Market Overview
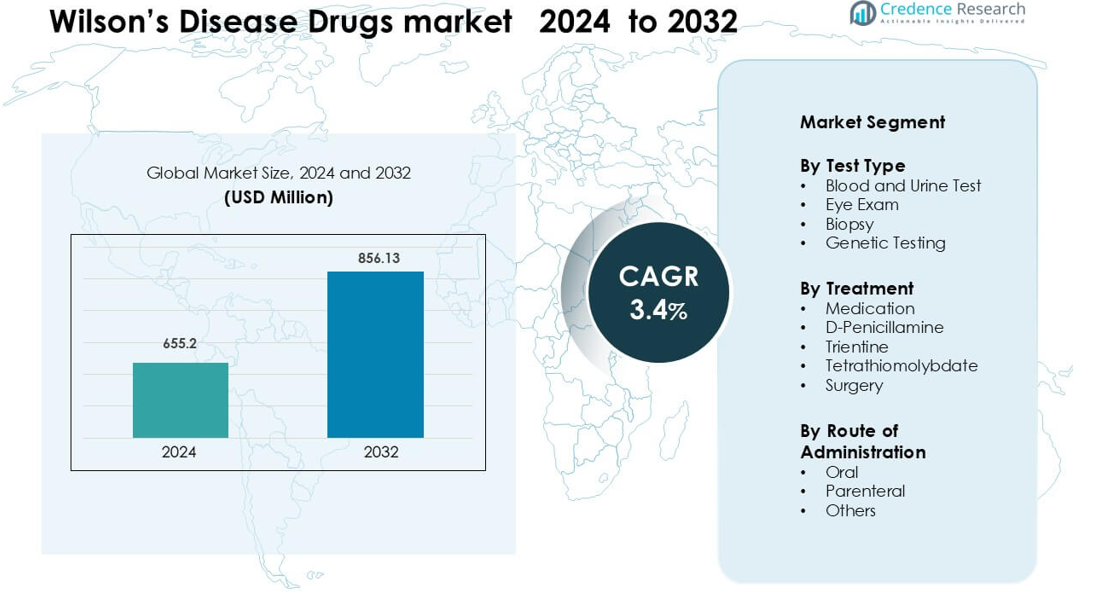
Wilson’s Disease Drugs market was valued at USD 655.2 million in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 856.13 million by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 3.4 % during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Wilson’s Disease Drugs Market Size 2024 |
USD 655.2 million |
| Wilson’s Disease Drugs Market, CAGR |
3.4% |
| Wilson’s Disease Drugs Market Size 2032 |
USD 856.13 million |
North America leads the Wilson’s Disease Drugs market with 42% share in 2024, supported by strong diagnostic capacity, established rare-disease programs, and broad access to chelating and maintenance therapies. Key players shaping the competitive landscape include Novartis, Bausch Health, Alnylam Pharmaceuticals, Sobi, Horizon Therapeutics, Mylan, Pfizer, Wilson Therapeutics, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Teva Pharmaceutical Industries. These companies compete through safer chelators, improved zinc formulations, and advancing next-generation options such as tetrathiomolybdate and gene-targeted therapies. Their focus on clinical partnerships, long-term adherence solutions, and expanded regional distribution reinforces market leadership and supports steady treatment uptake across both adult and pediatric populations.
Market Insights
- The Wilson’s Disease Drugs market was valued at USD 655.2 million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 856.13 million by 2032, growing at a 3.4% CAGR during the forecast period.
- Demand rises as diagnosis rates improve and early screening expands, with blood and urine tests holding about 46% share due to their wide clinical use and fast copper-level detection.
- New therapy research, including safer chelators and metabolic pathway innovations, strengthens market traction as companies explore advanced formulations and long-term adherence solutions.
- Competition intensifies as firms enhance drug tolerability and expand global access, while high treatment costs and limited reimbursement in many countries restrict wider uptake.
- North America leads with 42% share, followed by Europe at 29%, supported by strong diagnostic ecosystems and rare-disease programs, while Asia Pacific grows steadily with rising testing access and expanding specialist care.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Segentation Analysis:
By Test Type
Blood and urine tests lead this segment with around 46% share in 2024, driven by their role in detecting abnormal copper levels and ceruloplasmin concentration. Clinicians use these tests as the first diagnostic step because they offer fast results, low cost, and broad availability across hospitals and specialty centers. Eye exams and biopsies remain essential for confirmatory checks, especially when Kayser-Fleischer rings or liver injury are suspected. Genetic testing grows steadily as families seek early detection, but adoption remains lower due to higher cost and limited testing access in several regions.
