Market Overview
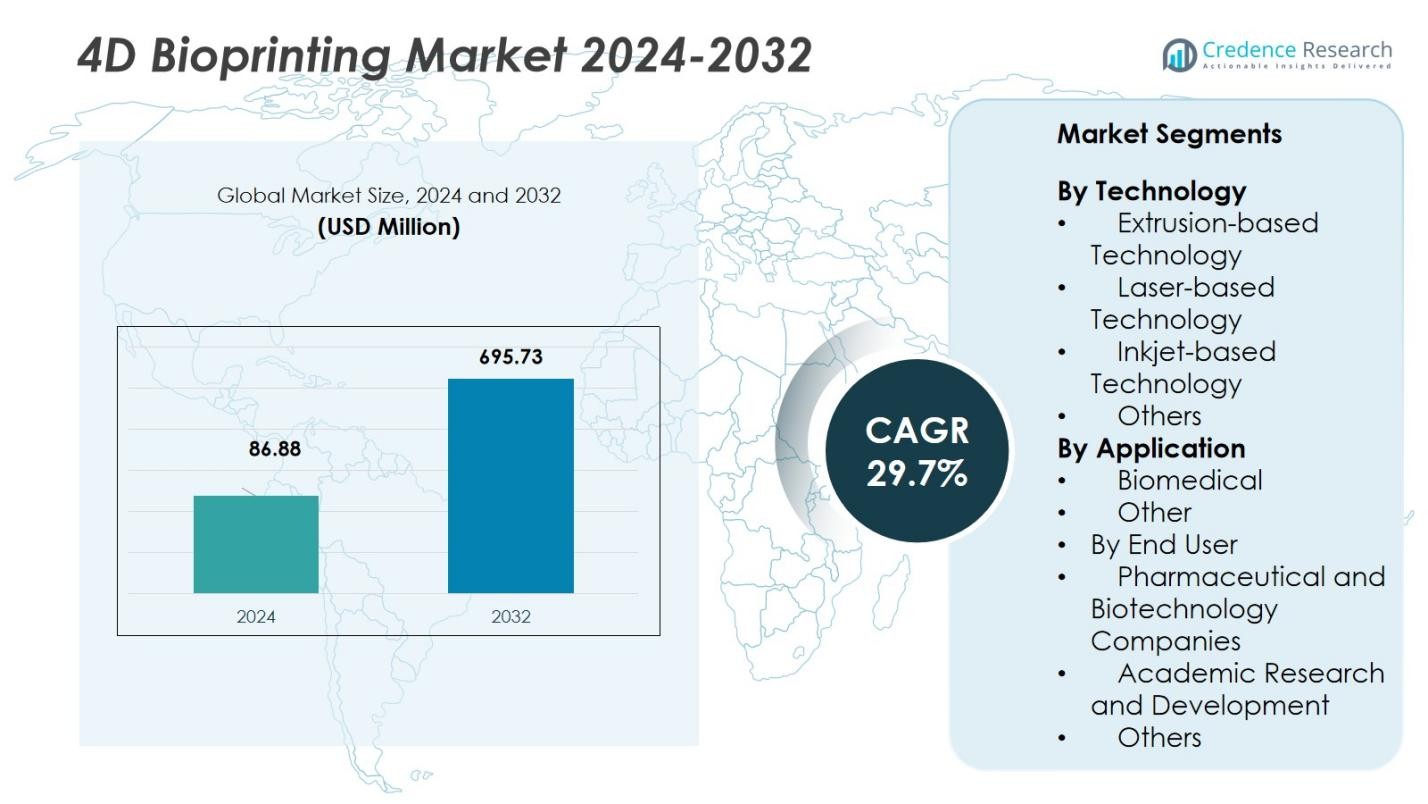
The 4D Bioprinting Market size was valued at USD 86.88 Million in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 695.73 Million by 2032, at a CAGR of 29.7% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| 4D Bioprinting Market Size 2024 |
USD 86.88 Million |
| 4D Bioprinting Market, CAGR |
29.7% |
| 4D Bioprinting Market Size 2032 |
USD 695.73 Million |
The 4D Bioprinting Market is led by key players such as DirectSync Surgical, Enovis, Ferentis, Poietis, REGENHU, and ROKIT Healthcare, who are at the forefront of advancing dynamic tissue fabrication and adaptive scaffold technologies. These companies focus on developing innovative bioprinting solutions, including high-throughput platforms, advanced bio-inks, and smart materials for regenerative medicine. North America holds the largest market share at 34%, driven by its well-established research infrastructure and robust healthcare sector. Europe follows with a 26% share, benefiting from strong public funding and bioprinting companies. Asia Pacific is experiencing rapid growth, capturing a 29% market share, fueled by increasing investments in healthcare and bioprinting technologies. These regions, along with strategic collaborations, are driving the ongoing expansion of the 4D bioprinting market, positioning the industry for continued growth across various applications.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Insights
- The 4D Bioprinting Market was valued at USD 86.88 million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 695.73 million by 2032 at a CAGR of 7%.
- Growth is driven by rising demand for personalized medicine and patient‑specific dynamic implants, with the extrusion‑based technology sub‑segment holding approximately 36% share and the biomedical application accounting for 6% of the market.
- Current trends include integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning into bioprinting workflows, expansion into drug discovery models and increased collaboration among bioprinter manufacturers and pharma companies.
- Market restraints involve high production costs for advanced bioprinting systems and bio‑inks, along with regulatory and ethical uncertainties surrounding dynamic bioprinted tissues.
