Market Overview
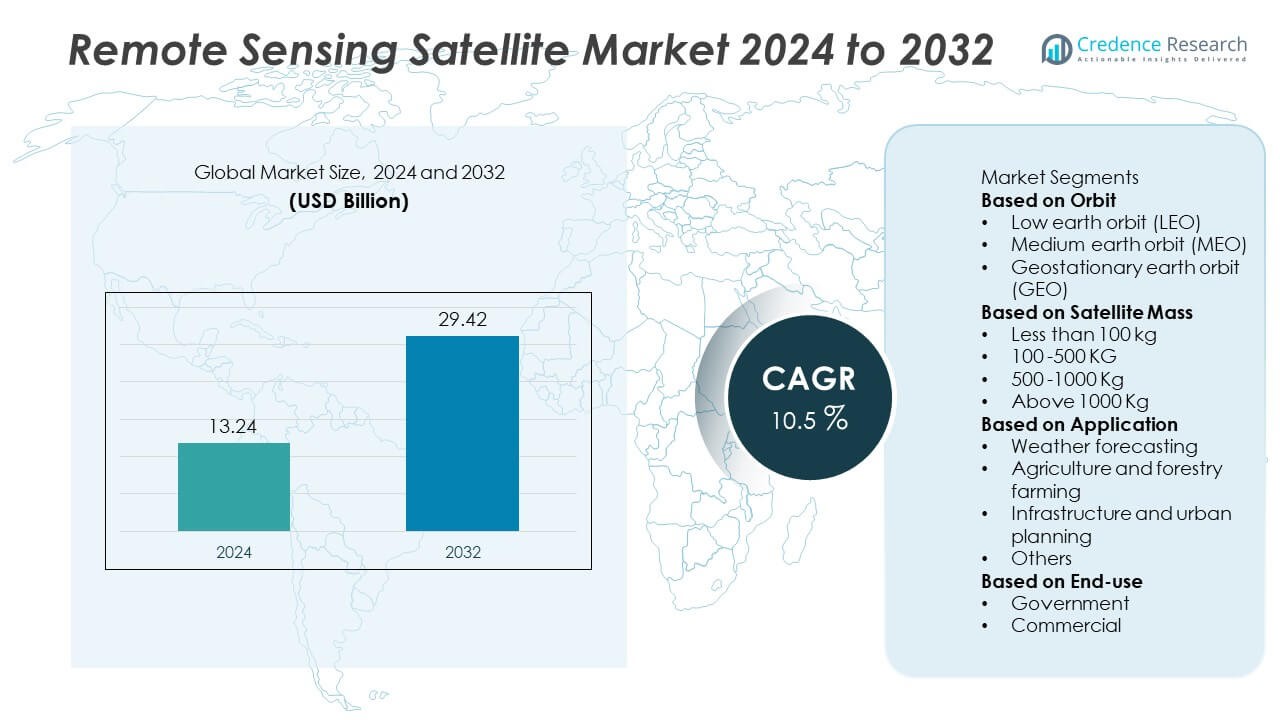
The global remote sensing satellite market was valued at USD 13.24 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 29.42 billion by 2032, registering a CAGR of 10.5% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Remote Sensing Satellite Market Size 2024 |
USD 13.24 Billion |
| Remote Sensing Satellite Market, CAGR |
10.5% |
| Remote Sensing Satellite Market Size 2032 |
USD 29.42 Billion |
The remote sensing satellite market is led by major players including Boeing, Lockheed Martin, Airbus, BAE Systems, Dhruva Space, EnduroSat, Blue Canyon Technologies, Beijing Smart Satellite, INVAP, and the Indian Space Research Organisation. These companies dominate through advanced imaging technologies, lightweight satellite platforms, and strategic government collaborations. North America emerged as the leading region with a 38% market share in 2024, supported by strong investments in defense, environmental monitoring, and commercial imaging. Asia-Pacific followed with a 30% share, driven by rapid growth in space programs across China, India, and Japan. Continuous innovation in AI-enabled analytics and satellite miniaturization further enhances market competitiveness globally.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Insights
- The global remote sensing satellite market was valued at USD 13.24 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 29.42 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 10.5% during the forecast period.
