Market Overview
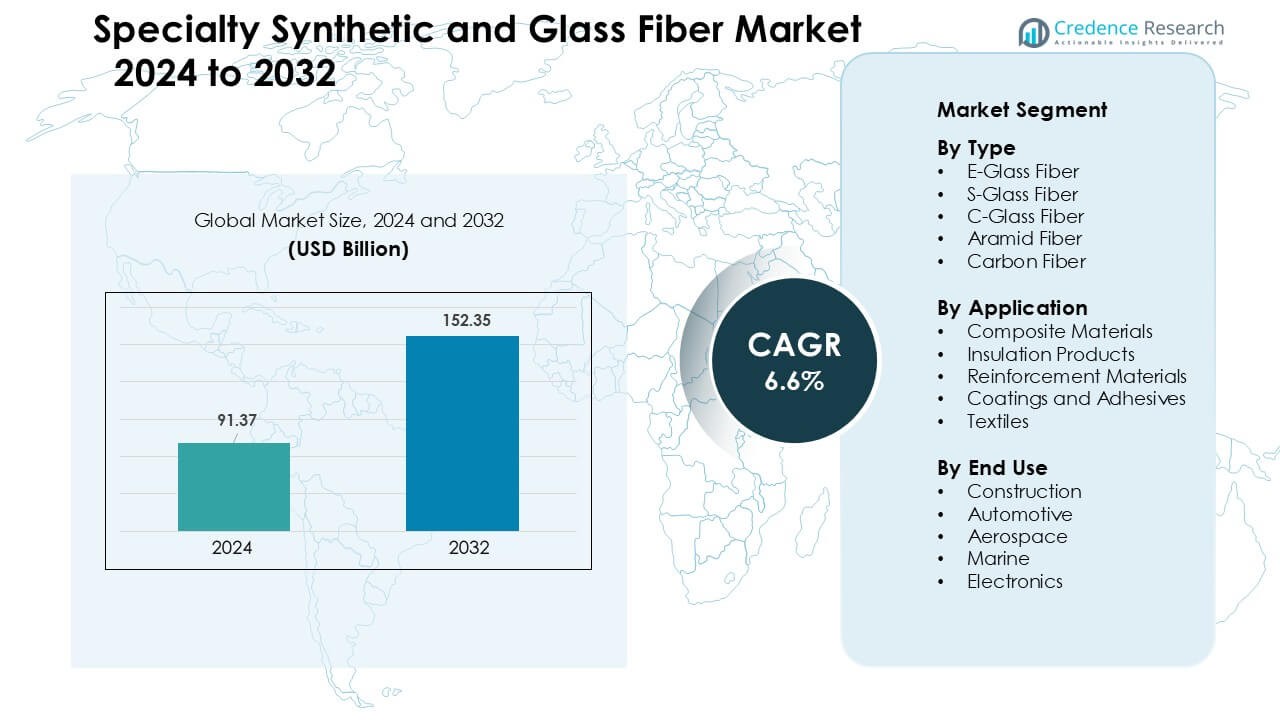
Specialty Synthetic and Glass Fiber Market was valued at USD 91.37 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 152.35 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 6.6 % during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Specialty Synthetic and Glass Fiber Market Size 2024 |
USD 91.37 Billion |
| Specialty Synthetic and Glass Fiber Market, CAGR |
6.6 % |
| Specialty Synthetic and Glass Fiber Market Size 2032 |
USD 152.35 Billion |
Top players in the Specialty Synthetic and Glass Fiber Market include Honeywell International, Jushi Group Co. Ltd., Royal DSM, Owens Corning, Mitsubishi Chemical Holdings Corporation, Hexcel Corporation, Toray Industries, Inc., DuPont, SGL Group, and Nippon Electrical Glass Co. These companies competed through capacity expansion, advanced composite technologies, and stronger partnerships with automotive, aerospace, and construction OEMs. North America emerged as the leading region in 2024 with 34% share, supported by strong aerospace production, expanding EV manufacturing, and high adoption of fiberglass and carbon-fiber-based structural materials across major industries.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Insights
- The Specialty Synthetic and Glass Fiber Market reached USD 91.37 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit USD 152.35 billion by 2032, growing at a 6.6 % CAGR.
- Demand grew as automotive, aerospace, and construction sectors increased adoption of lightweight and high-strength composite components, with E-glass fiber holding 48% share due to broad industrial usage.
- Key trends included rising use of carbon fiber in EV platforms, expansion of fiberglass in wind energy, and growing investment in recyclable composite technologies driven by sustainability targets.
