Market Overview
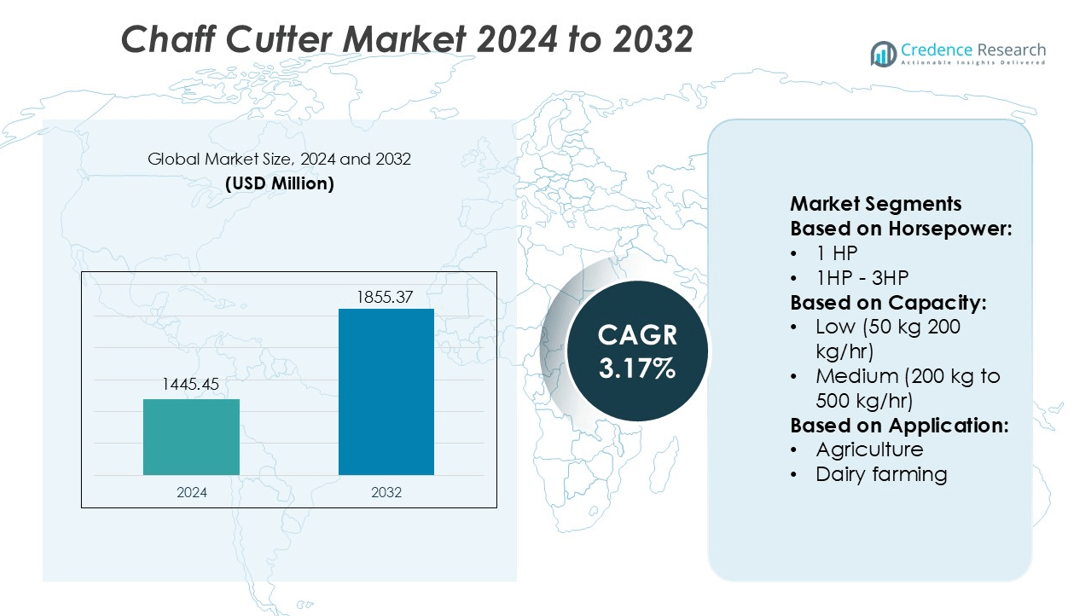
Chaff Cutter Market size was valued USD 1445.45 million in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 1855.37 million by 2032, at a CAGR of 3.17% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Chaff Cutter Market Size 2024 |
USD 1445.45 million |
| Chaff Cutter Market, CAGR |
3.17% |
| Chaff Cutter Market Size 2032 |
USD 1855.37 million |
The chaff cutter market focus on durable designs, faster cutting speeds, and user-friendly handling to serve both commercial and smallholder farms. Global manufacturers leverage wide dealer networks and strong after-sales support, while regional suppliers compete with affordable electric and manual models suited for rural use. Product portfolios continue to expand toward portable, low-maintenance, and rust-resistant machines that improve fodder quality and reduce wastage. Asia Pacific remains the leading region with 36% share, supported by large livestock populations, rising dairy commercialization, and increasing farm mechanization across India, China, and Southeast Asia.
Market Insights
- Chaff Cutter Market size was valued at USD 1445.45 million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 1855.37 million by 2032 at a 3.17% CAGR.
- Demand increases as dairy and livestock farms adopt mechanized fodder processing, with electric and tractor-mounted cutters gaining traction due to reduced labor needs and faster output.
- Manufacturers introduce portable, low-maintenance, and rust-resistant machines with improved blade durability, while dealers expand service networks to support rural and commercial users.
- Market restraints include high initial costs for large-capacity units and limited awareness in remote regions, slowing adoption among small farmers with low investment budgets.
- Asia Pacific holds the leading 36% share due to large cattle populations and rising dairy commercialization, while the 1-3 HP segment dominates product adoption as small and mid-sized farms prefer compact and energy-efficient cutters for daily fodder preparation.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Horsepower
The 1HP–3HP range holds the highest share in the chaff cutter market. Small and mid-size livestock owners prefer this category as it offers balanced power, lower maintenance, and affordable pricing. These machines can efficiently handle routine fodder cutting tasks for dairy and mixed farms. Their portability and compatibility with electric motors or diesel engines support both rural households and commercial users. Growing demand for compact mechanization solutions and rising small-scale dairy units continue to push this segment forward. Manufacturers also add safety shields and adjustable cutting settings to improve user experience and fodder quality.
