Market Overview
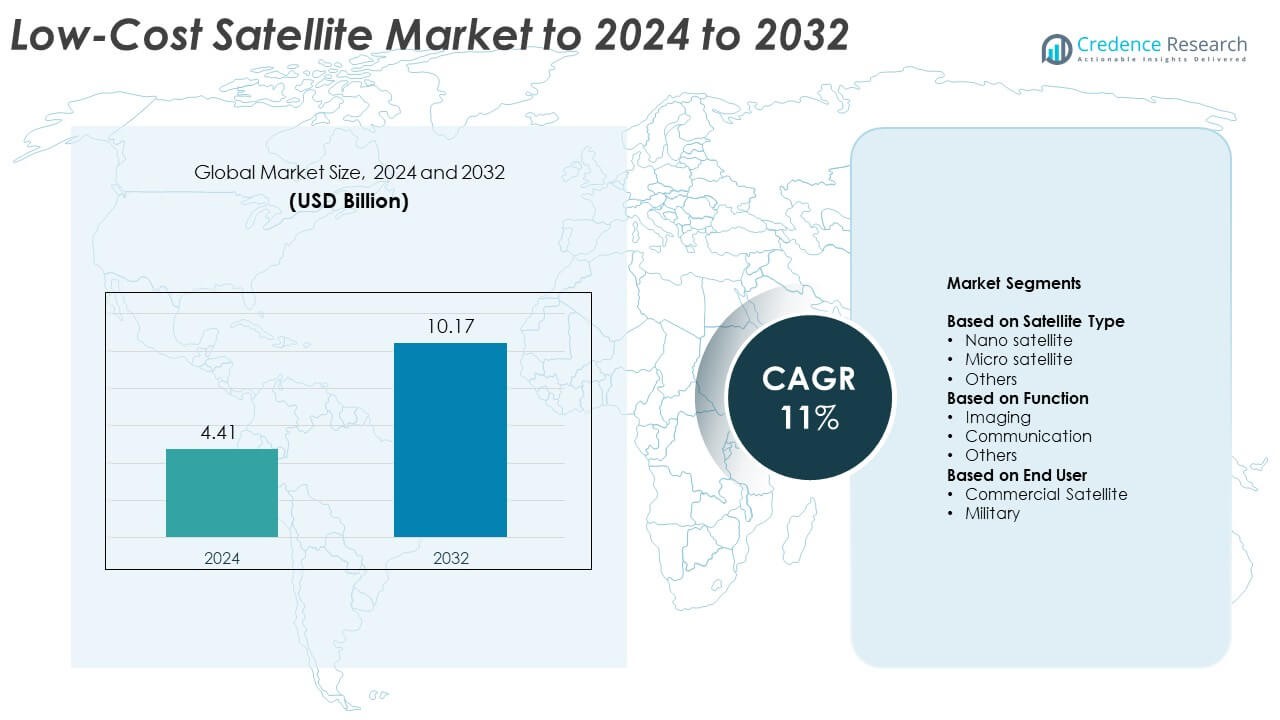
Low-Cost Satellite Market size was valued at USD 4.41 Billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 10.17 Billion by 2032, at a CAGR of 11% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Low-Cost Satellite Market Size 2024 |
USD 4.41 Billion |
| Low-Cost Satellite Market, CAGR |
11% |
| Low-Cost Satellite Market Size 2032 |
USD 10.17 Billion |
The Low-Cost Satellite Market features prominent players such as SpaceX, Planet Labs Inc, Lockheed Martin Corporation, OneWeb, OHB AG, Spire Global Inc, Terran Orbital, Axelspace Corporation, Dauria Aerospace, Geooptics Inc, and Sierra Nevada Corporation. These companies focus on developing cost-efficient satellite constellations, advanced imaging technologies, and reusable launch systems to enhance global connectivity and remote sensing capabilities. Strategic collaborations and increased private investment are strengthening their competitive positions. North America led the market in 2024 with a 37.4% share, supported by strong technological infrastructure, active government programs, and significant private sector participation in satellite development and deployment.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Insights
- The Low-Cost Satellite Market was valued at USD 4.41 Billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 10.17 Billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 11%.
- Growth is driven by the rising need for affordable earth observation, communication, and remote sensing systems across commercial and defense sectors.
- Key trends include expanding small satellite constellations, advancements in miniaturized payloads, and increasing adoption of AI for data processing.
- The market is competitive, with major players investing in reusable launch vehicles and partnerships to enhance production capacity and reduce costs.
- North America held a 37.4% share in 2024, followed by Europe with 28.1% and Asia-Pacific with 24.6%, while the nano satellite segment dominated overall with a 54.6% share.
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Satellite Type
The nano satellite segment dominated the Low-Cost Satellite Market in 2024 with a 54.6% share. Its dominance is driven by increasing adoption for earth observation, communication, and academic missions. Nano satellites offer lower launch costs, shorter development cycles, and flexible deployment options for small payloads. Technological advancements in miniaturized sensors and power systems have further enhanced their performance. The micro satellite segment is also expanding, supported by demand for medium-resolution imaging and scientific research applications requiring longer operational lifespans.
