Market Overview
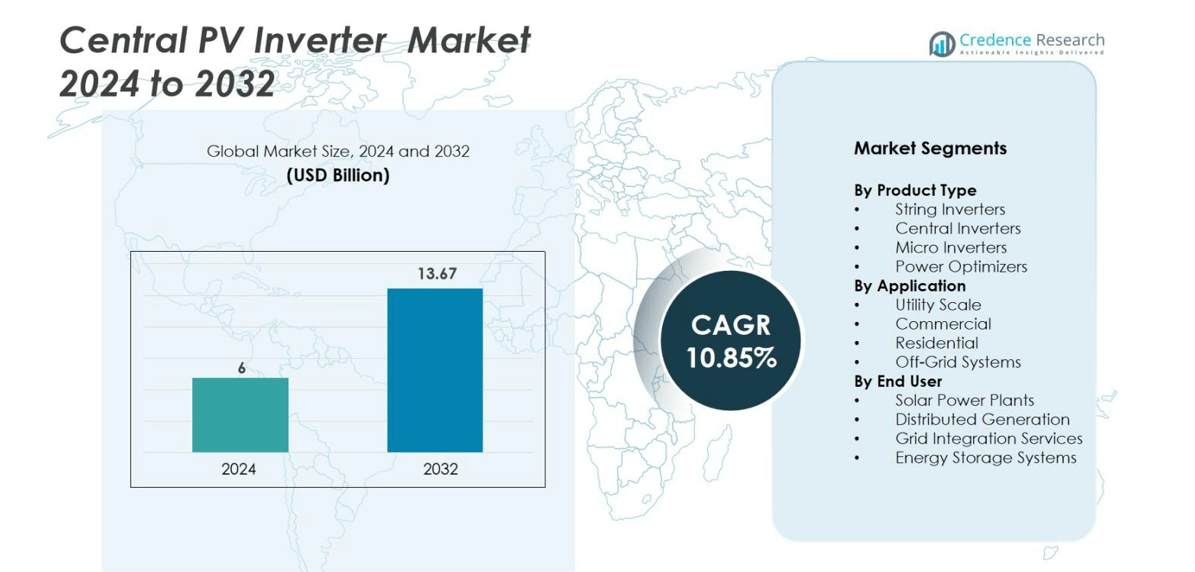
The Central PV Inverter market size was valued at USD 6 Billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 13.67 Billion by 2032, at a CAGR of 10.85% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Central PV Inverter Market Size 2024 |
USD 6 Billion |
| Central PV Inverter Market, CAGR |
10.85% |
| Central PV Inverter Market Size 2032 |
USD 13.67 Billion |
The Central PV Inverter market is led by key players including SMA Solar Technology AG, ABB Ltd, Schneider Electric SE, Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd, Sungrow Power Supply Co., Ltd, KACO New Energy GmbH, Power Electronics S.L., TBEA Co., Ltd, Ingeteam S.A., and Delta Electronics, Inc. These companies compete globally through technology innovation, regional manufacturing presence, and service-oriented business models. Regionally, Asia-Pacific leads with approximately 40.7% market share in 2024, driven by extensive solar installations and domestic manufacturing capabilities. Europe ranks second, followed by North America in third place. This competitive and regional structure defines the market dynamics, highlighting strong opportunities for technology differentiation, strategic partnerships, and expansion in emerging solar markets.
Market Insights
- The Central PV Inverter market was valued at USD 6 Billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 13.67 Billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 10.85%.
- Market growth is driven by rising utility-scale solar installations, supportive government policies, and technological advancements in high-capacity inverters for efficient grid integration.
- Key trends include integration with energy storage systems, adoption of smart and IoT-enabled inverters, and growing preference for central inverters in commercial and utility-scale projects. String inverters hold 30% share, while central inverters dominate with 48% share in the product segment.
- Competition is strong with players like SMA Solar Technology AG, ABB Ltd, Schneider Electric SE, Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd, Sungrow Power Supply Co., Ltd, KACO New Energy GmbH, Power Electronics S.L., TBEA Co., Ltd, Ingeteam S.A., and Delta Electronics, Inc. High initial investment and grid compliance remain market restraints.
