Market Overview
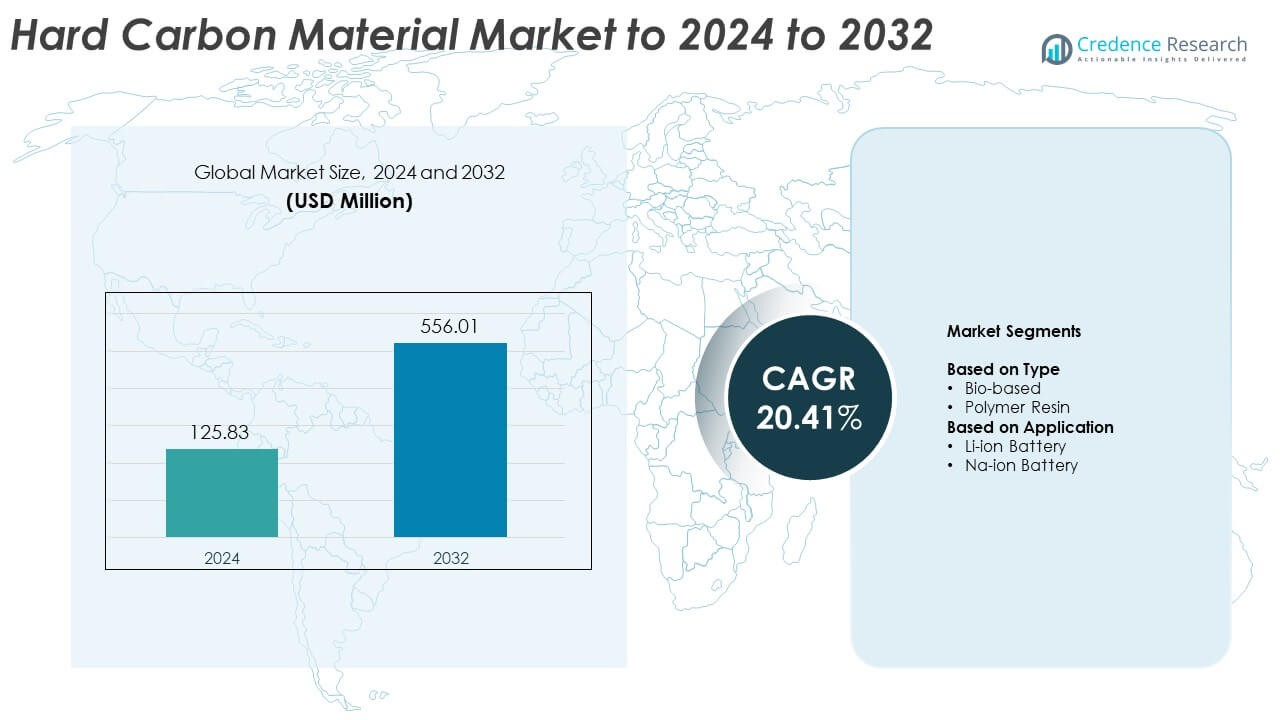
Hard Carbon Material Market size was valued USD 125.83 million in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 556.01 million by 2032, at a CAGR of 20.41% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Hard Carbon Material Market Size 2024 |
USD 125.83 Million |
| Hard Carbon Material Market, CAGR |
20.41% |
| Hard Carbon Material Market Size 2032 |
USD 556.01 Million |
The hard carbon material market includes leading companies such as Xiangfenghua, Stora Enso, Kuraray, Best Graphite, Indigenous Energy, Sumitomo, BRT, Putailai, Shengquan Group, JFE Chemical, HiNa Battery Technology, Kureha, Shanshan, and Jiangxi Zeto, each expanding production capacity and advancing precursor engineering to meet rising battery-grade material demand. These players focused on improving pore structure control, boosting first-cycle efficiency, and developing bio-derived variants to support sustainable battery manufacturing. Asia Pacific emerged as the dominant region with about 34% share in 2024, supported by large-scale Na-ion and Li-ion battery production, while North America and Europe followed with 31% and 28% shares respectively, driven by expanding gigafactory ecosystems and localized sourcing strategies.