- Regionally, North America leads with a 34% share, Europe holds 26%, Asia Pacific accounts for 29%, Latin America maintains 8%, and Middle East & Africa capture 3%, reflecting varying degrees of infrastructure and funding maturity.
 Market Segmentation Analysis:
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Technology
Within the technology segment of the 4D Bioprinting Market (comprising Extrusion-based, Laser-based, Inkjet-based, and Others), the Extrusion-based Technology sub-segment dominates with 36% share as of the early forecast period. Its leadership is underpinned by the technology’s capability to handle high-viscosity bio-inks, maintain high cell viability (95%+), and support large-volume, continuous tissue construction. Key growth drivers include the rising application of dynamic scaffolds in regenerative medicine and the scale-up of bioprinting operations in academic and commercial settings. Meanwhile, other technologies such as laser and inkjet remain important but face higher cost or complexity barriers.
- For instance, CELLINK’s BIO X6 extrusion bioprinter, equipped with six modular printhead slots and multi-material printing capabilities, enables researchers to fabricate complex tissue constructs by working with diverse biomaterials simultaneously.
By Application
In the application segment (Biomedical and Other), the Biomedical sub-segment holds the predominant position with 62.6% share in 2024 within the tissue-engineering-focused sub-market. This dominance reflects the strong demand for regenerative medicine, dynamic tissue implants, and patient-specific constructs that respond over time. Drivers include the shortage of donor organs, the push for personalized implants, and regulatory incentives for advanced therapies. The “Other” applications (such as drug delivery, in vitro models) represent growth areas, but the biomedical portion retains the lion’s share due to established clinical-research momentum.
- For instance, Zimmer Biomet’s custom triflange Patient-Matched Implants designed from CT scan data have demonstrated substantial clinical success in acetabular reconstruction, with Harris Hip Scores improving from an average of 41 preoperatively to 82 at final follow-up across 12 patients over a 50-month observation period, with 11 of 12 implants achieving stable fixation.