- For instance, Farmking’s 3 HP chaff cutter models typically run on a 3 HP motor with a blade speed of approximately 2880 RPM. The chopping capacity, varies by model and the type of fodder being processed.
By Capacity
The Medium capacity segment (200–500 kg/hr) remains dominant due to wider suitability in dairy and livestock operations. These machines offer higher throughput than entry-level models, supporting daily feeding needs for cattle, sheep, and goats. They provide strong chopping performance for green fodder, dry hay, and maize stalks while keeping power consumption moderate. Co-operatives, dairy societies, and medium-scale farmers invest in this category to maintain regular feeding cycles. The need for uniform fodder size, better digestion, and reduced feed wastage drives adoption. This segment also benefits from increasing availability of semi-automatic units.
- For instance, Mahindra & Mahindra’s rotary cutter implement (model SD5’) features a blade tip speed of 12,469 fpm (63.3 m/s) and a gearbox rated at 40 hp (30 kW), with a cutting width of 60 in (152 cm) as per the company’s brochure.
By Application
Dairy farming holds the largest market share, supported by rising cattle populations and higher demand for processed green fodder. Chaff cutters help improve feed conversion, milk yield, and animal health by delivering consistent fodder size. Dairy farms use manual, semi-automatic, and motorized systems depending on herd size and feed volume. Small farms mainly use portable cutters, while commercial dairies integrate medium and high-capacity models. Government subsidies on fodder processing equipment also strengthen adoption in developing regions. The need for year-round feed preparation and balanced nutrition continues to drive demand in the dairy segment.
Key Growth Drivers
Increasing Mechanization in Small and Medium Farms
Farmers shift from manual forage cutting to mechanized chaff cutters to improve feed preparation speed and reduce labor fatigue. Small and mid-sized farms adopt portable and low-horsepower machines because they handle fodder quickly and deliver uniform output for cattle and poultry feed. Rising labor shortages in rural areas strengthen this shift toward machinery. Government programs that support farm mechanization also boost adoption. As production efficiency becomes essential for livestock profitability, mechanized chaff cutters gain strong demand across developing agricultural markets.
- For instance, JAS Smith Machinery & Engineering manufactures the “Mini Chaff Cutter” which features a hardened steel flywheel typically driven by a motor running at approximately 1,440 RPM.
Rising Cattle Population and Dairy Expansion
Higher milk consumption and growing dairy exports increase the need for balanced animal nutrition. Chaff cutters help produce well-processed fodder that improves feed intake and digestion in cattle. Dairy cooperatives and commercial farms invest in high-capacity models to maintain continuous supply of fresh fodder. The growth of organized dairy clusters in Asia, Africa, and Latin America accelerates equipment purchases. Better fodder management shortens feeding time and supports healthier livestock, encouraging farmers to shift from traditional hand cutting.
- For instance, KisanKraft’s KK-FMC-500 model uses a 3 HP (2.2 kW) electric motor rated at 2,800 RPM (revolutions per minute). The machine delivers a dry fodder output of approximately 700 kg per hour in lab conditions and features a durable, hardened steel blade assembly that meets relevant industry material specifications as per the company manual.
Technological Advancements and Product Innovation
Manufacturers introduce energy-efficient motors, corrosion-resistant blades, and safety guards to enhance machine durability and user protection. Some models integrate automation features, such as variable cutting speed and overload protection, ensuring consistent fodder size and reduced maintenance. Solar-powered chaff cutters expand adoption in off-grid rural areas and reduce operating costs. Portable models with compact designs allow easy mobility around farms. These innovations attract small, marginal, and commercial livestock owners seeking reliable, long-life machinery with lower running expenses.
