CHAPTER NO. 1 : GENESIS OF THE MARKET
1.1 Market Prelude – Introduction & Scope
1.2 The Big Picture – Objectives & Vision
1.3 Strategic Edge – Unique Value Proposition
1.4 Stakeholder Compass – Key Beneficiaries
CHAPTER NO. 2 : EXECUTIVE LENS
2.1 Pulse of the Industry – Market Snapshot
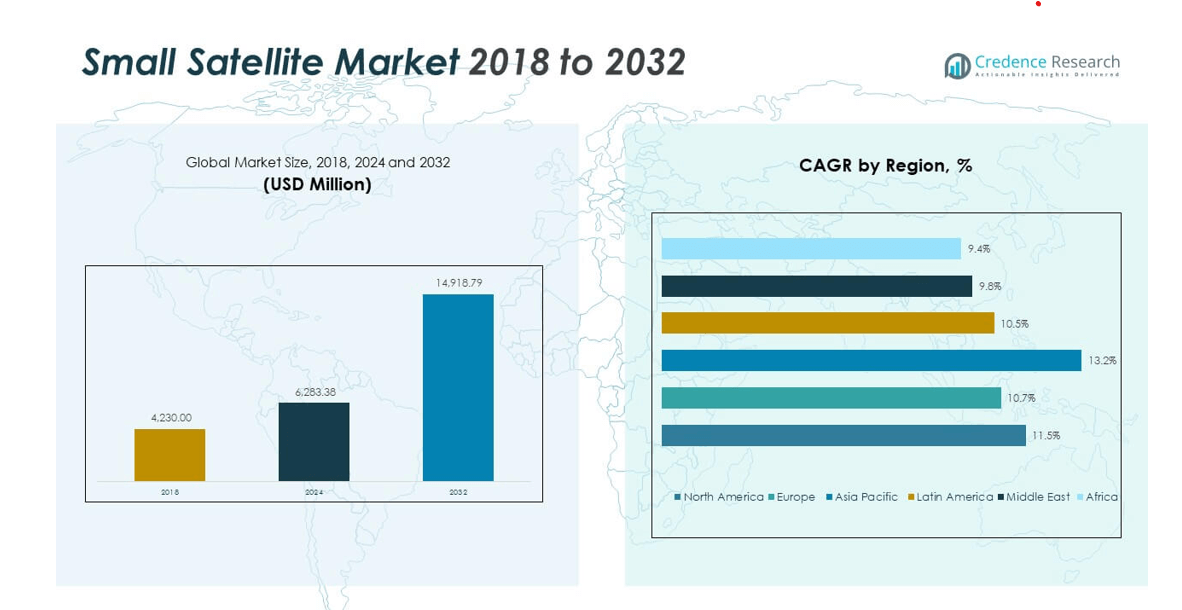
2.2 Growth Arc – Revenue Projections (USD Million)
2.3. Premium Insights – Based on Primary Interviews
CHAPTER NO. 3 : SMALL SATELLITE MARKET FORCES & INDUSTRY PULSE
3.1 Foundations of Change – Market Overview
3.2 Catalysts of Expansion – Key Market Drivers
3.2.1 Momentum Boosters – Growth Triggers
3.2.2 Innovation Fuel – Disruptive Technologies
3.3 Headwinds & Crosswinds – Market Restraints
3.3.1 Regulatory Tides – Compliance Challenges
3.3.2 Economic Frictions – Inflationary Pressures
3.4 Untapped Horizons – Growth Potential & Opportunities
3.5 Strategic Navigation – Industry Frameworks
3.5.1 Market Equilibrium – Porter’s Five Forces
3.5.2 Ecosystem Dynamics – Value Chain Analysis
3.5.3 Macro Forces – PESTEL Breakdown
3.6 Price Trend Analysis
3.6.1 Regional Price Trend
3.6.2 Price Trend by product
CHAPTER NO. 4 : KEY INVESTMENT EPICENTER
4.1 Regional Goldmines – High-Growth Geographies
4.2 Product Frontiers – Lucrative Product Categories
4.3 Application Sweet Spots – Emerging Demand Segments
CHAPTER NO. 5: REVENUE TRAJECTORY & WEALTH MAPPING
5.1 Momentum Metrics – Forecast & Growth Curves
5.2 Regional Revenue Footprint – Market Share Insights
5.3 Segmental Wealth Flow – Subsystem & Application Revenue
CHAPTER NO. 6 : TRADE & COMMERCE ANALYSIS
6.1. Import Analysis by Region
6.1.1. Global Small Satellite Market Import Revenue By Region
6.2. Export Analysis by Region
6.2.1. Global Small Satellite Market Export Revenue By Region
CHAPTER NO. 7 : COMPETITION ANALYSIS
7.1. Company Market Share Analysis
7.1.1. Global Small Satellite Market: Company Market Share
7.2. Global Small Satellite Market Company Revenue Market Share
7.3. Strategic Developments
7.3.1. Acquisitions & Mergers
7.3.2. New Product Launch
7.3.3. Regional Expansion
7.4. Competitive Dashboard
7.5. Company Assessment Metrics, 2024
CHAPTER NO. 8 : SMALL SATELLITE MARKET – BY SUBSYSTEM SEGMENT ANALYSIS
8.1. Small Satellite Market Overview by Subsystem Segment
8.1.1. Small Satellite Market Revenue Share By Subsystem
8.2. Satellite Bus
8.3. Payload
8.4. Solar Panel
