Market Overview
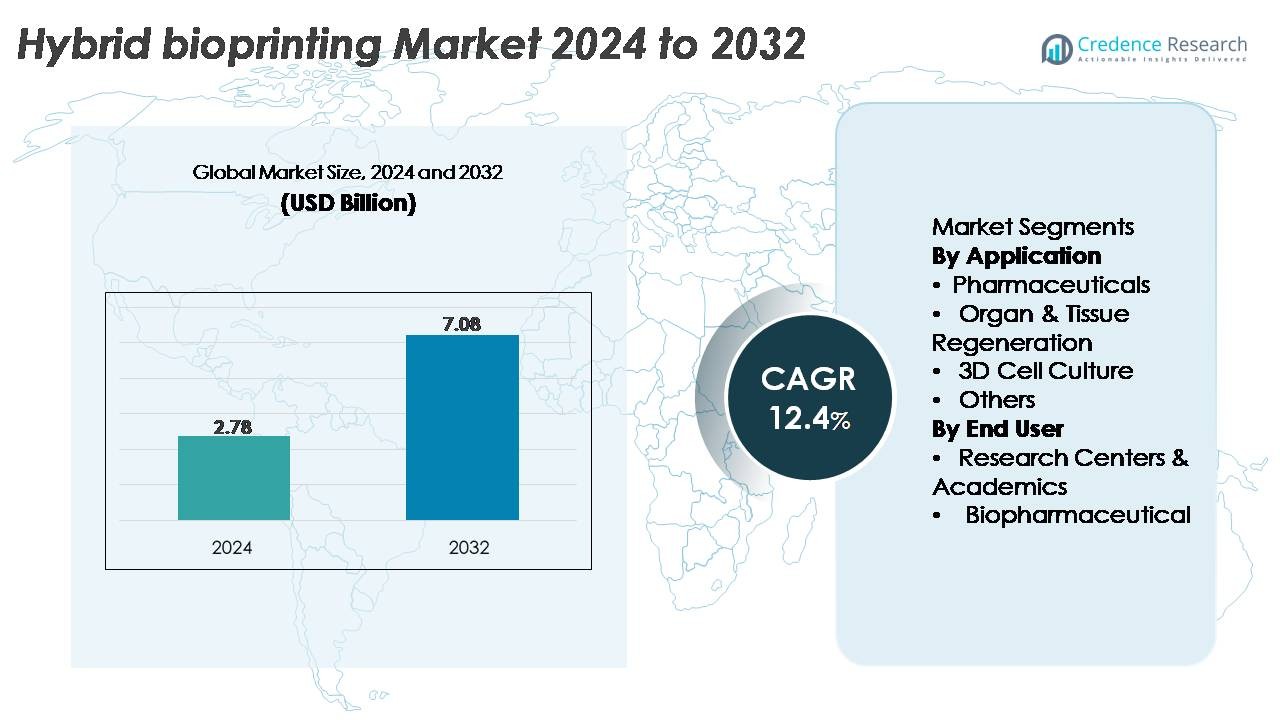
The hybrid bioprinting market was valued at USD 2.78 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 7.08 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 12.4% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Freezing of Gait Treatment Market Size 2024 |
USD 2.78 Billion |
| Freezing of Gait Treatment Market, CAGR |
12.4% |
| Freezing of Gait Treatment Market Size 2032 |
USD 7.08 Billion |
The hybrid bioprinting market is shaped by a mix of established innovators and emerging biofabrication specialists, with top players including Regemat 3D S.L., Vivax Bio LLC, Organovo Holdings Inc., Inventia Life Science PTY LTD, Cyfuse Biomedical K.K., Bico Group AB, Advanced Solutions Life Sciences LLC, Aspect Biosystems Ltd., CollPlant Biotechnologies Ltd., RegenHU, and EnvisionTEC Inc. These companies compete through advancements in multi-material printing, functional bioinks, and high-precision tissue-engineering platforms. North America leads the global market with approximately 38% share, driven by strong R&D ecosystems and rapid adoption in pharmaceutical and academic research. Europe follows with around 30% share, supported by well-established biofabrication infrastructures and active regenerative medicine initiatives.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Insights
- The hybrid bioprinting market reached USD 2.78 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow to USD 7.08 billion by 2032, expanding at a CAGR of 12.4%, supported by rising demand for advanced tissue-engineering platforms.
