Market Overview
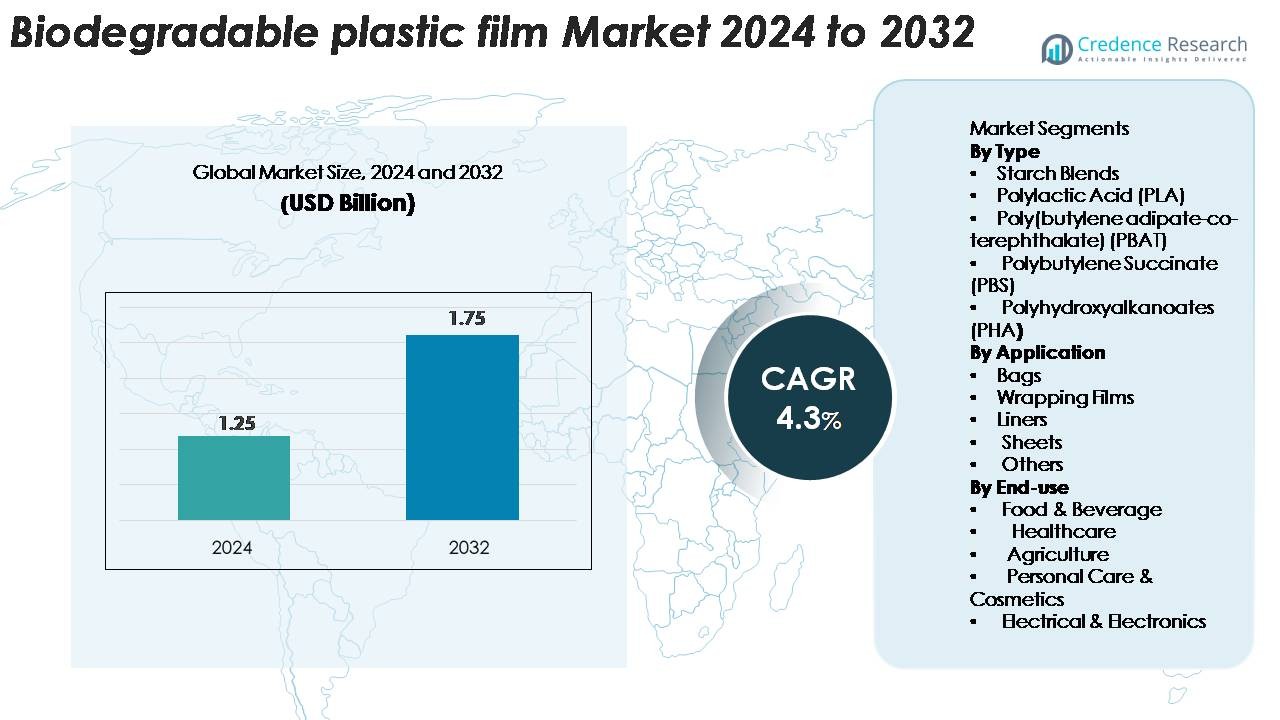
The biodegradable plastic film market was valued at USD 1.25 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 1.75 billion by 2032, registering a CAGR of 4.3% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Biodegradable Plastic Film Market Size 2024 |
USD 1.75 Billion |
| Biodegradable Plastic Film Market, CAGR |
4.3% |
| Biodegradable Plastic Film Market Size 2032 |
USD 4.3 Billion |
The biodegradable plastic film market is shaped by a diverse group of global players, including BASF SE, Tipa Corp. Ltd., Kingfa Sci. & Tech. Co., Ltd., Futamura Chemicals Co., Ltd., Plastchim-T, Cortec Corporation, Clondalkin Group Holding B.V., BioBag Americas, Inc., Brentwood Plastics, Inc., and Shreeji Stretch Film Industries. These companies strengthen the industry through innovations in compostable materials, bio-based formulations, and high-performance packaging solutions. Europe remains the leading region, holding an estimated 38–40% market share, driven by stringent environmental regulations and advanced composting infrastructure. North America and Asia-Pacific follow as strong growth regions, supported by expanding sustainability mandates and rising adoption in food, retail, and agricultural applications.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Insights
- The biodegradable plastic film market was valued at USD 1.25 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 1.75 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 4.3%, supported by rising global sustainability mandates.
