Market overview
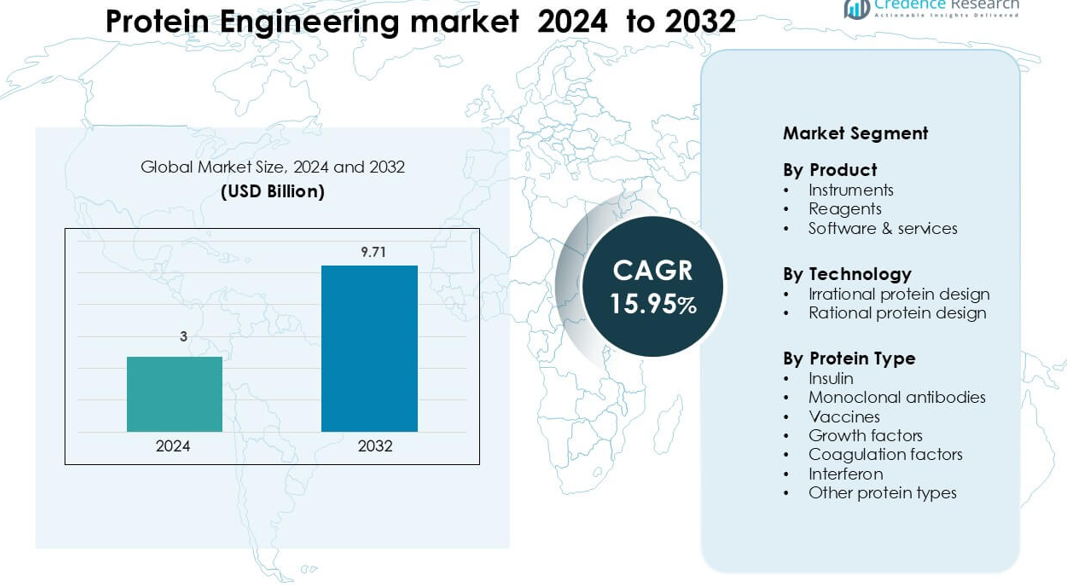
Protein Engineering market was valued at USD 3 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 9.71 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 15.95 % during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Protein Engineering Market Size 2024 |
USD 3 billion |
| Protein Engineering Market, CAGR |
15.95% |
| Protein Engineering Market Size 2032 |
USD 9.71 billion |
The Protein Engineering market is shaped by major players such as Lonza Group, Genentech, Inc., Bruker Corporation, Amgen Inc., Integrated DNA Technologies, Inc., Danaher Corporation, Merck KGaA, Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc., Agilent Technologies, Inc., and Bristol Myers Squibb Company. These companies lead the market through strong biologics pipelines, advanced screening systems, and growing adoption of AI-enabled protein design technologies. North America remains the dominant regional market with 41% share in 2024, supported by extensive R&D infrastructure, high investment in therapeutic protein development, and strong innovation across pharmaceutical and biotechnology sectors.
Market Insights
- The Protein Engineering market was valued at USD 3 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 9.71 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 15.95 %.
- Growth is driven by strong demand for monoclonal antibodies, which hold 46% share, along with rising adoption of AI-based design tools and high-throughput screening technologies across research labs and biopharma companies.
- Key trends include rapid expansion of next-generation biologics, increased use of engineered enzymes in diagnostics and industry, and growing investment in sustainable bioprocessing supported by advanced modeling platforms.
- Competitive landscape features Lonza Group, Genentech, Bruker Corporation, Amgen, IDT, Danaher, Merck KGaA, Bio-Rad, Agilent Technologies, and Bristol Myers Squibb, with companies competing through automation, predictive design, and expanded biologics manufacturing capacity.
- North America leads with 41% share, followed by Europe at 29% and Asia-Pacific at 23%, supported by strong R&D ecosystems and rising adoption of engineered therapeutic proteins.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Product
Instruments lead the Protein Engineering market with about 42% share in 2024. Research labs and biopharma companies rely on advanced analyzers, microfluidic platforms, and screening systems to speed protein modification and stability testing. The rise in automated workflows and high-throughput platforms strengthens the position of instruments in development pipelines. Reagents grow at a steady pace due to strong use in mutagenesis kits and expression systems. Software and services expand as AI-based modeling and sequence-prediction tools help shorten design cycles and improve structural accuracy.
- For instance, Thermo Fisher Scientific KingFisher Flex system can purify up to 96 protein samples in one run, completing the process in under 25-60 minutes using its 96-magnet head.
