Market Overview:
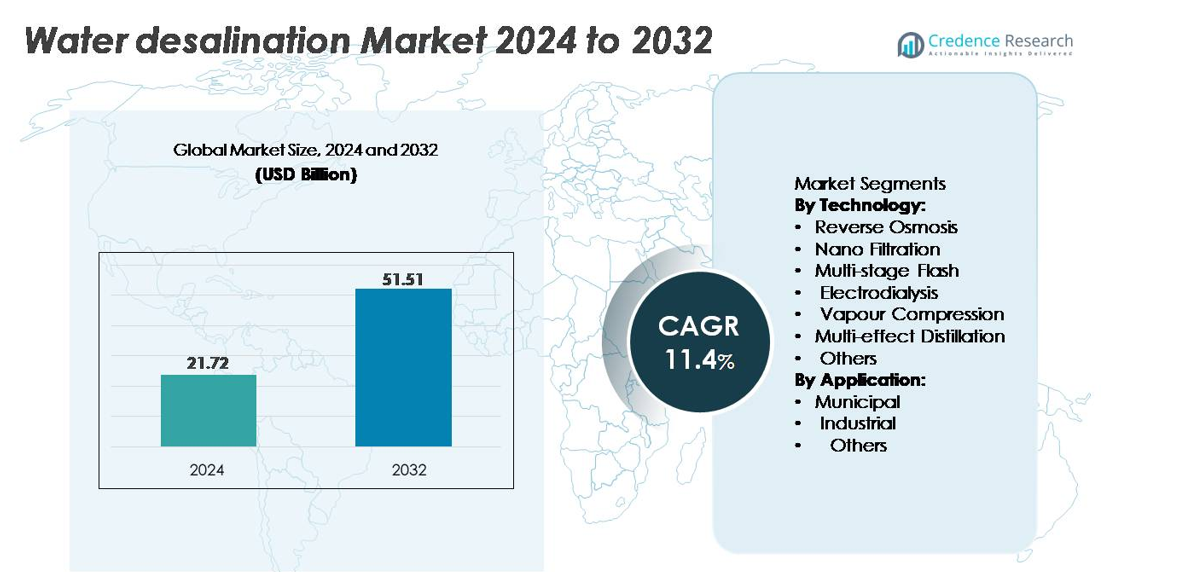
The global water desalination market size was valued at USD 21.72 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 51.51 billion by 2032, expanding at a CAGR of 11.4% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Water Desalination Market Size 2024 |
USD 21.72 billion |
| Water Desalination Market, CAGR |
11.4% |
| Water Desalination Market Size 2032 |
USD 51.51 billion |
The water desalination market is shaped by a competitive group of global leaders, with Xylem Inc., Acciona Agua, Hitachi Zosen Corporation, Aquatech International LLC, Pentair Plc, and Hyflux Ltd. driving technological innovation and large-scale project execution. These companies strengthen market presence through advanced RO systems, energy-efficient membranes, and turnkey EPC capabilities tailored to municipal and industrial customers. Regionally, the Middle East & Africa dominates the market with an approximate 45% share, supported by large coastal plants, government-backed investments, and continuous capacity expansion. Asia Pacific follows as a fast-growing region, while North America and Europe maintain steady adoption driven by drought resilience and regulatory compliance.
Market Insights:
- The global water desalination market reached USD 21.72 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 12.1% through 2032, supported by rising municipal and industrial demand in water-stressed regions.
- Growing need for reliable potable water supply, increasing drought frequency, and stricter industrial water-reuse regulations drive large-scale adoption of RO, thermal, and hybrid desalination systems across coastal economies.
- Technological shifts toward energy-efficient RO membranes, renewable-powered desalination, digital plant optimization, and advanced brine-management solutions define key market trends, accelerating cost reductions and operational sustainability.
- Competition remains strong as global players such as Xylem, Acciona Agua, Hitachi Zosen, Aquatech, Pentair, and Hyflux expand EPC capabilities, innovate high-recovery systems, and secure long-term O&M contracts across municipal and industrial segments.
- Middle East & Africa holds the largest regional share at ~45%, followed by Asia Pacific at ~25%; RO dominates technology share at ~60%, with municipal applications accounting for ~65% of total desalinated water demand.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Technology
Reverse Osmosis (RO) remains the dominant technology, accounting for the largest market share due to its high salt-rejection efficiency, modular design, and declining membrane replacement costs that support rapid deployment across municipal and industrial settings. Nanofiltration (NF) exhibits steady adoption for selective solute removal in brackish water and wastewater reuse applications. Multi-Stage Flash (MSF) and Multi-Effect Distillation (MED) maintain relevance in thermal-energy-rich regions, driven by operational compatibility with cogeneration plants. Electrodialysis (ED) gains traction for low-salinity and niche industrial applications requiring targeted ion separation. Vapour Compression (VC) systems serve remote installations with compact layouts, while other emerging technologies such as forward osmosis and membrane distillation advance pilot-scale testing for improved energy efficiency.