- For instance, a standard 24-hour urinary copper test in Wilson’s disease often shows excretion levels exceeding 100 µg per 24 hours in adults, which aligns with widely used cutoff thresholds for diagnosis.
By Treatment
Medication dominates this segment with nearly 58% share in 2024, supported by widespread use of chelating agents and zinc therapy for long-term disease management. D-Penicillamine and Trientine remain the primary treatment choices because they effectively promote copper excretion and have long clinical use histories. Tetrathiomolybdate gains traction in clinical programs due to its faster copper-binding capability, especially in neurological cases. Surgery, including liver transplantation, holds a smaller share because it is reserved for advanced cases with severe hepatic failure or non-response to drug therapy.
- For instance, in a large long-term study of 192 Wilson disease patients, baseline 24-hour urinary copper was ~ 466 µg/day in hepatic cases, and after 1–2 years of chelation therapy (penicillamine or trientine), there was a significant drop in both basal and challenge-excreted copper.
By Route of Administration
Oral administration leads this category with about 72% share in 2024, driven by strong patient preference and the dominance of oral chelating agents such as D-Penicillamine, Trientine, and zinc formulations. Oral therapy supports long-term compliance, which is essential for chronic management of copper overload. Parenteral administration records moderate use in acute cases or when patients cannot tolerate oral medicines. Other routes hold minimal share due to limited product availability and the chronic nature of Wilson’s Disease, which favors daily oral dosing for most treatment plans.
Key Growth Drivers
Rising Global Diagnosis Rates of Wilson’s Disease
Improved awareness, wider screening programs, and increased physician training continue to raise diagnosis rates of Wilson’s Disease, which directly drives demand for treatment drugs. Hospitals and specialty centers now perform copper metabolism tests more routinely for unexplained liver or neurological symptoms, allowing earlier detection and immediate treatment initiation. The availability of ceruloplasmin tests, 24-hour urinary copper tests, and genetic panels in both developed and emerging economies strengthens case identification across broader age groups. As families with known ATP7B mutations undergo preventive testing, diagnosed patient pools rise steadily. This improved diagnostic ecosystem increases reliance on first-line chelators and zinc therapy for lifelong management. Early detection also reduces the number of patients progressing to end-stage liver complications, increasing long-term therapy duration and expanding the treatment base. Overall, better diagnosis pipelines significantly expand patient volumes and fuel steady growth for Wilson’s Disease drug manufacturers.
- For instance, in Sardinia a region with a known founder effect population-based genetic studies have identified a Wilson’s disease prevalence reaching 36.6 per 100,000, underscoring how targeted familial or regional screening can unmask many previously unrecognized cases.
Growing Adoption of Safer and More Tolerable Chelating Agents
Safer and better-tolerated chelating drugs continue to strengthen market expansion as clinicians shift toward improved treatment options. D-Penicillamine has long served as a first-line therapy, but rising awareness of side effects such as hypersensitivity and nephrotoxicity pushes many specialists to adopt Trientine, which offers a more favorable safety profile for long-term use. Patients with neurological presentations also show strong response to alternative chelators and zinc formulations that reduce copper absorption rather than provoke redistribution effects. Pharmaceutical companies are advancing new formulations designed to minimize adverse reactions and improve adherence, including controlled-release tablets and lower-frequency dosing options. Better tolerability reduces treatment discontinuation rates and helps patients remain on long-term therapy, which is essential for disease control. As clinical guidelines increasingly endorse these improved agents, adoption widens across global markets, reinforcing demand throughout treatment pathways.
- For instance, a large pediatric cohort study found that among 50 treatment courses with trientine, only 2 (4%) were discontinued due to adverse effects, versus 16 out of 37 (45%) for D-penicillamine.
Expansion of Genetic Testing and Family Screening Programs
The rapid expansion of genetic testing and family screening programs acts as a major growth catalyst for Wilson’s Disease drugs. ATP7B mutation testing is now more accessible through hospital labs, private diagnostics, and direct-to-consumer genetic services, helping identify presymptomatic carriers and early-stage patients. When one affected individual is diagnosed, entire families often undergo screening, increasing the number of confirmed cases requiring long-term management. Earlier diagnosis through genetic routes encourages early intervention with zinc therapy or mild chelators, reducing disease progression and increasing medication longevity. Nations with improved reimbursement for rare-disease genetic testing show stronger increases in case identification, supporting downstream medication demand. Genetic screening also benefits pediatric cases, where early treatment leads to better outcomes and long-term therapy adherence. As genetic infrastructure expands, earlier detection becomes more common, sustaining robust market demand over the forecast period.