- Market growth is driven by rising demand for Earth observation data, expanding defense surveillance needs, and increasing investments in satellite constellations.
- Key trends include miniaturization of satellites, AI-driven image analysis, and the integration of cloud-based data platforms for faster processing.
- The competitive landscape is led by Boeing, Lockheed Martin, Airbus, Dhruva Space, and BAE Systems, focusing on advanced imaging payloads and cost-efficient launch technologies.
- North America held 38%, Asia-Pacific 30%, and Europe 27% market shares in 2024, while the Low Earth Orbit (LEO) segment dominated with 63% share, supported by rapid deployment of small and microsatellite constellations across government and commercial sectors.
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Orbit
The low Earth orbit (LEO) segment dominated the remote sensing satellite market with a 63% share in 2024. Its dominance is driven by shorter revisit times, higher image resolution, and lower launch costs compared to medium and geostationary orbits. LEO satellites are widely used for Earth observation, climate monitoring, and defense surveillance. Growing deployment of small satellite constellations by organizations such as SpaceX, Planet Labs, and Airbus enhances real-time imaging and data transmission capabilities. Increasing government and commercial investments in low-cost LEO missions further strengthen segment growth.
- For instance, Airbus operates the Pléiades Neo constellation composed of four 750-kilogram satellites orbiting at 620 kilometers altitude, providing imagery with 30-centimeter native resolution. Each satellite revisits the same location within 12 hours, transmitting data through laser communication links at speeds of 1.8 gigabits per second.
By Satellite Mass
Satellites weighing less than 100 kg held the largest share of 46% in 2024, owing to rising demand for small and microsatellites in Earth observation and agricultural monitoring. Miniaturization of components and advancements in lightweight materials enable cost-effective manufacturing and faster deployment. These compact satellites support high-frequency imaging for environmental and disaster monitoring. Governments and private operators favor them for quick constellation deployment and reduced launch expenses, driving the dominance of this segment across research and commercial applications.
- For instance, EnduroSat’s larger Endurance-15 platform, weighing 70–150 kg, can support a payload with a data rate of over 1 Gbps, with available payload mass up to 70 kg and power up to 200 W. A smaller satellite in a customer-requested sun-synchronous orbit, such as the Balkan-1, may carry a multispectral sensor to capture high-resolution imagery for specific tasks like agricultural or disaster monitoring.
By Application
The weather forecasting segment accounted for a 39% share in 2024, emerging as the leading application area. Growing climate change concerns and the need for accurate weather prediction drive investments in advanced remote sensing satellites. These systems provide real-time atmospheric, oceanic, and environmental data, supporting disaster management and agricultural planning. Increasing use of AI and data analytics enhances the precision of weather models. Global agencies such as NOAA, ESA, and ISRO continue to expand satellite fleets for improved forecasting accuracy, strengthening this segment’s leadership in the market.
Key Growth Drivers
Rising Demand for Earth Observation Data
The increasing need for high-resolution Earth observation data across defense, agriculture, and environmental sectors is driving market growth. Governments and private organizations use satellite imagery for resource mapping, climate tracking, and disaster response. Expanding use in precision agriculture and infrastructure development enhances adoption. The demand for near real-time geospatial information and predictive analytics further accelerates deployment of remote sensing satellite constellations worldwide.
- For instance, Lockheed Martin developed the LM 400 mid-sized satellite platform to support a variety of payloads, including electro-optical systems. The LM 400 uses Lockheed Martin’s SmartSat™ software-defined architecture, which enables on-board data processing to speed up the delivery of information.
Advancements in Miniaturization and Launch Technologies
Technological progress in satellite miniaturization and reusable launch vehicles is making remote sensing missions more cost-effective. The rise of small satellites and CubeSats enables frequent launches and shorter development cycles. Companies like SpaceX, Rocket Lab, and ISRO are reducing launch costs, encouraging broader participation from startups and research institutions. These innovations support rapid constellation deployment, expand imaging coverage, and lower entry barriers for new market players.