- Market growth is driven by rapid adoption of multi-material and multi-modal bioprinting systems in pharmaceuticals and regenerative medicine, with the pharmaceuticals segment holding the dominant application share due to strong use in drug screening and preclinical modeling.
- Key trends include innovations in functional bioinks, AI-enabled automation, and high-throughput tissue modeling, which enhance reproducibility and expand adoption across personalized medicine and organ-on-chip research.
- Competition intensifies as companies such as Bico Group AB, Organovo, RegenHU, and CollPlant expand biomaterial portfolios, though challenges persist due to regulatory ambiguity, technical complexity in vascularization, and high deployment costs.
- Regionally, North America leads with about 38% share, followed by Europe at 30% and Asia-Pacific at 24%, supported by strong research ecosystems and expanding regenerative medicine investments.
 Market Segmentation Analysis:
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Application
Pharmaceuticals represents the dominant application segment, accounting for the largest share of hybrid bioprinting adoption due to its extensive use in high-throughput drug screening, toxicity profiling, and disease modeling. Demand is driven by the shift toward physiologically relevant 3D tissue constructs that reduce reliance on animal studies and accelerate preclinical evaluation. Organ & tissue regeneration is expanding rapidly as hybrid bioprinting enhances vascularization, multi-material scaffolding, and cell–matrix integration. Meanwhile, 3D cell culture systems gain traction in oncology and stem-cell research, while the “Others” category supports niche uses such as cosmetic testing and personalized therapy development.
- For instance, Organovo’s bioprinted liver tissues demonstrate albumin secretion above 20 µg/day per million cells and maintain cytochrome P450 activity for over 28 days, enabling long-term drug toxicity studies.
By End User
Research Centers & Academics form the leading end-user segment, holding the largest market share as universities and institutes drive innovation in biomaterials, regenerative scaffolds, and multi-modal printer platforms. Their dominance is fueled by strong grant funding, interdisciplinary collaborations, and early-stage prototyping activities. Biopharmaceutical companies are increasing adoption to streamline drug discovery workflows and develop personalized tissue models, leveraging hybrid bioprinting for faster candidate validation. The “Others” segment, comprising CROs and specialized laboratories, is gradually expanding as demand rises for outsourced bioprinting capabilities, validation studies, and custom tissue fabrication services.
- For example, RegenHU’s R-GEN 100 is designed as a modular bioprinter that integrates multiple print heads, allowing combinations of extrusion and drop-on-demand jetting technologies. The platform supports multi-material workflows for advanced tissue-engineering research. These capabilities help academic groups fabricate detailed and customizable constructs across diverse bioink types.
Key Growth Drivers
Advancements in Multi-Material and Multi-Modal Printing Capabilities
Hybrid bioprinting adoption accelerates as platforms integrate extrusion, inkjet, and laser-assisted modalities to enhance structural precision, cell viability, and biomaterial compatibility. These systems enable simultaneous deposition of soft hydrogels, rigid scaffolds, and functional biomolecules, allowing researchers to create anatomically accurate tissue constructs with tunable mechanical properties. Improvements in crosslinking chemistry, microfluidic dispensing, and automated calibration further strengthen reproducibility, a key requirement for translational research and preclinical applications. The ability to fabricate vascularized constructs, multi-layer tissue interfaces, and dynamic microenvironments positions hybrid bioprinting as a versatile tool for drug discovery, regenerative medicine, and personalized therapeutics. As equipment manufacturers develop higher-resolution printheads, integrated imaging modules, and more advanced bioink cartridges, demand rises across academic labs and biopharmaceutical R&D programs seeking scalable, high-fidelity tissue models.
- For instance, BICO’s BIO X6 platform supports six independent printheads operating between 4°C and 250°C with pneumatic pressures up to 700 kPa, enabling simultaneous multi-material deposition for structurally complex tissues.
