Market Overview:
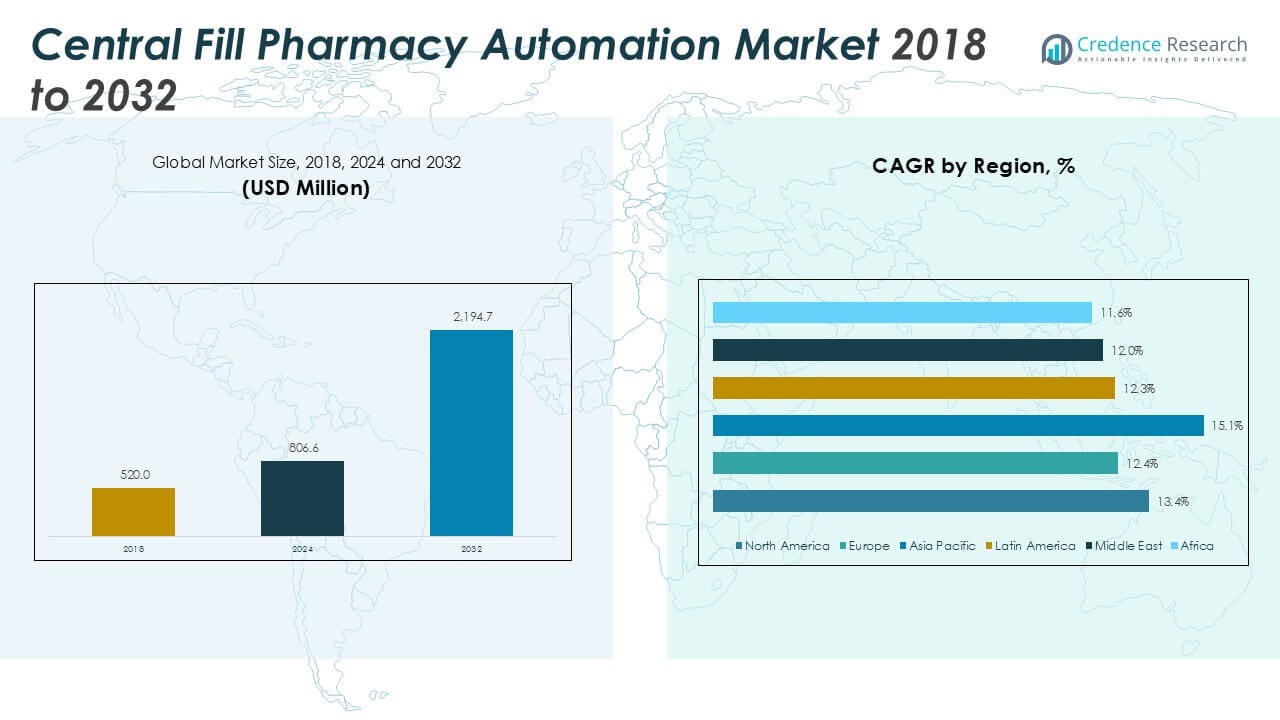
The Global Central Fill Pharmacy Automation Market size was valued at USD 520.0 million in 2018 to USD 806.6 million in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 2,194.7 million by 2032, at a CAGR of 13.4 % during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Central Fill Pharmacy Automation Market Size 2024 |
USD 806.6 Million |
| Central Fill Pharmacy Automation Market, CAGR |
13.4 % |
| Central Fill Pharmacy Automation Market Size 2032 |
USD 2,194.7 Million |
North America currently leads the market, primarily due to the high adoption rates of automation technologies in pharmacies, particularly in the U.S. The region benefits from an advanced healthcare infrastructure and regulatory frameworks that encourage the use of automation to improve medication safety and streamline pharmacy operations. Key players are increasingly focusing on providing solutions that enhance operational efficiency and safety, further driving the market’s growth in this region.
The Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness rapid growth, particularly in countries such as China, India, and Japan. Population growth, healthcare reforms, and a rising number of healthcare facilities are propelling the demand for central fill pharmacy automation systems. As healthcare infrastructure expands and technology adoption increases, the market in this region is poised for strong growth in the coming years. Additionally, government initiatives and investments in healthcare modernization are further accelerating the market’s development in the region.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Insights:
- The Global Central Fill Pharmacy Automation Market is projected to grow from USD 520.0 million in 2018 to USD 2,194.7 million by 2032, at a CAGR of 13.4%.
- North America dominates the market with a 45% share, driven by advanced healthcare infrastructure and high adoption of automation technologies.
- The Asia-Pacific region is expected to experience the highest growth, fueled by healthcare reforms, population growth, and expanding healthcare facilities in countries like China, India, and Japan.
- Increasing prescription volumes due to an aging population and rising chronic diseases drive the demand for automation, improving efficiency and reducing human errors in pharmacies.
- Technological advancements such as robotics, AI, and machine learning are enhancing pharmacy operations, optimizing medication dispensing, and improving operational efficiency.
- Patient safety remains a key priority, with automation helping to standardize dispensing processes and reduce errors, ensuring accurate medication delivery.
- Regulatory complexities and high initial investment costs are key challenges facing market growth, particularly for smaller pharmacies or healthcare facilities.
Market Drivers:
Increasing Prescription Volumes Drive Market Growth
The Global Central Fill Pharmacy Automation Market benefits from the growing prescription volumes, driven by an aging population and increasing incidences of chronic diseases. As healthcare systems face pressure to process high volumes of prescriptions efficiently, automation becomes critical in managing medication dispensing and packaging. Automated systems help pharmacies meet the increasing demand while reducing human error and improving the accuracy of prescriptions. This shift towards automation enables pharmacies to handle higher prescription volumes, resulting in enhanced service delivery and improved patient safety.
- For instance, Harris Health partnered with Capsa Healthcare to implement a new automated central fill solution, which is designed to triple its prescription processing capacity from 5,000 to 15,000 scripts per day.
Need for Improved Inventory Management
Inventory management remains a significant challenge in pharmacies, especially in larger operations. The Global Central Fill Pharmacy Automation Market is addressing this concern by offering automated solutions that streamline stock management. Automation enables real-time tracking of medications, reducing the risk of stockouts, overstocking, and expiration of drugs. By improving inventory accuracy, it reduces operational inefficiencies and ensures timely availability of medications. This factor drives the adoption of pharmacy automation systems, as organizations look for cost-effective and reliable solutions.
Advancements in Technology Enhance Pharmacy Operations
Technological advancements such as robotics, artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning are pivotal in transforming pharmacy operations. The Global Central Fill Pharmacy Automation Market has seen an uptick in the use of these technologies to optimize medication dispensing. AI-driven systems can analyze vast amounts of data to predict medication needs, while robotics handle the physical task of packaging and labeling medications. These technologies enhance operational efficiency by reducing manual labor, minimizing errors, and speeding up the overall process.
- For instance, Roche’s VENTANA TROP2 (EPR20043) RxDx Device utilizes an AI-powered algorithm to generate a quantitative TROP2 score from whole-slide images, enabling precise and personalized treatment decisions in oncology.
Focus on Patient Safety and Reducing Human Error
Patient safety is a top priority in healthcare, and the Global Central Fill Pharmacy Automation Market plays a significant role in ensuring this. Manual medication dispensing processes are prone to human errors, such as incorrect drug dosages or improper packaging. Automation systems provide a solution by standardizing dispensing processes and ensuring the accurate administration of medications. This focus on patient safety has accelerated the adoption of automation solutions in pharmacies, especially in regions with strict regulatory requirements for medication safety and quality assurance.
