Market Overview
The Global Biologic Excipients market was valued at USD 1,497.5 million in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 2,033.72 million by 2032, expanding at a CAGR of 3.9% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Biologic Excipients Market Size 2024 |
USD 1,497.5 million |
| Biologic Excipients Market, CAGR |
3.9% |
| Biologic Excipients Market Size 2032 |
USD 2,033.72 million |
The biologic excipients market is shaped by a mix of global leaders such as Roquette Frères, Croda International, BASF SE, Meggle USA, DuPont de Nemours, Ashland, Evonik Industries AG (Rag-Stiftung), Kerry Group PLC, and Colorcon Inc. (BPSI Holdings). These companies compete by offering high-purity, GMP-grade excipients designed to stabilize complex biologics, support high-concentration formulations, and meet stringent regulatory standards. Their portfolios span polymers, amino acids, surfactants, sugar alcohols, and multifunctional stabilizers used across monoclonal antibodies, vaccines, and biosimilars. North America leads the market with approximately 38% share, driven by advanced biologics manufacturing capacity, extensive CDMO networks, and sustained investment in high-performance formulation technologies.
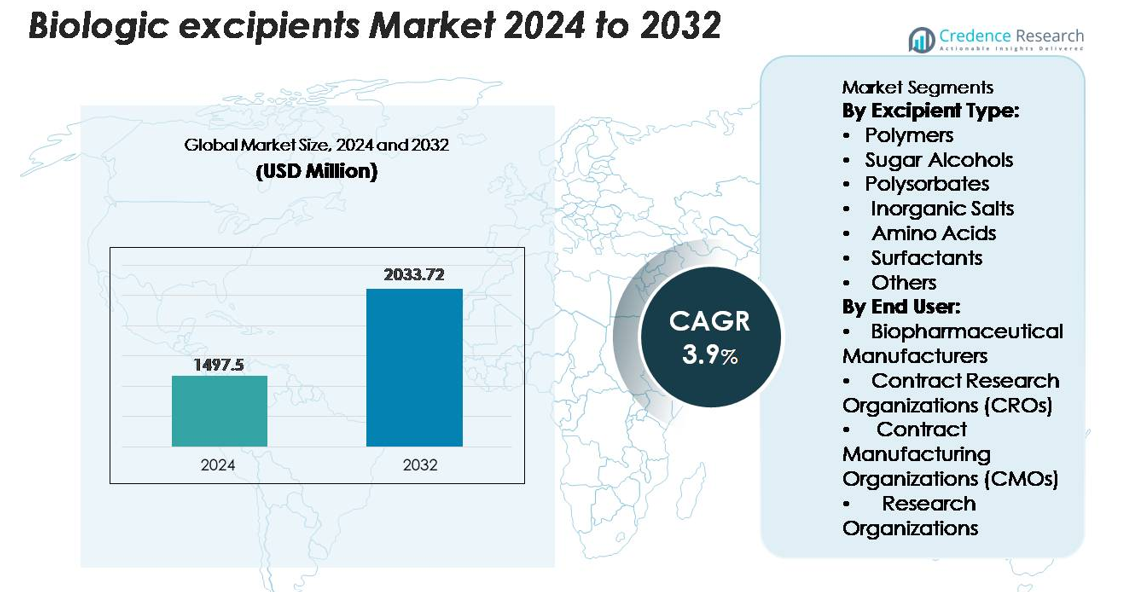
Market Insights
- The biologic excipients market reached USD 1,497.5 million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 2,033.72 million by 2032, expanding at a 3.9% CAGR during the forecast period.
- Demand grows as complex biologics, high-concentration mAbs, and advanced delivery systems require stabilizers, polymers, amino acids, and surfactants that ensure structural integrity, manufacturability, and extended shelf life.
- Trends include increased adoption of high-purity multifunctional excipients, rising biosimilar production, and expanded CDMO outsourcing for formulation, lyophilization, and aseptic fill-finish operations.
- Competition strengthens as global players invest in GMP-grade purification, low-endotoxin excipient lines, and scalable supply chains. Polymers hold the dominant segment share, driven by their critical role in protein stabilization and viscosity control.
- Regionally, North America leads with around 38%, followed by Europe at 28% and Asia-Pacific at 23%, supported by growing biomanufacturing capacity, biosimilar pipelines, and investments in high-performance formulation technologies.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Excipient Type
Polymers represent the dominant excipient class, accounting for the largest market share due to their essential role in stabilizing complex biologics, improving viscosity profiles, and supporting controlled-release formulations. High-performance polymers such as PEG derivatives and hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) support protein integrity across varied pH and temperature conditions, making them indispensable in monoclonal antibody (mAb) and recombinant protein formulations. Their versatility across injectables, vaccines, and emerging cell-based therapeutics continues to reinforce demand.