Market Insights
- The hard carbon material market reached USD 125.83 million in 2024 and is projected to hit USD 556.01 million by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 20.41%.
- Strong demand for Li-ion and Na-ion batteries drives market growth, with the Li-ion segment holding about 64% share in 2024 due to high adoption in EVs and storage systems.
- Bio-based hard carbon is a major trend, gaining nearly 52% share as producers shift to sustainable precursors and low-emission processing routes.
- Competition intensifies as global and regional players expand capacity, enhance precursor engineering, and secure long-term supply agreements with battery manufacturers.
- Asia Pacific leads the market with about 34% share, followed by North America at 31% and Europe at 28%, supported by gigafactory growth, localized sourcing, and rising Na-ion commercialization.
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Type
Bio-based hard carbon dominated the type segment in 2024 with about 52% share due to rising demand for sustainable anode materials in energy-storage projects. Manufacturers adopted bio-derived precursors such as biomass and cellulose because these sources deliver higher porosity, stable interlayer spacing, and lower environmental impact. Petroleum-based and polymer-resin variants maintained steady use in projects that require tighter structural control and higher initial coulombic efficiency, but bio-based grades expanded faster as battery producers aligned with decarbonization goals and stricter material-sourcing policies.
- For instance, Stora Enso confirms that its Sunila Mill produces 50,000 tons per year of kraft lignin, used as the industrial precursor for its bio-based hard-carbon material Lignode.
By Application
Li-ion battery applications led the application segment in 2024 with nearly 64% share, supported by wider adoption of hard carbon as a high-performance anode in next-generation fast-charging cells. Battery makers selected hard carbon for its high reversible capacity, stable SEI formation, and strong cycling stability in EV and energy-storage systems. Na-ion battery applications grew at a rapid pace as companies scaled pilot manufacturing lines for low-cost and cold-temperature-tolerant storage systems, increasing demand for optimized hard-carbon structures.
- For instance, HiNa Battery Technology officially commissioned a Na-ion battery production line with an annual output capacity of 1 GWh in 2022, during the initial phase of its commercial operations in Fuyang, Anhui Province.
Key Growth Drivers
Rising demand for advanced battery materials
Global growth in electric mobility and stationary storage increased the need for high-performance anode materials. Hard carbon gained preference because it supports fast charging, stable cycling, and broader temperature tolerance. Manufacturers expanded investments as next-generation cells required higher capacity and stable SEI properties. Wider adoption of Na-ion and all-solid-state batteries pushed demand further, since hard carbon delivers strong compatibility with emerging chemistries. This shift positioned hard carbon as a core material in long-duration storage and cost-optimized battery platforms.
- For instance, CATL publicly disclosed that its first-generation Na-ion battery reaches an energy density of 160 Wh/kg, enabled by optimized hard-carbon anode structures.
Expansion of Na-ion battery commercialization
Accelerated progress in Na-ion battery deployment created strong momentum for hard-carbon demand. Several battery developers announced large-scale pilot lines and early commercial launches, increasing consumption of optimized hard-carbon structures. Na-ion chemistry attracted interest due to low raw-material cost, strong cold-temperature tolerance, and reduced dependency on lithium supply chains. These advantages encouraged energy-storage companies and automotive suppliers to integrate Na-ion packs for grid, mobility, and backup applications, strengthening the long-term demand outlook for hard carbon.
- For instance, Faradion validated its Na-ion cells to operate effectively at −20 °C, demonstrating stable performance using engineered hard-carbon anodes.
Shift toward sustainable and bio-derived materials
Industries prioritized sustainable precursors to reduce lifecycle emissions in battery manufacturing. Bio-based hard carbon gained wide acceptance because biomass and agricultural waste sources reduce carbon footprint while offering favorable porosity and structural stability. Governments encouraged greener material sourcing through stricter traceability rules and sustainability standards. This trend accelerated R&D efforts focused on cleaner processing routes, improved precursor conversion, and reduced energy intensity, expanding the market for environmentally aligned hard-carbon grades.