Market Trends:
Increased Adoption of Artificial Intelligence and Robotics in Pharmacy Automation
The Global Central Fill Pharmacy Automation Market is increasingly incorporating artificial intelligence (AI) and robotics to enhance operational efficiency and accuracy. AI algorithms are being integrated into pharmacy automation systems to predict medication needs, streamline inventory management, and identify potential medication errors before they occur. Robotics, on the other hand, is significantly improving the dispensing and packaging processes by reducing human intervention. Automated systems now handle a wide range of tasks, including pill counting, labeling, and packaging, minimizing the risk of mistakes. These technological advancements are making pharmacy operations faster, more accurate, and cost-effective. With the continuous evolution of AI and robotics, pharmacies are increasingly adopting these systems to meet growing demands and improve service delivery.
- For instance, Diligent Robotics’ Moxi robot successfully completed over 300,000 deliveries within hospital pharmacies, a task which helped to free up pharmacists and technicians to focus on clinical work.
Integration of Pharmacy Automation with Healthcare IT Systems
The Global Central Fill Pharmacy Automation Market is experiencing a trend towards deeper integration with healthcare IT systems. Automation solutions are increasingly being designed to work seamlessly with electronic health records (EHR) and pharmacy management software. This integration enables real-time data sharing between healthcare providers and pharmacies, ensuring that the most accurate and up-to-date patient information is used during medication dispensing. It allows for better coordination between pharmacies and healthcare providers, reducing the risk of drug interactions and improving patient outcomes. With more healthcare providers adopting digital records and cloud-based solutions, the demand for interconnected pharmacy automation systems continues to rise. This trend is improving workflow efficiency and enhancing overall patient care.
- For instance, Walgreens successfully rolled out an artificial intelligence-driven patient engagement system across 1,000 of its pharmacies to reshape patient communication and improve medication adherence.
Market Challenges Analysis:
High Initial Investment and Maintenance Costs
The Global Central Fill Pharmacy Automation Market faces challenges related to the high initial investment required for automation systems. The upfront cost of purchasing, installing, and integrating advanced automation technology can be a significant barrier for smaller pharmacies or healthcare facilities. In addition to the initial expense, ongoing maintenance and software updates contribute to the total cost of ownership. Many pharmacies struggle to justify these costs, especially in regions with limited budgets or a high number of smaller, independent pharmacies. Despite the long-term savings and operational efficiencies, the financial burden of adopting automation systems remains a key challenge in the market.
Regulatory and Compliance Issues
The Global Central Fill Pharmacy Automation Market must navigate complex regulatory and compliance requirements that vary by region. Pharmacies must ensure that automated systems adhere to strict standards for medication safety, privacy, and operational transparency. These regulations can be cumbersome and costly to implement, especially for international deployments. Compliance with local, national, and international standards often requires additional investments in certification, system updates, and staff training. The dynamic nature of regulatory frameworks in the healthcare sector can slow the adoption of automation systems as pharmacies must stay current with changing requirements.
Market Opportunities:
Expansion in Emerging Markets and Increasing Healthcare Investments
The Global Central Fill Pharmacy Automation Market presents significant growth opportunities in emerging markets, where healthcare infrastructure is expanding rapidly. As countries like India, China, and Brazil invest in healthcare modernization, the demand for efficient and accurate pharmaceutical solutions is rising. These regions are increasingly adopting automation technologies to meet the growing need for medication management in both urban and rural areas. The availability of government funding and healthcare reforms further accelerates the adoption of pharmacy automation systems, allowing them to overcome operational challenges and improve healthcare delivery. Emerging markets offer substantial potential for growth, as pharmacies seek automation solutions to enhance efficiency and patient safety.
Integration of Automation with Telehealth and Home Care Services
The integration of pharmacy automation systems with telehealth and home care services offers another promising opportunity for the Global Central Fill Pharmacy Automation Market. With the rise of remote healthcare services and home-based patient care, pharmacies are increasingly tasked with ensuring timely and accurate medication delivery. Automation systems can streamline this process by improving medication dispensing, packaging, and delivery for home care patients. The growing trend of telehealth and the need for at-home treatment options are expanding the market’s potential. Automation systems that integrate with digital health platforms can provide seamless medication management, ensuring better care coordination and patient outcomes.