Sugar alcohols, polysorbates, inorganic salts, amino acids, surfactants, and other minor excipients collectively support specific stabilization and solubility requirements in biologic manufacturing. Sugar alcohols like mannitol enhance tonicity and lyophilization performance, while polysorbates reduce protein aggregation in high-concentration biologics. Amino acids such as arginine mitigate viscosity spikes, and inorganic salts balance ionic strength in formulation buffers. Although niche in volume, these categories remain essential for formulation optimization as biologics grow more structurally complex.
- For instance, Evonik’s RESOMER® PEG-PLA block-copolymer technology demonstrated controlled drug-release durations of up to 180 days and maintains polymer molecular weights between 10,000 and 45,000 g/mol, enabling long-acting biologic compatibility.
By End User
Biopharmaceutical manufacturers hold the dominant share of biologic excipient consumption, driven by large-scale production of mAbs, fusion proteins, vaccines, and next-generation biologics. Their reliance on high-purity excipients ensures batch consistency, regulatory compliance, and long-term product stability. As biologics pipelines expand and advanced formulation technologies gain adoption, manufacturers increasingly prefer multifunctional and high-grade excipients that enable improved processing efficiency and reduced degradation risks across cold-chain and high-stress manufacturing environments.
CROs, CMOs, and research organizations contribute steadily to excipient demand as outsourcing intensifies across discovery, development, and commercial-scale production. CMOs, in particular, are expanding capacity for biologics fill-finish, aseptic processing, and lyophilization boosting the need for excipients that support scalable, high-throughput manufacturing. CROs utilize specialized excipients in preclinical and formulation screening, while research organizations drive early-stage innovation. Collaboration models and increasing biologics complexity continue to elevate these segments’ contribution to overall excipient usage.
- For instance, in April 2022, Catalent announced a $350 million multi-year investment at its Bloomington facility to expand biologic drug substance and drug product manufacturing capabilities. This expansion included plans for additional lyophilized vial capacity and new syringe filling lines, along with new 2,000-liter single-use bioreactors.
Key Growth Drivers
Expansion of Monoclonal Antibodies and Complex Biologics Pipeline
The rapid expansion of monoclonal antibodies, antibody drug conjugates, recombinant proteins, and cell-based therapies significantly accelerates the demand for high-performance biologic excipients. As these therapies become more structurally complex and sensitive to temperature, pH shifts, and mechanical stress, manufacturers increasingly rely on stabilizers, polymers, surfactants, and buffering agents to maintain product integrity throughout development and commercialization. Biologics with high protein concentrations, in particular, require excipients that prevent aggregation, control viscosity, and optimize solubility without compromising activity. Growing investments in oncology and immunology biologics combined with rising approvals for biosimilars continue to intensify formulation challenges. This reinforces the strategic role of advanced excipients that enhance shelf life, enable cold-chain efficiency, and improve manufacturability, thereby becoming integral to next-generation biologics development.
- For instance, Bristol Myers Squibb uses polysorbate formulations and controlled manufacturing processes to manage protein aggregation and support the stability of its nivolumab product, a standard practice in the biopharmaceutical industry.
Rising Adoption of Advanced Formulation and Delivery Technologies
Biologic manufacturers increasingly adopt sophisticated formulation technologies such as lyophilization, controlled-release systems, high-concentration liquid formulations, and prefilled syringes. These technologies require excipients capable of supporting structural stability, improving reconstitution profiles, and ensuring compatibility with delivery devices. Growth in subcutaneous self-administration, autoinjectors, and long-acting injectables elevates the need for excipients that maintain low viscosity and high potency even at elevated protein loads. Additionally, the industry is shifting toward multifunctional excipients that streamline formulation steps and reduce reliance on multiple stabilizers. The push for patient-centric biologics and minimally invasive delivery routes also increases the use of tonicity agents, viscosity modifiers, and protein-protective surfactants. These advancements solidify excipients as critical enablers of innovation in biologic drug delivery.
- For instance, “Pharmaceutical companies, including those that were part of the former Baxter BioPharma Solutions (BPS) business, routinely validate trehalose-based lyophilized formulations as stabilizers for sensitive biological products, such as vaccines and proteins.
Increased Outsourcing to CDMOs and Standardization of GMP-Grade Inputs
The expansion of global outsourcing to CDMOs enhances demand for high-purity, GMP-compliant excipients needed for clinical and commercial biologics production. As more biopharma companies shift to flexible, outsourced manufacturing models, they rely on CDMOs to provide excipients that meet stringent regulatory, reproducibility, and quality-control standards. This increases adoption of low-endotoxin, low-particle-burden, and high-stability excipients across formulation, fill-finish, and aseptic processing workflows. Regulatory agencies also emphasize consistency and traceability, prompting wider use of excipients with robust documentation, validated supply chains, and pharmaceutical-grade specifications. CDMOs’ growing role in lyophilization, biologics scale-up, and cold-chain logistics further accelerates excipient demand across therapeutic categories. This structural outsourcing trend ensures recurring, long-term consumption of specialized excipients globally.
