Market Overview:
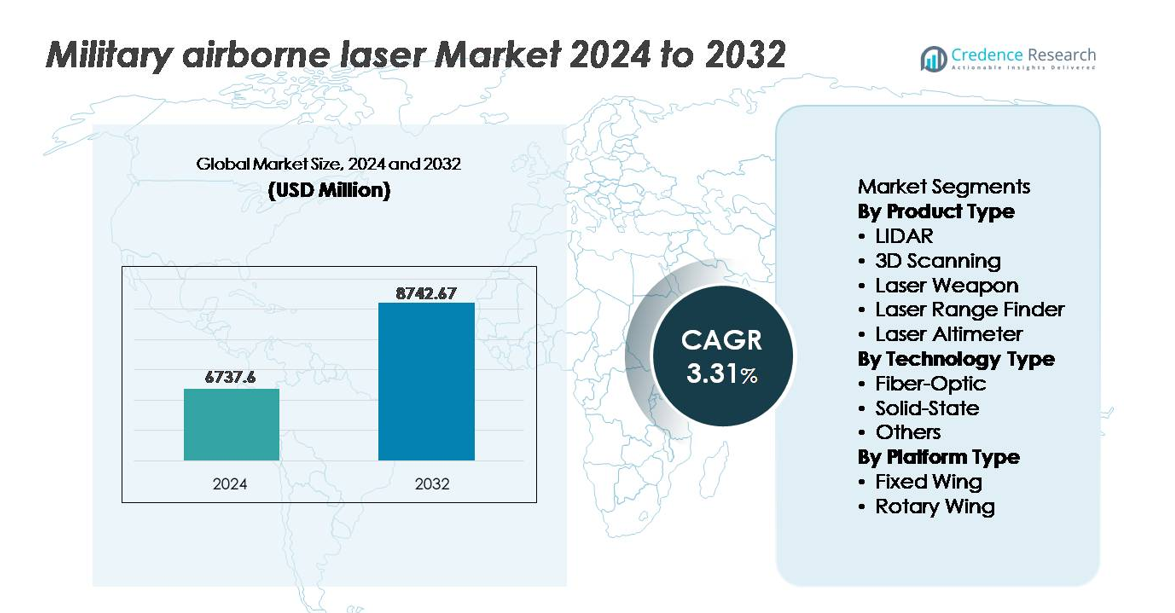
The global military airborne laser market was valued at USD 6,737.6 million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 8,742.67 million by 2032, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3.31% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Military Airborne Laser Market Size 2024 |
USD 6,737.6 million |
| Military Airborne Laser Market, CAGR |
3.31% |
| Military Airborne Laser Market Size 2032 |
USD 8,742.67 million |
The military airborne laser market is shaped by a competitive mix of global defense leaders and specialized laser technology providers, including Thales SA, Frankfurt Laser Company (FLC), American Laser Enterprises LLC, Saab AB, Coherent Corp, Northrop Grumman Corporation, Leonardo Electronics US Inc., RTX Corporation, BAE Systems plc, and Lockheed Martin Corporation. These companies focus on high-energy laser weaponization, airborne ISR support, and compact laser integration for fixed- and rotary-wing platforms. North America leads the global market with approximately 38% share, supported by sustained defense modernization, directed-energy deployment programs, and strong domestic aerospace supply chains, positioning the region at the forefront of laser-enabled combat capabilities.
Market Insights:
- The military airborne laser market was valued at USD 6,737.6 million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 8,742.67 million by 2032, expanding at a CAGR of 3.31% during the forecast period.
- Market growth is driven by rising demand for precision engagement, real-time ISR mapping, and counter-UAS operations as defense forces enhance battlefield intelligence and long-range strike capabilities.
- Solid-state technology holds the largest segment share due to higher energy efficiency and ruggedization for fixed-wing platforms, while compact fiber-based systems gain adoption in UAVs and rotary-wing fleets.
- Intensifying competitive strategies focus on directed-energy innovation, miniaturization, and modular upgrade frameworks, with major players aligning their portfolios with national modernization programs and export defense agreements.
- Regionally, North America leads with 38% share, followed by Europe at 27% and Asia-Pacific at 24%, driven by modernization agendas, increasing aerospace capabilities, and mounting cross-border threat surveillance requirements.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Product Type
LIDAR represents the dominant sub-segment in the military airborne laser market, holding the largest market share due to expanding deployment in intelligence, surveillance, reconnaissance (ISR), and target acquisition missions. Defense forces leverage high-resolution, real-time mapping to support precision strike coordination and autonomous navigation. The increasing integration of LIDAR with unmanned aerial platforms strengthens operational efficiency in contested environments. Meanwhile, laser weapons and 3D scanning systems are gaining traction as armed forces modernize counter-drone capabilities and enhance structural inspection accuracy for mission-critical airframes and infrastructure.
