Market Overview
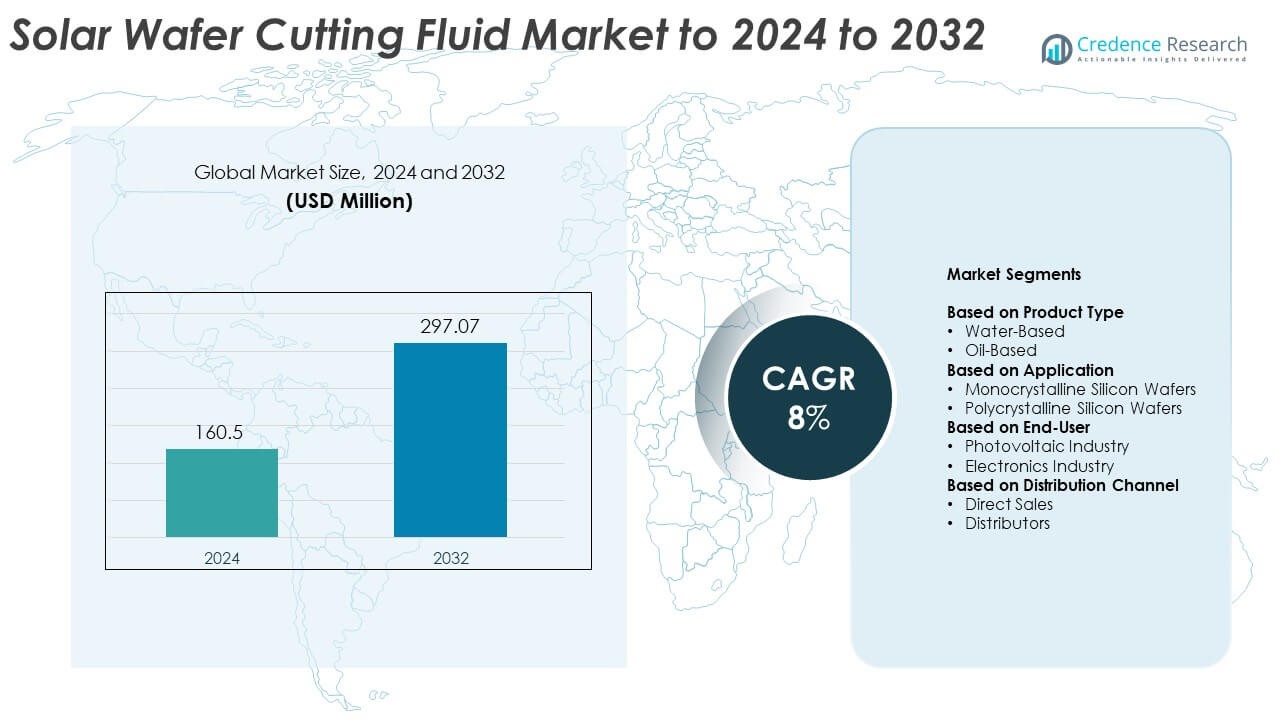
Solar wafer cutting fluid market size was valued USD 160.5 million in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 297.07 million by 2032, at a CAGR of 8% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Solar Wafer Cutting Fluid Market Size 2024 |
USD 160.5 Million |
| Solar Wafer Cutting Fluid Market, CAGR |
8% |
| Solar Wafer Cutting Fluid Market Size 2032 |
USD 297.07 Million |
Top players in the solar wafer cutting fluid market include Huntsman Corporation, BASF SE, Fujimi Incorporated, Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation, Exxon Mobil Corporation, Henkel AG & Co. KGaA, KCC Corporation, Linde plc, Dow Inc., and Applied Materials Inc., each strengthening capabilities through advanced formulations that improve wafer yield and cutting efficiency. These companies focus on water-based, low-contamination fluids that support high-precision monocrystalline wafer production. Asia Pacific remained the leading region in 2024 with about 46% share, driven by large-scale solar manufacturing hubs in China, Japan, South Korea, and Taiwan. North America and Europe followed with growing adoption of high-efficiency wafer slicing technologies.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Insights
- The solar wafer cutting fluid market reached USD 160.5 million in 2024 and is projected to hit USD 297.07 million by 2032, expanding at an 8% CAGR.