- Market growth is driven by increasing restrictions on single-use plastics, strong adoption in food & beverage packaging, and expanding use of compostable films in retail bags, waste liners, and agricultural mulch applications, particularly where compliance with compostability standards is required.
- Key trends include rapid development of high-performance PLA, PBAT, and PHA films, growing investments in compostable infrastructure, and rising demand for certified, traceable, and bio-based packaging solutions across FMCG, agriculture, and e-commerce sectors.
- Competitive intensity strengthens as players such as BASF SE, Tipa Corp., Kingfa, Futamura, and BioBag expand portfolios; however, high production costs and limited composting infrastructure remain key restraints.
- Regionally, Europe leads with 38–40% share, followed by North America at 28–30% and Asia-Pacific at 25–27%; by type, starch blends hold 38–42%, while by application, bags account for 45–50% of total demand.
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Type
Starch blends hold the dominant share in the biodegradable plastic film market, accounting for an estimated 38–42% of total demand due to their cost efficiency, wide availability, and strong compatibility with compostable packaging standards. Polylactic Acid (PLA) follows closely, supported by growing use in food packaging and retail applications. PBAT and PBS gain traction for their flexibility and durability in commercial-grade films, while PHA sees rising adoption in premium, marine-biodegradable applications. Overall, regulatory pressure to replace conventional plastics and advancements in bio-polymer compounding continue to strengthen demand across all material categories.
- For instance, NatureWorks’ Ingeo PLA grades deliver tensile strength values between 50 and 70 MPa, while BASF’s ecoflex PBAT exhibits elongation at break exceeding 600% and tear strength of 120 kN/m, enabling high-performance biodegradable film blends.
By Application
Bags represent the largest application segment, capturing roughly 45–50% share, driven by expanding bans on traditional plastic carry bags and increasing municipal adoption of compostable waste-collection liners. Wrapping films also see strong uptake in food service and retail packaging, benefiting from improved barrier properties and printability in modern bio-films. Liners and sheets gain momentum in agriculture, food processing, and hygiene sectors where controlled biodegradability offers operational advantages. Rising substitution of LDPE and PP films in regulated markets further accelerates adoption across diverse packaging and containment applications.
- For instance, BASF’s ecovio® M 2351 grade supports film production in typical thickness ranges of 10–120 microns, with down-gauging achievable to 8 microns while maintaining mechanical durability and certified compostability, making it suitable for high-performance shopping bags, waste-collection liners, and food-contact packaging applications.
By End-use
Food & beverage leads the end-use landscape with an estimated 50–55% share, supported by stringent sustainability goals among brands and rising use of compostable films in fresh produce, bakery packaging, and single-use service items. Healthcare applications grow steadily as hospitals adopt biodegradable disposal bags and sterile-grade wrap materials. Agriculture benefits from bio-mulch films that reduce soil contamination, while personal care & cosmetics increasingly deploy biodegradable film wrappers for eco-friendly product positioning. Electrical & electronics remain a niche but expanding segment where biodegradable protective films support low-impact, short-cycle packaging needs.
Key Growth Drivers
Regulatory Mandates Targeting Plastic Waste Reduction
Government-led restrictions on single-use plastics remain the strongest catalyst driving adoption of biodegradable plastic films worldwide. Major economies—including the EU, India, and parts of North America—have implemented bans, compliance mandates, and extended producer responsibility (EPR) frameworks compelling packaging manufacturers to transition toward bio-based and compostable alternatives. These policies accelerate procurement of certified biodegradable films for retail bags, food packaging, agricultural mulch, and municipal waste applications. Moreover, governments increasingly incentivize local production of biopolymers through tax credits, subsidies, and waste valorization initiatives, reducing cost barriers for manufacturers. Regulatory alignment with global sustainability goals, such as circular economy directives and carbon neutrality commitments, further strengthens market momentum. As industry stakeholders integrate life cycle assessments and environmental impact audits into procurement strategies, biodegradable films gain preference over traditional petroleum-based materials. Collectively, these policy-driven shifts create a robust and long-term demand foundation for compliant biodegradable film solutions.
