Market Overview
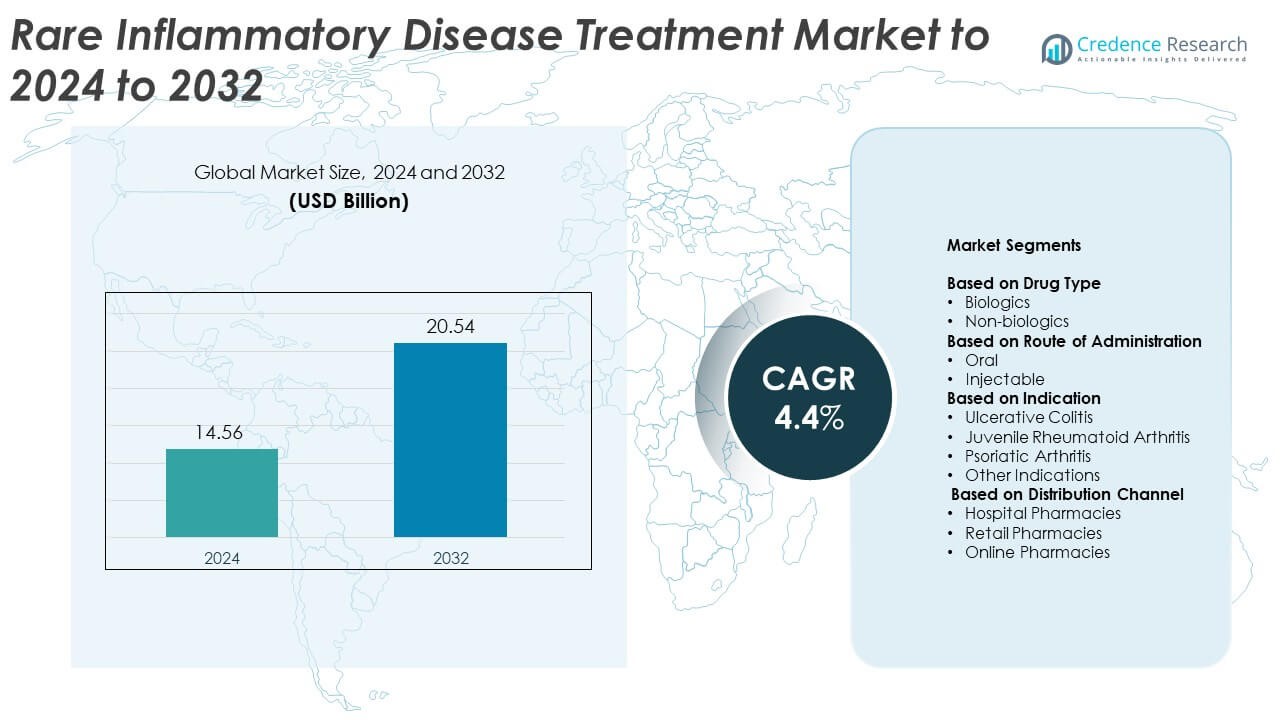
Rare Inflammatory Disease Treatment Market size was valued at USD 14.56 Billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 20.54 Billion by 2032, at a CAGR of 4.4% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Rare Inflammatory Disease Treatment Market Size 2024 |
USD 14.56 Billion |
| Rare Inflammatory Disease Treatment Market, CAGR |
4.4% |
| Rare Inflammatory Disease Treatment Market Size 2032 |
USD 20.54 Billion |
The Rare Inflammatory Disease Treatment Market is shaped by several global leaders that focus on expanding biologic therapies, advancing precision-based treatments, and strengthening clinical pipelines. These companies compete through innovation, wider indication approvals, and strategic collaborations that improve treatment access. North America leads the market with about 41% share in 2024, supported by strong reimbursement systems, advanced diagnostic capabilities, and rapid uptake of targeted immunology drugs. Europe follows with nearly 29% share due to structured healthcare frameworks and active clinical research activity, while Asia Pacific accounts for about 21% share and remains the fastest-growing region.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Insights
- The Rare Inflammatory Disease Treatment Market stood at USD 14.56 Billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 20.54 Billion by 2032, growing at a 4.4% CAGR.
• Strong demand for biologics drives market expansion as biologics hold nearly 62% share due to high clinical efficacy and broader treatment adoption.