Market Segmentation Analysis:
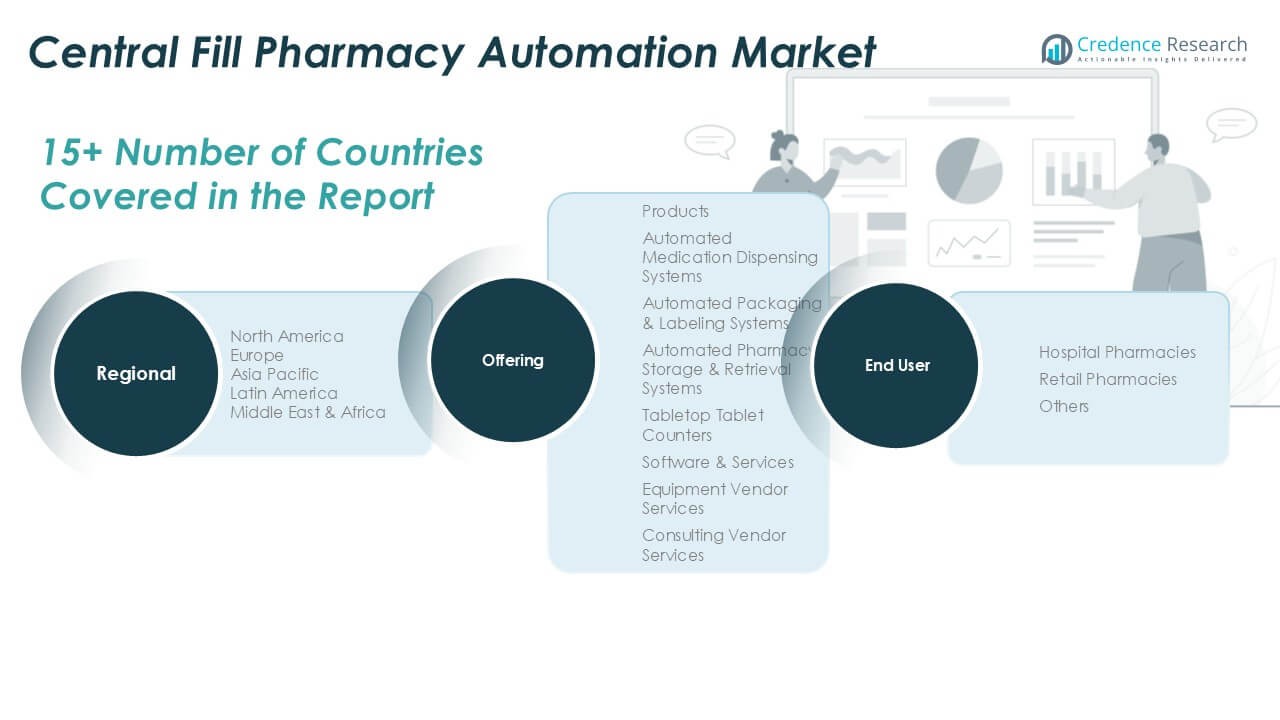
By Offering
The Global Central Fill Pharmacy Automation Market is segmented into key products and services that enhance operational efficiency and accuracy. These include Automated Medication Dispensing Systems, Automated Packaging & Labeling Systems, Automated Pharmacy Storage & Retrieval Systems, and Tabletop Tablet Counters. These products streamline medication dispensing processes, reduce human errors, and improve overall pharmacy efficiency. Additionally, Software & Services such as Equipment Vendor Services and Consulting Vendor Services support system integration and continuous performance optimization.
- For instance, the Pharmafill TC3 tablet counter from Deitz Co. is designed for automated packaging lines and features a single-discharge chute that achieves a bottle throughput of 50 containers per minute.
