Market Overview:
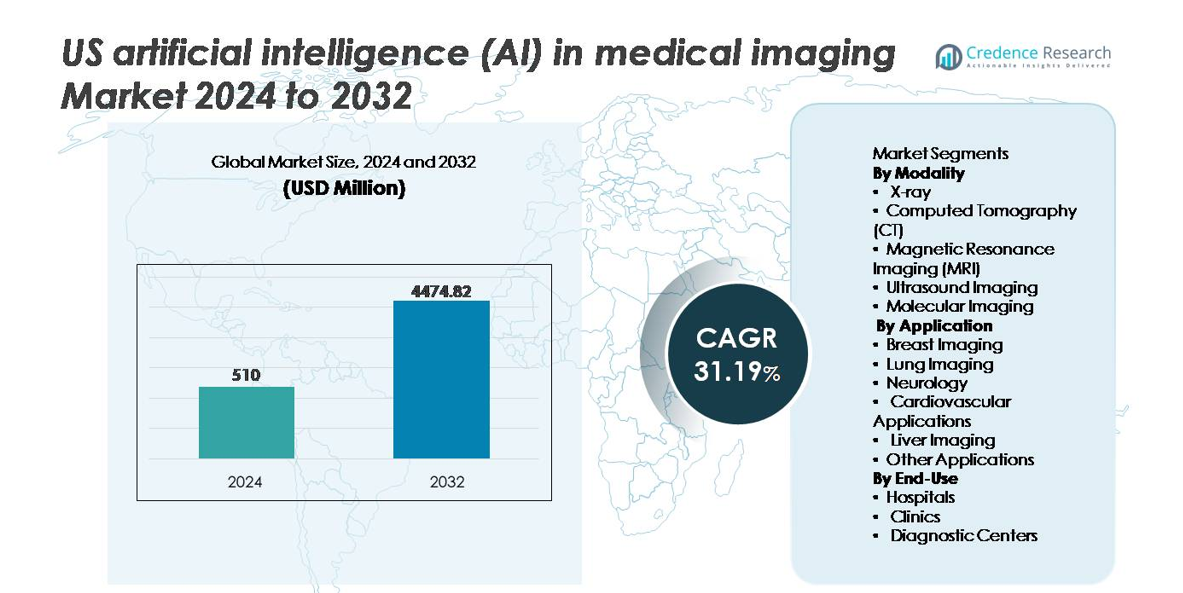
The U.S. artificial intelligence (AI) in medical imaging market was valued at USD 510 million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 4,474.82 million by 2032, registering a robust CAGR of 31.19% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| US Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Medical Imaging Market Size 2024 |
USD 510 million |
| US Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Medical Imaging Market, CAGR |
31.19% |
| US Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Medical Imaging Market Size 2032 |
USD 4,474.82 million |
The U.S. artificial intelligence (AI) in medical imaging market is shaped by a mix of global healthcare technology leaders and specialized AI innovators, including Nanox Imaging LTD., GE Healthcare, Lunit Inc., IBM Watson Health, InformAI LLC, Intel Corporation, and Koninklijke Philips N.V. These companies focus on developing AI-powered image interpretation, workflow automation, and predictive diagnostic solutions across CT, MRI, X-ray, and multimodal platforms. Strategic partnerships with healthcare systems, expanding FDA clearances, and cloud-enabled deployment models strengthen their competitive position. Regionally, the South leads the market with approximately 28% share, driven by a high number of diagnostic centers, rapid hospital expansion, and strong adoption of AI-assisted imaging for chronic disease management and high-volume screening.
Market Insights:
- The U.S. AI in medical imaging market was valued at USD 510 million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 4,474.82 million by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 31.19% during the forecast period.
- Market growth is driven by rising demand for early diagnostics, automation of radiology workflows, and AI-powered decision support tools that reduce reporting times and improve diagnostic accuracy across CT, MRI, and X-ray modalities, with CT holding the dominant segment share.