- Regionally, Asia-Pacific leads with 44% share, followed by Europe 25%, North America 20%, and Latin America & MEA 11%.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Segmentation Analysis
By Product Type
The Central PV Inverter market by product type is dominated by Central Inverters, holding 48% market share in 2024. Their high capacity and ability to manage large-scale solar installations drive adoption in utility projects. String Inverters follow with 30%, valued for modularity and ease of installation in commercial and residential projects. Micro Inverters and Power Optimizers collectively account for 22%, offering improved energy harvest and panel-level monitoring. Growth is fueled by rising solar PV installations, efficiency improvements, and declining costs, making high-capacity inverters essential for grid stability and optimized power output in large-scale solar farms.
- For instance, Sungrow offers central inverters with power outputs ranging from 500 kW up to 6.8 MW, designed specifically for large-scale installations in utility projects.
By Application
Utility-scale projects dominate the Central PV Inverter market by application, capturing 55% market share in 2024. Central inverters are widely deployed in these projects due to their ability to handle high voltages and centralize control. Commercial applications hold 25%, driven by rooftop solar adoption and cost savings. Residential applications account for 15%, where compact string and micro inverters are preferred. Off-grid systems make up the remaining 5%, primarily in remote regions. Market growth is driven by government renewable energy mandates, falling solar costs, and increasing corporate sustainability initiatives across commercial and industrial sectors.
- For instance, Chint Power Systems providing central inverters for large-scale solar projects with advanced MPPT technology for optimized energy output.
By End User
Solar power plants lead the Central PV Inverter market by end user, commanding 50% market share in 2024. Central inverters are preferred for large-scale PV projects, providing high reliability and centralized monitoring. Distributed generation contributes 25%, benefiting from modular inverters that integrate small-scale solar systems with the grid. Grid integration services represent 15%, as inverters enable efficient synchronization and voltage regulation. Energy storage systems account for 10%, leveraging inverters for bi-directional power management. Demand growth is fueled by expanding renewable capacity, energy policy incentives, and the increasing adoption of hybrid solar-plus-storage solutions worldwide.
Key Growth Drivers
Rising Utility-Scale Solar Installations
The expansion of utility-scale solar projects is a primary driver of the Central PV Inverter market. Governments worldwide are promoting large-scale renewable energy deployment to meet climate targets and reduce reliance on fossil fuels. Central inverters, with their high capacity and ability to manage large arrays, are ideal for these projects. Increasing investment in solar farms, particularly in Asia-Pacific, North America, and Europe, supports adoption. The need for efficient grid integration, real-time monitoring, and centralized control also drives demand. For instance, countries such as India and the U.S. are accelerating utility-scale PV projects, requiring robust inverter solutions capable of handling high voltages and improving overall system performance.
- For instance, GE Renewable Energy’s LV5+ Solar Inverter and FLEXINVERTER provide high-efficiency solutions with advanced grid management capabilities, supporting large solar projects in the U.S. and other regions.
Government Incentives and Renewable Policies
Supportive government policies and renewable energy incentives strongly drive market growth. Subsidies, tax credits, and feed-in tariffs reduce upfront costs and improve ROI for solar project developers. Central PV inverters benefit from these policies, particularly in utility-scale and commercial segments, where investment scale is significant. Mandates to integrate solar into energy grids encourage adoption of advanced inverters with smart monitoring and grid support features. For instance, the U.S. Investment Tax Credit (ITC) and Europe’s renewable energy targets have accelerated large-scale PV installations, directly increasing demand for central inverters.
- For instance, in Europe, the Renewable Energy Directive (EU/2023/2413) sets a binding target of 42.5% renewable energy by 2030, encouraging smart grid integration and increased deployment of advanced PV inverters, with Germany reporting a 35% rise in domestic PV installations supported by subsidies.