- For instance, DuPont’s FILMTEC™ SW30HRLE-440i membrane delivers a verified permeate flow of 6,000–6,500 GPD with a 99.7% salt-rejection rate, supported by automated iLEC™ interlocking couplers that eliminate O-ring leakage.
By Application
Municipal water supply constitutes the dominant application segment, supported by expanding urban populations, water-scarcity pressures, and government investments in large-scale desalination infrastructure to ensure resilient potable water production. Industrial demand grows as sectors such as power generation, oil & gas, chemicals, and food processing adopt desalination to secure reliable process water and reduce freshwater extraction. The “Others” category comprising agriculture, defense, and tourism experiences incremental growth driven by the need for decentralized, containerized desalination units and off-grid water security solutions in remote or arid zones.
- For instance, IDE Technologies’ Sorek I plant in Israel produces 624,000 m³/day using 16-inch RO membranes the world’s largest membrane diameter in municipal desalination while delivering energy consumption near 3.2 kWh/m³, demonstrating record-scale urban supply capability.
KEY GROWTH DRIVERS
Escalating Global Water Scarcity and Rising Municipal Demand
Accelerating freshwater depletion, rapid urbanization, and climate-induced droughts significantly increase pressure on countries to expand alternative water supply sources, positioning desalination as a cornerstone of long-term water security planning. Municipal utilities adopt large-scale desalination plants to safeguard drinking water availability, particularly in arid geographies where groundwater recharge rates remain insufficient. Governments in regions such as the Middle East, South Asia, and parts of North America invest in mega desalination programs to diversify supply portfolios and reduce dependence on rainfall. Growing reliance on decentralized and emergency-response desalination units further strengthens demand in coastal and drought-prone regions. As cities integrate resilience strategies and climate-risk adaptation measures, desalination becomes a strategic investment supporting population growth, industrialization, and environmental compliance, thereby reinforcing its long-term role in national water infrastructure.
- For instance, Saudi Arabia’s SWCC operates the Rabigh 3 IWP verified at 600,000 m³/day which holds a Guinness World Record as the largest reverse-osmosis desalination plant globally, supplying millions with climate-resilient potable water.
Advancements in Membrane Technology and Energy-Efficient Processes
Continuous improvements in membrane engineering, system optimization, and hybrid plant configurations drive cost reductions and operational efficiency, strengthening the economic viability of desalination. New-generation reverse osmosis membranes with enhanced permeability, fouling resistance, and longer service lifespans reduce maintenance frequency and lower total operating costs for large utilities and industrial facilities. Emerging concepts such as biomimetic membranes, graphene-oxide layers, and nanocomposite materials increase throughput and decrease energy intensity. Integration of energy recovery devices (ERDs), optimized high-pressure pumps, and digital monitoring systems further enhance plant performance. Hybrid RO-thermal configurations help maximize brine concentration while achieving peak operational resilience. As energy remains the largest cost component in desalination, innovations that reduce consumption directly improve scalability, making desalination increasingly accessible across regions with limited energy resources.
- For instance, Hydranautics’ ESPA2-4040membrane produces a verified permeate flow of 1,900 gallons per day at 150 psi with a 99.6% salt-rejection rating, reducing energy requirements for municipal utilities.
Rising Industrial Adoption and Compliance with Water-Reuse Regulations
Industries intensify desalination deployment as they face stricter wastewater discharge regulations, freshwater extraction limits, and sustainability requirements. Sectors such as oil & gas, power generation, mining, semiconductors, food processing, and chemicals rely on desalination to secure consistent process water supply and mitigate operational disruptions. Zero-Liquid Discharge (ZLD) mandates push companies to integrate desalination with advanced brine management systems to reduce environmental impact. Growing emphasis on circular water use accelerates adoption of membrane-based desalination for internal recycling and recovery of valuable salts and minerals. Industrial operators also benefit from modular containerized systems, enabling fast installation in remote or temporary operational zones. As corporations strengthen ESG commitments and resource-efficiency goals, desalination plays a critical role in achieving responsible water stewardship, driving sustained demand across high-water-intensity industries.