- For instance, the Northrop Grumman RQ-4 Global Hawk unmanned aerial system provides high-resolution surveillance using both an Integrated Sensor Suite (ISS) and, on Block 40 variants, the Multi-Platform Radar Technology Insertion Program (MP-RTIP) radar.
By Technology Type
Solid-state laser technology dominates the market, driven by its superior electrical-to-optical efficiency, structural compactness, and ability to withstand harsh operating conditions during high-vibration, high-altitude missions. Solid-state platforms are widely favored in advanced targeting, missile guidance, and airborne directed-energy applications due to improved beam stability and reduced thermal load. Fiber-optic technology is steadily emerging as a fast-growing segment as militaries explore lightweight, lower power-consumption solutions for rotary-wing and unmanned aircraft. The demand for scalable laser output and modular system architecture continues to accelerate adoption acrossair-launched defense programs.
- For instance, Lockheed Martin’s ATHENA solid-state laser demonstrator achieved a 30-kilowatt output during field testing, successfully disabling aerial targets through sustained, precision-directed energy.
By Platform Type
Fixed-wing aircraft constitute the dominant platform segment, attributed to their higher payload capacity, long-range sortie capability, and suitability for hosting large-format LIDAR, laser weapons, and ISR-focused systems. Strategic bombers, combat aircraft, and large surveillance platforms rely on multi-mission laser systems to enhance precision engagement and optimize reconnaissance operations. Rotary-wing aircraft represent a rising opportunity as armed forces retrofit helicopters with laser range finders and target designation equipment for close air support. Advancements in compact and lightweight laser payloads continue to expand deployment feasibility for multiple aircraft classes.
Key Growth Drivers:
Rising Demand for Precision Targeting and ISR Dominance
Advanced militaries prioritize precision strike capabilities, real-time intelligence, and contested-airspace superiority, which fuels the adoption of airborne laser systems. Enhanced beam accuracy allows units to detect, track, and neutralize small, fast-moving, and low-visibility targets more effectively than conventional kinetic platforms. These systems reduce collateral damage and support long-range engagement through cloud-penetrating and multi-spectral sensing capabilities. Growing investments in unmanned combat aerial vehicles (UCAVs), network-centric warfare, and electronic attack-resistant technologies further strengthen demand. Modern battlefield requirements for silent, light-speed engagement and reduced logistics tail reinforce airborne laser relevance across strategic, tactical, and homeland-defense missions.
- For instance, Northrop Grumman demonstrated precision laser tracking accuracy below 2 microradians during airborne field tests of its directed-energy prototype, enabling sustained lock on maneuvering targets at significant stand-off distances.
Government Modernization Programs and Directed Energy Initiatives
Defense modernization programs across North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific prioritize directed-energy weapons (DEWs) as future frontline assets, propelling procurement pipelines. Governments accelerate R&D in next-generation laser platforms to counter drones, hypersonic threats, and precision-guided munitions. Large-scale defense budgets facilitate prototype-to-deployment transitions and establish joint industrial-military development frameworks. These initiatives mitigate reliance on legacy projectiles and reduce lifetime operational costs through lower ammunition consumption. Cross-border defense alliances promote interoperability standards and shared testing environments, allowing faster system validation and supporting ecosystem scalability. This coordinated policy environment strengthens adoption as militaries shift toward energy-based deterrence.
- For instance, the U.S. Army’s Directed Energy Maneuver-Short Range Air Defense (DE M-SHORAD) program equipped Stryker vehicles with a 50-kilowatt laser developed by RTX Corporation, achieving successful live-fire interceptions during 2023 demonstrations.
Integration of Airborne Lasers with AI, Automation, and Networked Combat Systems
The integration of AI-enabled image processing, autonomous targeting, and predictive sensor analytics enhances airborne laser systems’ speed and reliability, enabling rapid threat recognition and engagement. Automated beam control minimizes human intervention, supporting multi-target tracking and precision designation in dynamic combat environments. Networked lasers linked through battlefield communication grids strengthen joint-force coordination, providing fused situational awareness across air, land, and naval platforms. As defense forces deploy swarms, smart munitions, and autonomous aircraft, interoperable laser systems become critical force multipliers. AI-driven mission planning, system diagnostics, and autonomous ISR tasks further elevate operational capability.