- Key market trends include the expansion of cloud-based AI platforms, generative AI for automated reporting, and multimodal diagnostic intelligence integrating imaging with clinical and genomic data for precision treatment planning.
- Competitive activity intensifies as major players and specialized vendors compete through FDA approvals, hospital partnerships, and AI marketplace integration, while high integration costs and interoperability challenges remain core restraints.
- Regionally, the South leads with 28% market share, followed by the West at 22%, Northeast at 20%, and Midwest at 18%, reflecting varied healthcare infrastructure and adoption maturity.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Modality
Computed Tomography (CT) represents the dominant modality segment in the U.S. AI medical imaging market, accounting for the largest share due to its extensive utilization in cancer detection, stroke evaluation, and trauma diagnostics. AI-powered CT platforms support workflow automation, rapid image reconstruction, and improved lesion characterization, significantly reducing reporting time and diagnostic variability. MRI and X-ray follow as fast-growing sub-segments driven by AI-enabled noise reduction and enhanced contrast analytics. Meanwhile, ultrasound and molecular imaging increasingly adopt AI for real-time decision support and pathology quantification, expanding clinical utility across cardiology and oncology.
- For instance, GE HealthCare’s Revolution Apex platform integrates its Deep Learning Image Reconstruction (DLIR) engine, which can generate high-resolution CT images from raw data at up to 1024 matrix output, enhancing clarity for small-structure evaluation while reducing the need for repeat scans.
By Application
Breast imaging holds the highest market share within the application segment, largely attributed to AI deployment in mammography, tomosynthesis interpretation, and early tumor detection. High screening volumes and regulatory support for computer-aided detection accelerate adoption and reimbursement alignment. Lung imaging follows closely, driven by AI–assisted nodule triaging and incidental finding management in COPD and lung cancer screening programs. Neurology, cardiovascular, and liver imaging leverage AI for anatomical modeling, perfusion analytics, and fibrosis scoring, while other emerging applications expand toward orthopedic, dental, and gastroenterology decision-support systems.
- For instance, Lunit Inc. reports that its INSIGHT MMG AI algorithm achieved an AUC of 0.99 in a real-world validation study of over 240,000 mammography cases, improving cancer detection sensitivity while helping reduce false-negative outcomes for dense-breast populations.
By End-Use
Hospitals dominate the end-use segmentation due to higher imaging volumes, larger integration budgets, and advanced IT infrastructure supporting AI-enabled PACS, workflow orchestration, and cross-departmental data exchange. AI adoption in hospitals also accelerates through enterprise-wide diagnostic pathways and precision-medicine programs, particularly for oncology and neurology. Diagnostic centers exhibit expanding uptake as providers prioritize rapid turnaround and competitive differentiation through AI-enabled triage and reporting optimization. Clinics adopt AI at a smaller yet growing scale, driven by cloud-based imaging analytics and reduced hardware dependency, enabling decentralized diagnostic capability.
Key Growth Drivers:
Rising Demand for Early Diagnostics and Precision Imaging
The growing emphasis on early disease detection, precision medicine, and targeted therapies drives rapid adoption of AI in U.S. medical imaging. Healthcare systems increasingly prioritize the reduction of diagnostic errors, accelerated report turnaround, and enhanced detection sensitivity for chronic conditions such as cancer, neurological disorders, and cardiovascular diseases. AI algorithms support radiologists with automated triaging, lesion quantification, risk stratification, and predictive analytics based on large image datasets. Hospitals benefit from improved workflow efficiency by reducing radiologist burdens and eliminating repetitive manual tasks. Moreover, AI platforms improve diagnostic consistency across complex multispecialty networks and facilitate earlier intervention through anomaly detection that surpasses conventional visual interpretation. As value-based care and quality-linked reimbursement models expand, providers continue to adopt AI-driven tools that demonstrate measurable clinical outcome improvements and resource optimization.