By End User
From the end-user perspective (Pharmaceutical & Biotechnology Companies; Academic Research & Development; Others), the Academic Research & Development segment currently leads the market, accounting for 43% of the total market share. Research institutions command the largest revenue share as they pioneer novel bio-inks, print processes, and dynamic tissue models. Key drivers include increasing grant funding, the growth of biofabrication centers, and industry-academia partnerships. However, pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies are poised to grow rapidly as they adopt 4D systems for advanced drug screening, in vitro tissue modeling, and personalized therapies creating a strong secondary growth stream beyond the academic base.
Key Growth Drivers
Increasing Demand for Personalized Medicine
The growing emphasis on personalized medicine is one of the primary drivers of the 4D Bioprinting market. As healthcare moves towards tailored treatments, 4D bioprinting technologies enable the creation of patient-specific tissues and implants that can respond dynamically to environmental stimuli. This advancement supports the development of highly customized and effective therapeutic solutions, particularly in the fields of regenerative medicine and tissue engineering. The ability to print tissues that mimic the patient’s biological structure fosters improved treatment outcomes and accelerates adoption in clinical applications.
- For instance, L’Oréal partnered with Organovo to develop 3D bioprinted skin tissue using the NovoGen Bioprinting Platform, which enables rapid and precise construction of bilayer artificial skin structures for evaluating product safety and performance on different skin types and ages without relying on human or animal testing.
Advancements in Bioprinting Technologies
Ongoing advancements in bioprinting technologies, including enhanced precision, material compatibility, and scalability, are contributing to the expansion of the 4D bioprinting market. The continuous development of bio-inks and improved printing techniques, such as extrusion-based and inkjet-based printing, enhances the versatility and functionality of printed tissues. These innovations facilitate the creation of more complex, functional structures for biomedical applications. As these technologies mature, the capacity to manufacture tissue scaffolds and implants with superior mechanical properties and biological compatibility is driving increased industry investment.
- For instance, Rokit Healthcare’s Dr. Invivo 4D6 bioprinter, equipped with six modular printheads, enables the fabrication of complex tissue structures with up to six different cell types and materials simultaneously, supporting applications in drug efficacy and toxicity testing.
Supportive Regulatory Environment
The regulatory environment is evolving to support the commercialization of 4D bioprinting technologies, which is accelerating market growth. Regulatory bodies, including the FDA and EMA, are increasingly adopting frameworks that allow for the clinical use of bioprinted tissues and implants. As these technologies prove their safety and efficacy, regulatory bodies are offering clearer pathways for approval, fostering confidence among industry players. This shift is crucial for enabling the widespread application of 4D bioprinting in clinical settings, particularly in regenerative medicine, and is contributing to the market’s expansion.
Key Trends & Opportunities
Integration of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
One of the most promising trends in the 4D Bioprinting market is the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) with bioprinting technologies. These technologies enable the automation of design and printing processes, improving accuracy, efficiency, and reproducibility in creating bioprinted tissues. By utilizing AI and ML algorithms, researchers can optimize the printing process, predict material behaviors, and enhance tissue functionality. This integration is expected to open up new opportunities in personalized drug testing, regenerative medicine, and organ-on-a-chip models, driving significant market growth.
- For instance, Organovo’s NovoGen Bioprinter Platform bioprints human liver tissue containing primary hepatocytes, liver endothelial cells, hepatic stellate cells, and HUVECs in a compartmentalized geometry onto 24-well transwell culture inserts, demonstrating sustained hepatocyte function through albumin secretion and CYP3A4 activity comparable to native liver tissue and maintaining functionality for up to 90 days in small animal disease models.
Expansion into Drug Discovery and Testing
The expansion of 4D bioprinting applications into drug discovery and testing presents a significant growth opportunity. By printing 3D tissue models that replicate human organs and disease environments, pharmaceutical companies can conduct more accurate drug testing and screening. These models offer improved prediction of drug efficacy and toxicity compared to traditional in vitro methods, reducing the reliance on animal testing. As drug developers seek more efficient and reliable testing methods, the demand for bioprinted tissue models is expected to grow, further boosting the market’s potential.
