Market Overview:
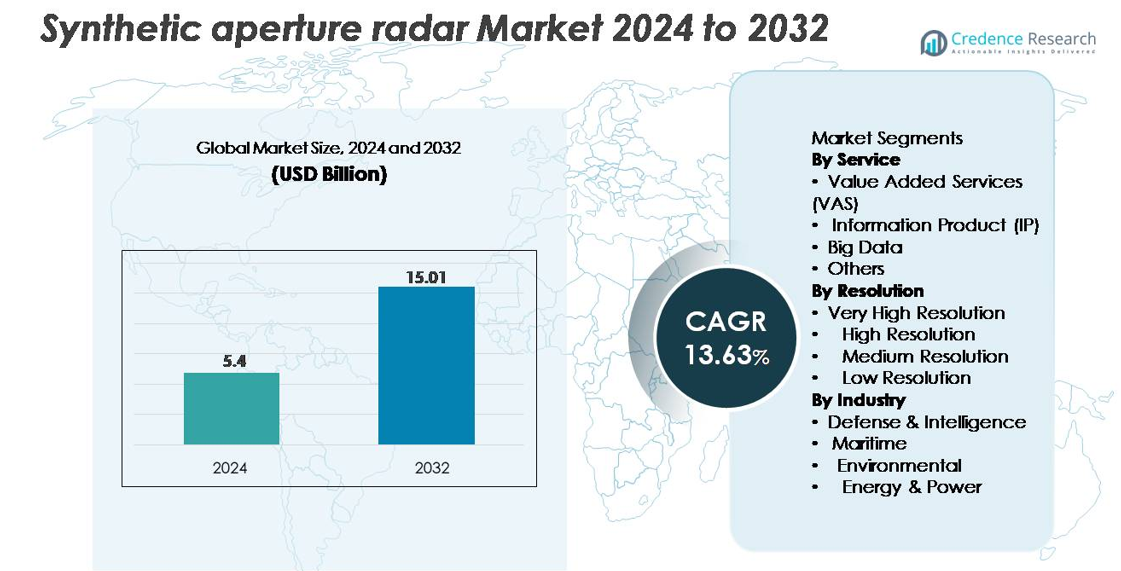
The synthetic aperture radar (SAR) market was valued at USD 5.4 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 15.01 billion by 2032, reflecting a robust CAGR of 13.63% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
Synthetic Aperture Radar Market Size 2024
|
USD 5.4 billion |
| Synthetic Aperture Radar Market, CAGR |
13.63% |
| Synthetic Aperture Radar Market Size 2032 |
USD 15.01 billion |
The synthetic aperture radar market is shaped by a diverse group of established aerospace firms and fast-growing commercial operators, including ICEYE, Capella Space, Maxar Technologies, Airbus S.A.S., L3Harris Technologies, Geocento, Viridien, Satim Inc., KappaZeta Ltd, and Aloft Sensing, Inc. These companies compete through advanced SAR payload engineering, high-revisit small-satellite constellations, and expanding value-added analytics services. North America leads the market with approximately 38% share, driven by strong defense spending, satellite programs, and commercial geospatial adoption. Europe follows with around 27% share, supported by major institutional missions and growing commercial SAR capabilities, reinforcing its strong competitive positioning globally.
Market Insights:
- The synthetic aperture radar market was valued at USD 5.4 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 15.01 billion by 2032, registering a 13.63% CAGR.
- Market growth is driven by rising deployment of SAR-equipped satellites, increasing defense surveillance needs, and expanding applications across maritime monitoring, environmental assessment, and infrastructure intelligence.
- Key trends include rapid adoption of AI-enabled image analytics, high-revisit small-satellite constellations, and strong demand for very high-resolution imagery, which holds the largest share within the resolution category.
- The competitive landscape features major players such as ICEYE, Capella Space, Airbus, Maxar Technologies, and L3Harris, all investing in advanced SAR payloads, multi-frequency radar modes, and scalable data platforms; however, high costs of payload development and complex data processing remain significant restraints.