Key Trends & Opportunities
Advancements in Novel Therapies and Research Pipelines
Research and development in Wilson’s Disease is accelerating, creating major opportunities for new therapeutics beyond conventional chelators. Several companies are exploring next-generation copper-binding agents, neuroprotective treatments, and metabolic stabilizers that can address neurological complications more effectively. Tetrathiomolybdate continues to draw interest for its rapid copper-binding capabilities and potential to reduce neurologic worsening during initial treatment. Gene therapy also emerges as a long-term opportunity, aiming to correct ATP7B mutations and reduce dependence on lifelong drug therapy. Expanded clinical trial activity across North America, Europe, and Asia is attracting investment in rare-disease research, supporting a more diverse future treatment landscape. As new mechanisms enter advanced trial phases, the market is expected to shift toward more personalized and targeted therapeutic approaches.
- For instance, Wilson Therapeutics AB’s lead molecule, bis-choline tetrathiomolybdate (WTX101), in a Phase 2 open-label study reduced non–ceruloplasmin-bound copper (NCC) to normal levels (≤ 2.3 µmol/L) or achieved at least a 25% reduction in 71% (20 out of 28) of patients by week 24.
Increasing Focus on Patient Adherence and Long-Term Disease Management
Long-term adherence is crucial in Wilson’s Disease because patients require lifelong treatment to maintain copper balance. This creates opportunities for improved drug formulations, easier dosing schedules, and patient-support programs. Companies are developing once-daily controlled-release Trientine and zinc formulations that simplify dosing and reduce pill burden. Digital adherence tools, including medication reminder apps and telehealth follow-ups, are gaining traction among younger patients and caregivers managing chronic therapy. Healthcare providers also promote structured monitoring through periodic copper tests, which strengthens treatment continuity. Better adherence solutions reduce disease fluctuations, preventing relapses and neurological deterioration. As patient-support ecosystems improve, long-term adherence rises, driving sustainable demand for Wilson’s Disease therapies.
- For instance, a prospective pilot study of once-daily trientine (15 mg/kg) in 8 stable Wilson’s disease patients showed a mean 24-hour urinary copper excretion of 313.4 ± 191.7 µg at 12 months, with no treatment stoppages or safety-related discontinuations, suggesting that simplifying to once-daily dosing may improve adherence.
Key Challenges
High Treatment Costs and Limited Reimbursement in Many Regions
High drug costs remain a major barrier to widespread access, especially in low- and middle-income regions where reimbursement for rare-disease treatment is limited. Chelating agents, especially newer formulations, often carry premium prices due to complex manufacturing requirements and orphan-drug status. Patients in regions without strong insurance systems may struggle to maintain long-term therapy, increasing the risk of disease progression. Delayed reimbursement approvals and limited inclusion of rare-disease drugs in public health programs further restrict accessibility. This financial burden creates significant disparities in treatment continuity and adoption, posing a major restraint on global market growth.
Shortage of Specialists and Delayed Clinical Recognition
Wilson’s Disease often presents with non-specific symptoms such as fatigue, psychiatric changes, or mild liver abnormalities, leading to misdiagnosis and treatment delays. Many regions face shortages of hepatologists, neurologists, and metabolic specialists trained to identify the early signs of copper overload. Limited awareness among general practitioners further contributes to delayed care, especially in rural areas. Late diagnosis often results in advanced liver disease or severe neurological complications, increasing treatment complexity and reducing drug therapy effectiveness. This diagnostic challenge restricts early therapeutic intervention and limits the potential patient pool that benefits from long-term drug therapy, slowing market penetration.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America holds the largest share of the Wilson’s Disease Drugs market at around 42% in 2024, driven by strong diagnostic infrastructure and early access to specialty care. Hospitals and clinics rely on established copper testing protocols, genetic screening programs, and structured treatment guidelines to support rapid diagnosis. High adoption of Trientine and D-Penicillamine strengthens long-term therapy demand, while growing clinical trial activity increases awareness among physicians. Favorable reimbursement and strong rare-disease support frameworks also help expand patient access. Increasing family screening initiatives continue to boost treatment volumes across the United States and Canada.
Europe
Europe accounts for roughly 29% share in 2024, supported by advanced hepatology centers, structured referral networks, and broad access to genetic testing. Countries such as Germany, France, and the UK maintain strong awareness programs for early detection of Wilson’s Disease, which increases long-term therapy uptake. The region shows high use of zinc-based maintenance therapy and steady adoption of safer chelators in pediatric and adult populations. Regulatory encouragement for rare-disease drug development also supports clinical innovation. Growing emphasis on early neurological management and improved monitoring practices further boosts market growth across Europe.