• Key trends include rising precision-medicine use, expanding immunology pipelines, and increasing reliance on real-world evidence for long-term treatment validation.
• Competition intensifies as leading companies advance targeted therapies, pursue regulatory designations, and strengthen global reach through partnerships and expanded specialty-care programs.
• North America leads with about 41% share, followed by Europe at 29%, Asia Pacific at 21%, Latin America at 6%, and Middle East & Africa at 3%, while injectables also dominate route of administration with nearly 68% share.
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Drug Type
Biologics lead this segment with about 62% share in 2024 due to strong clinical efficacy and targeted immune-modulating action used for complex inflammatory pathways. Demand rises as advanced monoclonal antibodies and next-generation biologics help manage severe symptoms with fewer systemic effects. Non-biologics maintain steady uptake in mild to moderate cases, yet biologics dominate because patients and clinicians prefer faster response rates, improved remission stability, and broader approvals across chronic rare conditions.
- For instance, Eli Lilly’s phase 3 LUCENT-1 ulcerative colitis trial enrolled 1,281 adults. At week 12, 24.2% on mirikizumab achieved clinical remission versus 13.3% on placebo, confirming strong biologic efficacy in difficult disease.
By Route of Administration
Injectables dominate this segment with nearly 68% share in 2024 because biologic therapies require parenteral delivery for optimal absorption and long-acting action. Hospitals and specialty clinics also prefer injectable formats due to controlled dosing and reliable therapeutic outcomes in severe inflammatory disorders. Oral drugs grow at a moderate pace as new small-molecule therapies improve convenience, yet injectables remain dominant due to strong efficacy, extended dosing intervals, and broader adoption in long-term immunomodulation.
- For instance, In the GEMINI 1 trial for ulcerative colitis, 47.1% of patients showed a clinical response after six weeks with intravenous vedolizumab, compared to 25.5% on placebo.
By Indication
Ulcerative colitis holds the largest share at around 34% in 2024 driven by rising diagnosis rates, expanding biologic approvals, and increased use of targeted therapies for chronic flare management. Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis show steady growth as advanced treatment options improve quality of life and reduce long-term joint damage. Other rare indications expand gradually through better screening and higher adoption of personalized immunology treatments, yet ulcerative colitis remains dominant due to strong treatment demand and wider therapeutic availability.
Key Growth Drivers
Rising Adoption of Advanced Biologic Therapies
Biologic therapies remain a major growth engine because they target highly specific immune pathways with strong clinical precision. These medicines deliver superior remission stability and reduced flare frequency, which makes them a preferred choice for complex and hard-to-treat rare inflammatory conditions. Expanded approvals across multiple indications, along with improved safety profiles, enhance clinician confidence. Hospitals and specialty centers also rely on biologics due to predictable outcomes and growing evidence supporting long-term disease control. This broad acceptance strengthens demand and keeps biologics at the center of market expansion.
- For instance, UCB confirms that its BE RADIANT psoriasis trial showed 85.5% of patients on bimekizumab reached PASI 90 at week 16, versus 74.3% on secukinumab.
Growing Prevalence and Earlier Diagnosis of Rare Inflammatory Disorders
Increasing global awareness has led to more frequent screening and faster diagnosis of rare inflammatory diseases. Modern diagnostic tools such as advanced imaging and immunology testing help detect conditions in earlier stages, allowing patients to begin treatment sooner. More referrals to specialist centers also raise treatment initiation rates. Public health campaigns and physician education programs further improve recognition of rare symptoms. As more patients receive timely diagnosis, long-term therapy needs rise, supporting steady growth across specialty drugs and advanced treatment platforms.
- For instance, Bristol Myers Squibb’s True North ulcerative colitis program randomized 645 adults 2:1 to ozanimod or placebo
Expansion of Personalized and Precision-Based Treatment Approaches
The market benefits from a strong shift toward precision medicine, where treatments are tailored to individual immune responses. Biomarker-based testing helps identify the most effective drug category for each patient, reducing trial-and-error therapy and boosting success rates. Clinicians increasingly rely on genetic and immunological profiling to manage chronic inflammation more effectively. This move toward customization encourages wider adoption of targeted therapies and stimulates investment in research pipelines. As precision-based approaches continue to evolve, the market gains greater treatment efficiency and higher overall demand.