Rising Demand for Personalized Medicine and Preclinical Modeling
Personalized medicine initiatives significantly boost hybrid bioprinting demand as institutions seek patient-specific tissue analogs for precision testing and therapeutic planning. Hybrid bioprinters enable fabrication of customized 3D models using autologous cells, facilitating tailored drug-response profiling and reducing trial-and-error in treatment selection. Pharma and biotech companies increasingly adopt bioprinted liver, cardiac, and tumor tissues to improve predictive accuracy during early-stage screening. These platforms also support physiologically relevant microenvironments that closely resemble in vivo biology, enhancing model validity and reducing reliance on animal testing. As regulatory agencies encourage advanced in vitro testing systems, hybrid bioprinting becomes central to next-generation preclinical workflows. Its capacity to replicate disease heterogeneity, complex tissue architecture, and dynamic perfusion environments drives strong uptake across oncology, neurology, and metabolic-disease research programs.
- For instance, CELLINK’s LUMEN X bioprinter uses a 405 nm light engine and delivers a voxel resolution down to 50 µm, enabling high-precision micro-architectures for disease-modeling and preclinical research.
Expanding Investments in Regenerative Medicine and Clinical Translation
The global push toward regenerative therapies fuels hybrid bioprinting innovations aimed at producing implant-ready tissues and scaffolds with functional integration potential. Funding for stem-cell engineering, tissue regeneration, and biofabrication centers continues to rise as governments, universities, and private investors support long-term clinical research. Hybrid bioprinting enables construction of vascularized grafts, multi-material organ scaffolds, and biomechanically robust structures essential for repairing cartilage, skin, bone, and soft tissues. Rapid advances in growth-factor-loaded bioinks, programmable architecture, and post-printing maturation systems further accelerate translational readiness. While full organ printing remains a long-term objective, near-term clinical applications—such as wound grafts, dental scaffolds, and orthopedic implants—create substantial commercialization pathways. As regulatory frameworks evolve to support bioprinted tissue evaluation and clinical-grade GMP production, hybrid bioprinting moves closer to routine therapeutic adoption.
Key Trends & Opportunities
Growth of Automated, AI-Driven, and High-Throughput Bioprinting Platforms
Automation and AI integration represent major opportunities as hybrid bioprinting evolves toward higher-throughput and more predictive workflows. Machine-learning algorithms increasingly support print-path optimization, real-time defect correction, and adaptive bioink flow control to enhance consistency across batches. Automated cell handling, closed-loop monitoring systems, and robotic material loading reduce human error and make bioprinting more accessible to non-specialist labs. High-throughput hybrid platforms enable simultaneous printing of dozens of tissue samples, significantly accelerating early-stage drug testing and biomaterial screening. As vendors introduce cloud-connected systems and remote monitoring dashboards, research facilities gain superior data traceability and reproducibility. These advancements create strong commercial opportunities in pharma R&D, CRO partnerships, and personalized drug-response modeling.
· For example, BICO Group reports an installed base of about 48,000 instruments across its portfolio, spanning bioprinters and other life-science tools. The company also offers software platforms such as CELLINK Heart that support automation and workflow management. These tools help standardize experimental processes for multi-site research teams.
Expansion of Bioink Innovation and Functional Biomaterial Development
Bioink innovation emerges as a central trend, opening new avenues for tissue fidelity, mechanical strength, and biological functionality. Hybrid bioprinting benefits from rapid advancements in shear-thinning hydrogels, ECM-mimicking polymers, decellularized tissue inks, and photo-curable biomaterials tailored for multi-modal deposition. Functional additives such as angiogenic growth factors, conductive nanoparticles, and immunomodulatory agents enable specialized applications ranging from neural scaffolds to vascular grafts. Customizable rheology and enhanced crosslinking chemistry allow precise control over pore size, stiffness, and degradation rates. As companies develop standardized, GMP-ready bioinks, commercial adoption expands across regenerative medicine trials, organ-on-chip fabrication, and personalized therapeutic modeling. This bioink diversification creates strong opportunities for material suppliers and hybrid printer manufacturers.