Technological Advancements and Efficiency Improvements
Continuous technological innovation in inverter design drives market expansion. Central inverters are evolving to deliver higher efficiency, improved thermal management, and enhanced grid support features. Innovations such as real-time diagnostics, remote monitoring, and integration with energy storage systems improve reliability and reduce downtime. For instance, companies like SMA and Huawei have launched advanced inverters with enhanced MPPT algorithms and modular designs for scalability. These advancements attract utility operators and commercial developers seeking optimal performance, lower maintenance costs, and improved energy yield. As PV system efficiency becomes a critical factor in cost-competitiveness, the demand for technologically advanced central inverters is projected to rise, making continuous innovation a key market driver.
Key Trends & Opportunities
Integration with Energy Storage Systems
The convergence of solar PV and energy storage creates significant opportunities for central inverters. Hybrid systems require inverters capable of bi-directional power flow, battery management, and seamless grid integration. Manufacturers are increasingly offering inverters with built-in storage compatibility to meet these requirements. For instance, Huawei’s FusionSolar series supports combined PV and storage operations, enabling efficient energy management and peak load optimization. This trend allows utilities and commercial developers to balance supply-demand fluctuations, enhance grid stability, and participate in energy trading. As renewable penetration rises, central inverters integrated with storage systems represent a growing market segment, providing new revenue streams and fostering technological differentiation among key players.
- For instance, Huawei’s FusionSolar LUNA2000-215 kWh model is a smart string energy storage system (ESS) that integrates hybrid cooling technology (liquid and air cooling) and a pre-integrated Power Conversion System (PCS).
Adoption of Smart and IoT-Enabled Inverters
Smart inverter technology is transforming PV system management and monitoring. IoT-enabled inverters allow real-time performance tracking, predictive maintenance, and remote troubleshooting, reducing operational costs. Central inverters with smart features can provide advanced grid support, voltage regulation, and reactive power control, critical for large-scale solar installations. Companies such as Sungrow and Schneider Electric are developing inverters with cloud-based monitoring platforms, enhancing energy efficiency and operational transparency. This trend opens opportunities for software-as-a-service models, performance analytics, and data-driven energy optimization. Increased awareness of grid stability and energy management solutions is accelerating the adoption of smart inverters, offering competitive advantages to manufacturers that integrate advanced digital capabilities.
- For instance, Sungrow’s 5kW hybrid inverter integrates smart monitoring and control systems, allowing users to optimize energy consumption and track system performance in real time while also supporting grid stability through voltage regulation.
Key Challenges
High Initial Investment and Capital Costs
The substantial upfront cost of central PV inverters poses a challenge for market growth, particularly in developing regions. High-capacity inverters require significant capital expenditure for procurement, installation, and commissioning. Smaller developers and residential projects often prefer string or micro inverters due to lower costs, limiting central inverter adoption outside utility-scale applications. Additionally, the integration of advanced monitoring and storage features further increases system costs. Price sensitivity in emerging markets and competition from cost-effective alternatives create pressure on manufacturers to optimize pricing without compromising quality.
Grid Integration and Regulatory Compliance
Ensuring compatibility with regional grid codes and meeting stringent regulatory standards presents ongoing challenges. Central PV inverters must support voltage, frequency, and reactive power requirements, which vary by country and utility operator. Non-compliance can result in operational inefficiencies, project delays, or penalties. For instance, integrating large-scale PV projects into existing grids requires sophisticated control systems and advanced fault detection to prevent instability. Manufacturers face the challenge of designing flexible inverters that adhere to diverse regulations while maintaining efficiency. Continuous updates to grid codes and evolving standards increase R&D costs and necessitate ongoing technical support, posing a hurdle to seamless market expansion.
Regional Analysis
Asia Pacific
The Asia Pacific region dominated the Central PV Inverter Market in 2024 with an estimated 44% market share. Rapid installations in China, supported by strong manufacturing ecosystems and government renewable-energy policies, drive this leadership. Growth accelerates in India and Southeast Asia as large-scale solar farms and utility projects adopt high-capacity central inverters. Regional manufacturers benefit from economies of scale and localized supply chains. The region’s trajectory remains strong due to favourable policy frameworks, rising energy demand, and ongoing grid-integration efforts.
