Market Overview
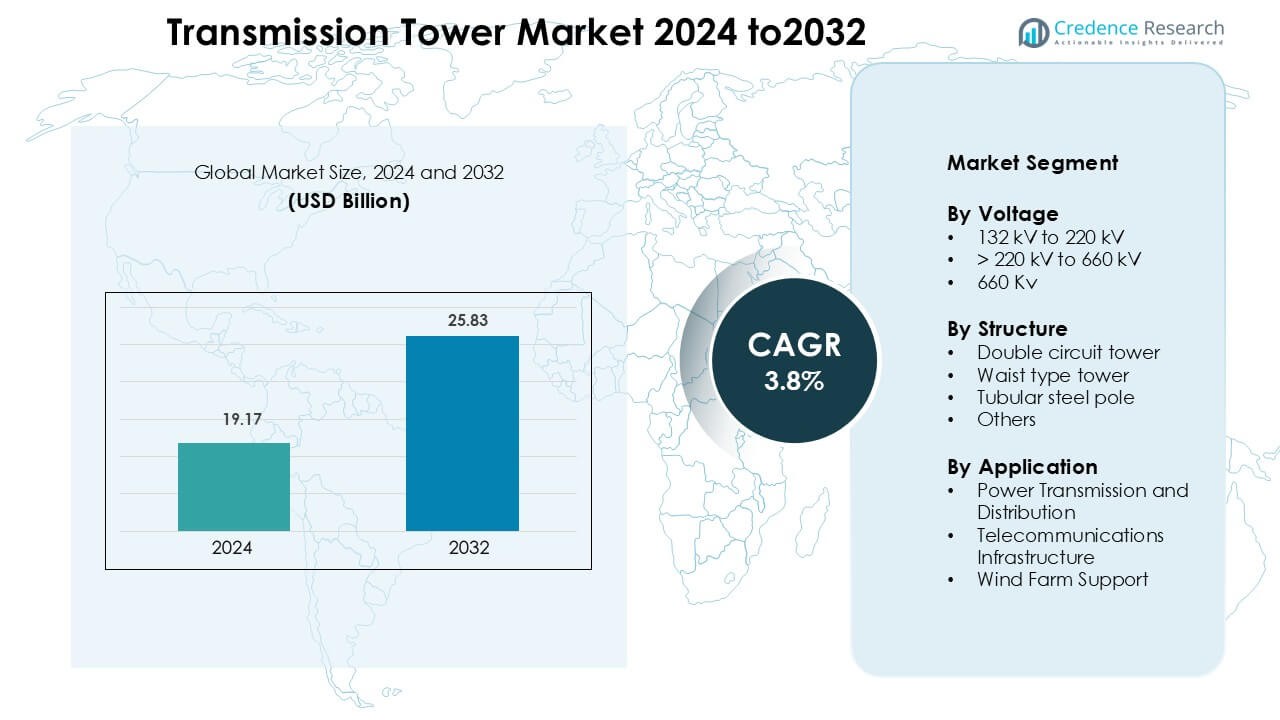
Transmission Tower Market was valued at USD 19.17 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 25.83 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 3.8 % during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Transmission Tower Market Size 2024 |
USD 19.17 Billion |
| Transmission Tower Market , CAGR |
3.8 % |
| Transmission Tower Market Size 2032 |
USD 25.83 Billion |
In the transmission tower market, major players such as Skipper Limited, KEC International Ltd., Ramboll Group A/S, Nanjing Daji Iron Tower Manufacturing Co. Ltd and Tata Power Company Limited drive innovation and project execution across global markets. These firms leverage strong manufacturing capabilities, supply‑chain integration and global EPC expertise to capture large high‑voltage line contracts. The Asia‑Pacific region leads the market with an exact share of 30%, benefitting from rapid grid expansion, renewable energy integration and intensive infrastructure investment.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Insights
- The global transmission tower market reached USD 19.17 billion in 2024 and will grow at a CAGR of 3.8 % through 2035.
- Demand drivers include rapid expansion in high‑voltage (>220 kV) transmission networks and renewables‑led grid upgrades, which boost segment shares of self‑supporting and lattice towers.
- Competitive analysis shows major firms focusing on global EPC contracts and offering full‑lifecycle services, while low‑cost regional players pressure margins.