- For instance, BASF’s ecovio® grades—rated compliant with EN 13432—are used for regulated waste-collection bags and deliver tensile strength values of 45 MPa in the machine direction and 25 MPa in the transverse direction at film thicknesses between 12 and 30 microns, ensuring durability while meeting mandated compostability requirements.
Rising Demand from Food & Beverage and Retail Packaging
The food & beverage industry drives a substantial portion of market growth as brands aggressively shift toward sustainable packaging that meets consumer and regulatory expectations. Biodegradable plastic films offer high clarity, printability, and tailored barrier properties suitable for fresh produce, bakery items, ready meals, and disposable service applications. Large retailers and global FMCG companies increasingly prioritize compostable packaging to reduce landfill waste and strengthen ESG commitments, creating a steady pipeline of demand for PLA-, starch-, and PBAT-based films. Additionally, e-commerce expansion fuels consumption of compostable mailer bags, cushioning films, and perishables packaging, strengthening demand across both B2B and B2C channels. Food safety standards now favor biodegradable films with improved oxygen and moisture resistance, enabling wider substitution of LDPE and PP films. As sustainability becomes a core brand differentiator, adoption accelerates across both mainstream and premium packaging formats.
- For instance BASF’s certified compostable PBAT polymer ecoflex® F Blend C1200 demonstrates an elongation at break exceeding 700% and a tensile strength of 21 MPa, enabling durable, food-safe biodegradable films used by major FMCG brands.
Advancements in Biopolymer Formulations and Processing Technologies
Technological advancements play a crucial role in improving the performance, scalability, and cost competitiveness of biodegradable plastic films. Innovations in polymer chemistry—including enhanced PLA crystallinity, PBAT flexibility, PBS heat resistance, and PHA biodegradability—enable films to match or exceed mechanical performance of conventional plastics. Multi-layer extrusion, improved compounding, and incorporation of functional additives further enhance barrier strength, tear resistance, and thermal stability, opening applications previously limited to petrochemical films. Downstream processing technologies such as precision casting, blown-film extrusion, and thermoforming increasingly support biodegradable materials with consistent throughput and high-quality output. Manufacturers also integrate renewable feedstocks such as agricultural waste and microbial fermentation, lowering environmental impact and mitigating supply volatility. These advancements facilitate broader industry acceptance across demanding sectors such as healthcare, agriculture, and electronics packaging, reinforcing market expansion.
Key Trends & Opportunities
Expansion of Compostable Packaging Infrastructure and Certification Frameworks
As composting networks expand globally, biodegradable plastic films gain stronger market viability and end-of-life value. Municipal and private-sector investments in industrial composting facilities create a scalable waste-processing ecosystem supporting increased adoption of compostable grocery bags, foodservice wraps, and organic waste liners. Certifications such as EN 13432, ASTM D6400, and ISO 17088 become central purchasing criteria for brands seeking verifiable environmental claims, driving demand for fully compliant materials. Opportunities emerge for film producers to partner with waste management operators, enabling closed-loop systems where biodegradable films decompose efficiently within standardized timelines. With greater consumer awareness of compostable packaging, brands leverage certified biodegradable films to enhance product sustainability narratives, reduce contamination in recycling streams, and improve overall waste management outcomes. This structural expansion of compostable infrastructure accelerates long-term growth prospects for the industry.
- For instance, Novamont’s Mater-Bi EF51 series—certified under EN 13432 and ASTM D6400—achieves complete disintegration in industrial composting environments within 90 days and shows a biodegradation rate exceeding 90% within 180 days, verified by TÜV Austria.
Growing Adoption in Agriculture and Specialty Industrial Applications
Biodegradable plastic films are increasingly adopted beyond traditional packaging, creating new revenue opportunities in agriculture, horticulture, construction, and consumer goods. Agricultural mulch films made from PBAT, PBS, and PHA reduce labor requirements for field retrieval, minimize soil contamination from microplastics, and enhance crop productivity—a compelling proposition for farms seeking sustainability and operational efficiency. Specialty industrial applications, such as biodegradable electronics wrap, compostable courier films, and bio-based protective sheets, emerge as promising niches where low environmental impact is commercially advantageous. Manufacturers also explore custom-engineered films for medical disposables, hygiene products, and water-soluble industrial liners. Growing interest in circular material innovation fosters collaborations between polymer developers, converters, and end-users to create high-performance biodegradable alternatives tailored to sector-specific requirements.