- For instance, ISRO used the SSLV-D3 launch vehicle to deploy the 175.5 kg EOS-08 microsatellite into orbit. Separately, ISRO has been developing and testing lightweight carbon-carbon (C-C) nozzles for the fourth stage of its PSLV rocket, a modification that could increase that rocket’s payload capacity by 15 kg.
Growing Government and Defense Investments
Rising investments in national security, border surveillance, and environmental monitoring programs are propelling market expansion. Governments across the U.S., China, and India are enhancing remote sensing capabilities for intelligence and infrastructure monitoring. Defense agencies rely on high-resolution imagery for reconnaissance and tactical decision-making. Collaborative programs between public and private sectors are strengthening global space-based observation networks and stimulating steady demand for advanced remote sensing satellites.
Key Trends & Opportunities
Integration of AI and Big Data Analytics
The integration of artificial intelligence and big data analytics is transforming remote sensing operations. AI-driven image classification, change detection, and pattern recognition enable faster and more accurate analysis of satellite imagery. These tools enhance applications in agriculture, environmental assessment, and urban planning. Companies are leveraging cloud-based analytics platforms to manage large data volumes efficiently, creating opportunities for software-driven service providers in the satellite imaging ecosystem.
- For instance, Airbus integrated AI and machine learning into its OneAtlas platform, which processes petabytes of imagery data annually. The system uses deep neural networks for land-cover classification and offers automated change detection, though specific accuracy levels and processing times can vary based on the service and customer requirements.
Expansion of Commercial Satellite Constellations
Private space companies are increasingly launching large constellations of small remote sensing satellites. These constellations deliver continuous global coverage and real-time imaging, supporting commercial and research applications. Firms like Planet Labs and BlackSky are leading this shift, providing affordable, high-frequency data. The growing commercialization of satellite data services offers opportunities for collaboration between aerospace manufacturers, analytics firms, and cloud providers to develop end-to-end Earth observation solutions.
- For instance, BlackSky Global operates a growing constellation of electro-optical satellites, with the newest Gen-3 satellites providing very-high-resolution imagery (as fine as 35 cm) and the entire fleet capable of delivering multiple revisits per day over critical locations.
Key Challenges
High Initial Development and Launch Costs
Despite advances in technology, the high cost of satellite design, integration, and launch remains a major barrier. Remote sensing missions require significant investment in payload development, imaging sensors, and ground infrastructure. Smaller companies face financial constraints in competing with established players. Although reusable rockets and miniaturized components reduce costs, large-scale constellations still demand substantial capital, slowing adoption in developing economies.
Data Security and Regulatory Concerns
Data privacy, export restrictions, and international regulations pose challenges to market expansion. Remote sensing satellites collect sensitive information that may have national security implications. Governments enforce strict policies on data sharing and commercial use, limiting cross-border collaborations. Ensuring secure data transmission and storage is critical to prevent misuse or cyberattacks. Evolving regulatory frameworks and licensing procedures also create operational delays for private satellite operators.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America held a 38% share in 2024, driven by strong government and commercial satellite programs. The United States leads the market with extensive investments from NASA, NOAA, and private companies like Planet Labs and Maxar Technologies. High adoption of remote sensing data for defense, weather forecasting, and agricultural applications supports growth. Technological advancements in AI-based data processing and satellite imaging systems enhance market competitiveness. Ongoing projects for LEO constellations and climate observation further strengthen the region’s leadership in remote sensing capabilities.
Europe
Europe accounted for a 27% share in 2024, supported by the European Space Agency’s (ESA) Copernicus program and regional collaborations. Countries such as France, Germany, and the United Kingdom are key contributors, focusing on environmental monitoring, urban planning, and defense imaging. The region emphasizes sustainability and precision mapping through high-resolution optical and radar satellites. Investments in small satellite missions and data-sharing initiatives strengthen commercial adoption. Strong public-private partnerships and innovation in Earth observation analytics continue to expand the region’s role in global satellite operations.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific dominated the market with a 30% share in 2024, driven by rapid advancements in space programs across China, India, and Japan. Government agencies such as ISRO, CNSA, and JAXA lead significant remote sensing satellite launches for agricultural mapping, disaster management, and resource exploration. Expanding commercial satellite manufacturing and launch capabilities further enhance regional competitiveness. Increasing use of satellite data for climate monitoring, infrastructure planning, and maritime surveillance supports sustained demand. Growing private participation and regional collaborations are expected to accelerate future market expansion.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa held a 3% share in 2024, supported by growing investments in environmental monitoring and defense applications. The UAE and Saudi Arabia are leading regional players, focusing on national satellite programs like KhalifaSat and SAT-2 for mapping and observation. Africa’s rising adoption of satellite data for agricultural and water resource management is also boosting demand. Regional governments are partnering with international space agencies to develop indigenous capabilities. Continuous advancements in affordable small satellites are expected to expand access to Earth observation technologies.
