Market Overview
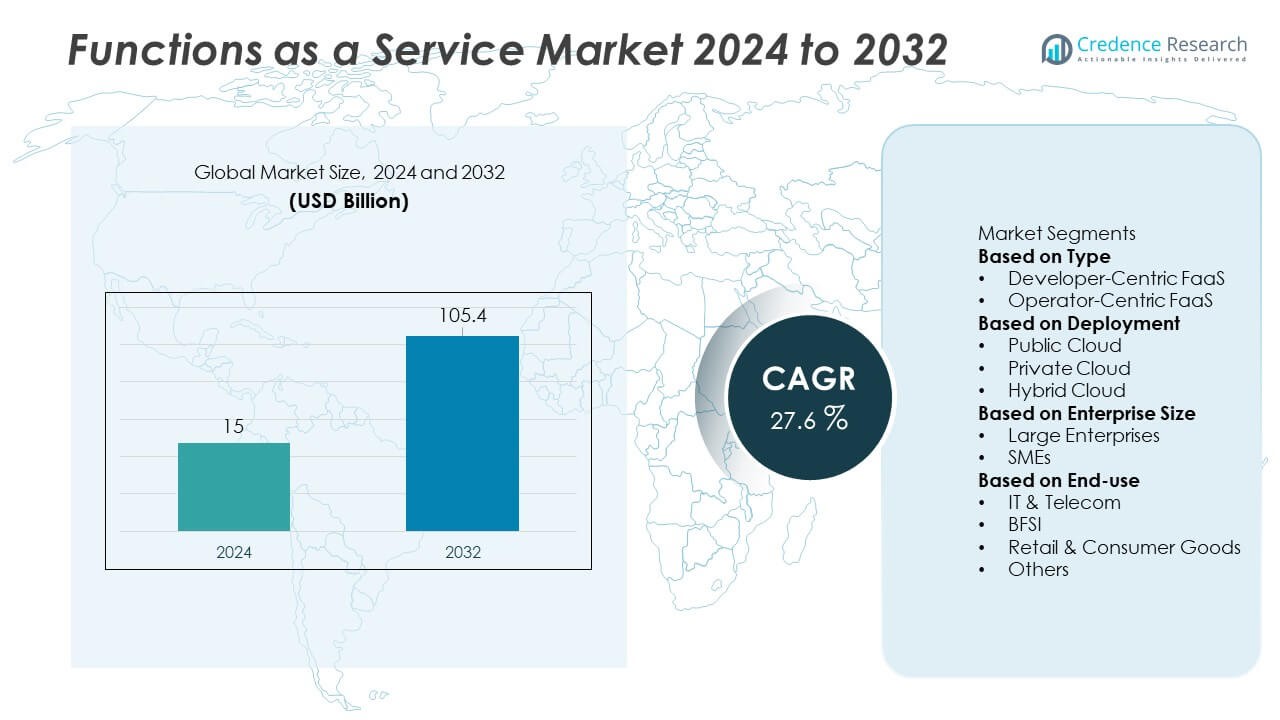
The Functions As A Service Market was valued at USD 15 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 105.4 billion by 2032. The market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 27.6% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Functions As A Service Market Size 2024 |
USD 15 Billion |
| Functions As A Service Market, CAGR |
27.6% |
| Functions As A Service Market Size 2032 |
USD 105.4 Billion |
The Functions as a Service market features strong competition from Amazon Web Services, Microsoft, Google, IBM, Oracle, SAP SE, Red Hat, Dynatrace LLC, Infosys Limited, and Fiorano Software. These vendors expand serverless capabilities to support faster deployment, event-driven processing, and AI-enabled automation. North America leads the market with a 39% share, driven by mature cloud adoption and heavy investment in digital transformation. Europe and Asia Pacific follow as enterprises accelerate microservices development, multi-cloud strategies, and cost-efficient cloud operations. Continuous innovation in runtime support, monitoring, and security strengthens the position of the top players across global cloud ecosystems.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Insights
- The Functions as a Service market reached USD 15 billion in 2024 and is set to grow at a 27.6% CAGR through 2032, driven by wider serverless adoption and real-time computing needs.
- Strong market drivers include rising demand for event-driven applications, faster deployment cycles, and reduced infrastructure costs, supported by dominant segments such as Developer-Centric FaaS with a 64% share.