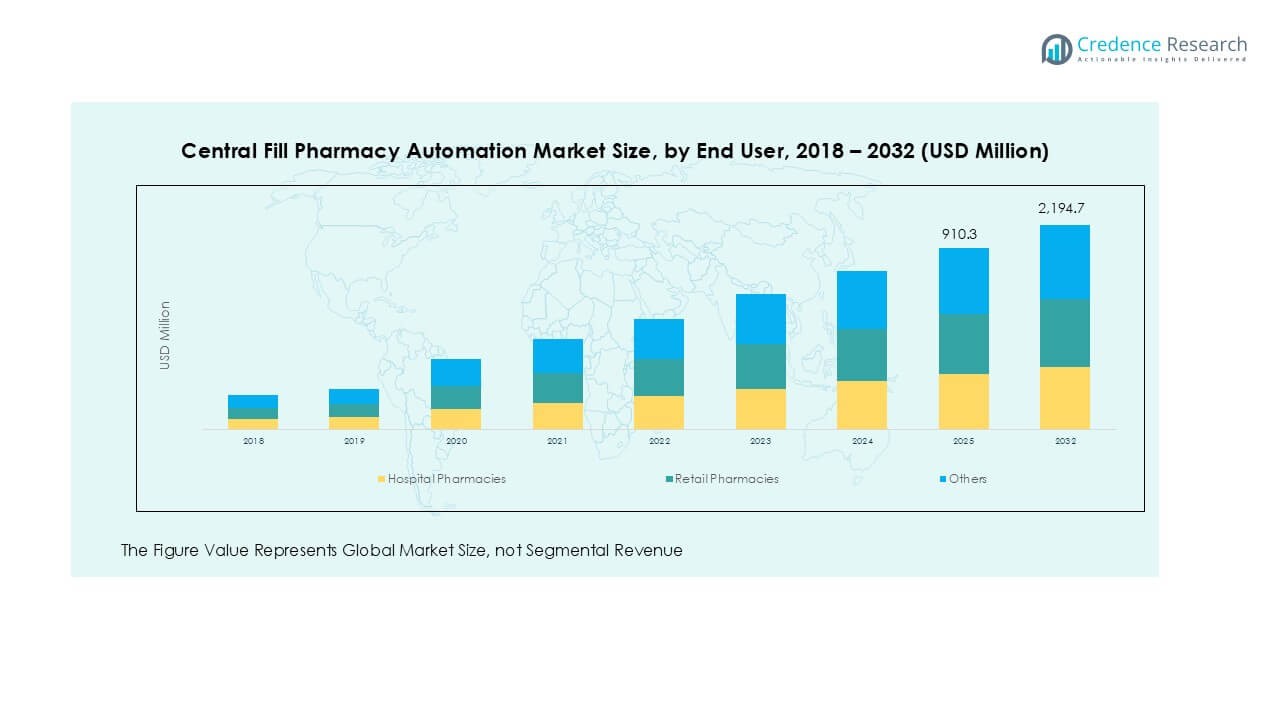
By End-User
The market is also segmented by End-User, with primary categories including Hospital Pharmacies, Retail Pharmacies, and Others. Hospital pharmacies benefit from automation systems that improve patient safety and handle higher prescription volumes more efficiently. Retail pharmacies, driven by customer demand for quick and accurate services, leverage automation to enhance service delivery. Other end-users, including institutions and clinics, adopt tailored automation solutions to meet their specific operational requirements.
- For instance, Walgreens utilizes robotic systems in its micro-fulfillment centers, where a single robot can fill up to 300 prescriptions in one hour, a task that would typically take a small pharmacy staff an entire day to complete.