Key Trends & Opportunities
Growing Demand for Fodder Processing Equipment in Dairy and Poultry Farms
Commercial farms prefer high-capacity and automated chaff cutters to process large fodder volumes faster. Uniform chopping improves animal digestion and reduces feed wastage, supporting higher milk and meat yields. Integration of chaff cutters with feed mixers and silage equipment creates opportunities for bundled machinery sales. Dealers expand rural sales networks and offer EMI financing, which encourages equipment adoption among small farmers. Rising interest in silage production also boosts demand for heavy-duty models.
- For instance, Balaji Agro Engineering’s heavy-duty model features a motor speed typically rated at 2,800 RPM, has a cutting width of approximately 320 mm, and is designed for continuous operation.
Expansion of Rural Equipment Rental Services
Farm equipment rental centers allow farmers to use machines without upfront purchase costs. Chaff cutters become part of shared machinery pools run by cooperatives, agri-service centers, and local entrepreneurs. This trend supports adoption in remote villages where farmers have limited budgets. Rental models reduce idle time and improve machine utilization. Government-supported custom hiring centers further expand access, creating strong market opportunities for both manufacturers and rental providers.
- For instance, Kirloskar Mega T 15 power tiller lists a specific fuel consumption of 270 g/kW·h, a weight of 138 kg, and features 6 forward and 2 reverse gears, according to the company’s product manual.
Shift Toward Electric and Solar-Powered Equipment
Electric chaff cutters lower noise, reduce emissions, and provide consistent performance compared to manual or diesel options. Solar-powered models gain popularity in off-grid areas by cutting energy spending. These models attract eco-conscious farms and regions with rising electricity costs. Manufacturers focus on energy-efficient motors, smart controls, and lightweight frames. The shift toward renewable-powered equipment opens new market opportunities in remote agricultural belts.
Key Challenges
High Initial Investment for Small Farmers
Many small farmers rely on low-budget tools, making advanced chaff cutters expensive for direct purchase. Even though the machines reduce labor and fodder waste, upfront cost is still a barrier. Limited financing access and irregular rural income cycles slow purchase decisions. Awareness programs and rental services help, but lack of capital remains a major challenge in developing regions.
Maintenance and Skill Requirements
Chaff cutters need trained users for safe operation, blade handling, and routine lubrication. Breakdowns can halt fodder preparation, affecting livestock feeding schedules. In remote areas, spare parts and service centers are limited. Poor maintenance causes faster blade wear and higher power consumption. Training and dealer-led service networks are important to solve this challenge, but adoption still rises slowly where technical support is weak.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America holds 28% of the chaff cutter market due to strong adoption of mechanized fodder processing across dairy and livestock farms. Large commercial dairy units in the U.S. and Canada invest in high-capacity electric and tractor-mounted models to support bulk fodder preparation. Farm modernization programs, rising labor costs, and technology-driven equipment replacement cycles increase product demand. Manufacturers expand distribution through dealership networks and after-sales service packages. Growth remains supported by rising demand for precision feeding, improved livestock nutrition, and compact chaff cutters designed for small and mid-sized farms.
Europe
Europe accounts for 22% of the global market, driven by advanced dairy farming systems in Germany, France, the Netherlands, and the U.K. The region favors energy-efficient, low-noise, and safety-enhanced chaff cutters aligned with EU machinery regulations. Demand rises for automated and portable units supporting grass-silage and hay processing. Sustainable farm practices increase the use of clean energy-powered models and equipment with reduced operational waste. Strong penetration of cooperative farming groups and high farm mechanization rates reinforce steady sales across both commercial and smallholder dairy operators.
Asia Pacific
Asia Pacific dominates the market with a 36% share due to large livestock populations and growing dairy commercialization in India, China, and Southeast Asia. Small and medium farms adopt low-cost electric and manual models to improve fodder quality and reduce feed wastage. Rapid rural mechanization, expanding government subsidies for dairy machinery, and growth of cattle feed industries accelerate product demand. Manufacturers introduce compact, rust-resistant machines suited for tropical climates and frequent outdoor use. Increasing shift from manual chopping to machine-based fodder processing strengthens long-term market penetration.