KEY TRENDS & OPPORTUNITIES:
Expansion of Renewable-Energy-Powered and Hybrid Desalination Systems
Integration of solar, wind, geothermal, and waste-heat recovery technologies represents one of the most transformative opportunities in the desalination industry. Renewable-energy-powered desalination addresses long-standing concerns around high operational costs and carbon emissions associated with conventional thermal and RO plants. Hybrid configurations combining solar PV with RO, or solar-thermal energy with multi-effect distillation support continuous water production while stabilizing electricity demand across peak and off-peak periods. Technological advances in thermal energy storage, battery integration, and grid-interactive smart controllers enhance the operational flexibility of renewable-powered systems. Governments and utilities increasingly pilot green desalination initiatives to meet decarbonization targets and align water infrastructure with sustainability mandates. The shift toward low-carbon desalination positions renewables as a major growth catalyst in future plant development.
- For instance, The Al Khafji Solar-Powered RO Plant developed by Abengoa (in partnership with Advanced Water Technology) is located in Al Khafji, Saudi Arabia. The facility is powered by an associated solar photovoltaic plant, which has a capacity generally cited as 10 MW or 15 MWac, enabling the continuous production of 60,000 m³/day of potable water.
Growth in Smart, Autonomous, and Digitally Optimized Desalination Plants
Adoption of digital twin models, predictive analytics, AI-enabled monitoring, and IoT-based process controls drives the modernization of desalination operations. Smart plants automate membrane cleaning cycles, detect fouling in early stages, and optimize system pressure and flow rates in real time to enhance energy efficiency and reduce unplanned downtime. Cloud-based supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) platforms enable remote management across distributed desalination assets, advancing scalability in regions with fragmented water infrastructure. Autonomous systems improve manpower efficiency, ensure consistent output quality, and support condition-based maintenance strategies. As desalination facilities grow in scale and complexity, digital transformation becomes essential for maximizing asset longevity, reducing operational risks, and improving cost predictability, creating a long-term opportunity for technology providers and utilities.
Key Challenges:
High Energy Consumption and Associated Operating Costs
Despite technological advancements, desalination remains energy-intensive, requiring substantial electricity for pressurization, thermal evaporation, or brine concentration processes. High energy consumption directly translates into elevated operating costs, creating financial barriers for regions with limited energy resources or volatile power markets. Energy price fluctuations, grid constraints, and carbon-emission implications add further operational complexity. Utilities struggle to maintain cost competitiveness when balancing water tariffs with rising energy expenditures. Although energy recovery devices and advanced membranes reduce consumption, large-scale plants still rely heavily on continuous power supply, limiting feasibility for low-income regions. Managing long-term energy affordability remains a critical challenge and a major determinant of project viability.
Environmental Concerns Associated with Brine Disposal and Ecosystem Impact
Brine disposal continues to pose significant environmental challenges, particularly for coastal regions with sensitive marine ecosystems. High salinity discharge, thermal pollution, and residual chemical additives can alter ocean water density, disturb aquatic habitats, and impact biodiversity when not properly managed. Land-based brine disposal options also raise concerns around soil salinization and groundwater contamination. Regulatory authorities impose stringent standards on outfall design, salinity mixing, and effluent quality, increasing project complexity and costs. While advanced brine concentration, mineral recovery, and zero-liquid-discharge solutions help mitigate environmental risks, their high capital and operational burdens limit widespread adoption. Sustainable brine management remains essential for long-term acceptance and environmental compliance of desalination projects.
Regional Analysis:
Middle East & Africa (MEA)
The Middle East & Africa holds the largest share of the global desalination market, accounting for around 45%, driven by chronic water scarcity, minimal freshwater resources, and extensive government-led infrastructure development. Countries such as Saudi Arabia, the UAE, Kuwait, and Israel operate some of the world’s largest reverse osmosis and thermal desalination plants, supported by substantial investments in renewable-powered and energy-efficient systems. National water strategies, population growth, and industrial expansion further strengthen demand. Ongoing mega-projects and technological modernization continue positioning MEA as the global hub for large-scale desalination capacity.
Asia Pacific
Asia Pacific represents approximately 25% of the market, supported by rising water stress, rapid urbanization, and industrial expansion across China, India, Australia, South Korea, and Singapore. Governments increase desalination deployment to stabilize municipal water supply and reduce vulnerability to fluctuating monsoon patterns. Australia and Singapore lead high-efficiency membrane desalination, while China advances large coastal RO facilities to secure industrial and domestic water demands. Growing adoption of brine-minimization technologies and hybrid solar-RO systems further accelerates growth. As climate variability intensifies, Asia Pacific emerges as the fastest-growing regional market in new project installations.