By Technology
Rational protein design dominates this segment with roughly 57% share in 2024. Rational design grows because researchers can modify amino acid sequences with predictable outcomes, supported by modeling platforms and structural databases. This method reduces trial-and-error steps and cuts development time in therapeutic protein pipelines. Irrational design continues to gain traction in directed-evolution programs, especially in enzyme engineering, where large variant libraries improve catalytic efficiency and stability.
- For instance, Creative Enzymes’ directed evolution service claims to generate libraries with more than 10^12 (one trillion) variants per campaign.
By Protein Type
Monoclonal antibodies remain the leading protein type with nearly 46% share in 2024. These antibodies dominate due to strong demand for targeted therapies in oncology, autoimmune disease, and infectious disease treatment. The pipeline expansion of next-generation antibodies, including bispecific and antibody-drug conjugates, supports segment strength. Insulin and vaccines show rising interest driven by chronic disease growth and improved recombinant platforms. Growth factors, interferons, and coagulation factors maintain steady adoption across regenerative medicine, antiviral therapy, and rare genetic disorder programs.
Key Growth Drivers
Expanding Therapeutic Demand for Advanced Biologics
Global demand for complex biologics drives strong growth in the Protein Engineering market. Pharmaceutical companies increase investment in engineered monoclonal antibodies, next-generation insulin variants, advanced vaccines, and enzyme-replacement therapies. Rising cases of cancer, autoimmune disorders, diabetes, and rare diseases push research teams to develop optimized protein structures with higher potency, improved stability, and reduced immunogenicity. Growth also comes from faster regulatory acceptance of engineered biologics supported by proven safety data. Increased R&D spending by major biopharma players strengthens the adoption of rational and AI-guided design platforms. Governments fund translational research programs and support innovation in recombinant protein production, boosting commercialization. Together, these factors keep demand for engineered proteins strong across clinical pipelines.
- For instance, Nabla Bio has signed a multi-year collaboration with Takeda Pharmaceuticals to use its AI platform (JAM) for de novo design of multispecific antibodies and other protein therapeutics; the platform reportedly delivers a design-to-lab testing feedback loop in 3–4 weeks, with double-digit hit rates and picomolar binding affinities.
Growth of AI-Driven Design Platforms and High-Throughput Tools
Rapid adoption of AI and machine-learning tools accelerates design, simulation, and prediction of protein structures. Research groups now model folding behavior, binding interactions, and stability profiles with higher accuracy, reducing wet-lab trial cycles. High-throughput screening instruments, automated mutation platforms, and microfluidic systems allow faster evaluation of thousands of variants in parallel. These tools improve hit-to-lead timelines and reduce failure rates in early development. Academic–industry partnerships expand access to predictive algorithms, structural databases, and cloud-based protein modeling suites. Pharmaceutical companies increasingly use hybrid approaches that combine rational design with directed evolution, improving optimization speed. These advancements help shorten development timelines and expand the market’s adoption of engineered proteins in therapeutics, diagnostics, and industrial enzymes.
- For instance, DeepMind’s AlphaFold (via its AlphaFold Database) provides over 214 million predicted protein structures in its most recent public release, enabling scientists to run in silico simulations across a massive structural universe.
Rising Use of Engineered Proteins in Industrial and Diagnostic Applications
Beyond therapeutics, engineered proteins gain strong traction in diagnostics, industrial biocatalysis, food processing, and environmental applications. Companies use modified enzymes to boost efficiency in biofuel production, biodegradable plastics, textile processing, and chemical synthesis. Diagnostic firms adopt engineered binding proteins and detection enzymes for high-sensitivity assays in infectious disease testing and chronic disease screening. Growth in point-of-care diagnostic devices increases demand for stable, engineered proteins that maintain accuracy under varied conditions. Food and agri-tech sectors adopt tailored enzymes for flavor formulation, nutrient processing, and crop protection. Expanding cross-industry use broadens revenue streams and reduces reliance on pharmaceutical cycles. This diversification positions protein engineering as a core enabling technology across multiple global industries.