- Restraints such as raw‑material price volatility and regulatory hurdles in land acquisition limit deployment speed in several geographies.
- Regional analysis reveals Asia‑Pacific commanding approximately 30 % of the market, driven by grid extensions in India and China and strong domestic manufacturing capabilities
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Voltage
In the voltage‑based segmentation of the transmission tower market, the > 220 kV to 660 kV sub‑segment dominates, capturing approximately 41.7% of the market. This leadership stems from the growing demand for high‑capacity transmission corridors linking power generation hubs to major load centres, especially in rapidly industrialising regions. The requirement for reliable long‑distance power transfer, the integration of renewables, and grid modernisation initiatives drive investment in towers covering this voltage range.
- For instance, KEC International Ltd. secured orders for 765 kV transmission-line and GIS-substation projects in India, underlining activity in the extra-high-voltage space.
By Structure
Within the structure type segmentation, double‑circuit towers hold the largest market share at about 36.4%. Their dominance is due to their technical advantages they carry two independent circuits per structure, improving land‑use efficiency and enabling redundancy in high‑voltage networks. Utility companies favour double‑circuit towers for new grid expansions and upgrades, as they reduce incremental material and installation costs compared to two single‑circuit structures.
- For instance, Sterlite Grid Limited completed full-scale type testing of its 765 kV double-circuit tower designs for the Dharamjaygarh–Jabalpur project and holds a portfolio of tested tower designs at that voltage for both single- and double-circuit configurations.
By Application
For applications, the Power Transmission and Distribution sub‑segment leads the market, accounting for the majority share the dominance arises because transmission towers are integral to the bulk transfer of electricity from generation sites to substations and end‑users. Growth in electricity demand, governmental grid modernisation programmes and renewable energy integration all reinforce the need for more robust transmission infrastructure in this segment.
Key Growth Drivers
Rising Electricity Demand and Grid Expansion
The global push for electricity access and reliable power supply is a major driver for the transmission tower market. Rapid urbanisation and industrialisation are causing electricity consumption to rise sharply, particularly in emerging economies, prompting governments and utilities to invest heavily in long-distance, high-voltage networks and associated infrastructure. In parallel, the need to replace ageing infrastructure in developed markets is further boosting tower installations. For example, one report noted that over half the new transmission towers in the Asia-Pacific region are linked to grid expansion in countries like India and China The cumulative effect of these trends is increased demand for structural support systems (i.e., towers) capable of handling higher voltages, longer spans and more complex grid topologies.
- For instance, Power Grid Corporation of India Ltd (PGCIL) received a letter of intent for a 765 kV interstate transmission line between Parli New, Maharashtra and Bidar, Karnataka, including two 765 kV bays and static reactors of 240 MVAr capacity at the Bidar station.
Renewable Energy Integration and Long-Distance Transmission
The transition to renewable energy sources is creating another significant growth vector for the transmission tower market. As more wind, solar and hydro generation comes online often in remote locations the need to transmit that power to load centres has increased. This means that new transmission corridors, often at ultra-high voltages (UHV) and over long distances, are being developed, necessitating robust tower infrastructure. According to one source, the >220 kV to 660 kV segment accounts for the largest share of new tower demand. Moreover, many nations’ grid-modernisation programmes link directly to renewable integration, further embedding towers into this growth pathway.
- For instance, Hitachi Energy will supply key HVDC equipment for the State Grid Corporation of China’s Gansu-Zhejiang ±800 kV UHVDC transmission project, which spans approximately 2,370 km and is designed to deliver ~36 billion kWh annually with more than half sourced from renewables.
Technological Innovation and Material Advances
Innovation in tower materials and manufacturing is also acting as a growth driver. Towers are increasingly made with lighter, stronger or hybrid materials (e.g., composite alloys, modular construction) and are being designed for faster assembly, better durability and lower lifecycle maintenance costs. For instance, one report noted that composite and hybrid towers are gaining market share due to their resistance to corrosion and reduced transportation/installation burden. These technological upgrades enable operators to deploy towers more efficiently in remote or difficult terrain, further broadening the addressable market.