- Leading companies such as Honeywell International, Jushi Group, DSM, Owens Corning, and Toray strengthened competitiveness through capacity expansions, material upgrades, and long-term OEM supply contracts, while cost volatility in raw materials remained a restraint.
- North America led the market with 34% share, supported by strong aerospace and EV output, while composite materials dominated applications with 52% share, and construction remained the top end-use segment with 39% share.
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Type
E-glass fiber dominated the type segment in 2024 with around 48% share. Buyers preferred E-glass fiber because the material offers strong tensile strength, low cost, and broad compatibility with polyester and epoxy systems. Demand stayed high in construction panels, wind-turbine blades, and transportation components due to strong mechanical reliability. S-glass and carbon fibers grew in high-performance sectors, but E-glass fiber remained ahead because producers scaled output efficiently and delivered stable supply for mass-market composite needs across global industries.
- For instance, Owens Corning, a major global composites firm, supports its high E-glass output across its extensive global network of manufacturing facilities (which includes 18 glass-fiber operations in 12 countries), enabling stable supply to wind blade and construction OEMs.
By Application
Composite materials led the application segment in 2024 with nearly 52% share. Industries used composite materials in structural parts for wind energy, vehicles, aircraft, and marine bodies due to strong stiffness-to-weight benefits. Fiberglass composites supported cost-effective production, while carbon and aramid composites served premium aerospace and defense uses. Growth came from wider adoption of lightweight designs and rising installation of composite-based infrastructure. Insulation and reinforcement uses expanded, but composite materials-maintained dominance because performance requirements favored advanced fiber-reinforced systems.
- For instance, Owens Corning supplies its Ultrablade® Triax glass‑fabric composites for wind turbine blades, enabling designers to produce rotor blades that are longer by up to 5 meters while still managing high fatigue loads because of the laminate’s stiffness and durability.
By End Use
Construction remained the largest end-use segment in 2024 with about 39% share. Builders used synthetic and glass fibers in rebar, roofing systems, façade panels, and insulation boards to boost durability, reduce corrosion, and enhance thermal efficiency. Demand increased as governments expanded infrastructure programs and developers adopted fiber-reinforced solutions to meet stricter safety rules. Automotive and aerospace gained pace with lightweighting programs, but construction held the lead because project volumes stayed high and fiber-enhanced materials delivered strong life-cycle and cost advantages for large-scale structural applications.
Key Growth Drivers
Growing Demand for Lightweight and High-Strength Materials
Lightweight and high-strength materials remained a major growth driver for the Specialty Synthetic and Glass Fiber Market in 2024. Manufacturers in automotive, aerospace, marine, and construction sectors adopted advanced fibers to replace steel and aluminum due to strong performance benefits. E-glass and carbon fibers helped reduce structural weight, improve energy efficiency, and enhance crash performance, which supported higher adoption across OEMs. Global electric vehicle programs boosted use of lightweight composites for battery enclosures, body panels, and structural reinforcements. Aerospace producers increased their reliance on carbon and aramid fibers for wings, fuselage sections, and interior components as fleets modernized. Construction firms accelerated the shift toward fiber-reinforced concrete and façade systems to increase durability. These combined shifts strengthened long-term demand.
- For instance, SGL Carbon developed a carbon-fiber‑reinforced plastic (CFRP) battery enclosure for NIO’s electric vehicles that is 40 percent lighter than an equivalent aluminium solution, improving crash dynamics and thermal insulation.
Infrastructure Expansion and Strong Construction Activity
Large-scale construction and infrastructure investments created strong momentum for specialty synthetic and glass fibers. Government spending on bridges, metro systems, industrial buildings, and renewable energy installations increased demand for fiber-reinforced concrete, insulation panels, rebar alternatives, and corrosion-resistant structural elements. E-glass fiber products gained wide use in roofing, cladding, pipe systems, and geotextiles due to their weather durability and low-maintenance benefits. The rise of smart cities and green-building certifications encouraged builders to choose materials with higher strength, longer service life, and improved thermal performance. The wind energy sector boosted consumption of glass and carbon fibers for turbine blades, nacelle covers, and support structures. In emerging markets, rapid urbanization increased requirements for lightweight and affordable composite-based construction products. Together, these factors strengthened construction-led fiber demand.
- For instance, Owens Corning markets its Cem-FIL® alkali‑resistant (AR) glass fibers for glass-reinforced concrete (GRC) applications, which have been used in architectural facades and precast concrete panels in over 100 countries for more than four decades.