- For instance, Lunit’s INSIGHT MMG demonstrated improved early detection by correctly localizing 31.3% of mammographically occult breast cancers in a specific study, including cases that were originally overlooked by human readers. The AI tool has been confirmed in various large-scale, real-world evaluations to help radiologists find cancers that were previously missed, increasing overall cancer detection rates.
Integration of AI-Enabled Clinical Decision Support (CDS)
AI-assisted clinical decision support systems transform radiology workflows by providing real-time alerts, prioritization recommendations, and contextual information to support more informed and timely decisions. Integration with PACS, EHRs, and RIS platforms enables radiologists to access consolidated patient histories, imaging comparisons, and risk indicators within the same interface. These CDS capabilities are particularly impactful in emergency and critical care settings where speed and accuracy are essential. Predictive AI models help forecast disease progression, recommend additional scans, or highlight urgent abnormalities requiring immediate review. As healthcare organizations expand tele-radiology services and distributed reading networks become more common, AI-enabled CDS platforms ensure consistent interpretation quality regardless of location. The move toward autonomous reporting assistants further strengthens AI’s role, improving throughput without compromising clinical accuracy.
- “For instance, Aidoc’s AI triage system supports 18FDA-cleared clinical indications and processes imaging data to deliver critical condition alerts, including intracranial hemorrhage and pulmonary embolism, with notifications reaching care teams in under two minutes from scan acquisition.
Expansion of Cloud-Based AI Imaging Platforms
Cloud-native AI architecture significantly reduces capital expenditure and enables scalable deployments across large health systems, imaging chains, and independent clinics. Cloud platforms facilitate rapid software updates, continuous model learning, and multi-institutional data aggregation for improved algorithm accuracy. This model supports remote diagnostics, allowing sub-specialist interpretation across geographically dispersed facilities without latency or storage constraints. Vendor-neutral cloud ecosystems also ensure compatibility with diverse imaging equipment, extending AI access beyond high-end radiology departments to smaller and rural facilities. The proliferation of cybersecurity frameworks, federated learning, and HIPAA-compliant data management boosts provider confidence in cloud adoption. Subscription-based pricing models improve affordability and democratize AI access, fostering broader market penetration across U.S. healthcare infrastructure.
Key Trends & Opportunities:
AI-Enabled Multimodal Diagnostic Intelligence
A key emerging opportunity lies in the integration of imaging data with genomics, pathology, and clinical records, forming multimodal diagnostic ecosystems. AI platforms combine structured and unstructured data to create comprehensive patient profiles that support disease risk prediction, treatment planning, and response monitoring. Oncology care benefits greatly as AI-enabled radiomics translates image-derived patterns into biomarkers that correlate with tumor aggressiveness and therapy effectiveness. Multimodal intelligence reduces reliance on invasive biopsies and helps clinicians intervene earlier. Partnerships between imaging vendors, biotech companies, and genomic research institutions accelerate the commercialization of integrated diagnostic solutions, unlocking new reimbursement paths and strengthening precision-medicine initiatives.
- For instance, Tempus’ multimodal AI platform analyzed more than 6 million de-identified clinical records and over 50 petabytes of oncology data to generate predictive models that correlate imaging signals with genomic mutations for precision therapy selection.
Generative AI and Automation of Radiology Reporting
Generative AI introduces compelling opportunities by automating structured report creation, summarizing radiology findings, and converting images into contextual written analyses. These models shorten reporting cycles, standardize terminology, and reduce administrative workloads for radiologists. Automation extends into appointment scheduling, protocol selection, and study prioritization, further optimizing department operations. The technology enhances training and knowledge transfer by helping junior clinicians learn interpretation patterns and differential diagnosis methodologies. Additionally, generative AI supports patient-facing communication by simplifying complex imaging results into plain-language summaries, improving engagement and comprehension. As validation frameworks for generative AI evolve, its broader clinical adoption will accelerate across hospitals, tele-radiology services, and urgent care centers.
- For instance, Nuance’s PowerScribe platform, enhanced by its AI-driven reporting engine, supports more than 6,500 U.S. healthcare facilities and automates voice-driven report creation for over 80% of radiologists across its network, demonstrating scale in generative documentation workflows.