Key Trends & Opportunities
Shift Toward High-Purity and Multifunctional Excipients for Stability Optimization
A major trend shaping the biologic excipients landscape is the shift toward high-purity, multifunctional excipients designed to stabilize sensitive molecules under increasing formulation stress. Biologic drugs now require tighter impurity specifications, lower endotoxin levels, and improved physicochemical consistency. Manufacturers are focusing on excipients that provide multiple benefits such as stabilizing proteins, improving solubility, and controlling viscosity thereby reducing overall formulation complexity. Multifunctional polymers, amino acids, and surfactants present strong opportunities for suppliers developing differentiated, regulatory-friendly products. As biologics grow more temperature-sensitive, cold-chain-dependent, and concentration-intensive, demand for excipients that minimize aggregation, prevent degradation, and extend shelf life is rising. These innovations create significant commercial opportunities for companies offering engineered excipients tailored to next-generation biologics.
Growing Opportunity in Biosimilars and Emerging Market Biologics Manufacturing
The global expansion of biosimilars presents a substantial long-term opportunity for excipient manufacturers. As more biosimilar versions of blockbuster biologics enter development, demand for excipients used in analytical comparability, formulation optimization, and scale-up increases. Emerging markets including Asia-Pacific, Eastern Europe, and Latin America are rapidly expanding their biologics manufacturing capacity, creating new demand pools for cost-efficient, compliant excipients. Suppliers that offer scalable production, strong regulatory documentation, and supply continuity are positioned to benefit. Additionally, biosimilars often require sophisticated stabilization systems to match the reference biologic’s performance, driving increased use of polymers, sugar alcohols, and amino acids. This trend strengthens long-term market growth prospects for excipient innovators.
- For instance, Roquette offers a range of PEARLITOL® mannitol products, including a PEARLITOL® BioPharma Low Endotoxin Mannitol grade that is intended for biopharmaceutical applications such as protein stabilization.
Key Challenges
Increasing Complexity of Biologics Driving High Formulation and Stability Barriers
Biologics are inherently unstable and sensitive to temperature fluctuations, mechanical stress, light exposure, and pH variability. Formulating these molecules requires excipients that can prevent denaturation, aggregation, or loss of bioactivity across manufacturing, storage, and administration. However, not all excipients interact predictably with high-concentration biologics, leading to risks of instability or incompatibility. The challenge intensifies as biologics become harder to stabilize, particularly large-molecule therapies and next-generation proteins with unconventional structures. Manufacturers must perform extensive screening, compatibility testing, and long-term stability studies, extending development timelines and increasing formulation costs. These scientific and technical complexities remain a significant constraint for the biologic excipients market.
Regulatory Constraints and Limited Innovation in Approved Excipients
Excipients used in biologics face stringent regulatory scrutiny, requiring comprehensive safety data, toxicological profiling, and reproducibility across batches. Introducing new excipients into biologic formulations is challenging because regulatory pathways favor established, well-characterized substances. This slows innovation, limits formulation flexibility, and forces manufacturers to repeatedly optimize a narrow set of approved excipients. Any deviation such as introducing a novel polymer or surfactant may necessitate extensive regulatory justification or additional clinical evaluation. Supply-chain compliance, GMP adherence, and quality-system requirements further increase operational burdens for manufacturers. These regulatory and documentation challenges restrict the pace of excipient innovation, acting as a significant market constraint.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America holds the largest share of the biologic excipients market, accounting for around 38% of global demand. The region benefits from advanced biologics research, strong FDA regulatory frameworks, and high-volume production of monoclonal antibodies and recombinant proteins. Major biopharmaceutical companies and CDMOs located in the United States drive continuous uptake of high-purity polymers, surfactants, and amino acid stabilizers. Growing biosimilars development, large clinical pipelines, and expanding investments in advanced drug-delivery technologies further strengthen regional consumption. Strategic emphasis on GMP-grade excipients and robust supply-chain capabilities reinforces North America’s leadership in the global market.