8.5. Satellite Antenna
8.6. Others
CHAPTER NO. 9 : SMALL SATELLITE MARKET – BY APPLICATION SEGMENT ANALYSIS
9.1. Small Satellite Market Overview by Application Segment
9.1.1. Small Satellite Market Revenue Share By Application
9.2. Communication
9.3. Earth Observation & Remote Sensing
9.4. Scientific Research
9.5. Education
9.6. Technology
9.7. Others
CHAPTER NO. 10 : SMALL SATELLITE MARKET – BY MASS SEGMENT ANALYSIS
10.1. Small Satellite Market Overview by Mass Segment
10.1.1. Small Satellite Market Revenue Share By Mass
10.2. Small Satellite
10.3. Mini Satellite
10.4. Micro Satellite
10.5. Nano Satellite
10.6. CubeSat
10.7. Others
CHAPTER NO. 11 : SMALL SATELLITE MARKET – BY FREQUENCY SEGMENT ANALYSIS
11.1. Small Satellite Market Overview by Frequency Segment
11.1.1. Small Satellite Market Revenue Share By Frequency
11.2. L-Band
11.3. S-Band
11.4. C-Band
11.5. X-Band
11.6. Ku-Band
11.7. Ka-Band
11.8. Q/V-Band
11.9. HF/VHF/UHF-Band
11.10. Laser/Optical
CHAPTER NO. 12 : SMALL SATELLITE MARKET – BY ORBIT SEGMENT ANALYSIS
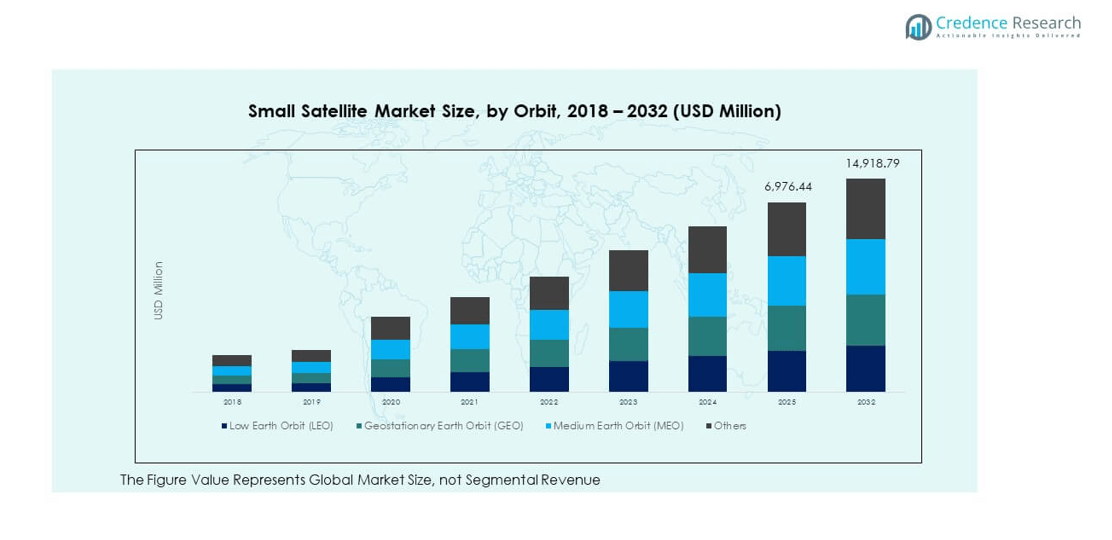
12.1. Small Satellite Market Overview by Orbit Segment
12.1.1. Small Satellite Market Revenue Share By Orbit
12.2. Low Earth Orbit (LEO)
12.3. Geostationary Earth Orbit (GEO)
12.4. Medium Earth Orbit (MEO)
12.5. Others
CHAPTER NO. 13 : SMALL SATELLITE MARKET – REGIONAL ANALYSIS
13.1. Small Satellite Market Overview by Region Segment
13.1.1. Global Small Satellite Market Revenue Share By Region
13.1.2. Regions
13.1.3. Global Small Satellite Market Revenue By Region
13.1.4. Subsystem
13.1.5. Global Small Satellite Market Revenue By Subsystem
13.1.6. Application
13.1.7. Global Small Satellite Market Revenue By Application
13.1.8. Mass
13.1.9. Global Small Satellite Market Revenue By Mass
13.1.10. Frequency
13.1.12. Global Small Satellite Market Revenue By Frequency
13.1.13. Orbit
13.1.14. Global Small Satellite Market Revenue By Orbit
CHAPTER NO. 14 : NORTH AMERICA SMALL SATELLITE MARKET – COUNTRY ANALYSIS
14.1. North America Small Satellite Market Overview by Country Segment
14.1.1. North America Small Satellite Market Revenue Share By Region
14.2. North America
14.2.1. North America Small Satellite Market Revenue By Country
14.2.2. Subsystem
14.2.3. North America Small Satellite Market Revenue By Subsystem
14.2.4. Application
14.2.5. North America Small Satellite Market Revenue By Application