- Market growth is driven by rising monocrystalline wafer production, which increases demand for high-performance water-based fluids that reduce breakage and enhance cutting precision.
- Key trends include rapid adoption of large-format wafers and growing preference for low-contamination, eco-friendly formulations that support advanced cell technologies.
- Competition intensifies as major suppliers focus on long-life fluids, strong cooling performance, and deeper collaboration with wafer manufacturers to improve process efficiency.
- Asia Pacific held about 46% share in 2024, driven by massive solar manufacturing capacity, while North America and Europe expanded steadily; water-based fluids remained dominant with nearly 63% share due to their cleaner processing advantages.
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Product Type
Water-based fluids led the product type segment in 2024 with about 63% share due to their strong cooling ability and lower contamination risk during high-precision wafer slicing. Manufacturers favored water-based formulations because these fluids reduce micro-cracks, support smoother kerf profiles, and help extend wire-saw life. Demand increased as solar cell producers shifted toward cleaner cutting environments to meet higher efficiency targets. Oil-based fluids maintained steady use in legacy wafer lines that required enhanced lubrication for thicker wafers.
- For insrance, Market analysis reports estimate that Fujimi Corporation was a leading supplier in the global silicon wafer CMP slurry market in 2023, holding a significant market share along with other top manufacturers like Entegris (CMC Materials) and DuPont. These top three manufacturers collectively hold an estimated share of over 80% of the market.
By Application
Monocrystalline silicon wafers dominated the application segment in 2024 with nearly 58% share, supported by rapid adoption of high-efficiency PERC, TOPCon, and heterojunction cells. Producers preferred cutting fluids optimized for monocrystalline wafers because they enhance edge quality and reduce slurry consumption. Growth accelerated as major module makers expanded mono-based capacity to meet rising demand for premium rooftop and utility installations. Polycrystalline wafers saw slower growth due to the global shift toward higher-performance mono technologies.
- For instance, LONGi targets monocrystalline wafer production capacity of 200 gigawatts within three years.
By End-User
The photovoltaic industry led the end-user segment in 2024 with around 72% share, driven by strong expansion in global solar module manufacturing. PV manufacturers adopted advanced cutting fluids to support tighter wafer tolerances, higher throughput, and reduced breakage rates in large-format G12 and M10 wafer production. Demand rose as producers focused on lowering operational costs and improving wafer surface integrity for next-generation solar cells. The electronics industry contributed stable revenue from semiconductor slicing and specialty silicon applications.
Key Growth Drivers
Expansion of Solar PV Manufacturing Capacity
Global solar PV manufacturing grew quickly as countries increased investments in utility-scale and rooftop projects. Producers scaled up monocrystalline wafer output, which increased the need for high-performance cutting fluids that reduce micro-cracks and improve wafer yield. The push toward larger wafer formats, such as M10 and G12, also raised demand for fluids that support stable thermal control and precise kerf quality. Rising deployment of high-efficiency cell technologies strengthened the market because cutting fluids help maintain consistent wafer surfaces during high-speed slicing.
- For instance, Trina Solar reported 55 gigawatts (GW) wafer capacity, 75 gigawatts (GW) cell capacity, and 95 gigawatts (GW) module capacity at the end of 2023, as detailed in its 2023 Annual Report Summary.
Shift Toward High-Efficiency Solar Technologies
The move from polycrystalline to mono-based technologies raised demand for advanced cutting fluids that enhance wafer smoothness and reduce defects. Higher adoption of TOPCon, PERC, and heterojunction cells required cleaner cutting environments and better cooling performance, prompting manufacturers to invest in upgraded formulations. These fluids helped maintain structural integrity under tighter tolerances, supporting higher conversion efficiency. Strong R&D efforts from solar wafer producers supported steady market growth as innovation remained essential for competitive module output.
- For instance, JinkoSolar continues to upgrade its production lines and aims to operate between 40 gigawatts (GW) and 50 GW of high-efficiency, third-generation n-type TOPCon module capacity by the end of 2025, a significant portion of its total module capacity target of 130 GW.