· For example, CollPlant’s Collink.3D bioink is formulated with recombinant human type I collagen and supports multiple printing methods, including extrusion, inkjet, LIFT, and stereolithography. The material is designed to preserve high cell viability in biofabricated constructs. Its tunable composition enables formation of stable soft-tissue structures for research and development.
Key Challenges
Technical Complexity in Achieving Vascularization and Functional Maturation
Despite significant progress, generating fully functional, vascularized tissue constructs remains a core challenge in hybrid bioprinting. Complex organs require hierarchical vasculature, precise nutrient diffusion, and synchronized cell–matrix interactions to sustain viability during maturation. Achieving stable perfusion networks and integrating multiple cell types within multi-material scaffolds demands advanced bioink formulations and intricate print-path design. Limited long-term structural stability, insufficient mechanical properties, and unpredictable tissue remodeling further complicate translational readiness. Additionally, the high-resolution imaging, real-time monitoring, and bioreactor systems required to support post-printing maturation increase cost and operational complexity. These technical barriers slow the progression from laboratory prototypes to clinically deployable solutions.
Regulatory Uncertainty and High Cost of Commercial-Scale Deployment
Hybrid bioprinting faces substantial regulatory and cost-related hurdles that limit broader clinical and industrial adoption. Agencies have yet to finalize standardized evaluation pathways for bioprinted tissues, leading to uncertainty around safety, reproducibility, and quality assurance requirements. Establishing GMP-compliant bioprinting facilities requires significant investment in sterile environments, validated materials, and controlled bioprocessing systems. High equipment costs, specialized training needs, and limited reimbursement frameworks create additional barriers for hospitals and smaller research institutions. As the industry navigates evolving guidelines for cell handling, scaffold fabrication, and post-printing maturation, companies must balance innovation with compliance, prolonging the time to market for therapeutic applications.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America holds the largest market share of about 38%, driven by strong investment in regenerative medicine, early adoption of multi-modal bioprinting platforms, and a well-established biomedical research ecosystem. The U.S. leads regional demand due to robust federal funding, advanced academic infrastructure, and extensive pharmaceutical R&D activity focused on personalized medicine and preclinical tissue modeling. Several major bioprinting manufacturers and start-ups operate in this region, accelerating technological advancements and commercialization pathways. Collaboration between universities, biotech firms, and clinical research centers further strengthens North America’s leadership in tissue engineering, drug testing, and clinical translation initiatives.
Europe
Europe accounts for approximately 30% of the global market, supported by strong biomedical research networks, growing translational medicine initiatives, and government-backed regenerative medicine programs. Countries such as Germany, the U.K., Sweden, and the Netherlands lead adoption due to specialized biofabrication centers, standardized research frameworks, and increasing investment in patient-specific therapeutic models. The region benefits from well-defined regulatory progress in advanced therapy medicinal products, which supports early-stage validation of bioprinted tissues. Partnerships between academic institutes, biotech firms, and EU-funded consortiums continue to expand hybrid bioprinting applications across drug discovery, organ-on-chip development, and clinical-grade scaffold engineering.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific captures around 24% market share, driven by rapid expansion of biotechnology infrastructure, significant public and private research funding, and rising demand for advanced medical technologies. China, Japan, South Korea, and Singapore lead the region due to increased investment in stem-cell engineering, tissue regeneration platforms, and hospital-based bioprinting programs. Local manufacturers are strengthening hybrid bioprinting capabilities with cost-efficient systems and innovative biomaterials, enabling broader adoption across research institutions. APAC’s expanding clinical research base, combined with strong government support for next-generation medical technologies, fosters accelerated growth in tissue modeling, precision medicine, and scalable regenerative applications.