- For instance, BASF’s ecovio® M 2351—engineered specifically for certified biodegradable agricultural mulch films—demonstrates tensile strength values of 23 MPa (MD) and 20 MPa (TD), along with elongation at break exceeding 400%, as reported in BASF’s technical data sheet
Key Challenges
Higher Production Costs and Price Competitiveness Constraints
Despite strong market momentum, biodegradable plastic films continue to face cost disadvantages compared to traditional petroleum-based plastics. Production of biopolymers such as PLA, PHA, and PBS requires specialized feedstocks, fermentation processes, and controlled manufacturing environments that increase capital and operational expenditure. Volatility in agricultural inputs and limited economies of scale further elevate pricing. For many end-users, especially in cost-sensitive markets like retail bags and agricultural mulch, premium pricing limits widespread adoption. Additionally, competition from partially biodegradable and oxo-degradable substitutes complicates procurement decisions, even though these materials may not meet compostability standards. Bridging the cost gap requires scaling biopolymer production, optimizing supply chains, and advancing process efficiencies—challenges that remain critical for accelerating mass-market penetration.
Inadequate Composting Infrastructure and Consumer Misinterpretation
A key barrier to market growth is the limited availability of industrial composting facilities capable of processing certified biodegradable films. In regions lacking these systems, materials intended for composting often end up in landfills, where biodegradation slows significantly. Consumer misunderstanding of terms like “biodegradable,” “home compostable,” and “compostable” frequently leads to improper disposal, contaminating recycling streams and reducing waste-processing efficiency. Variability in global regulatory definitions further complicates labeling and compliance. Without robust infrastructure and clear public education, biodegradable films cannot achieve their full environmental benefit, restricting adoption across major markets. Strengthening waste-processing capacity and harmonizing certification standards remain essential to overcoming this challenge.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America holds an estimated 28–30% share of the biodegradable plastic film market, supported by strong regulatory actions against single-use plastics and widespread adoption of compostable packaging in retail, foodservice, and municipal waste programs. The United States leads demand, driven by large FMCG brands integrating sustainable packaging into ESG commitments. Growth is reinforced by advancements in biopolymer R&D, well-established composting networks, and partnerships between packaging manufacturers and waste management operators. Canada accelerates uptake through nationwide bans on conventional plastic bags and growing deployment of compostable collection systems.
Europe
Europe dominates the global market with an estimated 38–40% share, driven by stringent EU directives promoting circular economy transitions, plastic reduction targets, and verified compostability standards such as EN 13432. Countries like Germany, France, Italy, and the Netherlands lead consumption across food packaging, retail bags, agriculture, and specialty films. High consumer awareness, mature bioplastic manufacturing capacity, and strong governmental incentives accelerate adoption across commercial and industrial sectors. Europe’s extensive network of industrial composting facilities creates favorable conditions for compliant biodegradable films, reinforcing the region’s leadership position.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific accounts for roughly 25–27% of global demand, expanding rapidly due to rising urbanization, regulatory crackdowns on plastic waste, and increased adoption of compostable packaging by foodservice chains and e-commerce platforms. China, Japan, India, and South Korea represent key growth engines, supported by large-scale biopolymer production and government policies promoting bio-based materials. Demand accelerates in agriculture through biodegradable mulch films, while retail and FMCG sectors shift toward eco-friendly packaging to meet sustainability targets. Increasing investments in local bioplastic processing capacity position APAC as a high-growth region.