Key Trends & Opportunities
Growth of fast-charging and high-rate battery designs
Manufacturers developed new cell architectures that required anodes with improved ion diffusion and structural stability. Hard carbon aligned well with these needs due to its large interlayer spacing and strong cycling performance. Fast-charging EV platforms, light mobility solutions, and energy-storage systems adopted hard carbon to boost rate performance. This trend encouraged material producers to create engineered pore structures and controlled precursor treatments, opening opportunities for premium high-rate hard-carbon variants.
- For instance, Echion Technologies reports that its XNO™ niobium-oxide anode material enables lithium-ion batteries to safely ultra-fast charge in less than 10 minutes (approximately a 6C charge rate), demonstrating high-rate capability relevant to hard-carbon competitive benchmarking.
Technological advances in precursor optimization
Producers invested in advanced precursor engineering to enhance consistency, capacity retention, and first-cycle efficiency. Controlled heat-treatment profiles, tuned pore size distribution, and hybrid precursor blends offered higher yield and better electrochemical stability. Companies explored cost-effective biomass sources and polymer-resin formulations to improve scalability. These innovations created opportunities for differentiated products that meet specific needs of Na-ion, Li-ion, and emerging large-format battery systems.
- For instance, Kureha announced in January 2009 that production capacity for carbon fiber thread at its Iwaki factory would increase from 1,100 tons per year to 1,450 tons per year, with a planned future increase to 1,800 tons per year.
Expansion of regional gigafactory ecosystems
The rise of gigafactory projects in Asia, Europe, and North America opened new supply opportunities for hard-carbon producers. Battery manufacturers prioritized local sourcing of anode materials to enhance supply security and reduce import dependency. This shift encouraged investments in regional processing units, precursor facilities, and strategic partnerships. Growing integration of hard carbon into local battery supply chains created long-term opportunities for capacity expansion and tailored material grades.
Key Challenges
High production cost and limited large-scale supply
Producing high-quality hard carbon requires controlled temperatures, long processing cycles, and optimized precursor conversion. These steps increase energy use and operating cost, limiting price competitiveness against conventional graphite. Limited large-scale production capacity also restricts supply reliability for major battery manufacturers. Scaling to gigafactory-level volumes requires significant investment in process automation, precursor sourcing, and thermal-treatment infrastructure, creating barriers for new entrants.
Inconsistent performance across precursor types
Different precursor sources produce varying porosity, interlayer spacing, and impurity levels, leading to inconsistent electrochemical performance. These variations complicate standardization for large-volume battery manufacturing. Achieving high first-cycle efficiency and stable SEI formation remains a challenge, especially for Na-ion applications. Material producers must invest heavily in R&D and precise process control to meet uniform quality standards, slowing commercialization and increasing development cost.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America held about 31% share in 2024, supported by strong investment in advanced battery technologies and expanding pilot-scale Na-ion programs. Growing demand for energy-storage systems in grid modernization projects increased the need for reliable hard-carbon supply. Battery manufacturers in the United States scaled research partnerships with material innovators to improve performance consistency and reduce import reliance. Adoption of bio-based carbon gained traction as producers aligned with sustainability rules. Canada’s focus on clean-energy transitions further supported demand, strengthening regional growth across Li-ion and Na-ion precursor applications.
Europe
Europe accounted for nearly 28% share in 2024, driven by rapid expansion of gigafactory projects and strong regulatory frameworks promoting localization of battery supply chains. The region’s push toward low-carbon materials encouraged adoption of bio-derived hard-carbon grades. Germany, France, and the Nordic countries increased research investments to improve precursor stability and first-cycle efficiency. Rising interest in Na-ion platforms, especially for stationary storage, supported broader material demand. Growing partnerships between cell manufacturers and hard-carbon suppliers helped strengthen regional capacity expansion and reduce sourcing risks.
Asia Pacific
Asia Pacific dominated the market with about 34% share in 2024, supported by strong manufacturing bases in China, Japan, and South Korea. The region led commercial deployment of Na-ion batteries, boosting hard-carbon consumption for large-scale production lines. China’s rapid growth in biomass-derived carbon manufacturing improved both cost structure and supply availability. Japan’s material suppliers advanced polymer-resin-based variants with tighter structural control. Expanding EV production and energy-storage installations across the region strengthened demand, while regional firms continued scaling processing capacities to support global battery manufacturers.