Growing Adoption of AI in Remote and Point-of-Care Imaging
Remote diagnostics and point-of-care ultrasound present significant growth opportunities for AI imaging solutions, particularly in underserved and rural U.S. regions. AI enhances the acquisition and interpretation of non-specialist imaging, enabling emergency physicians, primary care providers, and paramedics to perform scanning with decision-support guidance. The trend aligns with evolving care models that emphasize decentralization, home-based care, and rapid-response medical services. Portable imaging integrated with AI helps expedite care pathways for trauma, stroke, and cardiac events by enabling earlier triage before hospital arrival. As telehealth reimbursement expands and point-of-care devices become more affordable, AI-supported imaging will gain broader uptake beyond traditional radiology departments.
Key Challenges:
Regulatory Complexity and Validation Requirements
The regulatory environment for AI in medical imaging remains a significant challenge as the industry shifts from static algorithms to continuously learning models. Regulatory bodies require stringent clinical validation to ensure patient safety, algorithm reliability, and equitable performance across diverse demographic profiles. AI developers must address bias mitigation, explainability, and traceability of decision-making processes. Recertification requirements increase as models evolve through real-world data exposure. Compliance with HIPAA, FDA guidance, and state-by-state regulations adds cost and time to commercialization. These hurdles slow adoption and create barriers for smaller innovators facing resource constraints in regulatory navigation and documentation.
Interoperability, Data Fragmentation, and Integration Costs
Despite clear clinical value, successful AI adoption depends heavily on seamless interoperability with existing hospital IT ecosystems. Data fragmentation across disparate PACS, EHR, and RIS systems limits algorithm training quality and restricts real-time analytics. Retrofitting AI within aging legacy infrastructure imposes integration expenses that may deter smaller providers. Standardization gaps in imaging formats, labeling practices, and annotation datasets hinder cross-institutional model scalability. Concerns around data sharing, cybersecurity, and patient consent contribute to operational complexity. Without structured data governance frameworks, healthcare organizations risk inconsistent results, workflow disruptions, and incomplete clinical benefits from AI deployments.
Regional Analysis:
Northeast
The Northeast region accounts for approximately 20% of the U.S. AI in medical imaging market. High concentration of academic medical centers, leading research hospitals, and strong adoption of advanced radiology services support AI penetration. Large health systems in urban hubs drive early adoption of AI-based CT, MRI and mammography technologies, enabling fast triage and diagnostic workflows. Additionally, dense population and high screening volumes for cancer and cardiovascular diseases increase demand for AI-enabled imaging, making the Northeast a core region for growth and innovation.
Midwest
The Midwest holds around 18% market share in U.S. AI medical imaging. This region benefits from a robust network of community and regional hospitals, along with a growing number of diagnostic imaging centers spread across smaller cities and suburban areas. The high number of imaging centers (~3,304 as recently reported) provides a large base for deploying AI-powered imaging solutions. Providers in the Midwest increasingly adopt cloud-based AI platforms to modernize legacy imaging systems and improve diagnostic throughput, particularly for CT and ultrasound, meeting rising demand for chronic disease screening.
South (including Southeast)
The South, including the Southeast, represents roughly 28% of the U.S. AI in medical imaging market — the largest regional share among U.S. regions. The region hosts the greatest number of imaging centers (≈ 4,169), reflecting high demand for diagnostic services. Rapid population growth, rising prevalence of chronic illnesses, and expanding hospital infrastructure stimulate AI adoption across modalities (CT, X-ray, ultrasound) and applications (cardiovascular, oncology, general diagnostics). Many healthcare chains in the South implement AI to standardize imaging quality and handle large patient volumes efficiently, making it a major growth engine.