Key Trends & Opportunities:
Shift Toward Compact, Lightweight, and High-Energy Laser Systems
The miniaturization of airborne laser systems unlocks opportunities for deployment on tactical drones, lightweight rotary platforms, and unmanned cargo aircraft. Advances in thermal management, battery density, and solid-state laser engineering reduce system mass while increasing energy output. High-energy lasers provide greater destructive capability against low-cost aerial threats such as UAVs and cruise missiles. As battlefield focus shifts toward rapid mobility and flexible deployment, demand rises for scalable systems that combine high-power projection with low logistical burden. These innovations enable broader integration into multi-domain operations and emerging aircraft platforms.
- For instance, Lockheed Martin’s DEIMOS laser architecture, announced in 2024, is engineered as a scalable, modular system capable of delivering outputs in the 50-kilowatt class, configured within compact form factors optimized for future airborne deployments.
Expanding Role in Counter-UAS, Reconnaissance, and Border Defense
Military airborne lasers are evolving from niche tools into mission-critical assets for counter-UAS, reconnaissance, and perimeter defense operations. The proliferation of commercial and weaponized drones makes airborne lasers essential for precision interception without explosive risks. Border forces and maritime patrol fleets adopt laser-based detection and tracking to monitor illegal transport routes and stealth aircraft movement. Integration with communication relay systems offers real-time analytics for surveillance and interdiction. These applications position airborne lasers as cost-effective, reload-free alternatives to traditional air defense and ISR solutions, especially in sustained conflict or remote operations.
- For instance, RTX Corporation’s High-Energy Laser Weapon System (HELWS) demonstrated successful engagement of Group 1 and Group 2 drones at distances exceeding 1,000 meters during U.S. Air Force field evaluations, operating with a stabilized beam-director and radar-cueing architecture for real-time targeting.
Growing Opportunities in Joint Military-Industrial Laser Research Programs
Collaboration between defense agencies, industrial laser manufacturers, and academic research institutes accelerates prototype evolution, materials science breakthroughs, and system ruggedization. Joint development programs shorten technology cycles and reduce integration risks for high-value airborne platforms. These partnerships foster innovation in coherent beam combining, enhanced optical fibers, and atmospheric compensation algorithms. Dual-use technology applications in aerospace engineering, environmental sensing, and national security enable wider commercialization pathways, attracting private investment. As export regulations evolve, domestically co-developed airborne laser systems present opportunities for regional defense export strategies.
Key Challenges:
Atmospheric Interference and Range Limitations in Real-World Combat Environments
Despite performance improvements, airborne lasers face technical hurdles due to atmospheric distortion, fog, dust, and moisture, which degrade beam intensity over long ranges. Combat conditions rarely provide controlled environments, making adaptive optics and compensation algorithms vital but costly. Laser effectiveness may diminish in adverse weather or during high-speed aircraft maneuvers. Maintaining beam stability across variable altitudes and thermal gradients demands sophisticated hardware and real-time software correction. These limitations constrain mission reliability and require continuous investment in optical science, material engineering, and advanced sensor fusion to sustain operational viability.
High Cost of Development, Integration, and Lifecycle Support
Airborne laser programs involve high initial investment, complex integration with avionics and power systems, and stringent safety and certification requirements. Specialized materials, cooling architectures, and reinforced airframes elevate production and retrofitting costs. Sustaining system performance requires regular calibration, component replacement, and specialized maintenance infrastructure. The steep cost curve may restrict acquisition to major defense spenders, slowing global adoption. Budget uncertainties, export controls, and lengthy procurement cycles create commercial risk for suppliers, making long-term partnerships, modular upgrade pathways, and cost-sharing agreements critical to program sustainability.
Regional Analysis:
North America
North America holds the dominant position in the military airborne laser market, accounting for around 38% of global share, driven by extensive directed-energy investments and early adoption of laser-equipped aircraft for ISR and counter-UAS operations. The United States leads regional growth through modernization initiatives across bomber, fighter, and unmanned platforms, supported by large defense budgets and strong aerospace manufacturing ecosystems. Collaboration between defense agencies and private contractors accelerates prototype testing and platform integration. Increasing focus on hypersonic threat detection and border surveillance further motivates procurement of high-performance laser targeting and range-finding systems.