Key Trends and Opportunities
Rapid Pipeline Expansion with Novel Immunology Drugs
Drug makers continue to develop new immunology products designed for rare inflammatory conditions with limited existing treatments. The pipeline includes next-generation monoclonal antibodies, enzyme inhibitors, cell-based therapies, and novel oral agents targeting previously unaddressed pathways. These new candidates offer improved durability, fewer side effects, and broader therapeutic coverage. Strong research funding and rising clinical trial activity indicate sustained opportunity for launch-ready assets. As more innovative products join the market, companies gain a competitive edge and patients receive stronger treatment choices.
- For instance, Teva’s TL1A antibody duvakitug achieved clinical remission in 36.2% of low-dose and 47.8% of high-dose ulcerative colitis patients at week 14, compared with 20.45% on placebo, in a phase 2b trial now moving toward phase 3.
Growing Use of Real-World Evidence in Treatment Development
Real-world evidence has become a key tool for evaluating treatment performance outside controlled trials. Healthcare systems and regulators increasingly rely on real patient data to refine safety assessments, dosing patterns, and treatment durability. These insights help manufacturers strengthen approval pathways and support expanded treatment labels. Real-world datasets also guide payers in coverage decisions, improving adoption in clinical settings. As this evidence base grows, companies gain opportunities to enhance therapy outcomes and improve post-launch success.
- For instance, a Finnish nationwide real-world study of ustekinumab in ulcerative colitis reported treatment persistence of 87% at 16 weeks and 63% at 1 year, with 68% of patients in clinical remission and 62% in steroid-free remission at 52 weeks, confirming strong long-term effectiveness in routine practice.
Increasing Shift Toward Home-Based and Self-Administered Care
Self-administered biologics and long-acting formulations drive a growing trend toward home therapy for rare inflammatory diseases. Patients prefer flexible care models that reduce hospital visits, increase comfort, and improve daily disease management. Device makers support this shift by developing safe and easy-to-use autoinjectors and delivery systems. Healthcare providers also encourage home-based care to reduce treatment burden and free up clinical resources. This movement creates strong opportunities for companies offering long-duration drugs and patient-friendly delivery solutions.
Key Challenges
High Treatment Costs Limiting Patient Access
Advanced biologics and targeted therapies remain costly due to complex manufacturing and specialized distribution. Many patients struggle to afford long-term treatment, especially in regions with limited insurance coverage. High pricing places pressure on healthcare budgets and slows the adoption of premium therapies. Even where reimbursement is available, restrictive policies may limit full access. As cost challenges persist, market growth is constrained in middle-income and developing regions that lack strong subsidy systems.
Complex Regulatory Pathways Slowing Product Approvals
Rare inflammatory disease therapies often face lengthy regulatory processes because clinical trials require rigorous safety and efficacy data. Small patient populations make recruitment difficult and prolong study timelines, delaying product launches. Agencies also demand extensive long-term data for chronic conditions, increasing approval complexity. These hurdles slow innovation cycles and discourage smaller companies with limited resources. As regulatory demands remain high, new treatment introductions face significant timing and cost-related barriers.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America holds the largest share at about 41% in 2024 due to strong adoption of biologics, advanced diagnostic access, and high treatment awareness. The region benefits from extensive specialist networks, favorable reimbursement for rare disease therapies, and rapid uptake of precision-based immunology drugs. Growing investment in research pipelines and supportive regulatory incentives such as orphan drug designations further strengthen growth. Increasing real-world evidence programs and strong patient advocacy groups also expand treatment access across the United States and Canada, keeping North America the dominant contributor to market revenue.
Europe
Europe accounts for nearly 29% share in 2024 supported by structured healthcare systems, rising diagnosis rates, and expanding availability of advanced biologics. Strong adoption across Germany, France, and the United Kingdom is driven by established rare disease frameworks and active clinical trial participation. Government-backed reimbursement for targeted therapies improves patient reach and supports long-term treatment continuity. Growing use of personalized immunology tools and enhanced specialist collaboration also contribute to higher therapy initiation. Increasing regulatory support through EMA orphan drug programs further boosts innovation and strengthens Europe’s steady market expansion.