Key Trends & Opportunities
Smart Grid Enablement and Monitoring Capabilities
The evolution of power networks toward digital, responsive and resilient systems presents a strong opportunity for tower manufacturers and utilities alike. Smart grid initiatives frequently call for towers equipped with sensors, remote monitoring, structural health diagnostics and integration with communication systems. The deployment of modular towers and prefabrication also supports rapid installation, especially in time-sensitive grid expansion projects. For companies willing to invest in innovation, this trend offers a chance to differentiate and capture higher-value segments of the market.
- For instance, KEC International does leverage advanced technologies and digitalization for project monitoring and asset management, which aligns with the general concept of using modern tools for efficiency.
Growing Demand in Emerging Regions and Rural Electrification
Emerging markets especially in Asia-Pacific, Africa and Latin America offer large opportunities because many regions still lack full electricity transmission infrastructure. Government programmes for electrification and infrastructure investment are pushing tower demand upward. In addition, remote and rural deployment contexts drive demand for modular, lightweight towers that simplify logistics, opening a niche for specialised manufacturing and service models. For companies and utilities that can adapt to these market conditions (lower cost models, ruggedised designs, local supply chains), this represents a growth frontier.
- For instance, Reports confirm that 380-meter (1,247 ft) transmission towers were completed in the Zhoushan Islands, which are part of China’s Zhejiang Province.
Materials & Design Innovation for Harsh Environments
As transmission infrastructure expands into challenging terrains (mountains, forests, coastal zones) and faces more severe weather events, there is an opportunity to deploy towers built with advanced materials and designs suited for resilience and environmental compatibility. Reports highlight increased adoption of corrosion-resistant alloys, composite materials, modular designs and towers designed for extreme conditions This opens avenue for manufacturers to introduce premium solutions (higher reliability, lower maintenance) and for utilities to invest in infrastructure that reduces lifecycle risk and operational cost.
Key Challenges
Raw Material Price Volatility and Supply Chain Disruptions
A significant challenge for the transmission tower market is the vulnerability to fluctuations in raw material costs and supply chain bottlenecks. Steel comprises the bulk of tower materials and global steel price swings, logistics disruptions and material shortages can materially impact project budgets and timelines. Further complications arise from transportation of large components, heavy-haul constraints in remote or difficult terrain, and long lead-times for specialised fabrication. These factors can reduce margins, delay installations and raise risk for manufacturers and utilities alike.
Land Acquisition, Regulatory Approvals and Environmental / Community Constraints
Another major obstacle is obtaining the necessary land, permits and community acceptance to construct transmission towers and associated lines. Projects often face delays due to environmental impact assessments, land-use approvals, aesthetic objections, regulatory complexity and public opposition especially in densely populated or environmentally sensitive areas. These delays can stretch project timelines by years, raising financing cost and reducing the effective market growth rate. For tower manufacturers and utilities, navigating these regulatory and social hurdles remains a persistent barrier.
Regional Analysis
Asia‑Pacific
The Asia Pacific region holds a dominant 30% share of the global transmission tower market, benefiting from the rapid economic growth and industrialization in key countries such as China, India, and Southeast Asia. These nations are investing heavily in expanding their power grid networks, supporting rural electrification initiatives, and integrating renewable energy sources. As energy demand rises, particularly in emerging economies, the need for robust infrastructure to transmit power over long distances is accelerating the demand for high-voltage transmission towers. Notably, large-scale investments in high-voltage lines, especially those exceeding 220 kV to 660 kV, and even above 660 kV, are driving the need for advanced tower structures.
North America
North America accounts for about 28% of the global transmission tower market, with the U.S. and Canada leading the charge in grid modernization efforts. Both countries are focusing on the upgrade of their aging transmission infrastructure, deploying new high-voltage corridors, and improving the integration of renewable energy sources into the grid. This transformation is essential to meet the growing energy demands and improve the resilience of the existing infrastructure. The push for high-voltage transmission solutions is expected to continue as both nations aim to modernize and expand their grids. In the U.S., regulatory incentives and investments from utilities are encouraging the replacement of older transmission assets and supporting the construction of new systems.