- For instance, Spire Global operates 110+ CubeSats delivering weather, AIS, and ADS-B data.
By Function
The imaging segment held the largest share of 48.2% in 2024. Growth is fueled by rising demand for real-time monitoring in agriculture, environmental management, and disaster response. Low-cost imaging satellites provide high-resolution data for commercial and government uses at reduced operational expenses. Enhanced optical payloads and advanced onboard analytics improve image accuracy and data processing speed. The communication segment continues to grow as low-cost satellite constellations expand internet connectivity in remote regions, offering affordable broadband and IoT network coverage.
- For instance, Planet Labs operates a constellation of approximately 200 satellites in orbit at any given time, including SuperDoves which provide 3 to 4 meter resolution imaging, while its next-generation Pelican satellites, currently in the deployment phase, are designed to target a higher resolution of 30 cm imaging.
By End User
The commercial satellite segment accounted for 63.7% of the market share in 2024, leading the end-user category. Expanding private investment and the proliferation of startups in satellite manufacturing and services drive this dominance. Businesses utilize low-cost satellites for broadband delivery, asset tracking, and data analytics. The military segment is also gaining traction due to increased defense modernization programs that use small satellites for surveillance and secure communication. The affordability and quick deployment of these systems support rapid situational awareness and tactical operations.
Key Growth Drivers
Rising Demand for Earth Observation and Remote Sensing
Growing use of low-cost satellites for environmental monitoring, agricultural mapping, and urban planning is driving market growth. Governments and private firms rely on nano and micro satellites for real-time imaging and data collection. Their cost-effective deployment and improved payload capacity enable frequent launches and faster data acquisition. The rising need for climate monitoring and disaster management further supports adoption across both developed and emerging economies.
- For instance, ICEYE operates a constellation of over 54 operational SAR satellites and offers high-resolution imagery.
Expanding Commercial Satellite Applications
Commercial sectors are increasingly using low-cost satellites for broadband communication, IoT connectivity, and navigation services. Startups and telecom companies invest heavily in small satellite constellations to expand global coverage. Affordable launch options and advancements in reusable rockets reduce mission costs, making satellite operations more accessible. These developments create new business opportunities for satellite operators and component manufacturers seeking scalable, low-cost networks.
- For instance, Eutelsat OneWeb deployed ~648 LEO satellites enabling global broadband coverage.
Technological Advancements in Miniaturization and Integration
Continuous innovation in compact electronics, lightweight materials, and onboard systems enhances satellite performance and lifespan. Miniaturized sensors and advanced propulsion technologies support high-efficiency missions at lower costs. Integration of AI and cloud analytics improves data accuracy and transmission speed. These advancements are transforming small satellite design, enabling more complex missions and higher reliability in commercial and government applications.
Key Trends & Opportunities
Proliferation of Small Satellite Constellations
The deployment of large satellite constellations for global communication is a major trend. Companies are launching hundreds of low-cost satellites to provide high-speed internet and remote sensing data worldwide. This expansion reduces latency, increases coverage, and opens opportunities in IoT and defense connectivity. Growing collaborations between private space firms and national agencies further accelerate constellation-based infrastructure development.
- For instance, SpaceX Starlink launched 10,177 satellites as of October 29, 2025, with approximately 8,795 of those currently operational.
Rising Private Investment in Space Startups
Venture capital and government-backed funds are supporting startups focused on low-cost satellite design, manufacturing, and launch services. These investments are driving innovation and competition across the supply chain. Affordable access to space encourages the creation of new service models in imaging, navigation, and data analytics. This growing financial ecosystem fosters faster commercialization and global market expansion.
- For instance, Seraphim Space counted 601 global space-tech VC deals in 2024.
Increasing Focus on Reusable Launch Vehicles
Reusable rockets are revolutionizing cost structures for satellite deployment. Leading space launch providers are achieving multiple reuses of boosters, cutting per-launch expenses. This trend allows small satellite operators to deploy constellations more frequently and efficiently. The adoption of reusable technology enhances market scalability and sustainability while reducing entry barriers for emerging space companies.
Key Challenges
Regulatory and Spectrum Management Issues
The increasing number of low-cost satellite launches has created challenges in frequency allocation and orbital management. Overcrowding in low Earth orbit heightens the risk of signal interference and collision. Governments and international agencies are tightening regulations for licensing and debris mitigation. Compliance with evolving standards requires continuous coordination, adding operational complexity for new entrants and smaller operators.
Short Lifespan and Reliability Concerns
Low-cost satellites often have limited lifespans due to size, component quality, and lack of redundancy systems. Frequent replacements increase long-term mission costs and raise sustainability issues. Harsh space conditions can impact system reliability, data accuracy, and transmission efficiency. Manufacturers are focusing on improving durability and radiation resistance to overcome these limitations and ensure consistent performance.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America dominated the low-cost satellite market in 2024 with a 37.4% share. The region’s leadership stems from major investments in commercial satellite constellations and defense-related space programs. The United States leads due to advanced manufacturing capabilities, robust launch infrastructure, and active participation from private companies developing small satellite networks. NASA and the U.S. Department of Defense continue to drive adoption through government contracts supporting low-cost missions. Canada also contributes through earth observation and communication satellites, enhancing overall market strength across the continent.