Advancements in Composite Manufacturing Technologies
Technological improvements in composite manufacturing created a strong growth path for specialty fibers. Automated fiber placement, resin transfer molding, pultrusion, and additive composite manufacturing increased production efficiency and lowered unit costs. These advancements helped carbon and aramid fibers expand into mid-range automotive, industrial, and consumer goods applications. Material suppliers improved fiber surface treatments and sizing chemistry to enhance bonding with resin matrices, which improved structural performance. Integration of digital monitoring and simulation tools helped manufacturers optimize fiber alignment and reduce defects. Recycling technologies for thermoplastic composites also advanced, supporting sustainability goals. Widespread adoption of Industry 4.0 tools strengthened process accuracy and helped producers meet strict quality standards in aerospace and defense.
Key Trends & Opportunities
Rising Adoption of Sustainable and Recyclable Fiber Solutions
Sustainability trends created new opportunities in the Specialty Synthetic and Glass Fiber Market. Manufacturers developed recyclable thermoplastic composites, bio-based resins, and low-emission glass fiber production methods to comply with new environmental standards. Construction firms demanded materials with low embodied carbon for green infrastructure. Automotive OEMs shifted toward circular material flows and long-life components. Glass fiber producers expanded electric furnace capacity to cut energy use, while carbon-fiber developers worked on reclaiming fibers from cured composite waste. This shift toward cleaner production methods opened new market segments and attracted investment in greener fiber technologies.
- For instance, Toray Industries has developed a recycling technology that recovers carbon fibers from CFRP while retaining over 95 percent of the original tensile strength, using a low-temperature decomposition agent.
Growth of Electric Mobility, Renewable Energy, and High-Performance Applications
Specialty fibers benefited from rapid adoption of electric mobility and renewable energy systems. EV makers required lightweight composites for battery housings, underbody shields, seat structures, and motor components. Wind turbine manufacturers continued to integrate longer blades, which increased the need for high-strength glass and carbon fibers. Aerospace OEMs pursued composite-intensive airframes to reduce fuel burn and meet emission targets. Industrial sectors used advanced fibers in pressure vessels, filtration systems, and protective gear. These high-performance fields generated long-term opportunities as global investments in clean technology accelerated.
- For instance, the Boeing 787 Dreamliner integrates approximately 32,000 kg of CFRP composites, including carbon fiber, in its airframe to lower weight while maintaining structural integrity.
Key Challenges
High Production Costs and Price Volatility of Raw Materials
The market faced cost challenges because carbon and aramid fibers required energy-intensive production routes and expensive precursors. Fluctuations in petroleum-based raw materials influenced pricing for synthetic fibers, while energy price spikes increased furnace operating costs for glass fiber producers. These factors made specialty fibers costlier than metals, limiting adoption in price-sensitive industries. Smaller manufacturers struggled to scale production because capital needs for advanced composite facilities remained high. Cost pressures also affected OEM procurement strategies, pushing some buyers toward cheaper alternatives or hybrid composite solutions.
Technical Integration Barriers and Skilled Workforce Shortages
Adoption of specialty synthetic and glass fibers required advanced design, engineering, and processing knowledge, creating barriers for new users. Composite manufacturing demanded strict curing control, precise fiber placement, and specialized tooling, which limited adoption in smaller factories. Many regions lacked skilled composite technicians and engineers, slowing project execution timelines. Repair and recycling of composite structures remained technically complex, adding operational challenges for builders and OEMs. Certification standards in aerospace and defense increased the time and cost required to introduce new materials. These technical limitations restrained the market’s speed of expansion in several developing regions.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America led the Specialty Synthetic and Glass Fiber Market in 2024 with about 34% share. Demand stayed strong due to high composite use in aerospace, automotive, wind energy, and construction. The U.S. commanded most of the regional share because manufacturers adopted carbon, aramid, and E-glass fibers for aircraft components, EV structures, façade panels, and industrial applications. Renewable energy expansion supported wider use of fiberglass in wind turbine blades. Advanced manufacturing facilities and strong R&D networks helped producers deliver high-performance materials that met strict federal standards.
Europe
Europe accounted for nearly 29% share in 2024, driven by strong aerospace programs, electric mobility adoption, and strict sustainability rules. Germany, France, and the U.K. increased demand for carbon and glass fibers in automotive lightweighting and next-generation aircraft. EU green-building policies encouraged use of fiber-reinforced insulation, façade systems, and corrosion-resistant structures. Wind energy installations in countries such as Denmark and Spain boosted fiberglass consumption. Europe’s advanced composite clusters and material innovation centers strengthened supply capabilities and supported steady market growth.