Latin America
Latin America captures 8% share, supported by dairy and cattle farming activities in Brazil, Argentina, and Mexico. Farmers prefer mid-capacity cutters for grass, maize, and sugarcane fodder. Growth is driven by expanding commercial dairy cooperatives and a shift toward packaged and silage-based feed systems. Budget-friendly electric and tractor-mounted units gain traction because of their durability and low maintenance. Government and private sector programs supporting livestock productivity enhance adoption in rural regions. Local distributors and farm equipment retailers play a key role in sales and service availability.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region holds 6% share, influenced by livestock-dependent economies in Kenya, Ethiopia, Nigeria, and parts of the GCC. Dairy and cattle feeding systems increasingly adopt mechanized cutters to improve fodder uniformity and reduce manual labor strain. Portable and fuel-efficient units suit smallholder farmers with limited grid access. Rising investments in dairy cooperatives, milk processing infrastructure, and animal nutrition programs stimulate demand. Import-led supply and partnerships with international manufacturers support availability of low-maintenance and weather-resistant models for dry and semi-arid conditions.
Market Segmentations:
By Horsepower:
By Capacity:
- Low (50 kg 200 kg/hr)
- Medium (200 kg to 500 kg/hr)
By Application:
- Agriculture
- Dairy farming
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape in the chaff cutter market players such as Kovai Classic Industries, Farm King, Gray-Nicolls, Mahindra and Mahindra, JAS Smith Machinery and Engineering, Kisankraft, Balaji Agro Engineering, KMW by Kirloskar, Dawn Agro Machinery, and Deere and Company. The chaff cutter market features a mix of global manufacturers and regional equipment suppliers offering electric, manual, and tractor-mounted machines. Companies compete on performance, blade strength, cutting speed, motor efficiency, and ease of handling for varied farm sizes. Product portfolios continue to expand toward portable and compact designs that suit smallholder farmers, while high-capacity cutters support commercial dairy operations and silage production units. Automation, safety guards, and improved feeding systems help reduce wastage and prevent crop clogging. Many manufacturers focus on durable, rust-resistant materials and low-maintenance components to operate in harsh field conditions. Strong dealership networks, spare part availability, and installation support improve customer retention. Partnerships with agro-service centers and financing programs further drive adoption, especially in emerging markets. After-sales service and warranty benefits remain key differentiators, encouraging repeat purchases and long-term user loyalty.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
- Kovai Classic Industries
- Farm King
- Gray-Nicolls
- Mahindra and Mahindra
- JAS Smith Machinery and Engineering
- Kisankraft
- Balaji Agro Engineering
- KMW by Kirloskar
- Dawn Agro Machinery
- Deere and Company
Recent Developments
- In March 2025, Linde Engineering and Voestalpine AG announced a partnership that will jointly develop a welding wire technique for ammonia tank welding. This aims to minimize the complexities of ammonia tank storage construction by the selection of proper welding consumables together with an increased degree of automation in the welding process.
- In March 2025, Miller, a leading welding brand, announced the release of Copilot Builder, the newest addition to its Collaborative Robots product portfolio. The robot is developed to address unique welding challenges with flexibility.
- In July 2024, Lincoln Electric acquired Vanair Manufacturing LLC, an Indiana-based company that specializes in vehicle-mounted power solutions for the U.S. service truck market.
- In February 2023, AMADA Co. Ltd. announced the launch of its NC Equipping machines with “AMNC. 4ie” advances them into environmentally friendly machines that can be used by anyone, anywhere
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Horsepower, Capacity, Application and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- Demand is expected to rise as dairy farms shift toward mechanized fodder preparation.
- Portable and compact cutters will gain adoption among small and remote farms.
- Electric models with lower power consumption will replace older manual units.
- Tractor-mounted chaff cutters will expand in large farms and silage-making units.
- Manufacturers will introduce safer feeding mechanisms to reduce operator risk.
- Digital monitoring and automation features will enter high-capacity machines.
- Sustainable materials and energy-efficient motors will influence product development.
- Leasing, rental, and financing options will support purchases in rural markets.
- After-sales service networks will expand to improve maintenance convenience.
- Growth will increase in Asia and Africa as livestock populations continue rising.