- Regionally, North America leads with ~38% share, followed by Europe at ~27% and Asia-Pacific at ~24%, supported by strong defense spending and expanding Earth observation programs.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Service
Value Added Services (VAS) dominate the service segment due to growing demand for curated analytics, mission-specific insights, and rapid-delivery data layers supporting defense surveillance, environmental monitoring, and infrastructure analysis. VAS holds the largest market share as users increasingly prefer processed intelligence over raw imagery, enabling faster decision-making. Information Products (IP) continue to gain traction for applications such as land deformation mapping and maritime tracking, while Big Data services expand with rising SAR constellation deployments. The “Others” category supports niche applications including historical data archiving and specialized interferometric analysis workflows.
- For instance, ICEYE’s analytics platform can generate over 150 automated flood-extent maps per day using its SAR constellation, each processed at 3–5 meter resolution to deliver near-real-time intelligence to emergency agencies.
By Resolution
Very High Resolution (VHR) imagery accounts for the dominant market share, driven by its critical role in defense reconnaissance, precision targeting, change detection, and infrastructure monitoring. Growing requirements for sub-meter detail and advanced InSAR capabilities reinforce its leadership across government and commercial users. High Resolution SAR follows due to strong adoption in environmental mapping and maritime domain awareness, offering a balance between coverage and granularity. Medium and Low Resolution segments remain essential for large-area monitoring, climate analysis, and disaster response, particularly where frequent revisit rates and wide-swath imaging are prioritized.
- For instance, ICEYE’s Gen4 satellites achieve 16 cm ground resolution and can expand their high-resolution imaging coverage area to 400 km per pass, enabling precise detection of small vessels, vehicles, and structural anomalies. A single satellite can produce up to 500 images per day, allowing for extensive daily coverage.
By Industry
Defense & Intelligence represents the dominant industry segment, capturing the largest share as global militaries increasingly integrate SAR for border surveillance, terrain mapping, night-time reconnaissance, and all-weather mission support. Its market strength is reinforced by rising procurement of SAR-equipped satellites and UAV payloads. The Maritime segment expands steadily with demand for vessel detection, oil spill tracking, and illegal fishing monitoring. Environmental applications benefit from SAR’s ability to support flood mapping, forest cover assessment, and land deformation analysis. Energy & Power users adopt SAR for pipeline monitoring, ground subsidence detection, and offshore infrastructure inspections.
Key Growth Drivers:
Rising Deployment of Earth Observation Constellations
Global expansion of Earth observation constellations drives substantial demand for synthetic aperture radar systems capable of delivering continuous, all-weather imagery. Governments and private operators increasingly prioritize SAR satellites to overcome limitations of optical sensors, particularly for cloud-covered regions and night-time monitoring. The proliferation of small satellites and commercial launches enables operators to deploy higher revisit-rate constellations, enhancing real-time monitoring capabilities for defense, agriculture, maritime security, urban planning, and disaster response. Growing investment in space-based intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR) programs strengthens the adoption of high-resolution SAR payloads. Additionally, public–private partnerships encourage innovation in satellite bus miniaturization, advanced radar electronics, and low-cost launch solutions, further accelerating constellation expansion. Together, these factors position SAR as a core technology for next-generation global Earth observation infrastructures.
- For instance, ICEYE’s growing constellation exceeding 30 operational SAR satellites supports revisit intervals of under 3 hours for priority tasking zones, enabling persistent surveillance across defense, maritime, and environmental application
Increasing Adoption Across Defense, Surveillance, and Security Applications
Defense and intelligence agencies remain the largest adopters of synthetic aperture radar due to its ability to deliver precise terrain mapping, wide-area surveillance, target tracking, and all-weather operational awareness. Military modernization programs worldwide integrate SAR-equipped satellites, UAVs, and manned aircraft to support reconnaissance missions, border monitoring, and tactical planning. SAR’s ability to penetrate clouds, smoke, and darkness offers a decisive operational advantage, particularly for contested and high-risk environments. High-resolution interferometric SAR (InSAR) further enables monitoring of troop movement, infrastructure deformation, and underground activity. Expanding geopolitical tensions and rising security spending contribute to increased procurement of advanced SAR platforms. Enhanced processing algorithms, automatic object classification, and AI-based feature extraction also improve mission readiness and intelligence yield, strengthening SAR adoption in defense operations.
