer demand. Strong compliance with safety and audit regulations pushed wider integration of electronic tracking and verification features. Growing emphasis on digital health transformation supported continued expansion of dispensing machines across key EU markets.
Asia Pacific
Asia Pacific captured around 24% share in 2024 and remained the fastest-growing region. Demand rose due to expanding hospital infrastructure, higher prescription volumes, and rapid digitalization of healthcare in China, India, Japan, and South Korea. Large hospital chains invested in centralized automation to improve accuracy and reduce staff burden. Retail pharmacy networks grew quickly, driving demand for compact and scalable machines. Governments promoted smart healthcare initiatives, which boosted interest in connected dispensing systems. Rising chronic disease rates and growing private healthcare investment strengthened regional adoption.
Latin America
Latin America held roughly 6% of the market share in 2024. Adoption increased as hospitals in Brazil, Mexico, and Colombia sought automation to improve medication safety and reduce error rates. Budget constraints slowed implementation, but private hospital networks drove steady demand. Retail pharmacy chains also introduced automated units to enhance service speed and cut manual labor. Gradual digital transformation and the spread of e-prescriptions supported growth. Vendors focused on offering cost-effective models tailored to regional needs, helping expand penetration across urban healthcare centers.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region accounted for about 3% share in 2024. Adoption grew in Gulf countries as advanced hospitals upgraded medication management systems to match global standards. Investments in smart healthcare infrastructure across the UAE and Saudi Arabia encouraged wider use of automated dispensing. Africa’s adoption remained slower due to cost barriers, but private hospitals in South Africa and select urban centers increased interest in automation. Expanding digital health programs and rising focus on safe and accurate medication delivery supported long-term potential across the region.
Market Segmentations:
By Application
By End Use
- Hospitals
- Retail Drug Stores and Pharmacies
By Operation
- Centralized Pharmacies
- Decentralized Pharmacies
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
The Pharmacy Dispensing Machines Market features strong competition among leading players such as Capsa Healthcare, ScriptPro LLC, Omnicell, Inc., Accu-Chart and BD. These companies compete by offering advanced automation platforms that improve medication accuracy, streamline pharmacy workflows, and support high-volume dispensing in both hospital and retail settings. Vendors focus on integrated systems with barcode verification, real-time inventory tracking, and seamless connectivity with electronic prescriptions and EHR platforms. Product portfolios continue to expand through robotics, compact modular designs, and secure dispensing features for controlled substances. Companies also strengthen market presence through service partnerships, centralized automation hubs, and training programs. Growing demand for digital health integration, medication safety, and efficient pharmacy operations supports intense competition as vendors work to deliver scalable, reliable, and cost-efficient solutions across global healthcare systems.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
Recent Developments
- In July 2025, Capsa Healthcare Capsa unveiled its Consolidated Services Pharmacy Platform (CSPP), a unified hub designed to process, manage, order, fill, distribute and deliver medications and supplies across inpatient and outpatient channels to support health-system centralization efforts.
- In May 2025, Omnicell, Inc. Omnicell announced a new line of RFID products (MedTrack) aimed at improving medication accuracy and visibility in perioperative and clinic settings extending Omnicell’s portfolio beyond ADCs and robotic systems into RFID-enabled medication tracking.
- In March 2025, Capsa Healthcare Capsa opened a new Innovation Center to give customers immersive access to advanced point-of-care and pharmacy automation technologies, positioning the company to accelerate adoption of its central-fill and point-of-care solutions.
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Application, End-Use, Operation and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- Adoption of automated dispensing will rise as hospitals aim for higher medication accuracy.
- Retail pharmacy chains will expand compact robotic systems to handle growing prescription loads.
- Centralized pharmacy hubs will gain traction to support large-volume dispensing across networks.
- AI-driven forecasting will improve inventory planning and reduce stockouts.
- Integration with electronic prescriptions and EHR platforms will strengthen data flow.
- Demand for secure dispensing of high-risk drugs will push investment in advanced verification tools.
- Hybrid centralized–decentralized models will spread across major healthcare systems.
- Vendors will develop modular, space-saving machines for smaller clinics and pharmacies.
- Cybersecurity upgrades will become essential as connected systems expand.
- Emerging markets will adopt automation faster due to rising healthcare digitalization and chronic-care growth.