Europe
Europe represents approximately 27% of market share, propelled by joint-defense initiatives, cross-border military industrial cooperation, and modernization of fixed-wing and rotary fleets across NATO members. The United Kingdom, France, and Germany lead development and field testing of directed-energy technology for missile defense, reconnaissance, and autonomous aircraft support. Growing geopolitical tensions and commitments to collective deterrence drive investment into multi-domain sensing and counter-drone capabilities. EU programs focusing on digital battlefield integration create opportunities for lightweight, modular airborne laser payloads. However, procurement cycles and export regulations slightly temper short-term deployment velocity.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific captures around 24% of market share, emerging as the fastest-advancing region due to escalating defense expenditures and accelerated deployment of indigenous airborne laser systems. China, India, South Korea, and Japan prioritize laser-based ISR and targeting technologies to support contested-airspace operations, island defense strategies, and border surveillance. Domestic aerospace manufacturing capability continues to scale, supporting integration of airborne lasers into UAVs and tactical aircraft. Regional competition, territorial disputes, and drone proliferation stimulate demand for range finders, LIDAR reconnaissance systems, and counter-UAS capabilities tailored to mountainous and maritime environments.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East and Africa collectively account for approximately 7% of the global market, driven by sustained security modernization, cross-border threat surveillance, and investments in advanced reconnaissance aircraft. Gulf nations deploy airborne laser systems to enhance protection of infrastructure, maritime trade routes, and critical energy assets. Partnerships between regional defense ministries and global aerospace companies facilitate technology transfers and customization for harsh climatic conditions. Meanwhile, gradual fleet upgrades among African nations support incremental adoption of laser range-finding and mapping payloads. Budget constraints, however, continue to limit large-scale directed-energy procurement.
Latin America
Latin America holds about 4% market share, supported mainly by selective investments in airborne surveillance, anti-smuggling operations, and natural disaster response mapping. Brazil and Mexico lead adoption, integrating laser range finders and LIDAR mapping systems to enhance defense intelligence and border patrol missions. Regional governments explore cost-efficient upgrades to existing air fleets rather than large-scale procurement of new directed-energy platforms. Opportunities emerge from environmental monitoring, illegal mining detection, and maritime enforcement. However, fiscal limitations, slower procurement pipelines, and reliance on foreign defense suppliers moderate overall market expansion.
Market Segmentations:
By Product Type
- LIDAR
- 3D Scanning
- Laser Weapon
- Laser Range Finder
- Laser Altimeter
By Technology Type
- Fiber-Optic
- Solid-State
- Others
By Platform Type
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape:
The competitive landscape of the military airborne laser market is characterized by a concentrated group of defense prime contractors, laser technology specialists, and aerospace integrators competing to advance high-energy capability, miniaturization, and operational resiliency. Companies prioritize partnerships with defense ministries to secure long-term procurement and development contracts, while joint ventures support system co-manufacturing and export positioning. Investment in solid-state laser engineering, directed-energy weapons, and AI-enabled beam tracking strengthens differentiation as militaries pursue precision engagement solutions. Competitive momentum is influenced by prototype-to-field deployment speed, integration with fixed- and rotary-wing platforms, and modular upgrade pathways that reduce lifecycle cost. Suppliers also focus on ruggedization for extreme altitudes, atmospheric compensation algorithms, and interoperability with autonomous and unmanned aircraft systems. As national defense strategies evolve toward multi-domain command and rapid threat interception, market competition intensifies around compact, higher-output laser platforms capable of neutralizing hypersonic and low-altitude aerial threats at greater distance with reduced collateral impact.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis:
- Thales SA
- Frankfurt Laser Company (FLC)
- American Laser Enterprises, LLC
- Saab AB
- Coherent Corp
- Northrop Grumman Corporation
- Leonardo Electronics US, Inc.
- RTX Corporation
- BAE Systems plc
- Lockheed Martin Corporation
Recent Developments:
- In August 2025, Thales SA the French Defence Procurement Agency (DGA) placed an order for a high-power laser weapon demonstrator, SYDERAL (New Generation Laser Defence System), with Thales as part of a consortium.
- In February 2025, Saab signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) to collaborate on the Laser Warning System-310 (LWS-310), enabling HAL to manufacture the laser warning system locally in India.
- In November 2024, Thales Australia partnered with the University of Adelaide to explore long-range counter-UAS laser technology, aiming to develop advanced directed-energy weapons for drone threats.
Report Coverage:
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Product type, Technology type, Platform type and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook:
- Adoption of high-energy laser weapons will accelerate as militaries shift toward cost-efficient precision engagement.
- Compact and lightweight laser payloads will expand integration across UAVs, helicopters, and next-generation tactical aircraft.
- AI-enabled target recognition and autonomous beam control will enhance response speed in multi-domain operations.
- Counter-UAS capabilities will remain a primary deployment focus amid rising drone swarm threats.
- Solid-state and fiber-laser systems will gain dominance due to improved thermal management and power efficiency.
- Cross-border defense partnerships will increase joint development and technology-sharing programs.
- Ruggedized lasers will support operations in extreme climates and high-altitude environments.
- Directed-energy solutions will complement kinetic weapons rather than fully replace them in the near term.
- Modular upgrade pathways will reduce lifecycle cost and extend platform relevance.
- Regional defense strategies will influence adoption pace, with Asia-Pacific emerging as a high-growth deployment zone.