Key Trends & Opportunities
Expansion of AI-Native Protein Design and Predictive Modeling
AI-native design platforms create new opportunities by accelerating prediction and optimization of protein structures. Deep-learning models help identify beneficial mutations, analyze folding patterns, and predict binding efficiency with greater accuracy than before. Companies integrate generative AI to design proteins with novel properties that do not exist in nature, opening opportunities in enzyme engineering, immune-modulating proteins, and therapeutic peptides. Cloud-based modeling and automated code-free design interfaces support adoption among smaller biotech firms. This trend encourages faster candidate selection and improves project scalability. As AI systems become validated in clinical programs, investors show higher confidence in AI-first drug discovery and protein design workflows, creating long-term growth opportunities.
- For instance, Generate Biomedicines’ Chroma platform is trained on 160,000 experimentally solved protein structures and 190 million genetic sequences, enabling it to generate de novo proteins with tailored functionalities.
Expansion of Next-Generation Therapeutic Modalities
Protein engineering plays a central role in next-generation modalities such as bispecific antibodies, antibody-drug conjugates, fusion proteins, and long-acting biologics. These therapies offer better targeting, lower dosing frequency, and improved patient outcomes. Companies invest in engineering proteins that can cross physiological barriers, resist degradation, and deliver higher therapeutic payloads. Growth in cell and gene therapies creates new demand for engineered viral proteins, regulatory factors, and delivery vectors. Vaccine development also benefits from engineered antigens with enhanced stability and immunogenicity. As these modalities advance through pipelines, demand for highly optimized proteins grows, expanding commercial opportunities across biopharma portfolios.
- For instance, Sutro Biopharma uses its XpressCF+ cell-free protein synthesis platform to build site-specific ADC candidates (like STRO-001 and STRO-002), allowing conjugation at defined positions to improve pharmacokinetics.
Rising Opportunity in Sustainable and Green Biomanufacturing
A major opportunity emerges from the shift toward sustainable bioprocessing. Engineered enzymes help reduce energy use, lower chemical waste, and improve conversion efficiency in industrial operations. Bioplastic manufacturing, green solvents, and enzyme-supported chemical synthesis rely on robust engineered variants with higher stability and catalytic rates. Companies adopt protein engineering to replace petrochemical-based processes with biodegradable and bio-based pathways, creating environmental and economic advantages. Regulatory incentives for sustainable technologies encourage adoption of high-performance industrial enzymes. This trend positions protein engineering as a key enabler of global sustainability goals, creating long-term opportunities beyond healthcare.
Key Challenges
High Development Cost and Complex Manufacturing Requirements
Developing engineered proteins requires expensive instruments, screening systems, and specialized infrastructure. Companies face high costs across mutagenesis, expression optimization, purification, and stability testing. Complex production steps often demand advanced bioreactors, quality-control systems, and skilled expertise, increasing overall project investment. Early failures in protein design or expression add financial risk, especially for smaller biotechs. Regulatory approval for new engineered proteins also involves lengthy data requirements and strict safety evaluations. These cost and compliance barriers slow adoption and limit competitiveness for emerging players in the market.
Structural Complexity and Unpredictable Performance Risks
Proteins are structurally sensitive, and small sequence changes can lead to misfolding, aggregation, or loss of function. Designing stable and functional variants remains challenging due to complex folding pathways and dynamic interactions. Even well-modeled mutations can behave unpredictably during large-scale production or in physiological settings. Companies must invest in iterative testing, advanced simulation, and robust formulation strategies to reduce risks. Stability issues, immunogenic responses, and off-target activity increase development difficulty in therapeutics. These uncertainties make protein engineering projects time-intensive and require significant validation, slowing development cycles and raising technical barriers.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America leads the Protein Engineering market with about 41% share in 2024. Strong biopharmaceutical pipelines, wide adoption of monoclonal antibodies, and heavy investment in AI-driven design tools support this dominance. The U.S. hosts major R&D hubs, advanced CRO networks, and strong regulatory pathways that speed biologics development. Canada expands capacity through public-funded research programs and growing biotech clusters. High demand for engineered proteins in oncology, autoimmune therapy, and diagnostics keeps the region ahead. Mature infrastructure and strong collaborations between academia and industry strengthen innovation and drive sustained market growth.
Europe
Europe holds nearly 29% share in 2024, driven by strong biotechnology frameworks and active funding by national and regional health agencies. Germany, the U.K., France, and Switzerland lead in protein modification research, supported by advanced structural biology centers and high-throughput screening labs. The region emphasizes next-generation biologics, biosimilars, and industrial enzyme innovation. Increasing investment in green bioprocessing and sustainable enzyme engineering fuels new applications. Regulatory harmonization through EMA accelerates clinical evaluation of engineered proteins. Research clusters across Scandinavia and Western Europe continue to expand, strengthening the region’s long-term innovation pipeline.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific accounts for about 23% share in 2024, emerging as the fastest-growing regional market. China, Japan, South Korea, and India expand protein engineering capacity through rising biologics manufacturing, academic partnerships, and government-backed life science initiatives. Increasing demand for therapeutic antibodies, recombinant insulin, and vaccine proteins accelerates market expansion. Domestic biopharma companies invest in AI-integrated design systems and high-throughput mutation platforms. Contract research and manufacturing services grow rapidly due to cost advantages and strong talent pools. The region’s expanding healthcare spending and large patient base continue to boost adoption of engineered protein technologies.
Latin America
Latin America holds roughly 4% share in 2024, with growth driven by expanding biotechnology activity in Brazil, Mexico, and Argentina. Regional research institutes invest in recombinant protein studies, vaccine development, and enzyme engineering for agriculture and food processing. Adoption of engineered proteins in diagnostics increases as public-health systems modernize. Limited infrastructure and funding constraints slow growth, but partnerships with North American and European biotech firms improve access to tools and expertise. Rising demand for chronic disease biologics and improved regulatory pathways support gradual market expansion across the region.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region accounts for around 3% share in 2024, supported by growing biomedical research activity in the UAE, Saudi Arabia, and South Africa. Investments in genomic medicine, vaccine development, and advanced diagnostics create opportunities for engineered protein technologies. Healthcare modernization efforts expand demand for recombinant therapies and immunoassay enzymes. Adoption remains slower due to limited manufacturing facilities and research funding, but strategic collaborations with global biotech companies improve technology access. Expanding clinical research hubs in the Gulf region continue to support long-term market development.
Market Segmentations:
By Product
- Instruments
- Reagents
- Software & services
By Technology
- Irrational protein design
- Rational protein design
By Protein Type
- Insulin
- Monoclonal antibodies
- Vaccines
- Growth factors
- Coagulation factors
- Interferon
- Other protein types
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
Competitive landscape in the Protein Engineering market features leading players such as Lonza Group, Genentech, Inc., Bruker Corporation, Amgen Inc., Integrated DNA Technologies, Inc., Danaher Corporation, Merck KGaA, Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc., Agilent Technologies, Inc., and Bristol Myers Squibb Company. These companies compete by advancing high-throughput screening platforms, AI-powered structure-prediction tools, and next-generation mutagenesis technologies. Major firms strengthen portfolios through acquisitions, strategic research partnerships, and expanded biologics manufacturing capacity. Growth comes from rising demand for monoclonal antibodies, engineered enzymes, and optimized therapeutic proteins across clinical pipelines. Companies also invest in cloud-based modeling suites and automated design systems to shorten development cycles. Increased focus on sustainable bioprocessing, recombinant vaccine platforms, and precision biologics drives further innovation.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
- Lonza Group
- Genentech, Inc.
- Bruker Corporation
- Amgen Inc.
- Integrated DNA Technologies, Inc.
- Danaher Corporation
- Merck KGaA
- Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.
- Agilent Technologies, Inc.
- Bristol Myers Squibb Company
Recent Developments
- In 2025, Lonza Group Lonza agreed to acquire Redberry, a biotech firm specializing in rapid microbiology testing using solid-phase cytometry, to enhance quality control across biologics and vaccine manufacturing workflows that rely on engineered proteins and mRNA platforms.
- In August 2025, Genentech, Inc. Genentech and Roche broke ground on a new 700,000-square-foot Holly Springs, North Carolina manufacturing facility designed to support large-scale production of next-generation metabolic biologics, expanding capacity for complex protein-based therapies
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Product, Technology, Protein Type and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- Demand for engineered therapeutic proteins will rise as biologics gain wider clinical use.
- AI-driven design and predictive modeling will reshape discovery and shorten development timelines.
- High-throughput screening systems will become standard in research and commercial labs.
- Next-generation antibodies and fusion proteins will expand treatment options across major diseases.
- Industrial enzymes will see broader adoption in green manufacturing and sustainable processes.
- Automated design workflows will reduce development failures and improve structural accuracy.
- Partnerships between biopharma, AI firms, and academic institutes will accelerate innovation.
- Growth in personalized medicine will increase demand for tailored protein variants.
- Improvements in recombinant production will enhance scalability and lower manufacturing barriers.
- Emerging markets will invest heavily in protein engineering capabilities to strengthen local biologics pipelines.