West
The Western region captures about 22% share of the U.S. AI imaging market. The West features a mix of large metropolitan hospitals, regional health networks, and an increasing number of outpatient diagnostic centers. Adoption of AI in imaging is driven by innovation hubs, technology-savvy healthcare providers, and early adoption of cloud-native imaging platforms. Growing demand in urban and suburban areas, particularly in states with expanding populations and modern healthcare infrastructure, fuels uptake of AI-enabled MRI, CT, and molecular imaging solutions. The West’s balanced distribution of hospitals and diagnostic centers positions it as a strong growth region.
Southwest & Other Regions (incl. rural / smaller states)
The Southwest and smaller U.S. regions together hold about 12% of the market. Though infrastructure is more fragmented and fewer high-end imaging centers exist compared to major metro regions, there is steady growth fueled by rural hospital upgrades and diagnostic center expansions. AI adoption in these areas is rising thanks to cloud-delivered AI services and mobile imaging solutions, which lower the barrier to entry for smaller facilities. As rural populations age and demand for imaging increases, these regions are poised to contribute modest but growing portions of overall market revenue.
Market Segmentations:
By Modality
- X-ray
- Computed Tomography (CT)
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
- Ultrasound Imaging
- Molecular Imaging
By Application
- Breast Imaging
- Lung Imaging
- Neurology
- Cardiovascular Applications
- Liver Imaging
- Other Applications
By End-Use
- Hospitals
- Clinics
- Diagnostic Centers
By Geography
- Northeast
- Midwest
- South
- West
- Southwest
Competitive Landscape:
The U.S. artificial intelligence (AI) in medical imaging market exhibits a highly competitive and rapidly evolving landscape, characterized by collaboration between global imaging OEMs, pure-play AI vendors, cloud providers, and health IT companies. Large imaging manufacturers and platform players focus on integrating FDA-cleared AI applications directly into PACS, scanners, and enterprise imaging suites, strengthening their position with end-to-end workflow solutions. Specialized AI firms concentrate on niche use cases such as stroke detection, lung nodule analysis, breast cancer screening, and triage tools, often partnering with hospitals and radiology groups for clinical validation and scaled deployment. Cloud and analytics providers enable secure, vendor-neutral AI marketplaces and subscription-based models that lower adoption barriers for mid-sized hospitals and diagnostic centers. Mergers, acquisitions, and strategic alliances remain frequent as companies seek to expand modality coverage, broaden indication portfolios, and achieve interoperability across heterogeneous imaging and health record environments.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis:
Recent Developments:
- In November 2025, Nanox announced a strategic partnership with 3DR® Labs, under which 3DR Labs will distribute Nanox.AI’s FDA-cleared imaging solutions to its network of 1,800+ hospitals and imaging centers across the U.S.
- In 2025, GE Healthcare announced that it will acquire Intelerad — a medical-imaging software provider — for about $2.3 billion, a strategic move that boosts GE’s cloud-based and AI-enabled imaging offerings for outpatient care markets.
- In December 2024, Nanox Imaging LTD. obtained FDA clearance for its Nanox.ARC imaging system for general use (including pulmonary indications).
Report Coverage:
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Modality, Application, End-User and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook:
- AI will become integral to diagnostic decision support, improving accuracy and reducing interpretation errors across major imaging modalities.
- Generative AI will automate structured reporting and enhance clinical documentation efficiency for radiologists.
- Multimodal AI platforms will integrate imaging, genomics, and electronic health records to support precision medicine.
- Adoption of cloud-based AI solutions will expand, enabling scalable deployments across hospitals and diagnostic centers.
- Real-time AI-assisted imaging at point-of-care settings will increase, supporting remote and rural healthcare delivery.
- AI-driven predictive analytics will assist clinicians in forecasting disease progression and treatment response.
- Federated learning will strengthen algorithm performance without compromising patient data privacy.
- Regulatory frameworks for adaptive AI models will evolve, accelerating approvals while ensuring safety.
- AI marketplaces will grow, offering plug-and-play diagnostic applications integrated into PACS and imaging systems.
- Partnerships between healthcare providers, technology firms, and research organizations will accelerate innovation and adoption.