Latin America
Latin America represented a 2% share in 2024, with growth driven by expanding applications in agriculture, forestry, and disaster response. Brazil and Mexico dominate regional activity, supported by national agencies such as INPE and AEM. Increasing satellite collaborations with the U.S. and Europe promote technology transfer and data access. Governments are enhancing climate and land-use monitoring programs to support sustainable development goals. Growing interest from private firms in commercial imaging and analytics is gradually improving the region’s contribution to the global remote sensing satellite market.
Market Segmentations:
By Orbit
- Low earth orbit (LEO)
- Medium earth orbit (MEO)
- Geostationary earth orbit (GEO)
By Satellite Mass
- Less than 100 kg
- 100 -500 KG
- 500 -1000 Kg
- Above 1000 Kg
By Application
- Weather forecasting
- Agriculture and forestry farming
- Infrastructure and urban planning
- Others
By End-use
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape of the remote sensing satellite market includes major players such as Boeing, Dhruva Space, Lockheed Martin, EnduroSat, Beijing Smart Satellite, INVAP, Indian Space Research Organisation, Airbus, Blue Canyon Technologies, and BAE Systems. These companies compete through advancements in imaging technologies, satellite miniaturization, and cost-efficient launch solutions. Leading firms focus on developing high-resolution sensors, multispectral imaging systems, and AI-driven data analytics to enhance real-time Earth observation capabilities. Strategic partnerships between government space agencies and private enterprises are expanding access to satellite data and services. Manufacturers are emphasizing reusable satellite platforms, lightweight structures, and improved data transmission technologies to enhance mission performance. Increasing collaborations for joint satellite missions and technology transfer are fostering global competitiveness. The entry of small satellite developers and commercial launch providers continues to intensify competition, driving innovation across defense, environmental monitoring, and agricultural applications.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
- Boeing
- Dhruva Space
- Lockheed Martin
- EnduroSat
- Beijing Smart Satellite
- INVAP
- Indian Space Research Organisation
- Airbus
- Blue Canyon Technologies
- BAE Systems
Recent Developments
- In September 2025, Boeing delivered the second spacecraft of its ViaSat-3 series (F2) to launch preparation, built on the 702MP+ platform, featuring all-electric propulsion and a next-generation payload with adaptive, reconfigurable beamforming.
- In August 2025, Lockheed Martin completed environmental testing (thermal vacuum and acoustic) for its first Next-Gen OPIR GEO missile warning satellite designed to monitor infrared signatures for early‐warning applications.
- In 2024, Dhruva Space launched its commercial satellite imagery service, AstraView, which provides access to EO, SAR, RF, and hyperspectral data.
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Orbit, Satellite Mass, Application, End-use and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- The market will expand with rising investments in Earth observation and climate monitoring programs.
- Adoption of AI and machine learning will improve image analysis and data interpretation accuracy.
- Low Earth Orbit satellites will continue to dominate due to lower cost and shorter revisit times.
- Governments will increase collaborations with private firms to enhance space-based observation networks.
- Demand for small and microsatellites will grow in commercial and research applications.
- Defense and security agencies will rely more on remote sensing data for surveillance and intelligence.
- Cloud-based platforms will support faster data processing and global accessibility.
- Miniaturization and reusable launch systems will reduce overall mission costs.
- Environmental monitoring and disaster management will emerge as key growth areas.
- Asia-Pacific will experience strong growth with expanding space programs in China, India, and Japan.