- For instance, ICEYE’s tactical SAR imagery captured at 16 cm resolution supports military users with the ability to identify vehicles as small as 2–3 meters in length, even under cloud cover or nighttime conditions.
Growing Use of SAR for Environmental Monitoring and Climate Resilience
The accelerating need for environmental assessment, climate monitoring, and natural disaster management fuels strong demand for synthetic aperture radar solutions. SAR’s ability to measure land deformation, glacial movement, flood extent, soil moisture, and deforestation makes it indispensable for climate research organizations and environmental agencies. Rising frequency of extreme weather events pushes governments to invest in remote sensing technologies that offer reliable, rapid, and high-resolution data under challenging atmospheric conditions. Additionally, SAR-based InSAR techniques support early warning systems for landslides, subsidence, and earthquake-related ground displacement. Agriculture, forestry, and water resource management also increasingly utilize SAR analytics to optimize sustainability programs. As climate resilience becomes a global priority, SAR emerges as a critical technology for continuous, data-driven environmental monitoring.
Key Trends & Opportunities:
Integration of AI, Machine Learning, and Cloud Analytics
Advances in AI and cloud-native analytics create major opportunities to enhance SAR data interpretation, automate insights, and expand commercial adoption. Machine learning models increasingly support automated feature extraction, anomaly detection, vessel identification, and land-change analytics, reducing dependency on manual interpretation. Cloud platforms enable large-scale processing of SAR time-series data, accelerating delivery of actionable intelligence to end-users across defense, energy, environmental, and maritime sectors. AI-driven SAR processing workflows also improve coherence analysis, interferometric accuracy, and noise reduction. The convergence of SAR data with other geospatial layers optical, LiDAR, and IoT sensor networks further strengthens value-added services for customers. As analytics become more sophisticated and cost-efficient, opportunities emerge for subscription-based services, near-real-time dashboards, and multi-sensor intelligence platforms.
- For instance, Maxar Technologies integrates advanced artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to process vast quantities of high-resolution opticalsatellite data (part of an archive exceeding 125 petabytes), enabling automated detection of infrastructure damage and maritime assets with industry-leading sub-meter precision (up to 30 cm resolution).
Expansion of Commercial SAR Services and New Business Models
The commercial SAR sector is rapidly expanding as new entrants deploy small-satellite constellations and offer imaging-as-a-service models tailored to industries such as insurance, agriculture, infrastructure, and mining. Subscription-based access to SAR imagery, analytics, and alerts allows organizations to integrate geospatial intelligence without building in-house remote sensing capabilities. Innovations in data delivery, API-based access, and automated platform integration enhance customer convenience and scalability. Opportunities also grow for niche markets, including nighttime maritime vessel tracking, illegal mining monitoring, renewable energy site assessment, and precision agriculture. As commercial pricing becomes competitive and resolution performance improves, SAR is transitioning from a government-centric domain to a mainstream commercial geospatial asset.
- For instance, Capella Space’s commercial platform delivers high-resolution SAR imagery via a flexible API and web console, featuring Spotlight imagery that achieves 50 cm resolution for commercial customers(with sub-0.25 meter for U.S. government) for infrastructure and asset monitoring.