Latin America
Latin America holds an estimated 5% share, supported by growing adoption of advanced biomedical research tools in Brazil, Mexico, and Argentina. While still emerging, the region’s interest in tissue engineering and 3D cell culture applications is increasing as universities and specialized research institutes integrate hybrid bioprinting into regenerative medicine studies. Government-funded innovation programs and collaborations with North American and European institutions enhance access to training and advanced technologies. Despite limited manufacturing presence, rising demand for personalized therapeutics, improved academic capabilities, and strengthening biotech ecosystems support steady growth in hybrid bioprinting applications across preclinical research and biological modeling.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region accounts for approximately 3% of global share, with growth primarily concentrated in technologically advanced markets such as the UAE, Saudi Arabia, and South Africa. Investment in healthcare modernization and biomedical research infrastructure supports early adoption of hybrid bioprinting for tissue engineering, wound care research, and academic studies. Strategic partnerships with global universities and research companies introduce advanced bioprinting platforms to regional innovation hubs. However, limited funding, skill availability, and slower regulatory development constrain broader market penetration, though ongoing national initiatives in precision medicine and medical technology innovation are expanding long-term potential.
Market Segmentations:
By Application
- Pharmaceuticals
- Organ & Tissue Regeneration
- 3D Cell Culture
- Others
By End User
- Research Centers & Academics
- Biopharmaceutical
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape of the hybrid bioprinting market is characterized by a mix of established biotechnology companies, specialized biofabrication firms, and emerging start-ups focused on advanced multi-material printing technologies. Leading players invest heavily in developing high-precision printheads, multi-modal deposition systems, and next-generation bioinks engineered for improved cell viability and mechanical performance. Many companies pursue strategic collaborations with academic institutions to accelerate innovation in vascularized tissue constructs, organ scaffolding, and high-throughput 3D tissue modeling. Partnerships with pharmaceutical firms are strengthening commercialization pathways, particularly in drug discovery and personalized medicine applications. Vendors increasingly differentiate through integrated workflow solutions that combine imaging, AI-driven process control, and automated cell-handling modules. As regulatory frameworks evolve and clinical translation advances, competition intensifies around GMP-compliant systems, standardized bioinks, and scalable manufacturing platforms. Continuous product innovation, intellectual property expansion, and strategic funding initiatives remain central to retaining market leadership in this rapidly evolving segment.
Key Player Analysis
- Regemat 3D S.L.
- Vivax Bio LLC
- Organovo Holdings Inc.
- Inventia Life Science PTY LTD
- Cyfuse Biomedical K.K.
- Bico Group AB
- Advanced Solutions Life Sciences LLC
- Aspect Biosystems Ltd.
- CollPlant Biotechnologies Ltd.
- RegenHU
- EnvisionTEC Inc.
Recent Developments
- In March 2025, Cyfuse and PHC Corporation jointly announced a new production technology enabling real-time monitoring of 3D cell-product quality. This development allows continuous tracking of glucose and lactate concentrations during culture, thereby automating medium replacement and stabilizing long-term cell viability and product consistency.
- In June 2024, BICO continued expansion of its life-science automation portfolio, reinforcing its leadership in 3D bioprinting, lab automation, and cell-culture solutions for drug discovery and tissue engineering. The company operates globally with tens of thousands of instruments already deployed, supporting a broad base of academic and biotech users.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Application, End-User and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- Hybrid bioprinting will advance toward clinically viable tissue constructs as vascularization, maturation, and biomaterial engineering improve.
- Adoption will increase in pharmaceutical R&D as bioprinted tissues become standard tools for preclinical testing and toxicity evaluation.
- AI-driven automation and closed-loop monitoring will enhance printing precision, reproducibility, and scalability for complex tissue structures.
- Bioink innovation will accelerate, with ECM-mimicking, growth-factor-loaded, and patient-specific formulations becoming widely available.
- Hospitals and surgical centers will gradually integrate bioprinting for personalized grafts, wound repair materials, and orthopedic implants.
- Multi-material and multi-modal printers will enable more accurate replication of organ interfaces and heterogeneous tissue environments.
- Regulatory frameworks will progress, providing clearer guidelines for bioprinted tissues and improving pathways for clinical translation.
- Collaborative ecosystems between academia, biotech firms, and medical institutions will expand, driving innovation and validation studies.
- High-throughput hybrid bioprinting will strengthen organ-on-chip development and personalized therapeutic modeling.
- Emerging markets will adopt hybrid bioprinting as biotech infrastructure grows and government investments in advanced healthcare technologies increase.

 Market Segmentation Analysis:
Market Segmentation Analysis:

