Market Overview
Space Cryogenics Market size was valued at USD 18273.37 million in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 31256.49 million by 2032, at a CAGR of 6.94% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Space Cryogenics Market Size 2024 |
USD 18273.37 million |
| Space Cryogenics Market, CAGR |
6.94% |
| Space Cryogenics Market Size 2032 |
USD 31256.49 million |
Top players in the Space Cryogenics Market include Air Liquide, Oxford Instruments, Creare, Bluefors, Absolut System, Chart Industries Inc., Linde, Advanced Cooling Technologies Inc. (ACT), and Northrop Grumman Corporation, all competing through advanced cryocooler technologies, long-life cooling systems, and high-performance thermal solutions for space missions. These companies focus on improving reliability, reducing vibration, and supporting deep-cryogenic temperatures needed for scientific, defense, and commercial satellites. North America led the market in 2024 with a 38% share, driven by strong investment in space exploration and defense programs. Europe followed with 28%, supported by active research missions and expanding cryogenic technology development.
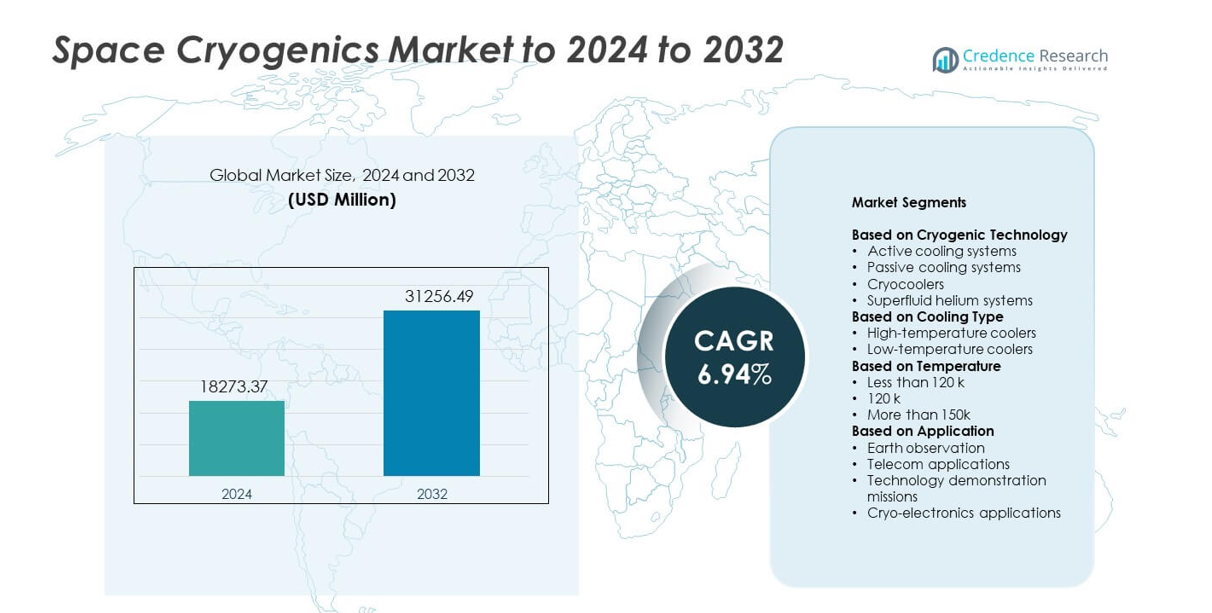
Market Insights
- The Space Cryogenics Market reached USD 18273.37 million in 2024 and is projected to hit USD 31256.49 million by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 6.94%.
- Growing demand for high-sensitivity detectors and deep-space missions drives strong adoption of cryocoolers, with cryocoolers holding the largest segment share at about 58%.
- Trends highlight rapid progress in miniaturized, low-power cooling systems and rising use of cryogenic technology in quantum sensing and commercial satellite constellations.
- Competition intensifies as leading companies advance long-life, low-vibration cooling platforms while expanding partnerships with global space agencies to strengthen market presence.
- North America led the market with 38% share in 2024, followed by Europe at 28% and Asia Pacific at 24%, supported by expanding satellite programs and steady investment in scientific and defense missions.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Cryogenic Technology
Cryocoolers held the dominant position in 2024 with about 58% share. Demand rose due to strong use in satellite sensors, infrared detectors, and long-duration space missions. Cryocoolers support stable thermal control, low vibration, and high reliability, which helped adoption across commercial and defense programs. Active cooling systems grew at a steady rate with rising deployment in deep-space missions that need continuous thermal management. Passive cooling systems and superfluid helium units saw focused use in scientific payloads that require ultra-low temperatures for high-precision measurements.
- For instance, Northrop Grumman’s JWST MIRI cryocooler was matured to TRL 7 and delivers a 6.2 K remote cold-head interface for the instrument’s focal plane modules, showing space-proven active cooling for sensitive mid-infrared detectors.
By Cooling Type
Low-temperature coolers led the market in 2024 with nearly 64% share. Growth came from broad use in high-sensitivity payloads, including infrared imaging, quantum sensors, and deep-space telescopes. Low-temperature systems support stable operation below 120 K, which enhanced detector accuracy and reduced thermal noise. High-temperature coolers remained important for communication satellites and medium-sensitivity sensors where moderate cooling is enough. Rising investment in miniaturized cooling modules supported demand across small satellite platforms.
- For instance, Honeywell’s long-life Stirling cryocoolers provide cooling powers from 0.5 W to 5 W at 80 K with demonstrated operating lifetimes exceeding 188,000 hours, which supports low-temperature and high-temperature space payload needs over multi-year missions.
By Temperature
The less than 120 K segment dominated in 2024 with about 61% share. Adoption increased as advanced scientific missions, space telescopes, and defense payloads required deep-cryogenic temperatures for enhanced sensitivity and reduced background noise. This range supports high-precision imaging, spectrometry, and thermal sensing. The 120 K category saw stable demand from operational satellites that rely on moderate cooling levels. The more than 150 K range continued to serve applications needing basic thermal management, mainly in navigation, communication, and Earth-observation systems.
Key Growth Drivers
Rising demand for high-sensitivity space instruments
Space missions now use advanced sensors that need deep cryogenic cooling for stable performance. Infrared telescopes, quantum detectors, and scientific payloads rely on cryogenic systems to reduce noise and improve measurement accuracy. Growing investments in astronomy, Earth observation, and defense imaging increased adoption of cryocoolers and passive cooling units. Expanding satellite fleets also pushed demand for compact, low-vibration cooling technologies that support longer mission life.
- For instance, Sumitomo Heavy Industries’ 4K/1K cryocooler, used on missions like Hitomi, delivers 40 mW of cooling at 4.5 K and 10 mW at 1.7 K, supporting microcalorimeter detectors that operate near 50 mK for high-resolution X-ray spectroscopy.
Expansion of small satellite and commercial space programs
Commercial operators launched more small satellites that use compact cryogenic systems to support imaging, communication, and climate monitoring. Lower launch costs and rapid deployment cycles increased interest in miniaturized coolers. Companies preferred low-power designs to extend satellite lifespan and enhance thermal stability in harsh orbits. This shift supported steady demand growth across startups, constellations, and private exploration missions seeking high-performance thermal control.
- For instance, Ricor’s K562S mini rotary Stirling cooler provides 200 mW at 110 K at 23 °C ambient temperature (or 350 mW at 110 K at 71 °C ambient), with a typical continuous power consumption of less than 3 WDC when operating at its standard configuration (200 mW @ 95K @ 23 °C).
Growth in deep-space and planetary exploration missions
Agencies expanded missions aimed at observing distant planets, cosmic origins, and extreme environments. These missions use detectors that must operate at very low temperatures to capture faint signals. Deep-space spacecraft rely on robust cryogenic technology to handle long-duration operations and extreme thermal loads. Rising international collaborations and broader funding boosted deployments of high-end cryocoolers and superfluid helium systems.
Key Trends & Opportunities
Advances in miniaturized cryocoolers
Manufacturers are developing smaller, lighter, and more energy-efficient cryocoolers that support new satellite classes. These systems help reduce the size, weight, and power load of spacecraft while maintaining high cooling capacity. Demand is rising across commercial constellations and defense payloads as operators seek flexible integration options. Miniaturized units also open opportunities in quantum space technologies and compact spectrometers.
- For instance, Sunpower’s CryoTel DS1.5 Stirling cryocooler provides a nominal 1.4 W heat lift at 77 K using approximately 30 W of nominal electrical power input with a 1.2 kg mass.
Integration of cryogenics with quantum space technologies
Space agencies and private firms are testing quantum communication, sensing, and timing systems that require deep-cryogenic temperatures. This trend creates opportunities for high-stability cooling solutions designed for ultra-low vibration environments. Increased funding for quantum payloads accelerates innovation in next-generation coolers and passive radiation shields. These technologies expand market scope across security, navigation, and scientific research.
- For instance, Oxford Instruments’ TritonXL cryogen-free dilution refrigerator achieves base temperatures below 5 mK and offers 5 µW of cooling power at 10 mK and 25 µW at 20 mK, performance already used for quantum computing experiments that informs future quantum-enabled space sensors.
Rising focus on long-life and low-maintenance systems
Operators are prioritizing cryogenic technologies that offer long operational life with minimal maintenance. Extended-life cryocoolers reduce mission risk and support multi-year operations in harsh space environments. This trend encourages development of durable compressors, advanced materials, and improved heat-transfer designs. Demand is expanding across deep-space probes, climate satellites, and defense missions that require long-term reliability.
Key Challenges
High development and integration costs
Cryogenic systems require advanced components, precision engineering, and extensive testing to meet space-grade standards. These factors raise development costs, making adoption difficult for smaller mission budgets. Integration with sensitive instruments also adds complexity, requiring vibration control and strict thermal management. This limits deployment in low-cost commercial missions and slows entry for emerging players.
Reliability and performance risks in harsh environments
Cryogenic equipment must operate under extreme temperature cycles, radiation exposure, and long mission durations. Failures can degrade sensor performance or jeopardize entire missions. Ensuring stable operation over years demands advanced materials, redundant components, and rigorous qualification. These challenges increase engineering effort and limit the speed of innovation in next-generation cooling systems.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America held about 38% share in 2024 due to strong funding for space missions, scientific payloads, and defense programs. The region saw high adoption of cryocoolers and low-temperature systems for infrared telescopes, missile-warning satellites, and deep-space probes. Leading agencies and private launch companies supported steady growth through investments in advanced cryogenic designs. Expanding commercial constellations and research projects increased demand for compact, long-life cooling units across small satellite platforms.
Europe
Europe accounted for nearly 28% share in 2024, driven by rising investments in space science, climate monitoring, and exploration missions. Regional agencies adopted cryogenic systems for high-precision instruments on observatories and deep-space spacecraft. Strong focus on sustainable mission design boosted interest in energy-efficient coolers and long-duration thermal solutions. Demand grew across Earth observation programs and collaborative scientific missions, supporting the steady expansion of cryogenic technology across major European manufacturers.
Asia Pacific
Asia Pacific captured around 24% share in 2024, supported by rapid growth in national space programs and commercial satellite activities. Countries expanded Earth-observation and communication constellations that rely on cryogenic cooling for improved imaging and sensor accuracy. Investments in deep-space missions and advanced detector technologies increased adoption of low-temperature coolers. Strong manufacturing capability and rising launch capacity helped the region scale production and deploy cryogenic systems across diverse applications.
Latin America
Latin America held close to 6% share in 2024, with growth driven by emerging satellite programs and regional collaboration in scientific missions. Rising interest in Earth-observation and environmental monitoring supported early adoption of cryogenic components for research payloads. Countries partnered with global agencies to gain access to advanced cooling technologies. Although deployment remains limited, increasing investment in space infrastructure is gradually expanding demand for reliable and cost-effective cryogenic systems.
Middle East & Africa
Middle East & Africa accounted for nearly 4% share in 2024, supported by growing investments in national space strategies and technology development. The region adopted cryogenic systems for climate monitoring, remote-sensing satellites, and security applications. Partnerships with international agencies improved access to advanced cooling solutions and scientific payload capabilities. As more countries expand space research and satellite operations, demand for long-life cryogenic technologies is expected to grow at a steady pace.
Market Segmentations:
By Cryogenic Technology
- Active cooling systems
- Passive cooling systems
- Cryocoolers
- Superfluid helium systems
By Cooling Type
- High-temperature coolers
- Low-temperature coolers
By Temperature
- Less than 120 k
- 120 k
- More than 150k
By Application
- Earth observation
- Telecom applications
- Technology demonstration missions
- Cryo-electronics applications
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
Air Liquide, Oxford Instruments, Creare, Bluefors, Absolut System, Chart Industries Inc., Linde, Advanced Cooling Technologies Inc. (ACT), and Northrop Grumman Corporation lead the competitive landscape of the Space Cryogenics Market. The market features strong competition driven by advances in cryocooler efficiency, long-life cooling systems, and miniaturized thermal solutions for satellites. Companies focus on enhancing vibration control, improving energy efficiency, and extending operational life to meet the needs of deep-space and high-precision missions. Rising demand for compact systems in commercial constellations encourages innovation in low-power and lightweight designs. Strategic partnerships with space agencies support technology adoption, while investments in next-generation cooling platforms strengthen competitive positions across scientific, defense, and commercial programs.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
- Air Liquide
- Oxford Instruments
- Creare
- Bluefors
- Absolut System
- Chart Industries Inc.
- Linde
- Advanced Cooling Technologies, Inc. (ACT)
- Northrop Grumman Corporation
Recent Developments
- In 2025, Linde agreed to design and build a major cryogenic cooling facility for a quantum computer.
- In 2024, Bluefors expanded its Delft lab by adding the high-capacity XLD1000sl dilution refrigerator, boosting quantum research, and promoted its LH horizontal dilution system, ideal for beamline/telescope detectors in astronomy/high-energy physics, offering high cooling power and large port access for space-instrument cryogenics and fundamental research.
- In 2023, At APS 2023, Oxford Instruments NanoScience showcased integrations of SCALINQ hardware with its Proteox dilution-refrigerator platforms, strengthening cryogenic infrastructure for quantum and detector experiments that can feed into future space-instrument development
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Cryogenic Technology, Cooling Type, Temperature, Application and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- The market will see rising demand from deep-space and planetary exploration missions.
- Cryocooler innovation will shift toward lighter, low-power, long-life designs.
- Small satellite programs will adopt more compact cryogenic systems for advanced sensors.
- Quantum communication and sensing payloads will expand the need for ultra-low-temperature cooling.
- Defense programs will increase investment in cryogenic technologies for high-sensitivity infrared imaging.
- International collaborations will accelerate development of next-generation cooling technologies.
- Reliability improvements will focus on reducing vibration and enhancing thermal stability.
- Manufacturers will adopt advanced materials to boost performance in extreme space environments.
- Automation and digital control systems will improve cryogenic system efficiency and lifespan.
- Growing commercial space activity will broaden market opportunities across new mission types.