- Key trends include the expansion of AI-enabled automation, multi-cloud deployments, and Public Cloud leadership with a 58% share, strengthening adoption across digital enterprises.
- Competitive activity intensifies as players like AWS, Microsoft, Google, IBM, and Oracle enhance observability, security, and hybrid integration while addressing restraints such as vendor lock-in and complexity in debugging distributed functions.
- Regional growth is led by North America with a 39% share, followed by Europe at 28% and Asia Pacific at 22%, while Large Enterprises drive demand with a 62% share, reinforcing global market momentum.
 Market Segmentation Analysis:
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Type
Developer-Centric FaaS holds a 64% share and remains the dominant type due to stronger adoption among cloud-native teams and software-driven enterprises. Developer-focused platforms simplify coding tasks, reduce infrastructure overhead, and support faster release cycles, which drives wider integration across digital products. Rising use of event-driven applications, microservices, and continuous deployment practices strengthens demand for these developer-aligned tools. Operator-Centric FaaS grows steadily as enterprises automate backend processes, but its share remains lower due to limited flexibility and slower workflow customization compared with developer-focused models.
- For instance, AWS Lambda processed more than 10 trillion invocations in a single month during 2024, supported by a cold-start latency improvement of 35 milliseconds through its updated Firecracker-based runtime.
By Deployment
Public Cloud leads the market with a 58% share, supported by strong uptake of pay-as-you-go models and wide availability of managed serverless services. Companies rely on public cloud platforms to deploy scalable functions without investing in dedicated infrastructure. This wider accessibility drives stronger usage across digital commerce, streaming, and enterprise SaaS workflows. Hybrid Cloud expands as firms combine on-premise control with cloud flexibility, while Private Cloud adoption stays smaller due to higher setup demands. The public cloud’s broad ecosystem, global reach, and fast provisioning continue to reinforce its leading position.
- For instance, Google Cloud expanded Cloud Functions (2nd gen) availability to many more regions, building upon its global network of over 40 operational regions. This service, which leverages the underlying Cloud Run infrastructure, has benefited from ongoing engineering efforts and enhancements to the build pipelines to improve overall performance and developer experience, including features like concurrency and minimum instances designed to minimize cold starts and improve latency.
By Enterprise Size
Large Enterprises account for a 62% share, maintaining dominance due to deeper investment capacity and faster adoption of serverless automation across complex workflows. These organizations integrate FaaS to streamline microservices, scale applications, and reduce operational burdens across global environments. SMEs adopt FaaS at a rapid pace but hold a smaller share due to limited migration budgets and slower modernization cycles. Large enterprises accelerate growth through AI-driven analytics, high-volume processing, and cloud transformation programs that rely heavily on automated, event-driven computing frameworks.
Key Growth Drivers
Growing Shift Toward Serverless Architectures
The market grows as enterprises replace traditional infrastructure with serverless architectures to reduce operational load and boost development speed. Companies adopt Functions as a Service to execute code on demand, minimize idle resource costs, and scale workloads efficiently. The shift accelerates due to rising digital service usage, cloud-native deployments, and event-driven applications. Developers gain faster release cycles and improved agility, which supports wider modernization across industries such as banking, e-commerce, and media. This transition strengthens long-term adoption as organizations align IT investments with flexible, consumption-based cloud models.
- For instance, Microsoft Azure Functions expanded its runtime environment to support numerous languages, including C#, Java, JavaScript, Python, PowerShell, and TypeScript, plus others via custom handlers.
Rising Adoption of Microservices and Event-Driven Computing
Microservices expansion drives wider implementation of FaaS platforms as businesses break complex systems into independent, lightweight functions. Event-driven computing supports real-time processing for activities such as payments, tracking, analytics, and automated notifications. Companies integrate FaaS to handle spikes in traffic and manage distributed workflows with greater precision. This driver grows stronger as industries prioritize modular architecture, low-latency execution, and rapid scaling. Cloud vendors enhance toolkits that support multi-language development, orchestration, and lifecycle management, which boosts enterprise confidence in FaaS for mission-critical tasks.
- For instance, Netflix uses AWS Lambda for various event-driven automation, data processing, and security tasks, and their data pipeline, Keystone, ingests hundreds of billions of data events daily, some of which are processed in real-time through services like Amazon Kinesis and Apache Kafka.