Europe
Europe represents approximately 24% of the global market, with a strong emphasis on renewable energy targets, cross-border interconnection, and enhancing the resilience of energy networks. The region is heavily investing in high-voltage and ultra-high-voltage transmission towers to support cross-border power flows and enable better integration of renewable energy into the grid. Regulatory frameworks across Europe are pushing for sustainability and cleaner energy solutions, prompting investments in new tower technologies that incorporate sustainable materials and digital monitoring capabilities. These towers are designed to support the transmission of energy over long distances, enabling countries to meet their renewable energy commitments and facilitate the flow of electricity across borders.
Latin America
Latin America accounts for about 10% of the global transmission tower market, with the largest growth occurring in Brazil, Mexico, and Chile. These countries are investing in grid expansion, especially in rural areas, as well as addressing industrial load growth in urban centers. The region is also focusing on long-distance transmission and constructing double circuit towers to improve grid reliability. However, compared to the other regions, Latin America faces challenges such as slower deployment rates, economic constraints, and political instability that can impede rapid market growth. While these obstacles may slow the pace of adoption, the demand for transmission towers remains steady, particularly as countries push for greater electrification and the expansion of their power grid systems to meet growing energy needs.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region holds a 8% share of the global transmission tower market, with demand driven by the need for growing power infrastructure, large-scale renewable energy projects, and cross-border transmission corridors, particularly in the GCC (Gulf Cooperation Council) countries and Sub-Saharan Africa. The expansion of renewable energy capacity, including solar and wind projects, requires significant infrastructure upgrades to transport power from generation sites to consumption areas. Harsh environmental conditions and complex terrain, particularly in desert regions and mountainous areas, create unique challenges for the development of transmission towers, leading to the adoption of advanced technologies designed to withstand extreme conditions.
Market Segmentations:
By Voltage
- 132 kV to 220 kV
- > 220 kV to 660 kV
- > 660 kV
By Structure
- Double circuit tower
- Waist type tower
- Tubular steel pole
- Others
By Application
- Power Transmission and Distribution
- Telecommunications Infrastructure
- Wind Farm Support
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
In the competitive landscape of the global transmission tower market, several industry players hold prominent positions and continuously evolve to maintain or enhance their market share. Companies such as KEC International Ltd., Skipper Limited, Kalpataru Power Transmission Ltd., and China XD Group distinguish themselves through integrated manufacturing, EPC services, and global project execution. These firms invest heavily in research and development, supply‐chain optimisation and capacity expansion to address raw‐material volatility and regulatory shifts. They also engage in strategic alliances, international tenders and turnkey contracts to secure large high‐voltage projects. The competitive pressure from regional low‐cost manufacturers compels leading players to differentiate via advanced tower designs, digital monitoring solutions and lifecycle services. As a result, companies that deliver end‐to‐end value fabrication, erection, testing, monitoring command stronger positioning and respond more swiftly to evolving grid expansion and renewal demand cycles.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
- Utkarsh India Limited
- Jyoti Structures Limited
- KEC International Ltd.
- QUANTA SERVICES
- NEXANS
- Valard Construction
- Burns & McDonnell
- PLH Group
- Wilson Construction
- Power Line Services, Inc
Recent Developments
- In October 2025, KEC International Ltd.: secured a ₹1,064 crore contract to design, supply, and install a 380 kV transmission line in Saudi Arabia.
- In August 2025, Utkarsh India Limited: announced a 20,000 MT order for 765 kV transmission towers to support 3.5 GW renewable evacuation in Rajasthan.
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Voltage, Structure, Application, and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- Growth will accelerate as utilities expand high‑voltage corridors to support remote renewable generation.
- Modular and prefabricated tower designs will gain traction to reduce installation time and project costs.
- Smart sensor integration and digital monitoring will emerge as standard features in new tower infrastructure.
- Demand for towers in harsh environments (deserts, offshore, mountainous) will increase as grid reach extends.
- Material innovation composite, corrosion‑resistant steel will drive lifecycle cost savings and asset resilience.
- Cross‑border grid interconnections and regional power trading will underpin new tower deployments.
- Urban and suburban networks will adopt monopole and compact tower forms to address space constraints.
- Replacement of aging transmission assets in mature markets will create sustained retrofit and upgrade work.
- Supply‑chain resilience and raw‑material cost control will become strategic priorities for tower suppliers.
- Environmental regulations and land‑use constraints will push manufacturers to develop lower‑footprint tower solutions.