14.2.6. Mass
14.2.7. North America Small Satellite Market Revenue By Mass
14.2.8. Frequency
14.2.9. North America Small Satellite Market Revenue By Frequency
14.2.10. Orbit
14.2.11. North America Small Satellite Market Revenue By Orbit
14.3. U.S.
14.4. Canada
14.5. Mexico
CHAPTER NO. 15 : EUROPE SMALL SATELLITE MARKET – COUNTRY ANALYSIS
15.1. Europe Small Satellite Market Overview by Country Segment
15.1.1. Europe Small Satellite Market Revenue Share By Region
15.2. Europe
15.2.1. Europe Small Satellite Market Revenue By Country
15.2.2. Subsystem
15.2.3. Europe Small Satellite Market Revenue By Subsystem
15.2.4. Application
15.2.5. Europe Small Satellite Market Revenue By Application
15.2.6. Mass
15.2.7. Europe Small Satellite Market Revenue By Mass
15.2.8. Frequency
15.2.9. Europe Small Satellite Market Revenue By Frequency
15.2.10. Orbit
15.2.11. Europe Small Satellite Market Revenue By Orbit
15.3. UK
15.4. France
15.5. Germany
15.6. Italy
15.7. Spain
15.8. Russia
15.9. Rest of Europe
CHAPTER NO. 16 : ASIA PACIFIC SMALL SATELLITE MARKET – COUNTRY ANALYSIS
16.1. Asia Pacific Small Satellite Market Overview by Country Segment
16.1.1. Asia Pacific Small Satellite Market Revenue Share By Region
16.2. Asia Pacific
16.2.1. Asia Pacific Small Satellite Market Revenue By Country
16.2.2. Subsystem
16.2.3. Asia Pacific Small Satellite Market Revenue By Subsystem
16.2.4. Application
16.2.5. Asia Pacific Small Satellite Market Revenue By Application
16.2.6. Mass
16.2.7. Asia Pacific Small Satellite Market Revenue By Mass
16.2.8. Frequency
16.2.9. Asia Pacific Small Satellite Market Revenue By Frequency
16.2.10. Orbit
16.2.11. Asia Pacific Small Satellite Market Revenue By Orbit
16.3. China
16.4. Japan
16.5. South Korea
16.6. India
16.7. Australia
16.8. Southeast Asia
16.9. Rest of Asia Pacific
CHAPTER NO. 17 : LATIN AMERICA SMALL SATELLITE MARKET – COUNTRY ANALYSIS
17.1. Latin America Small Satellite Market Overview by Country Segment
17.1.1. Latin America Small Satellite Market Revenue Share By Region
17.2. Latin America
17.2.1. Latin America Small Satellite Market Revenue By Country
17.2.2. Subsystem
17.2.3. Latin America Small Satellite Market Revenue By Subsystem
17.2.4. Application
17.2.5. Latin America Small Satellite Market Revenue By Application
17.2.6. Mass
17.2.7. Latin America Small Satellite Market Revenue By Mass