Key Challenges:
High Costs of SAR Payload Development, Launch, and Processing Infrastructure
Despite rapid innovation, synthetic aperture radar systems require significant capital investment for payload design, advanced radar electronics, antenna structures, and high-power transmission components. Launch costs, though declining, remain substantial for operators deploying medium- or large-class SAR satellites. Additionally, SAR data processing demands high-performance computing resources capable of handling large datasets, complex interferometric processing, and AI-assisted analytics. These cost burdens can limit entry of smaller operators and constrain large-scale constellation deployment. For many commercial customers, affordability and accessibility of SAR data remain challenges, especially in comparison to lower-cost optical imagery. Addressing cost reductions across payload manufacturing, launch services, and cloud-based processing remains essential for broader market penetration.
Technical Complexity and Data Interpretation Limitations
SAR technology involves significant technical complexity in system design, calibration, and data interpretation. Raw SAR data requires advanced processing, radiometric correction, noise filtering, and geometric adjustment to produce usable imagery. Interpreting SAR outputs demands specialized expertise, particularly for phase-based applications such as InSAR displacement mapping. Misinterpretation risks can hinder adoption in sectors unfamiliar with radar-based imaging. Furthermore, integrating SAR with other data sources optical, LiDAR, hyperspectral requires sophisticated multi-modal fusion algorithms. Limited availability of skilled analysts and the steep learning curve associated with SAR analytics remain major challenges. Overcoming these barriers will require improved user-friendly platforms, automated analytics, and broader capacity-building initiatives.
Regional Analysis:
North America
North America holds the largest share of the synthetic aperture radar market at around 38%, driven by strong defense spending, advanced satellite programs, and robust adoption of SAR analytics in federal agencies. The U.S. leads with extensive use of SAR for border surveillance, homeland security, climate mapping, and disaster response. Expanding investments by commercial satellite operators and partnerships with defense contractors strengthen regional dominance. Demand for high-resolution SAR imagery and AI-enabled analytics continues to rise across agriculture, maritime monitoring, and infrastructure sectors, maintaining North America’s leadership in both technology development and operational deployment.
Europe
Europe accounts for approximately 27% of the global SAR market, supported by major institutional programs such as Copernicus, Sentinel-1 missions, and national space initiatives across Germany, Italy, France, and the U.K. Strong environmental regulatory frameworks and climate monitoring mandates drive extensive use of interferometric SAR for land deformation, flood assessment, and forestry management. Defense modernization and maritime security requirements further accelerate adoption. European companies lead in SAR payload engineering, antenna systems, and radar electronics, reinforcing regional competitiveness. Growing commercial analytics platforms and public–private satellite partnerships contribute to sustained market expansion.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific represents about 24% of the global SAR market, propelled by increasing investments in Earth observation satellites, national security programs, and disaster-resilience initiatives. China, Japan, India, and South Korea deploy SAR satellites for maritime domain awareness, agricultural monitoring, and infrastructure planning. Frequent natural disasters and large geographic diversity amplify demand for all-weather, high-revisit SAR imagery. Rapid industrialization drives adoption across energy, mining, and environmental sectors. Regional governments and commercial operators are expanding small-satellite SAR constellations, strengthening Asia-Pacific’s position as a fast-growing hub for both SAR payload development and downstream analytics.
Latin America
Latin America holds roughly 6% of the SAR market, with adoption primarily led by Brazil, Mexico, Chile, and Argentina. The region increasingly utilizes SAR for rainforest monitoring, illegal mining detection, maritime surveillance, and agricultural assessment. Frequent floods, landslides, and climate-driven disruptions elevate the need for reliable all-weather imaging capabilities. Governments collaborate with international agencies and private Earth observation companies to access high-resolution SAR data. Growth is further supported by emerging UAV-based SAR applications across infrastructure and environmental management. Although still developing, the market shows steady progress with rising geospatial investment.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region accounts for around 5% of the SAR market, driven by expanding defense requirements, border surveillance needs, and environmental monitoring programs. Countries such as the UAE, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, and Nigeria increasingly integrate SAR for oil pipeline monitoring, maritime security, desert mapping, and land deformation analysis. Harsh weather conditions and vast remote landscapes make SAR’s all-weather capabilities particularly valuable. Investments in national space initiatives and satellite partnerships enhance data accessibility. Although adoption remains in the early stages, growing demand for security and climate intelligence supports gradual market expansion.