Rising Focus on Production Cost Reduction
Producers targeted lower operating expenses while expanding manufacturing lines, which increased the need for cutting fluids that extend wire life and reduce slurry waste. Improved formulations offered longer fluid cycles, reduced equipment wear, and minimized wafer breakage, helping cut per-wafer costs. Manufacturers also favored fluids that supported automated recycling systems to reduce consumption. This cost-driven shift supported strong adoption across major wafer facilities, especially in regions expanding large-scale, price-sensitive solar module production.
Key Trends & Opportunities
Transition Toward Water-Based, Low-Contamination Formulations
Manufacturers increased the use of water-based cutting fluids because these formulations reduce impurities and support advanced wafer slicing requirements. Cleaner chemistries lowered defect rates and improved surface texture, which aligned with the growing need for higher power conversion efficiency. Producers also adopted eco-friendly and low-VOC variants to meet stricter sustainability targets. This trend created strong opportunities for suppliers offering formulations optimized for next-generation wafer and wire-saw technologies.
- For instance, Wacker polysilicon shows dopant levels as low as 5 parts per trillion atoms.
Integration of Automated Fluid Recycling Systems
Wafer lines increasingly installed automated recycling and filtration units that extend fluid life and reduce waste. These systems supported lower operating costs and improved production continuity, creating a new opportunity for cutting fluid suppliers to offer compatible long-life formulations. Automation also helped stabilize fluid performance under high-volume wafer slicing, meeting the needs of advanced mono wafer factories. Growing use of digital monitoring for viscosity, temperature, and particle load strengthened this trend across leading PV hubs.
- For instance, HighQ-Factory’s slurry recycling module recycles 1.7 cubic meters of water per hour.
Growth in Large-Format Wafer Production
The shift toward larger wafer sizes created a need for fluids with stronger cooling properties and improved edge stability. As manufacturers adopted M10 and G12 formats, cutting fluids that supported uniform slicing and minimized thermal stress gained traction. This transition offered suppliers a chance to introduce fluids tailored for high-tension wire saws and faster cycle speeds. Expanding demand for high-performance modules strengthened opportunities for innovation in advanced fluid formulations.
Key Challenges
Stringent Quality Requirements for Advanced Cell Technologies
The rise of TOPCon and heterojunction cells increased the need for extremely consistent wafer surfaces. Cutting fluids must maintain precise thermal control and lubrication under narrow tolerance limits, which increased the burden on suppliers to deliver highly stable formulations. Any inconsistency can lead to micro-cracks, kerf deviation, or yield loss. Meeting these strict quality demands remained a major challenge as wafer lines moved toward higher-speed, high-precision slicing.
Volatile Raw Material Supply and Cost Pressure
Producers faced fluctuations in key chemical inputs used in advanced cutting fluids, which increased pricing pressure and supply uncertainty. Manufacturers required stable long-term supply chains to support continuous wafer production, yet raw material volatility disrupted planning cycles. These cost swings challenged suppliers attempting to balance performance, reliability, and affordability. Competitive pricing in the solar industry intensified these pressures, making raw material stability a persistent market constraint.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America held around 22% share in 2024 as demand increased from expanding solar manufacturing activities and growing investments in advanced wafer processing technologies. The United States supported market growth through rising adoption of monocrystalline wafer production for domestic module assembly. Manufacturers preferred high-performance water-based fluids to improve wafer quality and reduce operational costs. Supportive clean-energy policies and plans for reshoring solar supply chains further strengthened regional consumption. Canada contributed steady demand through specialty electronics applications, although growth remained slower than large-scale PV capacity expansion in the United States.
Europe
Europe accounted for nearly 19% share in 2024, supported by strong demand from advanced semiconductor and photovoltaic industries. Germany, France, and Italy expanded production of high-efficiency solar modules, increasing the need for fluids that ensure precise wafer slicing under strict quality standards. European producers emphasized sustainable manufacturing, which raised adoption of low-contamination, water-based formulations. Ongoing investments in heterojunction and TOPCon cell technologies also strengthened market growth. The region benefited from mature R&D capabilities and strong environmental regulations that encouraged the use of high-purity cutting fluids.