Latin America
Latin America held close to 4% share in 2024, with demand driven by early-stage adoption of grid-scale storage and clean-energy programs. Countries such as Brazil and Chile focused on integrating cost-efficient energy-storage technologies, increasing interest in emerging Na-ion solutions. Local supply chains remained limited, encouraging collaboration with Asian and European suppliers to secure high-quality hard-carbon materials. Growing emphasis on sustainable raw-material sourcing created opportunities for biomass-derived hard-carbon production, especially in regions with strong agricultural waste availability.
Middle East and Africa
Middle East and Africa captured nearly 3% share in 2024, supported by rising renewable-energy investments and growing interest in long-duration storage technologies. Utility developers in the Gulf region explored Na-ion and alternative storage solutions that rely on cost-efficient hard-carbon anodes. The region’s limited material-processing base encouraged long-term supply agreements with global producers. Africa’s expanding solar-storage projects opened new demand prospects, while efforts to localize clean-energy supply chains gradually improved market visibility for hard-carbon suppliers.
Market Segmentations:
By Type
By Application
- Li-ion Battery
- Na-ion Battery
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
The hard carbon material market features active competition among major players such as Xiangfenghua, Stora Enso, Kuraray, Best Graphite, Indigenous Energy, Sumitomo, BRT, Putailai, Shengquan Group, JFE Chemical, HiNa Battery Technology, Kureha, Shanshan, and Jiangxi Zeto. Companies strengthened their positions through capacity expansion, advanced precursor engineering, and improved thermal-treatment technologies to ensure higher material consistency. Producers focused on optimizing pore structures, interlayer spacing, and first-cycle efficiency to meet the performance needs of Li-ion and Na-ion battery manufacturers. Sustainability initiatives accelerated the shift toward bio-derived precursors, pushing firms to enhance traceability and reduce processing emissions. Strategic partnerships with battery makers and gigafactory developers boosted long-term supply agreements, while regional players invested in localized production to reduce dependency on imported anode materials. Continuous R&D efforts supported commercialization of high-rate, low-cost, and high-capacity hard-carbon variants, reinforcing competitive differentiation in a rapidly expanding battery materials ecosystem.
Key Player Analysis
- Xiangfenghua (China)
- Stora Enso (Sweden)
- Kuraray (Japan)
- Best Graphite (China)
- Indigenous Energy (Australia)
- Sumitomo (Japan)
- BRT (China)
- Putailai (China)
- Shengquan Group (China)
- JFE Chemical (Japan)
- HiNa Battery Technology (China)
- Kureha (Japan)
- Shanshan (China)
- Jiangxi Zeto (China)
Recent Developments
- In 2025, Putailai New Energy Technology entered into a Joint Development Agreement with OneD Battery Sciences to scale production of next-generation silicon-graphite anode materials, integrating OneD’s SINANODE technology with Putailai’s carbon substrate expertise.
- In 2025, Shengquan completed the construction of a 10,000-ton-scale hard carbon anode production line, part of a broader plan to reach an eventual capacity of 100,000 tons per year.
- In 2024, Sumitomo Corporation announced its investment in Inherit Carbon Solutions, focusing on CO2 removal from biogas, which ties into carbon-neutral initiatives relevant for biomass-based hard carbon materials, aiming to create carbon credits from 2025 onward.
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Type, Application and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- Hard carbon demand will rise as Na-ion battery commercialization accelerates worldwide.
- Bio-based precursors will gain wider adoption due to sustainability and lower emissions.
- Battery makers will invest in engineered pore structures to improve capacity retention.
- Gigafactory expansions will strengthen regional sourcing and shorten supply chains.
- Fast-charging cell designs will push demand for high-rate hard-carbon variants.
- Producers will scale large-volume thermal-treatment facilities to reduce cost.
- Material consistency will improve through tighter precursor and heat-treatment control.
- Adoption will grow in grid-scale storage as performance needs shift toward durability.
- Collaboration between cell makers and material suppliers will accelerate product refinement.
- Hard carbon will become a core anode choice for next-generation cost-optimized batteries.