Asia Pacific
Asia Pacific held the largest growth momentum and captured around 28% share in 2024. China, Japan, and India expanded production capacity for glass and carbon fibers to meet rising demand from construction, automotive, electronics, and marine sectors. Rapid urbanization increased the use of fiber-reinforced concrete, insulation boards, and composite structural elements. Electric vehicle manufacturing expanded sharply, driving adoption of lightweight composite components. Aerospace development programs in China and Japan also raised consumption of advanced fibers. Strong domestic manufacturing ecosystems helped the region become a key global supplier.
Latin America
Latin America represented roughly 5% share in 2024, supported by growing construction and transportation applications. Brazil and Mexico increased adoption of fiberglass composites in building panels, pipes, wind turbine components, and automotive parts. Economic recovery and infrastructure upgrades raised usage of fiber-reinforced materials for bridges, industrial facilities, and public structures. Wind energy projects, especially in Brazil, supported additional demand. However, limited local production capacity and higher import dependence slowed wider penetration of premium carbon and aramid fibers.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region accounted for nearly 4% share in 2024, driven by expanding construction, oil & gas, and infrastructure projects. GCC countries increased use of fiberglass piping, tanks, panels, and reinforcement products due to strong corrosion resistance in harsh climates. Mega-projects in Saudi Arabia and the UAE supported demand for fiber-reinforced concrete and lightweight façade systems. Africa’s industrial growth created moderate demand for specialty fibers in automotive assembly, electronics, and marine applications. Despite growth, limited composite manufacturing capabilities kept adoption rates lower than other regions.
Market Segmentations:
By Type
- E-Glass Fiber
- S-Glass Fiber
- C-Glass Fiber
- Aramid Fiber
- Carbon Fiber
By Application
- Composite Materials
- Insulation Products
- Reinforcement Materials
- Coatings and Adhesives
- Textiles
By End Use
- Construction
- Automotive
- Aerospace
- Marine
- Electronics
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
Major players such as Honeywell International, Jushi Group Co. Ltd., Royal DSM, Owens Corning, Mitsubishi Chemical Holdings Corporation, Hexcel Corporation, Toray Industries, Inc., DuPont, SGL Group, and Nippon Electrical Glass Co. shaped the competitive landscape of the Specialty Synthetic and Glass Fiber Market in 2024. These companies focused on expanding production capacity, improving fiber performance, and enhancing compatibility with advanced resin systems. Many producers invested in automated manufacturing, high-strength fiber technologies, and sustainable glass melt processes to meet global regulatory standards. Partnerships with automotive, aerospace, and construction OEMs strengthened long-term supply agreements. Several companies introduced lightweight composite solutions to support EV platforms and next-generation aircraft programs. The competitive environment remained intense as suppliers increased R&D spending to deliver better mechanical properties, durability, and thermal stability. Regional players also expanded presence in Asia Pacific, increasing pressure on global leaders through cost-competitive fiberglass and carbon fiber offerings.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
- Honeywell International
- Jushi Group Co. Ltd.
- Royal DSM
- Owens Corning
- Mitsubishi Chemical Holdings Corporation
- Hexcel Corporation
- Toray Industries, Inc.
- DuPont
- SGL Group
- Nippon Electrical Glass Co.
Recent Developments
- In 2025, DuPont agreed to sell its aramid fiber business, including Kevlar and Nomex, to Arclin, further streamlining its portfolio toward water, industrial technologies, and advanced materials outside aramid fibers.
- In 2025, Honeywell announced leadership and structural moves for its Advanced Materials unit (to be renamed Solstice Advanced Materials) as part of a planned spin-off of its advanced-materials business; David Sewell was named head as the unit is prepared for separation (spin-off expected late 2025 / early 2026). This is material because the unit covers Honeywell’s specialty chemicals and materials portfolio that serves composite/specialty markets.
- In July 2024, Jushi commissioned the second glass-fiber production line at its Huai’an carbon-neutral intelligent manufacturing base (the new line was declared successfully put into operation on July 26, 2024), increasing its glass-fiber output capacity.
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Type, Application, End-Use and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- The market will expand as industries increase adoption of lightweight composite structures.
- Carbon and aramid fiber usage will grow with rising demand for high-performance applications.
- Glass fiber consumption will rise in wind energy due to larger turbine blade designs.
- EV manufacturing will drive higher use of composite battery housings and structural parts.
- Construction projects will adopt more fiber-reinforced concrete for durability and corrosion resistance.
- Automated composite manufacturing technologies will improve efficiency and reduce production costs.
- Recycling and sustainable fiber solutions will gain traction as environmental rules tighten.
- Aerospace programs will integrate more advanced composites for next-generation aircraft.
- Asia Pacific will strengthen its position as a global production hub for specialty fibers.
- Companies will expand R&D to deliver fibers with better strength, thermal stability, and chemical resistance.