Europe
Europe held approximately 25% of the market share in 2024 and serves as the second-largest region for central PV inverters. Regulatory targets for carbon neutrality by mid-century, coupled with a significant uptake of utility- and commercial-scale solar deployments, underpin this market size. Manufacturers benefit from well-established supply chains and robust grid infrastructure. However, slower growth in residential segments and higher installation costs moderate expansion. Investments in smart grid integration and large-scale projects continue to support demand for central inverters across the region.
North America
North America accounted for roughly 20% of the market share in 2024, placing it as the third-largest region. The U.S. leads growth through expansive utility-scale solar projects and supportive energy-transition policies. Developers increasingly deploy central inverters for large solar farms and hybrid solar-storage systems. Nonetheless, challenges such as fluctuating policy incentives, tariff pressures, and competition from string-inverter systems constrain further gains. Technological upgrades for grid compliance and modularity offer opportunities to expand regional adoption.
Latin America & Middle East & Africa (MEA)
Combined, Latin America and MEA represent the remaining 11% of the global market share as of 2024. These regions exhibit emerging demand for central PV inverters driven by growing electricity needs, solar resource potential, and increasing utility-scale investment. Infrastructure gaps and lower per-capita capacity pose hurdles, yet falling system costs and expanding solar tender pipelines support future growth. Countries in the Middle East are deploying mega-solar farms, while several Latin American nations ramp up solar incentives and large-scale installations.
Market Segmentations
By Product Type
- String Inverters
- Central Inverters
- Micro Inverters
- Power Optimizers
By Application
- Utility Scale
- Commercial
- Residential
- Off-Grid Systems
By End User
- Solar Power Plants
- Distributed Generation
- Grid Integration Services
- Energy Storage Systems
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape of the central PV inverter market reflects intense rivalry among established global manufacturers such as SMA Solar Technology AG, ABB Ltd, Schneider Electric SE, Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd, Sungrow Power Supply Co., Ltd, KACO New Energy GmbH, Power Electronics S.L., TBEA Co., Ltd, Ingeteam S.A. and Delta Electronics, Inc.. These key players compete through product innovation, global expansion and strategic alliances. They invest in next‑generation power electronics, digital monitoring platforms and integrated storage solutions to differentiate their offerings. Many firms adopt partnerships, mergers and geographic diversification to capture emerging markets and lower regional entry barriers. Also, price competition remains strong, particularly in regions with high-cost sensitivity and strong local manufacturing ecosystems. The high level of competition intensifies the need for continuous R&D, operational efficiency and strategic positioning to maintain or grow market share.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
Recent Developments
- In September 2025, Sungrow introduced its 4.8 MW SG4800UD-MV-US modular inverter for the North American market at RE+ 2025, combining central and string inverter benefits with modular architecture and grid-forming features.
- In May 2025, Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd’s Digital Power division launched its “All-Scenario Grid Forming ESS” strategy and next-generation PV+ESS products at Intersolar Europe 2025.
- In April 2025, Sungrow Power Supply Co., Ltd unveiled its 1+X 2.0 Modular Inverter at the Global Renewable Energy Summit, offering a scalable block design (800 kW–9.6 MW) with grid-forming capabilities and AI-driven diagnostics
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Product Type, Application, End-User and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- The Central PV Inverter market will see strong expansion as solar installations scale across utility and commercial sectors.
- Manufacturers will invest heavily in modular, high‑capacity inverters to address large‑scale solar farm demands and reduce installation time.
- Inverters will increasingly integrate with energy‑storage systems, enabling hybrid solar‑plus‑storage solutions and enhancing grid flexibility.
- Digitisation and IoT features will emerge as standard, allowing real‑time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and operational optimisation in inverter management.
- Regions such as Asia‑Pacific will lead growth, followed by Europe and North America, driven by favourable policies and infrastructure upgrades.
- Efficiency enhancements, such as wide‑bandgap semiconductors and transformerless designs, will reduce system costs and increase adoption.
- Standardisation of grid‑code compliance and support for higher voltage inverters will simplify rollout across diverse markets.
- Developers will favour central inverters in large‑scale projects to lower balance‑of‑system costs and streamline operations.
- Competitive pressure will push vendors to expand service offerings and build long‑term partnerships with project developers.
- Regulatory shifts and evolving financing models will open new opportunities, but also require flexible business strategies to adapt.