Asia Pacific
Asia Pacific holds an estimated 21% share in 2024, driven by rising diagnosis rates in China, Japan, South Korea, and India. Expanding access to genetic testing and greater clinical focus on liver disorders increase identification of Wilson’s Disease cases. Japan and South Korea show strong adoption of zinc therapy and chelating agents due to structured rare-disease programs, while China records rising demand linked to population size and improving healthcare capacity. Awareness campaigns targeting pediatric liver disorders and neurological symptoms support early intervention. Growing specialist training and improved laboratory capabilities continue to expand treatment uptake.
Latin America
Latin America represents about 5% share in 2024, influenced by growing access to hepatology care and gradual improvements in diagnostic capabilities. Brazil, Mexico, and Argentina lead adoption due to improved testing infrastructure and better availability of copper-modulating drugs. However, delayed diagnosis remains common because many regions lack specialist access and structured screening programs. Limited reimbursement slows uptake of newer, safer chelators, increasing reliance on older therapies. Growing investment in rare-disease awareness campaigns and expanding private healthcare access are expected to support modest growth across the region over the coming years.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region accounts for nearly 3% share in 2024, constrained by limited specialist availability and slower adoption of advanced diagnostic methods. Wealthier Gulf countries, including Saudi Arabia and the UAE, show better access to chelating agents and zinc therapy due to improved healthcare infrastructure. In contrast, much of Africa faces challenges such as underdiagnosis, minimal genetic testing access, and inconsistent treatment availability. Growing investment in rare-disease programs, rising medical tourism, and increased collaborations with international health institutions gradually improve diagnosis and treatment access across select markets.
Market Segmentations:
By Test Type
- Blood and Urine Test
- Eye Exam
- Biopsy
- Genetic Testing
By Treatment
- Medication
- D-Penicillamine
- Trientine
- Tetrathiomolybdate
- Surgery
By Route of Administration
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
The Wilson’s Disease Drugs market features a concentrated competitive landscape shaped by global pharmaceutical companies advancing treatment options for lifelong copper management. Key players such as Novartis, Bausch Health, Alnylam Pharmaceuticals, Sobi, Horizon Therapeutics, Mylan, Pfizer, Wilson Therapeutics, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Teva Pharmaceutical Industries drive innovation through chelating agents, zinc-based therapies, and emerging metabolic and genetic solutions. Manufacturers compete by improving safety profiles, reducing side effects, and enhancing long-term adherence through improved formulations. Several companies invest in next-generation candidates such as tetrathiomolybdate and gene-therapy research aimed at correcting ATP7B mutations, expanding the future treatment pathway. Market leaders also strengthen distribution networks to expand access in underserved regions with historically low diagnosis rates. Clinical partnerships with hepatology centers and rare-disease foundations further support trial participation and physician education. As regulatory agencies promote orphan-drug development, competition increases around differentiated therapies and long-term management strategies.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
- Bristol-Myers Squibb (US)
- Sobi (SE)
- Novartis (CH)
- Horizon Therapeutics (IE)
- Wilson Therapeutics (SE)
- Mylan (US)
- Alnylam Pharmaceuticals (US)
- Teva Pharmaceutical Industries (IL)
- Bausch Health
- Pfizer
Recent Developments
- In 2025, Bausch Health completed the acquisition of DURECT Corporation, expanding its hepatology portfolio.
- In September 2024, Prime Medicine confirmed it would receive $110 million upfront from BMS in that collaboration.
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on TestType, Treatment, Route of Administration and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- The market will expand as early diagnosis increases through wider copper testing and genetic screening.
- Safer and more tolerable chelating agents will gain stronger adoption across global treatment pathways.
- Gene-therapy research will advance and create long-term opportunities for disease-modifying solutions.
- Zinc-based maintenance therapy will remain essential as more patients begin lifelong management earlier.
- Digital adherence tools will support better long-term treatment compliance in adult and pediatric cases.
- Clinical trials for next-generation copper-binding agents will accelerate across major regions.
- Access will improve in emerging markets as specialist training and diagnostic capacity expand.
- Reimbursement policies for rare-disease drugs will gradually strengthen in several countries.
- Pediatric diagnosis rates will rise as family screening programs grow across global healthcare systems.
- Companies will invest more in patient-support programs to improve monitoring and long-term therapy outcomes.