Europe
Europe accounted for 28.1% of the low-cost satellite market share in 2024. The region benefits from strong collaboration among space agencies and private firms under programs such as Copernicus and Horizon Europe. Increasing demand for climate monitoring, navigation, and broadband connectivity supports market growth. Countries like the United Kingdom, Germany, and France are expanding small satellite manufacturing facilities. Continuous funding from the European Space Agency and commercial ventures ensures innovation in propulsion and imaging technologies, enhancing Europe’s competitive position in global low-cost satellite deployment.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific held a 24.6% share of the low-cost satellite market in 2024. Rapidly developing space economies such as China, India, and Japan are fueling regional growth. Expanding investments in remote sensing, communication, and navigation satellite constellations are strengthening regional infrastructure. India’s ISRO and China’s CASC continue to promote cost-effective launch vehicles, supporting both domestic and international clients. Private firms in South Korea and Australia are also entering the market with small satellite manufacturing projects, contributing to regional competitiveness and technological advancement.
Latin America
Latin America captured a 5.3% share of the global low-cost satellite market in 2024. Growth is driven by the region’s increasing focus on agricultural monitoring, disaster management, and connectivity expansion. Brazil and Mexico are leading developments with growing participation in small satellite research and international collaborations. Governments are encouraging public-private partnerships to enhance local production and satellite data utilization. The presence of emerging startups and educational initiatives in aerospace technology further supports Latin America’s long-term contribution to the satellite ecosystem.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East and Africa region accounted for 4.6% of the low-cost satellite market in 2024. Rising investments in defense communication, environmental monitoring, and broadband connectivity are driving growth. The United Arab Emirates, Saudi Arabia, and South Africa are spearheading satellite projects to improve national capabilities. Increasing partnerships with global space agencies and private satellite operators support local expertise development. Expanding government-backed initiatives for space research and digital infrastructure continues to strengthen the region’s presence in the global satellite landscape.
Market Segmentations:
By Satellite Type
- Nano satellite
- Micro satellite
- Others
By Function
- Imaging
- Communication
- Others
By End User
- Commercial Satellite
- Military
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape of the low-cost satellite market is defined by the presence of global players such as SpaceX, Planet Labs Inc, Lockheed Martin Corporation, OneWeb, OHB AG, Spire Global Inc, Terran Orbital, Axelspace Corporation, Dauria Aerospace, Geooptics Inc, and Sierra Nevada Corporation. The market is characterized by a mix of established aerospace companies and emerging private firms focusing on satellite manufacturing, imaging services, and communication networks. Competition centers on technological innovation, cost optimization, and the ability to deploy satellite constellations efficiently. Companies are prioritizing miniaturized designs, reusability in launch systems, and enhanced data processing capabilities. Strategic partnerships with governments and research organizations are expanding the global reach of satellite services, while mergers and acquisitions are consolidating production capabilities. Continuous investment in advanced payload technologies, propulsion systems, and AI-based analytics further strengthens competitiveness, positioning market leaders to capture future demand across commercial and defense applications.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
- SpaceX
- Planet Labs Inc
- Lockheed Martin Corporation
- OneWeb
- OHB AG
- Spire Global Inc
- Terran Orbital
- Axelspace Corporation
- Dauria Aerospace
- Geooptics Inc
- Sierra Nevada Corporation
Recent Developments
- In 2025, Planet Labs launched their first Tanager satellite (Tanager-1) as part of a mission to collect hyperspectral data, enhancing their commercial Earth observation constellation.
- In 2024, SpaceX continued the rapid launch of its Gen 2 (V2 Mini) Starlink satellites to expand its global internet constellation
- In 2024, Terran Orbital Partnered with Lockheed Martin to launch a batch of 10 small satellites for a U.S. Space Force missile warning program, demonstrating the capabilities of their low-cost, mass-produced satellite buses.
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Satellite Type, Function, End-User and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- Rising adoption of small satellite constellations will expand global communication and imaging coverage.
- Technological innovations will enhance payload efficiency and extend satellite operational lifespan.
- Growing private investments will accelerate commercialization of satellite manufacturing and launch services.
- Integration of AI and data analytics will improve real-time satellite data processing and decision-making.
- Increased government funding will support defense, weather monitoring, and disaster management applications.
- Reusable launch vehicles will continue to reduce deployment costs and enable frequent launches.
- Expanding IoT connectivity needs will drive low-cost satellite demand across industrial sectors.
- International collaborations will promote shared infrastructure and improve spectrum management efficiency.
- Enhanced miniaturization technologies will boost production of lightweight and high-performance satellites.
- Rising environmental concerns will encourage development of sustainable and debris-free satellite systems.