Asia Pacific
Asia Pacific holds around 21% share in 2024 and showcases fast growth as awareness of rare inflammatory diseases improves across China, Japan, South Korea, and Australia. Expanding hospital infrastructure and better access to specialty immunology care raise treatment uptake. Governments in major markets invest heavily in rare disease diagnosis and support advanced screening. Local manufacturing of targeted drugs and supportive pricing reforms improve affordability. Rising clinical trial activity and growing adoption of biologics strengthen long-term outlook, positioning Asia Pacific as the fastest developing regional contributor.
Latin America
Latin America captures nearly 6% share in 2024, supported by improving access to specialty care and progressive adoption of targeted therapies. Countries such as Brazil, Mexico, and Argentina expand diagnostic capabilities through national rare disease programs. However, limited reimbursement and high biologic costs still restrict broad uptake. Gradual expansion of private healthcare, partnerships with international drug manufacturers, and increasing awareness among clinicians help drive steady growth. As treatment guidelines modernize and screening improves, Latin America continues to open opportunities for advanced immunology therapies.
Middle East & Africa
Middle East & Africa hold about 3% share in 2024, influenced by limited diagnostic availability and restricted access to high-cost biologics. Growth is led by Gulf countries such as the UAE and Saudi Arabia, where modernization of healthcare systems supports earlier detection and specialist referrals. Expansion of tertiary care centers and growing interest in targeted immunology therapies gradually improve treatment adoption. However, many regions in Africa face significant affordability and infrastructure barriers. International partnerships, improved health insurance coverage, and government investment help strengthen gradual market development.
Market Segmentations:
By Drug Type
By Route of Administration
By Indication
- Ulcerative Colitis
- Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Psoriatic Arthritis
- Other Indications
By Distribution Channel
- Hospital Pharmacies
- Retail Pharmacies
- Online Pharmacies
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
The Rare Inflammatory Disease Treatment Market features major companies such as Mallinckrodt Plc., Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc., Abbvie Inc., Swedish Orphan Biovitrum AB, Johnson & Johnson, Pfizer, Inc., Valeant Pharmaceutical International Inc. (Bausch Health), Novartis AG, and Abbott Laboratories. Competition grows as firms expand biologic portfolios and strengthen targeted immunology pipelines. Companies invest in advanced monoclonal antibodies, improved delivery systems, and long-acting formulations to enhance patient outcomes. Strategic partnerships with research centers help accelerate innovation and support faster clinical progress. Firms also pursue regulatory designations to secure earlier approvals in high-need indications. Growing focus on real-world evidence improves long-term treatment insights and guides market expansion. Competitors enhance commercial reach through broader physician engagement and patient-support programs. Regional expansion strategies aim to improve therapy access in developing markets. Overall, the landscape remains dynamic as innovation, clinical success, and pricing strength drive competitive positioning.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
- Mallinckrodt Plc.
- Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc.
- Abbvie Inc.
- Swedish Orphan Biovitrum AB
- Johnson & Johnson
- Pfizer, Inc.
- Valeant Pharmaceutical International Inc. (Bausch Health)
- Novartis AG
- Abbott Laboratories
Recent Developments
- In 2025, Novartis received FDA accelerated approval for Vanrafia (atrasentan) as a foundational therapy for IgA nephropathy (IgAN), a rare kidney disease involving autoimmune-mediated inflammation.
- In 2025, AbbVie entered a collaboration with ADARx to develop next-generation siRNA therapies targeting gene silencing for autoimmune skin diseases, which represent a subset of rare inflammatory disorders.
- In 2025, Regeneron announced positive Phase 3 trial results for garetosmab in adults with fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva (FOP), an ultra-rare genetic inflammatory disease.
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Drug Type, Route of Administration, Indication, Distribution Channel and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- The market will grow as biologics and targeted therapies gain wider global adoption.
- Precision medicine will expand as biomarker-based treatment selection becomes standard practice.
- Earlier diagnosis will rise with improved screening tools and broader specialist access.
- Self-administered and home-based therapies will see stronger demand due to patient convenience.
- Real-world evidence will play a larger role in supporting approvals and treatment optimization.
- Pipeline activity will increase as companies invest in novel immunology and cell-based therapies.
- Digital platforms will enhance patient monitoring and long-term disease management.
- Partnerships between biotech firms and research institutions will accelerate innovation.
- Reimbursement frameworks will improve in several regions, increasing treatment access.
- Expanded rare disease policies will support faster approvals and stronger global market growth.