North America
North America accounts for roughly 15% of global desalination demand, driven by water scarcity in southwestern U.S. states, population growth, and industrial water security needs. The U.S. expands municipal and industrial RO installations, particularly in California, Texas, Florida, and Arizona, where drought conditions persist. Canada and Mexico invest selectively in coastal desalination projects to strengthen regional water resilience. Growing emphasis on digital optimization, energy-recovery devices, and low-pressure membranes enhances plant performance. Policy support for drought mitigation, combined with rising industrial reuse requirements, sustains North America’s medium-term desalination project pipeline.
Europe
Europe holds around 10% of the market, driven by Mediterranean nations such as Spain, Italy, Cyprus, and Greece that rely on desalination to stabilize seasonal water shortages. Spain remains the region’s largest adopter, operating a substantial network of RO plants supporting agriculture, tourism, and municipal supply. Northern Europe deploys desalination on a smaller scale for island communities and high-purity industrial applications. Strong regulatory emphasis on energy efficiency promotes adoption of renewable-powered desalination solutions and advanced brine management practices. EU funding for climate-resilient water infrastructure further encourages long-term project development.
Latin America
Latin America represents approximately 5% of the desalination market, supported by rising adoption across mining, power generation, and coastal municipalities. Chile leads regional deployment due to intensive copper mining operations requiring reliable non-freshwater sources, supported by large RO installations along the Atacama Desert corridor. Mexico and Brazil expand municipal desalination capacity to alleviate urban water shortages and reduce dependence on depleted reservoirs. Increasing drought frequency and industrial diversification drive new project pipelines. Although the region remains in early adoption stages, policy support for sustainable water solutions accelerates long-term desalination expansion.
Market Segmentations:
By Technology:
- Reverse Osmosis
- Nano Filtration
- Multi-stage Flash
- Electrodialysis
- Vapour Compression
- Multi-effect Distillation
- Others
By Application:
- Municipal
- Industrial
- Others
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape:
The competitive landscape of the water desalination market features a mix of global engineering firms, membrane technology specialists, and utility-scale water companies that collectively drive advancements in large-scale and decentralized desalination solutions. Key players include Veolia, SUEZ, Acciona, Doosan Enerbility, IDE Technologies, Abengoa, and Aquatech, each investing heavily in high-efficiency RO systems, renewable-powered desalination, and advanced brine-management technologies. Companies strengthen competitiveness through EPC capabilities, long-term O&M contracts, digital optimization platforms, and energy-recovery integration that reduces lifecycle costs. Membrane innovators such as DuPont, Toray, Hydranautics, and LG Chem enhance market differentiation through high-permeability, fouling-resistant membranes supporting reduced energy consumption. Regional utilities in the Middle East, Asia Pacific, and North America partner with global vendors to scale hybrid RO-thermal facilities and smart water infrastructure. Strategic collaborations, technology licensing, and expansion into modular containerized units further intensify competition, positioning leading suppliers to capture rising demand from municipal and industrial sectors.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis:
- Xylem Inc.
- Acciona Agua
- Hitachi Zosen Corporation
- Aquatech International LLC
- Pentair Plc
- Hyflux Ltd.
Recent Developments:
- In November 2025, Xylem became a strategic investor in Flocean, which is developing the world’s first commercial subsea desalination plant. This move aims to help scale novel desalination solutions globally, signaling Xylem’s push into next-generation desalination technologies.
- In June 2025, Aquatech International LLC was selected as the desalination-technology partner for the forthcoming seawater desalination facility at Corpus Christi’s Inner Harbor Water Treatment Campus in Texas. When completed, this will be the third-largest seawater desalination plant in the Americas (and the first major one in Texas).
- In December 2023, ACCIONA announced significant milestones for two major desalination plants in Saudi Arabia, highlighting their ramp-up in production: the Jubail 3B Desalination Plant and the Shuqaiq 4 Desalination Plant
Report Coverage:
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Technology, Application and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook:
- Desalination capacity will expand rapidly as more countries prioritize long-term water security amid intensifying drought and climate variability.
- Reverse osmosis will strengthen its dominance as membrane efficiency improves and energy consumption continues to decline.
- Renewable-powered desalination plants will gain traction as utilities seek low-carbon and cost-stable operational models.
- Digital twins, AI-based optimization, and predictive maintenance will become standard across new and upgraded facilities.
- Industrial sectors will increasingly adopt desalination to comply with stricter discharge rules and reduce freshwater dependency.
- Hybrid RO-thermal systems will see wider adoption to achieve higher recovery rates and improved brine management.
- Decentralized and modular desalination units will expand in remote, island, and emergency-response applications.
- Brine-valorization technologies will progress, enabling recovery of minerals and reducing environmental impact.
- Public–private partnerships will accelerate project development, especially in water-stressed emerging markets.
- Regional leaders such as MEA and Asia Pacific will drive global capacity additions through large-scale infrastructure investments.