Asia Pacific
Asia Pacific dominated the market with about 46% share in 2024, driven by massive wafer production capacity in China, Japan, South Korea, and Taiwan. China remained the global hub for monocrystalline and large-format wafer manufacturing, which boosted high-volume demand for advanced cutting fluids. Producers adopted formulations that deliver improved cooling and reduced breakage rates during high-speed slicing. India also expanded PV manufacturing under national solar programs, adding to regional growth. Strong supply chains, competitive production costs, and rapid technology upgrades kept Asia Pacific the leading contributor.
Latin America
Latin America captured close to 7% share in 2024 as solar adoption expanded in Brazil, Mexico, and Chile. Growing interest in domestic PV manufacturing and regional investment in renewable energy projects supported steady consumption of wafer cutting fluids. Manufacturers focused on improving wafer yields for modules assembled locally. Demand also rose from electronics production in Mexico that required precision-grade silicon components. Although regional output remained smaller than major Asian markets, increasing policy support for renewable energy encouraged gradual market expansion.
Middle East and Africa
Middle East and Africa held around 6% share in 2024, driven by expanding solar infrastructure across the United Arab Emirates, Saudi Arabia, and South Africa. Investments in regional module assembly plants and interest in developing wafer processing capabilities supported emerging demand for cutting fluids. Growth came from efforts to diversify energy sources and strengthen renewable manufacturing ecosystems. The region adopted high-quality formulations to support early-stage production lines focused on premium solar applications. However, limited large-scale wafer production kept overall consumption moderate compared with other regions.
Market Segmentations:
By Product Type
By Application
- Monocrystalline Silicon Wafers
- Polycrystalline Silicon Wafers
By End-User
- Photovoltaic Industry
- Electronics Industry
By Distribution Channel
- Direct Sales
- Distributors
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape of the solar wafer cutting fluid market features leading participants such as Huntsman Corporation, BASF SE, Fujimi Incorporated, Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation, Exxon Mobil Corporation, Henkel AG & Co. KGaA, KCC Corporation, Linde plc, Dow Inc., and Applied Materials Inc. These companies strengthen their position through innovations in water-based and low-contamination formulations that support advanced monocrystalline wafer production. Manufacturers focus on improving cooling efficiency, reducing breakage rates, and extending wire-saw lifespan to meet the needs of high-speed slicing lines. Many competitors invest in large-scale R&D programs to deliver stable chemistries compatible with next-generation solar cell technologies, including TOPCon and heterojunction. Strategic collaborations with wafer producers help optimize process performance and reduce slurry consumption. Suppliers also expand regional distribution and technical support networks to address growing PV manufacturing hubs across Asia Pacific, North America, and Europe. Sustainability-aligned product development and long-life fluids further intensify market competition.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
- Huntsman Corporation
- BASF SE
- Fujimi Incorporated
- Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation
- Exxon Mobil Corporation
- Henkel AG & Co. KGaA
- KCC Corporation
- Linde plc
- Dow Inc.
- Applied Materials Inc.
Recent Developments
- In 2025, Dow launched DOWSIL EG-4175 silicone gel for high-voltage power electronics in renewable energy and EVs. The gel improves insulation and thermal management in inverters and power modules used with solar-generated power and wafer-based power devices.
- In 2024, BASF and Chinese PV manufacturer Worldlight introduced a polyurethane frame for solar panels to replace aluminum, reducing weight and carbon footprint. This strengthens BASF’s role in photovoltaic components and related chemicals used along the solar wafer value chain.
- In 2024, Henkel introduced a new high-thermal-performance capillary underfill for advanced semiconductor packaging targeting AI and high-power devices.
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Product Type, Application, End-User, Distribution Channel and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- The market will grow as global solar manufacturing capacity expands across major PV hubs.
- Demand will rise for water-based fluids that support cleaner and low-defect wafer slicing.
- Large-format wafer production will increase the need for advanced cooling and stability performance.
- Automation in wafer lines will push adoption of long-life fluids compatible with recycling systems.
- Manufacturers will invest in formulations that reduce breakage and improve wafer surface quality.
- High-efficiency cell technologies will require cutting fluids with tighter thermal and lubrication control.
- Sustainability goals will shift producers toward low-VOC and eco-friendly chemicals.
- AI-driven monitoring systems will enhance fluid optimization and process accuracy.
- Supply chains will localize as countries strengthen domestic solar manufacturing capabilities.
- Competition will intensify as suppliers develop specialized fluids for next-generation wafer technologies.