17.2.8. Frequency
17.2.9. Latin America Small Satellite Market Revenue By Frequency
17.2.10. Orbit
17.2.11. Latin America Small Satellite Market Revenue By Orbit
17.3. Brazil
17.4. Argentina
17.5. Rest of Latin America
CHAPTER NO. 18 : MIDDLE EAST SMALL SATELLITE MARKET – COUNTRY ANALYSIS
18.1. Middle East Small Satellite Market Overview by Country Segment
18.1.1. Middle East Small Satellite Market Revenue Share By Region
18.2. Middle East
18.2.1. Middle East Small Satellite Market Revenue By Country
18.2.2. Subsystem
18.2.3. Middle East Small Satellite Market Revenue By Subsystem
18.2.4. Application
18.2.5. Middle East Small Satellite Market Revenue By Application
18.2.6. Mass
18.2.7. Middle East Small Satellite Market Revenue By Mass
18.2.8. Frequency
18.2.9. Middle East Small Satellite Market Revenue By Frequency
18.2.10. Orbit
18.2.11. Middle East Small Satellite Market Revenue By Orbit
18.3. GCC Countries
18.4. Israel
18.5. Turkey
18.6. Rest of Middle East
CHAPTER NO. 19 : AFRICA SMALL SATELLITE MARKET – COUNTRY ANALYSIS
19.1. Africa Small Satellite Market Overview by Country Segment
19.1.1. Africa Small Satellite Market Revenue Share By Region
19.2. Africa
19.2.1. Africa Small Satellite Market Revenue By Country
19.2.2. Subsystem
19.2.3. Africa Small Satellite Market Revenue By Subsystem
19.2.4. Application
19.2.5. Africa Small Satellite Market Revenue By Application
19.2.6. Mass
19.2.7. Africa Small Satellite Market Revenue By Mass
19.2.8. Frequency
19.2.9. Africa Small Satellite Market Revenue By Frequency
19.2.10. Orbit
19.2.11. Africa Small Satellite Market Revenue By Orbit
19.3. South Africa
19.4. Egypt
19.5. Rest of Africa
CHAPTER NO. 20 : COMPANY PROFILES
20.1. Airbus SE (Netherlands)
20.1.1. Company Overview
20.1.2. Product Portfolio
20.1.3. Financial Overview
20.1.4. Recent Developments
20.1.5. Growth Strategy
20.1.6. SWOT Analysis
20.2. SpaceMobile
20.3. Exolaunch
20.4. Boeing Co. (US)
20.5. Lockheed Martin Corporation (US)
20.6. Northrop Grumman Corporation (US)
20.7. Planet Labs Inc. (US)
20.8. Spire Global Inc. (US)
20.9. Thales Alenia Space (France)
20.10. Ball Corporation (US)
20.11. Sierra Nevada Corporation (US)
20.12. Maxar Technologies Inc. (Canada)
20.13. GomSpace Group AB (Denmark)
20.14. OneWeb Satellites (US)
20.15. Kepler Communications (Canada)
20.16. OHB SE (Germany)
20.17. Axelspace Corporation (Japan)