Segmentations:
By Offering
- Products
- Automated Medication Dispensing Systems
- Automated Packaging & Labeling Systems
- Automated Pharmacy Storage & Retrieval Systems
- Tabletop Tablet Counters
- Software & Services
- Equipment Vendor Services
- Consulting Vendor Services
By End-User
- Hospital Pharmacies
- Retail Pharmacies
- Others
By Regional
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East
- Africa
Regional Analysis:
North America Central Fill Pharmacy Automation Market
The North America Central Fill Pharmacy Automation Market was valued at USD 240.2 million in 2018, and it is projected to reach USD 1,003.1 million by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 13.4% during the forecast period. North America holds the largest share of the Global Central Fill Pharmacy Automation Market, with a dominant 45% market share. The region’s growth is fueled by strong healthcare infrastructure, early adoption of automation technologies, and an increased focus on improving medication safety and efficiency. The U.S. leads this growth, with its vast healthcare facilities and pharmaceutical chains driving the demand for automation systems. Technological advancements, such as AI and robotics, are further accelerating the adoption of automation solutions. The region also benefits from regulatory frameworks that encourage the use of automated systems to reduce medication errors and streamline pharmacy operations. The growing volume of prescriptions and an emphasis on patient safety continue to support market growth.
Europe Central Fill Pharmacy Automation Market
The Europe Central Fill Pharmacy Automation Market was valued at USD 116.0 million in 2018 and is anticipated to reach USD 436.2 million by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 12.4%. Europe represents 30% of the Global Central Fill Pharmacy Automation Market. Countries like Germany, the UK, and France are leading the region’s growth due to increased healthcare investments and digital health initiatives. Strong regulatory frameworks and government funding for automation technologies in pharmacies are propelling the adoption of pharmacy automation systems. Rising demand for efficient and error-free medication dispensing also contributes to the market’s expansion. The growing number of aging populations and the focus on improving medication delivery further drive automation integration across pharmacies. The European market is also benefiting from greater integration with healthcare IT systems to ensure better coordination in patient care.
Asia-Pacific Central Fill Pharmacy Automation Market
The Asia-Pacific Central Fill Pharmacy Automation Market was valued at USD 98.3 million in 2018 and is expected to reach USD 494.8 million by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 15.1%. This region holds a 20% share of the Global Central Fill Pharmacy Automation Market. Rapid growth in healthcare infrastructure, population expansion, and ongoing healthcare reforms in countries like China, India, and Japan drive the demand for pharmacy automation. These countries are adopting automation technologies to enhance service delivery, reduce medication errors, and manage the rising volume of prescriptions. Automation in pharmacies helps streamline operations and improves efficiency in both urban and rural settings. The shift toward more efficient healthcare systems and the growing focus on improving patient safety are key factors driving market growth. Government initiatives to support healthcare modernization also contribute to the market’s expansion in Asia-Pacific.
Latin America Central Fill Pharmacy Automation Market
The Latin America Central Fill Pharmacy Automation Market was valued at USD 32.4 million in 2018, and it is expected to reach USD 125.5 million by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 12.3%. Latin America represents a smaller portion of the Global Central Fill Pharmacy Automation Market, with 10% market share. The growing demand for cost-effective healthcare solutions and the rise in prescription volumes are key drivers for automation adoption. As healthcare systems modernize across countries like Brazil and Mexico, there is an increasing need for automation in pharmacies to improve operational efficiency and patient safety. The region is also witnessing greater integration with digital health platforms and the need for accurate medication delivery. With rising investments in healthcare infrastructure, the Latin American market is poised for significant growth as automation systems become a vital component in pharmacy operations.
Middle East Central Fill Pharmacy Automation Market
The Middle East Central Fill Pharmacy Automation Market was valued at USD 20.2 million in 2018 and is projected to reach USD 72.4 million by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 12.0%. The region accounts for 5% of the Global Central Fill Pharmacy Automation Market. The increasing healthcare investments, along with government initiatives to improve healthcare infrastructure, are boosting the demand for pharmacy automation in countries like the UAE, Saudi Arabia, and Qatar. Rising prescription volumes and the focus on improving healthcare services contribute to the adoption of automation technologies. The growing demand for improved accuracy, faster medication dispensing, and better inventory management is also driving market growth in the region. As healthcare reforms continue, the Middle East market is expected to expand with a focus on improving efficiency and patient outcomes.