Europe
Europe represents approximately 28% of the biologic excipients market, supported by strong biopharmaceutical manufacturing hubs across Germany, Switzerland, the U.K., and France. The region’s emphasis on high-quality standards, regulatory compliance through EMA guidelines, and advanced biologics R&D drives steady demand for stabilizers, buffering agents, and multifunctional excipients. Expansion of biosimilar approvals and investment in next-generation biologics enhances adoption across fill-finish and formulation workflows. Europe also benefits from a well-established network of CDMOs specializing in aseptic manufacturing and lyophilization, further boosting excipient utilization across both clinical and commercial biologic production.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific accounts for around 23% of the global market and is the fastest-growing regional segment. Strong expansion in biologics manufacturing across China, India, South Korea, and Singapore fuels demand for high-purity excipients used in vaccines, monoclonal antibodies, and biosimilars. Government incentives supporting biomanufacturing, coupled with increased investments from multinational pharma companies, elevate regional capacity. Asia-Pacific CDMOs are rapidly strengthening fill-finish, fermentation, and formulation capabilities, further accelerating excipient consumption. Growing domestic pipelines and competitive biosimilar development make the region a strategic growth hub for suppliers offering cost-efficient, GMP-compliant excipients.
Latin America
Latin America holds about 6% of the biologic excipients market, driven by expanding pharmaceutical manufacturing activity in Brazil, Mexico, and Argentina. The region’s biologics sector is gradually advancing, supported by rising adoption of biosimilars, improvements in regulatory frameworks, and increasing investments in local bioprocessing infrastructure. Demand for excipients is strongest in vaccine production, oncology biologics, and contract manufacturing operations. However, dependency on imported pharmaceutical-grade excipients remains significant, shaping procurement strategies. Growing partnerships with global biopharma companies and CDMOs help the region improve formulation quality, thereby supporting gradual but consistent expansion of excipient usage.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region contributes approximately 5% to global market revenue, with growth concentrated in the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries and South Africa. Increasing investment in healthcare infrastructure and the establishment of localized biopharmaceutical manufacturing units support excipient demand. Vaccine production, plasma-derived therapies, and biosimilar imports drive usage of stabilizers, polymers, and tonicity agents. Although the region still relies heavily on imported excipients, government-led initiatives aimed at developing domestic pharmaceutical capabilities strengthen prospects. Growing research collaborations and targeted investments in biotechnology contribute to a steady growth trajectory across the region.
Market Segmentations:
By Excipient Type:
- Polymers
- Sugar Alcohols
- Polysorbates
- Inorganic Salts
- Amino Acids
- Surfactants
- Others
By End User:
- Biopharmaceutical Manufacturers
- Contract Research Organizations (CROs)
- Contract Manufacturing Organizations (CMOs)
- Research Organizations
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
The biologic excipients market features a moderately consolidated competitive landscape, shaped by global suppliers specializing in high-purity polymers, stabilizers, surfactants, amino acids, and buffering systems tailored for complex biologics. Leading companies compete through advancements in GMP-grade production, low-endotoxin specifications, and multifunctional excipient technologies that support high-concentration formulations and cold-chain stability. Strategic priorities include expanding biopharmaceutical partnerships, strengthening supply-chain resilience, and enhancing documentation packages to meet stringent regulatory requirements. Several players are investing in upgraded purification systems, continuous manufacturing lines, and excipient innovations optimized for monoclonal antibodies, vaccines, and biosimilars. Collaborations with CDMOs and biopharma manufacturers further intensify competition as firms seek to secure long-term supply agreements. Meanwhile, regional suppliers in Asia-Pacific enhance market competitiveness by offering cost-efficient, globally compliant excipients, adding pressure to established Western producers.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
Recent Developments
- In October 2025 Ashland launched its Vialose™ sucrose high-purity sugar excipient tailored for parenteral biologic medicines, meeting endotoxin levels below 0.2 EU/g.
- In June 2025, BASF announced the expansion of its GMP “Solution Center” in Wyandotte (USA) under its Pharma Solutions business, affirming commitment to customized formulation and biologics manufacturing support.
- In October 2024, Croda launched its Super Refined™ Poloxamer 188, a high-purity granular excipient engineered for cell culture and biopharmaceutical formulations.
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Excipients type, End-User and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- Demand for high-purity and multifunctional excipients will increase as biologics become more structurally complex and concentration-intensive.
- Adoption of advanced delivery formats such as autoinjectors, prefilled syringes, and long-acting injectables will elevate the need for stabilizers and viscosity-reducing excipients.
- Growth in biosimilars manufacturing across emerging markets will expand global consumption of polymers, amino acids, and surfactants.
- CDMO capacity expansion will drive higher procurement of GMP-grade excipients for formulation, scale-up, and aseptic fill-finish workflows.
- Innovation will accelerate in engineered excipients designed to minimize aggregation and improve protein stability under thermal and mechanical stress.
- Regulatory expectations for traceability and low-endotoxin specifications will push suppliers to upgrade purification technologies.
- Lyophilization-focused excipients will gain traction as freeze-dried biologics rise across vaccines and specialty therapeutics.
- Digital formulation tools and predictive modeling will optimize excipient selection and compatibility studies.
- Supply-chain resilience efforts will encourage regionally diversified excipient production.
- Collaboration between biopharma firms and excipient manufacturers will strengthen development of customized, molecule-specific excipient systems.