Market Segmentations:
By Service
- Value Added Services (VAS)
- Information Product (IP)
- Big Data
- Others
By Resolution
- Very High Resolution
- High Resolution
- Medium Resolution
- Low Resolution
By Industry
- Defense & Intelligence
- Maritime
- Environmental
- Energy & Power
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape:
The competitive landscape of the synthetic aperture radar (SAR) market is characterized by a mix of established aerospace contractors, emerging commercial satellite operators, and specialized radar technology providers. Leading defense-focused companies continue to dominate high-end SAR payload development, leveraging advanced antenna architectures, multi-frequency radar modes, and long-duration mission capabilities. At the same time, commercial players accelerate market disruption through small-satellite constellations offering higher revisit rates and cost-effective data services. AI-driven analytics platforms further enhance competitiveness by enabling automated feature extraction, change detection, and maritime monitoring. Strategic partnerships, government contracts, and multi-sensor integration remain critical differentiators, with companies increasingly aligning around end-to-end SAR ecosystems that combine payload manufacturing, satellite operations, cloud processing, and downstream value-added services. As demand expands across defense, environmental monitoring, energy, and maritime sectors, competition intensifies around resolution performance, data delivery speed, and scalable analytics.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis:
- KappaZeta Ltd (Estonia)
- Maxar Technologies (U.S.)
- ICEYE (Finland)
- Aloft Sensing, Inc. (U.S.)
- Viridien (France)
- L3Harris Technologies, Inc. (U.S.)
- Satim Inc. (Poland)
- Capella Space (U.S.)
- Airbus S.A.S. (Netherlands)
- Geocento (U.K.)
Recent Developments:
- In November 29, 2025, ICEYE (Finland) it launched five new SAR satellites via a SpaceX rideshare mission, expanding its constellation to serve both commercial customers and sovereign missions, thereby enhancing global Earth observation and ISR (intelligence, surveillance, reconnaissance) capacity.
- In August 2025, Aloft Sensing, Inc. (U.S.) alongside the U.S. space-science agency NASA, Aloft Sensing demonstrated a new compact radar instrument (HALE InSAR) flown on a high-altitude long-endurance (HALE) platform enabling detection of millimeter-scale ground deformation and precise Earth-surface monitoring without reliance on GPS.
- In May 2025, KappaZeta was featured in the “ESA BIC Estonia Startup Story” after being selected for incubation by ESA BIC Estonia, highlighting its radar-data analysis capabilities for agriculture, forestry, and environmental monitoring.
Report Coverage:
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Service, Resolution, Industry and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook:
- The market will see accelerated deployment of multi-satellite SAR constellations delivering higher revisit rates and persistent global coverage.
- AI and machine-learning models will increasingly automate SAR data interpretation, enabling faster insights and broader commercial adoption.
- Very high-resolution SAR imaging will expand across defense, maritime, and infrastructure monitoring as demand for precision analytics intensifies.
- Cross-sensor data fusion combining SAR, optical imagery, LiDAR, and hyperspectral data will enhance multi-domain intelligence capabilities.
- Cloud-native SAR processing pipelines will reduce latency and improve access for commercial and government users.
- Growth in climate resilience initiatives will drive wider use of SAR for flood mapping, land deformation, and environmental monitoring.
- Defense modernization programs will continue to prioritize SAR-equipped platforms for surveillance and all-weather operational awareness.
- Energy and utilities sectors will increasingly adopt SAR for pipeline monitoring, offshore asset inspection, and ground subsidence detection.
- Advancements in compact radar electronics will support lighter, more efficient SAR payloads for small satellites and UAVs.
- Emerging markets will adopt SAR imaging to strengthen disaster management, food security programs, and infrastructure planning.