Latin America
Latin America captures about 4–5% of the biodegradable plastic film market, with growth concentrated in Brazil, Mexico, Chile, and Colombia. Regional demand is shaped by emerging plastic waste regulations, rising environmental awareness, and adoption of compostable bags and food packaging in urban retail hubs. Agricultural applications—particularly biodegradable mulch films—drive additional uptake due to the region’s large farming footprint. While composting infrastructure remains limited, ongoing policy reforms and partnerships with global biopolymer manufacturers support gradual market expansion. Retailers and consumer brands increasingly integrate bio-based packaging to align with sustainability initiatives.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region holds an estimated 3–4% market share, characterized by early-stage adoption but growing interest in sustainable packaging alternatives. Government-led environmental initiatives, especially in the UAE, South Africa, and Saudi Arabia, encourage the transition away from conventional plastics. Demand emerges from retail, food packaging, and agriculture, where biodegradable films offer benefits in soil-friendly applications. Limited industrial composting capacity and cost sensitivity remain challenges, but increasing regulatory pressure and international sustainability commitments stimulate long-term growth potential.
Market Segmentations:
By Type
- Starch Blends
- Polylactic Acid (PLA)
- Poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) (PBAT)
- Polybutylene Succinate (PBS)
- Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA)
By Application
- Bags
- Wrapping Films
- Liners
- Sheets
- Others
By End-use
- Food & Beverage
- Healthcare
- Agriculture
- Personal Care & Cosmetics
- Electrical & Electronics
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape of the biodegradable plastic film market is defined by a mix of global chemical companies, specialized biopolymer producers, and emerging sustainability-focused innovators. Key players—including BASF SE, Tipa Corp., Futamura Chemicals, Kingfa Sci. & Tech., BioBag Americas, Plastchim-T, Cortec Corporation, Clondalkin Group, Brentwood Plastics, and Shreeji Stretch Film Industries—compete through advancements in compostable formulations, improved mechanical performance, and scalable production technologies. Companies increasingly invest in PLA, PBAT, PHA, and starch-blend film innovations to meet rising regulatory and consumer demands. Strategic partnerships with retailers, agricultural producers, and waste-management providers strengthen market positioning, while certifications such as EN 13432 and ASTM D6400 become essential differentiators. Despite strong momentum, competition is intensified by cost pressures, feedstock dependency, and the need for regionally aligned composting infrastructure. Overall, innovation capability, sustainability certifications, and supply-chain integration shape the competitive dynamics of the industry.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
- Tipa Corp. Ltd.
- Plastchim-T
- BASF SE
- Clondalkin Group Holding B.V.
- Cortec Corporation
- Brentwood Plastics, Inc.
- BioBag Americas, Inc.
- Shreeji Stretch Film Industries
- Futamura Chemicals Co., Ltd.
- Kingfa Sci. & Tech. Co., Ltd.
Recent Developments
- In February 2025 a home‐compostable high‐barrier film designed for snack packaging, addressing moisture and oil resistance for compostable applications.
- In October 2024, TIPA Corp. Ltd. announced an expanded portfolio of zero‐waste, compostable packaging solutions at Pack Expo, including new compostable film and laminate offerings.
- In April 2024, Plastchim‑T completed the acquisition of Manucor expanding its supply-chain platform across Europe, Middle East and Africa and increasing capacity in film production.
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Type, Application, End-Use and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- Demand for biodegradable plastic films will rise steadily as global regulations tighten around single-use plastics and mandate certified compostable alternatives.
- Advancements in PLA, PBAT, PBS, and PHA formulations will improve film strength, heat resistance, and barrier performance, expanding application potential.
- Adoption across food & beverage packaging will accelerate as brands align packaging strategies with circular economy and sustainability goals.
- Agricultural use of biodegradable mulch films will grow due to operational advantages and reduced soil contamination.
- Investment in industrial composting facilities will increase, enabling more effective end-of-life processing for certified biodegradable films.
- E-commerce and retail sectors will integrate more compostable bags, mailers, and protective wraps to meet corporate ESG commitments.
- Manufacturers will focus on lowering production costs through scale expansion, bio-feedstock optimization, and improved supply chain efficiency.
- Collaboration between polymer developers, converters, and waste-management operators will strengthen closed-loop systems.
- Certification and labeling transparency will become crucial to reduce consumer confusion and ensure correct disposal.
- Regional adoption will broaden as emerging markets implement stricter environmental policies and promote bio-based material innovation.