Increasing Demand for Cost-Efficient Cloud Operations
Organizations adopt FaaS to cut infrastructure costs and shift from fixed server expenses to consumption-based billing. Businesses pay only for executed functions, enabling better cost control during variable workloads and unpredictable traffic patterns. This cost advantage supports adoption among digital-first firms, global enterprises, and SMEs pursuing efficient cloud modernization. Automated scaling and reduced maintenance demands further lower operational spending. As budgets tighten across IT departments, FaaS becomes a preferred solution for optimizing cloud investment without compromising performance, resilience, or development velocity.
Key Trends & Opportunities
Growth of AI-Enhanced and Automation-Centric FaaS Platforms
AI-driven automation strengthens platform capabilities by improving function optimization, error detection, and predictive scaling. Providers embed intelligent monitoring, smart resource allocation, and automated debugging tools that support smoother production workflows. This creates opportunities for advanced analytics, intelligent routing, and faster processing pipelines. AI-enabled FaaS positions itself strongly in sectors such as fintech, healthcare, and retail, where real-time decision-making and high-volume transactions drive system demands. The trend supports deeper integration with cloud-native DevOps pipelines and accelerates enterprise adoption.
- For instance, IBM Cloud Code Engine, the successor service to the now-deprecated IBM Cloud Functions, provides automatic scaling capabilities that adjust the number of running instances based on incoming workloads, including scaling to zero instances when idle.
Expansion of Multi-Cloud and Edge-Based FaaS Deployments
Enterprises adopt multi-cloud strategies to avoid vendor lock-in and gain more flexibility in function placement. FaaS at the edge opens new opportunities in IoT, autonomous systems, and low-latency applications by processing data closer to end users. This trend supports faster response times for logistics tracking, smart manufacturing, and connected retail. Edge-enabled FaaS also improves resilience through distributed execution layers. Providers expand global edge networks, allowing companies to scale functions across regions while meeting data residency and performance requirements.
- For instance, Cloudflare Workers operates across more than 330 edge locations (cities) worldwide, helping to ensure that 95% of the internet-connected population is within approximately 50 milliseconds of the network, and eliminating cold starts with execution times often under 5 milliseconds for real-time apps.
Key Challenges
Complexity in Monitoring and Debugging Distributed Functions
Monitoring FaaS workloads becomes challenging because functions run in short bursts across distributed environments. Teams face difficulty identifying bottlenecks, tracing event flows, and debugging issues without full control over underlying infrastructure. Log aggregation, tracing tools, and performance insights require advanced observability frameworks that many organizations lack. These complexities slow adoption for enterprises with strict performance and reliability requirements. The challenge intensifies as applications scale and integrate multiple cloud services, increasing the need for deeper visibility across function chains.
Vendor Lock-In and Integration Limitations
Many enterprises hesitate to adopt FaaS due to the risk of dependency on specific cloud providers. Platform-specific runtimes, APIs, and development tools make migration difficult and costly. Companies also face integration challenges when connecting FaaS with legacy systems, on-premise applications, or multi-cloud environments. This slows adoption in regulated sectors where IT teams prioritize long-term flexibility. To address this, organizations seek open standards, container-based alternatives, and interoperable frameworks, but full portability remains a significant barrier for large-scale deployments.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America leads the Functions as a Service market with a 39% share, driven by strong cloud adoption across technology, finance, healthcare, and retail sectors. Enterprises in the region invest heavily in serverless platforms to reduce infrastructure costs and accelerate application delivery. Major providers expand advanced orchestration, AI-backed automation, and edge integration features, which boosts enterprise uptake. The region benefits from a mature digital ecosystem, large developer community, and strong presence of hyperscalers. Rising demand for microservices, API-driven workflows, and real-time analytics continues to reinforce the region’s dominant position.
Europe
Europe holds a 28% share, supported by rising digital transformation programs and growing preference for efficient cloud-native development. Enterprises adopt FaaS to manage fluctuating workloads, cut operational expenses, and improve software release cycles. Strict regulatory frameworks drive interest in secure, compliant, and privacy-aligned serverless models. Demand grows in industries such as banking, automotive, manufacturing, and telecommunications. Multi-cloud strategies expand as organizations balance cost, resilience, and data residency requirements. Increased investment in edge data centers and AI-enhanced automation further accelerates adoption across major European economies.