Africa Central Fill Pharmacy Automation Market
The Africa Central Fill Pharmacy Automation Market was valued at USD 12.9 million in 2018, and it is anticipated to reach USD 62.8 million by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 11.6%. Africa holds a smaller share of the Global Central Fill Pharmacy Automation Market, contributing 3% of the market. The region faces challenges in healthcare infrastructure but is increasingly adopting pharmacy automation as part of efforts to improve efficiency and patient care. Governments are investing in healthcare modernization, particularly in countries like South Africa, Nigeria, and Kenya. Automation in pharmacies helps address inefficiencies and improves medication accuracy. Rising urbanization and increased healthcare access are contributing to the growth of pharmacy automation systems across Africa. The market is expected to grow as regional healthcare systems evolve and demand for automation technologies increases.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis:
- McKesson Corporation
- Omnicell, Inc.
- Arxium, Inc.
- ScriptPro LLC
- RxSafe, LLC
- Tension Packaging & Automation
- Parata Systems, LLC (part of BD)
- TCGRx (BD’s pharmacy workflow solutions)
- Swisslog Healthcare (KUKA)
- Cornerstone Automation Systems, LLC (CASI)
- PillPick Automation System
Competitive Analysis:
The Global Central Fill Pharmacy Automation Market is characterized by a competitive landscape featuring several key players. Companies such as Omnicell, ARxIUM, ScriptPro LLC, McKesson Corporation, and RxSafe LLC hold significant market shares. These firms focus on enhancing operational efficiency and medication safety through advanced automation solutions. Omnicell, for instance, has introduced innovations like the XT Amplify program to optimize automated dispensing systems in healthcare facilities. ARxIUM offers solutions like the RIVA system, which integrates robotic compounding with pharmacy workflows. ScriptPro LLC provides comprehensive pharmacy automation systems that streamline dispensing processes. McKesson Corporation delivers a range of automation solutions to improve pharmacy operations. RxSafe LLC specializes in automated storage and retrieval systems to enhance medication management. These companies compete by offering tailored solutions that address the diverse needs of hospital pharmacies, retail pharmacies, and other healthcare providers. Their strategic focus on innovation, customer service, and regulatory compliance positions them to meet the growing demand for efficient and accurate pharmacy automation systems.
Recent Developments:
- In October 2024, McKesson Corporation launched InspiroGene, a new business unit dedicated to guiding the commercialization of cell and gene therapies.
- In May 2025, Omnicell, Inc. announced the launch of MedTrack, a new RFID-enabled product line, and MedVision, a web-based software for managing inventory in outpatient clinics.
- In May 2025, Omnicell, Inc. opened a new Innovation Lab in Austin, Texas, to accelerate the development of new technologies for the healthcare industry.
Report Coverage:
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Offering, End-User and Region. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook:
- The demand for pharmacy automation will continue to rise due to increasing prescription volumes and the need for greater operational efficiency.
- Technological advancements in artificial intelligence and robotics will play a key role in enhancing the accuracy and speed of pharmacy operations.
- Automation systems will increasingly integrate with healthcare IT systems to streamline patient care coordination and improve service delivery.
- The focus on patient safety will drive adoption, as automated systems reduce medication errors and improve prescription accuracy.
- The growing preference for cost-effective solutions will lead to wider adoption in both large and small pharmacies.
- Regulatory compliance requirements will influence market development, with companies focusing on systems that meet stringent standards.
- The expansion of healthcare infrastructure, especially in emerging markets, will further boost the adoption of automation in pharmacies.
- Integration of telehealth and remote monitoring will enable pharmacies to offer more personalized and efficient services through automation.
- Competitive pressure among key players will drive innovation in product offerings, creating more specialized and customizable solutions.
- Market players will continue to focus on enhancing customer support and offering training services to ensure seamless adoption of automation systems.