- For instance, L’Oréal partnered with Organovo to develop 3D bioprinted human skin tissue models for cosmetics and product evaluation, leveraging the NovoGen Bioprinting Platform to scale production of reconstructed human epidermis samples, which previously required a week to produce through traditional methods but could be accelerated through bioprinting technology.
Key Challenges
High Production Costs
One of the major challenges in the 4D Bioprinting market is the high production costs associated with bioprinting technologies. The specialized bio-inks, advanced printers, and equipment required for 4D bioprinting are expensive, which limits widespread adoption, particularly in emerging markets. Additionally, the complexity of developing and scaling up bioprinting processes for industrial applications poses significant financial barriers. While technological advancements are expected to reduce costs over time, the high initial investment remains a key obstacle for many organizations looking to integrate 4D bioprinting into their workflows.
Regulatory and Ethical Challenges
While the regulatory environment is evolving to support 4D bioprinting, significant regulatory and ethical challenges persist. The approval process for bioprinted tissues and organs is complex, and there are still uncertainties regarding the long-term safety and efficacy of these products. Additionally, ethical concerns around the use of bioprinted tissues in humans and the potential for creating complex biological structures, such as functional organs, create hesitations within certain regulatory bodies and the public. Overcoming these challenges will require clear and comprehensive regulatory frameworks to ensure the responsible development and application of 4D bioprinting technologies.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America commands a 34% share of the 4D Bioprinting Market, driven by its strong research infrastructure, robust regulatory frameworks, and high adoption of advanced bioprinting technologies. Leading academic institutions and commercial players collaborate extensively on next‑generation dynamic tissue constructs. The region’s established pharmaceutical and biotechnology ecosystem supports translation of 4D bioprinting from lab to clinic, while reimbursement pathways and high healthcare spending accelerate uptake. Growth persists as US and Canadian stakeholders increasingly invest in responsive biomaterials and adaptive implants for regenerative medicine.
Europe
Europe accounts for a 26% share of the market, benefitting from comprehensive healthcare systems, strong public research funding and a growing base of bioprinting companies across the region. Key markets such as Germany, France and the UK lead in 4D scaffold development and bio‑ink innovation. The region’s regulatory harmonisation under the European Medicines Agency and increasing cross‑border collaborations reinforce its competitive position. Market momentum is enhanced by government initiatives supporting advanced therapy medicinal products and regional manufacturing hubs for bio‑fabrication technologies.
Asia Pacific
Asia Pacific holds a 29% share of the market, underpinned by rapid growth in China, India, Japan and South Korea. The region benefits from large patient populations, rising healthcare investment and expanding academic‑industry partnerships in bioprinting. Governments in the region actively support regenerative medicine programmes and encourage local manufacturing of bioprinting systems. Competitive labour and material costs attract global players to establish research centres, while domestic bioprinting start‑ups are gaining traction. As the region scales regulatory pathways and infrastructure, it is positioned for significant commercial expansion.
Latin America
Latin America contributes an 8% share of the 4D Bioprinting Market, with growth largely emanating from Brazil and Mexico. While infrastructure and funding remain less mature versus leading regions, increasing interest in regenerative therapies and cost‑effective bioprinting solutions are fostering market uptake. Public‑private collaborations and niche research programmes in academic institutions are driving initial commercial applications. The region faces challenges in reimbursement and regulatory frameworks; however, targeted investments and regional manufacturing could elevate its share over the forecast period.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region captures a 3% share of the market, reflecting a nascent but evolving ecosystem for 4D bioprinting. Growth is supported by governmental initiatives in Gulf countries to build bio‑fabrication hubs and invest in advanced healthcare technologies. Adoption is slower due to infrastructure and regulatory constraints, yet increasing interest in medical tourism, customised implants and research collaborations is opening opportunities. As regulatory frameworks mature and regional centres of excellence emerge, the region is poised to gradually increase its participation in the global market.