Asia Pacific
Asia Pacific accounts for a 22% share, reflecting rapid expansion of digital services, e-commerce platforms, and mobile-first enterprises. SMEs and large enterprises adopt FaaS to scale applications during peak traffic and reduce infrastructure complexity. Strong growth in India, China, Japan, and South Korea drives wider use of event-driven systems and API-based workflows. Cloud providers expand regional availability zones and local data centers, improving access to low-latency serverless computing. Demand rises across fintech, gaming, logistics, and online marketplaces, strengthening the region’s long-term growth potential.
Latin America
Latin America captures a 6% share, supported by growing migration to public cloud platforms and higher demand for cost-efficient development models. Businesses adopt FaaS to support digital banking, online retail, and streaming applications where traffic spikes require reliable scaling. Startups and SMEs use serverless architectures to reduce upfront investment and accelerate product delivery. Regional constraints such as limited cloud infrastructure gaps slow adoption, but modernization programs improve access. As cloud providers expand local zones, enterprises show stronger interest in automation-driven and event-based computing.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region holds a 5% share, driven by ongoing digital transformation in government, energy, telecom, and financial services. Enterprises use FaaS to modernize legacy systems, support real-time applications, and optimize operational spending. Investments in smart city initiatives and national cloud strategies promote greater serverless adoption. Increasing deployment of hybrid and multi-cloud models strengthens opportunities across major economies. Despite lower market penetration, rising interest in automation, AI-driven workflows, and scalable digital platforms positions the region for steady long-term growth.
Market Segmentations:
By Type
- Developer-Centric FaaS
- Operator-Centric FaaS
By Deployment
- Public Cloud
- Private Cloud
- Hybrid Cloud
By Enterprise Size
By End-use
- IT & Telecom
- BFSI
- Retail & Consumer Goods
- Others
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape is shaped by major players such as Amazon Web Services, Microsoft, Google, IBM, Oracle, SAP SE, Red Hat, Dynatrace LLC, Infosys Limited, and Fiorano Software. These vendors strengthen their positions by expanding serverless orchestration, real-time function execution, and AI-driven automation capabilities. Leading cloud providers focus on improving multi-language runtime support, predictive scaling, and advanced observability to attract enterprise workloads. Partnerships with system integrators and SaaS vendors extend their reach into industry-specific use cases across banking, retail, healthcare, and telecom. Companies invest in edge computing expansion to support low-latency applications and distributed architectures. Open-source adoption also rises as vendors promote portable, hybrid-ready FaaS frameworks to reduce concerns around vendor lock-in. Continuous upgrades in monitoring tools, security layers, and integration support fuel stronger competition as enterprises demand higher performance and seamless interoperability across cloud environments.
Key Player Analysis
- Dynatrace LLC.
- Oracle
- Infosys Limited
- Microsoft
- Fiorano Software and Affiliates
- Google
- Red Hat
- Amazon Web Services, Inc.
- SAP SE
- IBM
Recent Developments
- In March 2025, Dynatrace LLC acquired Metis — adding AI-driven database observability to its platform, bolstering support for cloud-native and serverless environments.
- In August 2024, Google completed the process of renaming Cloud Functions (2nd gen) to Cloud Run functions and folding the offering into its Cloud Run platform—shifting future Functions-as-a-Service (FaaS) in Google Cloud to the unified Cloud Run functions for improved scalability, performance, and security.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Type, Deployment, Enterprise Size, End-use and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- Adoption of serverless computing will rise as enterprises seek faster development and reduced operational load.
- Event-driven architectures will expand across industries that depend on real-time processing.
- AI-enabled automation will enhance function optimization, scaling, and error detection.
- Multi-cloud and hybrid FaaS deployments will grow as firms avoid vendor lock-in.
- Edge-based FaaS models will gain traction to support low-latency applications and IoT workloads.
- Developer-centric platforms will strengthen due to wider microservices adoption.
- Public cloud dominance will continue as providers expand global availability zones.
- Security and observability tools for serverless environments will improve to address complexity.
- Industry-specific FaaS solutions will grow across banking, retail, telecom, and healthcare.
- SMEs will increase adoption as cost-efficient serverless models support scalable digital operations.

 Market Segmentation Analysis:
Market Segmentation Analysis:

