Market Overview
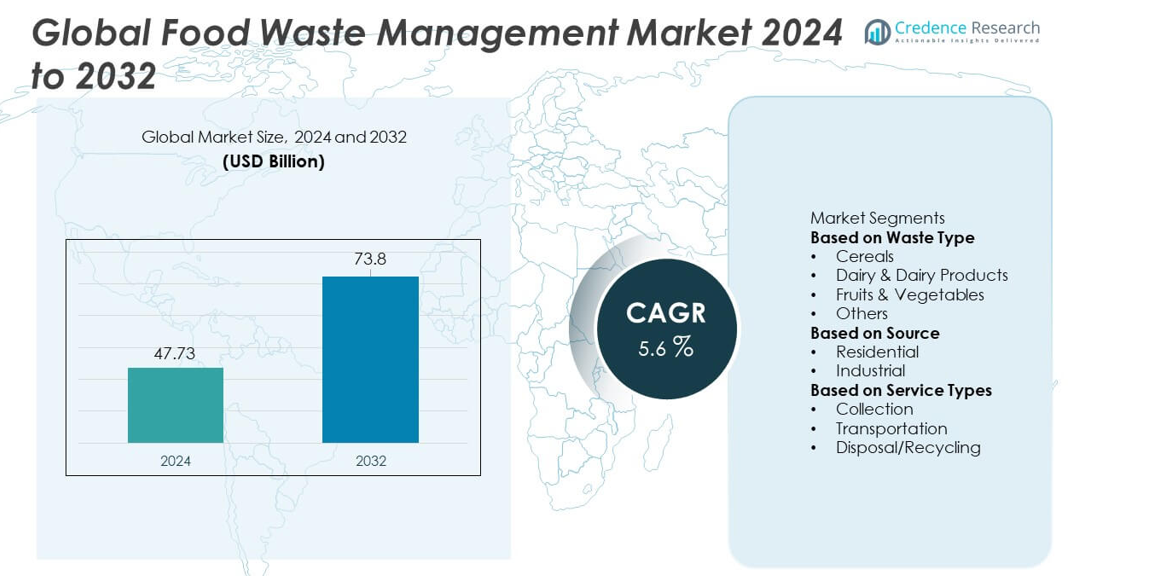
The Global Food Waste Management market reached USD 47.73 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow to USD 73.8 billion by 2032, supported by a 5.6% CAGR during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Global Food Waste Management Market Size 2024 |
USD 47.73 billion |
| Global Food Waste Management Market, CAGR |
5.6% |
| Global Food Waste Management Market Size 2032 |
USD 73.8 billion |
Top players in the Global Food Waste Management market include Veolia, Suez, Waste Management, Inc., Republic Services, Inc., Covanta Ltd., Stericycle, Remondis SE & Co. KG, Clean Harbors, Biffa, and Rumpke. These companies expand their presence by providing integrated collection, recycling, composting, and waste-to-energy solutions that support municipalities and industries. They invest in anaerobic digestion, advanced sorting systems, and digital monitoring tools to improve efficiency and reduce landfill dependence. North America leads the market with a 37% share, driven by strict disposal regulations and strong waste-to-energy adoption, followed by Europe at 33%, supported by circular economy mandates. Asia Pacific holds a 25% share, growing rapidly due to rising urban waste volumes and increased investment in recycling infrastructure.
Market Insights
- The Global Food Waste Management market reached USD 47.73 billion in 2024 and will grow at a 5.6% CAGR, supported by rising demand for efficient waste handling and recycling solutions.
- Key growth comes from stricter sustainability policies and higher waste generation across residential and industrial sources, driving strong adoption of recycling, composting, and conversion technologies.
- Major trends include wider use of anaerobic digestion, digital tracking systems, and advanced sorting, while collection services dominate the service segment with a 46% share due to heavy reliance on organized waste handling networks.
- Competition intensifies as leading players expand recycling capacity, invest in waste-to-energy facilities, and strengthen partnerships with municipalities, while high operational costs and fragmented waste streams remain key restraints.
- North America leads with a 37% share, followed by Europe at 33% and Asia Pacific at 25%, while fruits and vegetables remain the dominant waste type with a 41% share driven by high spoilage and supply chain losses.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Waste Type
Fruits and vegetables lead the waste type segment with a 39% share, driven by high perishability, supply chain losses, and improper storage across developing and developed markets. Their short shelf life results in significant waste during harvesting, transportation, and retail handling. Growing urban consumption and increased demand for fresh produce further intensify waste volumes. Cereals hold a notable share due to post-harvest losses in storage and milling, while dairy waste rises from cold-chain gaps and overproduction. Rising global focus on composting, anaerobic digestion, and waste-to-energy systems continues to support effective management across all waste categories.
- For instance, Veolia expands its anaerobic digestion network by processing organic waste across various regions, including Europe. The company increases biogas output, which improves conversion efficiency across food waste streams and contributes to the production of renewable energy, compost, and other valuable resources.
By Source
The industrial segment dominates the source category with a 58% share, supported by large volumes of waste generated across food processing plants, restaurants, hotels, and institutional kitchens. Industries adopt advanced recycling, composting, and energy recovery systems to meet sustainability goals and regulatory requirements. Strong emphasis on reducing disposal costs and improving operational efficiency drives investment in waste segregation and treatment technologies. The residential segment contributes steady growth as households increase food consumption and face challenges related to portion planning and storage. Awareness programs and municipal collection initiatives enhance participation in structured waste disposal.
- For instance, Republic Services has made significant investments and upgrades to its organics processing infrastructure across various locations, including the expansion of some facilities to meet regional compliance needs.
By Service Types
Disposal and recycling services lead the segment with a 46% share, driven by rising adoption of composting, anaerobic digestion, and biofuel production processes. These solutions help convert organic waste into energy, fertilizers, and valuable by-products, supporting circular economy goals. Collection services also hold significant importance as municipalities and private operators expand door-to-door waste segregation programs. Transportation services grow steadily due to rising waste volumes and the need for specialized logistics systems. Increasing government policies targeting landfill reduction and improved recycling efficiency continue to strengthen demand across all service categories.
Key Growth Drivers
Rising Food Waste Generation Across Supply Chains
Growing food production, rapid urbanization, and expanding retail networks increase waste at every stage of the supply chain. Losses occur during harvesting, processing, distribution, and household consumption, driving strong demand for efficient waste management solutions. Governments enforce stricter waste disposal rules, pushing businesses to adopt recycling, composting, and waste-to-energy technologies. Rising awareness of environmental impacts and methane emissions encourages investment in advanced treatment systems. As global food consumption rises, companies and municipalities expand infrastructure to handle larger waste volumes and meet sustainability targets.
- For instance, Waste Management, Inc. processes organic waste through its organics recycling facilities, contributing to resource recovery. The company also utilizes automated collection trucks, incorporating technology that aids in efficiency and potentially helps manage waste streams.
Increasing Adoption of Circular Economy and Resource Recovery
The shift toward circular economy practices accelerates demand for technologies that convert food waste into valuable products. Anaerobic digestion, composting, and bioconversion generate energy, organic fertilizers, and bio-based materials that support sustainable agriculture and renewable energy goals. Industries invest in closed-loop systems to reduce disposal costs and improve resource efficiency. Governments promote recycling incentives, landfill restrictions, and renewable energy programs that encourage waste valorization. This growing focus on resource recovery strengthens long-term opportunities for food waste management providers across global markets.
- For instance, Suez operates numerous anaerobic digestion plants that treat millions of tons of organic material annually. These units produce significant amounts of biogas, supporting large-scale circular economy programs.
Stringent Environmental Regulations and Sustainability Commitments
Governments implement strict regulations to reduce landfill use, control methane emissions, and encourage responsible waste disposal. Industries and municipalities face compliance requirements that mandate waste segregation, recycling targets, and sustainable management practices. Corporate sustainability commitments and ESG reporting drive investments in advanced treatment technologies and efficient collection systems. Food processors, retailers, and hospitality operators adopt structured waste monitoring and reduction programs. These evolving regulatory and environmental priorities significantly accelerate market adoption and infrastructure development.
Key Trends & Opportunities
Growth of Waste-to-Energy and Biofuel Production
Waste-to-energy technologies gain traction as industries and municipalities seek renewable alternatives to fossil fuels. Anaerobic digestion and gasification convert food waste into biogas, electricity, and heat, helping reduce energy costs and emissions. Investments in biofuel production rise as governments promote clean energy transitions. Opportunities expand through partnerships between waste processors, energy companies, and agricultural sectors. Rising landfill bans and emission controls continue supporting waste-to-energy expansion worldwide.
- For instance, Covanta processed more than 21 million tons of waste across its energy-from-waste facilities in 2023, generating 10 million megawatt-hours of electricity. The company also recovered 430,000 tons of metal through advanced extraction systems.
Digitalization and Smart Waste Management Solutions
Technology adoption accelerates with the use of IoT sensors, AI-enabled sorting, and automated collection systems. Smart bins improve waste segregation, while data analytics optimize routing, reduce operational costs, and enhance recycling efficiency. Digital platforms help businesses track food waste levels, identify reduction opportunities, and strengthen compliance. These innovations drive new opportunities for service providers and support more sustainable waste handling processes across urban and industrial environments.
- For instance, Stericycle manages regulated waste each year, using automated tracking systems and specialized vehicles to record every collection point.
Key Challenges
High Operational Costs and Infrastructure Limitations
Food waste management requires significant investment in collection systems, treatment facilities, and advanced recycling technologies. Developing regions face limited infrastructure, slow regulatory implementation, and inadequate funding for large-scale projects. High transportation and labor costs add pressure on municipal budgets and service providers. Small businesses struggle with adoption due to limited financial capacity, slowing market expansion. These operational and infrastructural constraints remain major barriers to efficient waste management.
Complexity in Waste Segregation and Contamination Issues
Improper segregation and contamination of food waste hinder recycling efficiency and increase processing costs. Mixed waste streams reduce the quality of recovered materials and limit opportunities for composting and anaerobic digestion. Households and commercial establishments often lack awareness or infrastructure for proper sorting. Contaminated waste also poses hygiene, safety, and odor challenges during collection and treatment. Improving waste segregation practices remains essential to unlocking full recycling and recovery potential.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America holds a 33% share of the Global Food Waste Management market, driven by strong regulatory frameworks, advanced recycling infrastructure, and high food waste generation across residential and commercial sectors. The United States leads due to strict landfill diversion policies, increasing adoption of anaerobic digestion, and widespread use of composting systems. Large retail chains and food service companies invest in waste reduction programs to meet sustainability commitments. Canada supports growth through eco-friendly waste initiatives and expanding municipal recycling networks. Rising consumer awareness and technology adoption continue to strengthen market development across the region.
Europe
Europe accounts for a 31% share of the market, supported by stringent waste management directives, strong circular economy policies, and high recycling standards. Countries such as Germany, France, and the UK lead adoption with advanced composting and waste-to-energy facilities. EU legislation mandates waste reduction, segregation, and resource recovery, driving significant investment in sustainable treatment technologies. Food manufacturers and retailers adopt structured waste monitoring systems to meet compliance targets. Growing emphasis on bioenergy production and reduced landfill dependency further supports market expansion across the region.
Asia Pacific
Asia Pacific holds a 27% share, driven by rapid population growth, rising food consumption, and expanding urban centers that generate large volumes of organic waste. China, India, and Japan lead adoption through government-backed waste reduction programs, improved collection systems, and investment in anaerobic digestion plants. Industrial and commercial sectors adopt recycling and composting solutions to meet tightening environmental regulations. Growing awareness of food loss, increasing retail expansion, and rising focus on resource recovery push market growth. Infrastructure development and smart waste technologies continue to accelerate adoption across emerging economies.
Latin America
Latin America represents a 6% share of the market, influenced by rising urbanization, increasing food waste from households and hospitality sectors, and improving municipal waste initiatives. Brazil and Mexico lead regional demand through expanding composting programs, landfill diversion strategies, and growing investments in recycling infrastructure. Government policies promoting sustainable waste handling support market progress, though infrastructure gaps remain in rural areas. Food processors and retailers adopt waste reduction practices to improve sustainability performance. Growing public awareness and private-sector participation drive steady regional market development.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region accounts for a 3% share, supported by rising food consumption, increasing waste generation, and growing government focus on sustainable waste solutions. Gulf countries such as the UAE and Saudi Arabia invest in waste-to-energy plants, recycling initiatives, and advanced collection systems as part of national sustainability goals. African countries experience gradual growth through urban waste management projects, though infrastructure and funding constraints remain major challenges. Expanding retail activity, tourism growth, and awareness campaigns support adoption of better waste disposal and recycling practices across the region.
Market Segmentations:
By Waste Type
- Cereals
- Dairy & Dairy Products
- Fruits & Vegetables
- Others
By Source
By Service Types
- Collection
- Transportation
- Disposal/Recycling
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
Major players in the Global Food Waste Management market include Veolia, Suez, Waste Management, Inc., Republic Services, Inc., Covanta Ltd., Stericycle, Inc., Remondis SE & Co. KG, Clean Harbors, Inc., Biffa, and Rumpke. These companies compete by expanding waste collection networks, upgrading recycling facilities, and investing in advanced processing technologies such as anaerobic digestion, composting, and waste-to-energy systems. Leading providers focus on long-term municipal contracts, industrial service agreements, and integrated waste handling solutions to strengthen market presence. Many players enhance operational efficiency through automation, digital tracking, and route optimization systems. Sustainability commitments also drive investments in circular economy initiatives, including nutrient recovery and renewable energy generation. Strategic mergers, acquisitions, and regional expansions help companies broaden service portfolios and address rising food waste volumes across residential, commercial, and industrial sectors. Continuous innovation, regulatory compliance expertise, and strong service reliability remain central to maintaining competitive advantage in the global market.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
Recent Developments
- In 2025, Rumpke, in partnership with bp’s Archaea Energy, launched two renewable natural gas (RNG) plants, at its Beech Hollow and Pike Sanitation landfills in Ohio.
- In November 2024, Biffa expanded its food waste capabilities through the acquisition of Keenan Recycling, which enhances its end-to-end food waste solutions, including anaerobic digestion for recycling food waste into biogas and liquid fertilizer.
- In April 2024, Covanta officially announced its rebranding as Reworld, highlighting its expanded leadership in sustainable waste management and resource recovery
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Waste Type, Source, Service Types and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- Demand for advanced recycling and composting solutions will rise across all regions.
- Governments will strengthen food waste reduction policies to support sustainable waste systems.
- Adoption of anaerobic digestion will grow as companies seek renewable energy generation.
- Digital tracking and AI-based waste analytics will improve collection and processing efficiency.
- Retailers and food producers will expand partnerships to reduce supply chain waste.
- Circular economy initiatives will increase conversion of food waste into fertilizers and biogas.
- Smart bins and automated sorting technologies will gain wider use in urban areas.
- Industrial sectors will invest more in on-site waste processing to meet compliance norms.
- Community-level composting and decentralized treatment models will grow in developing markets.
- Rising consumer awareness will push food service operators to adopt waste-minimizing practices.