Market Segmentations:
By Technology
- Extrusion-based Technology
- Laser-based Technology
- Inkjet-based Technology
- Others
By Application
By End User
- Pharmaceutical and Biotechnology Companies
- Academic Research and Development
- Others
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape of the 4D bioprinting market highlights key players such as DirectSync Surgical, Enovis, Ferentis, Poietis, REGENHU and ROKIT Healthcare, each advancing unique niche capabilities in smart biomaterials, dynamic tissue fabrication, and adaptive scaffold technologies. DirectSync Surgical focuses on sensor‐embedded implantables and patient‑feedback driven smart constructs; Enovis leverages its medical device platform to integrate bioprinting in orthopedic and regenerative segments. Ferentis and Poietis are strong in laser‑based biofabrication and research‐tie implementations, while REGENHU and ROKIT Healthcare capitalise on high‑throughput solutions and bioprinter hardware systems. Together these companies foster an ecosystem of innovation, forming collaborations, licensing deals and technology co‑developments to accelerate product commercialization and market penetration. They drive differentiation through proprietary bio‑inks, stimulus‑responsive materials and scalable bioprinting platforms, thereby positioning themselves ahead of smaller entrants. However, the fragmentation of the supply base and rapid technological change mean that alliances, acquisitions and R&D investments will continue to shape leadership in this dynamic market.
Key Player Analysis
- Sculpteo
- ROKIT Healthcare
- SMART3D
- Enovis
- Stratasys
- REGENHU
- DirectSync Surgical
- Ferentis
- Poietis
- BICO Group
Recent Developments
- In November 2025, BIO INX announced a strategic partnership with Yamato Scientific Co., Ltd. in Japan to distribute its advanced bio‑inks, marking a key expansion step.
- In October 2024, UpNano secured €7 million in Series A financing co-led by aws Gründungsfonds, Novacapital, and IGO Innovation GmbH, with participation from existing investor ILUM Tec.
- In July 2022, Carl Zeiss Meditec and Precise Bio announced a partnership to develop and commercialize fabricated corneal tissue using Precise Bio’s 4D bio-fabrication platform.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Technology, Application, End User and Region. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- The market will witness sustained expansion as tissue engineering and regenerative medicine increasingly adopt dynamic, shape‑changing constructs to meet unmet clinical needs.
- Manufacturers will invest heavily in smart bio‑inks and stimuli‑responsive materials to enable adaptive behaviour in printed tissues, thereby enhancing functionality and enabling new therapeutic modalities.
- Integration of artificial intelligence, machine learning, and real‑time monitoring into bioprinting workflows will boost precision and reproducibility, improving yield and reducing development lead times.
- Broader adoption of 4D bioprinting in pharmaceutical applications—such as advanced in vitro tissue models for drug screening and toxicity testing—will open new revenue streams beyond pure clinical implants.
- Geographic expansion into faster‑growing markets in Asia Pacific and Latin America will accelerate as infrastructure, funding, and regulatory support mature in those regions.
- Strategic collaborations and mergers among bioprinter manufacturers, biomaterials providers, and pharmaceutical companies will consolidate capabilities and accelerate commercialization of 4D bioprinted products.
- Cost‑reduction in high‑throughput bioprinting systems and materials will make 4D bioprinting accessible to smaller research organizations and mid‑tier hospitals, broadening the end‑user base.
- Regulatory frameworks will evolve to accommodate adaptive implants and printed tissues, reducing approval time and increasing confidence among investors and end‑users.
- As standardization and reproducibility improve, the gap between custom research applications and full‑scale commercial manufacturing will narrow, enabling scalable production of 4D biologic constructs.
- Ethical and sociocultural acceptance of dynamic bioprinted implants will strengthen as clinicians demonstrate successful case‑studies, thereby reducing barriers to patient adoption and reimbursement.

 Market Segmentation Analysis:
Market Segmentation Analysis:

