Market Overview:
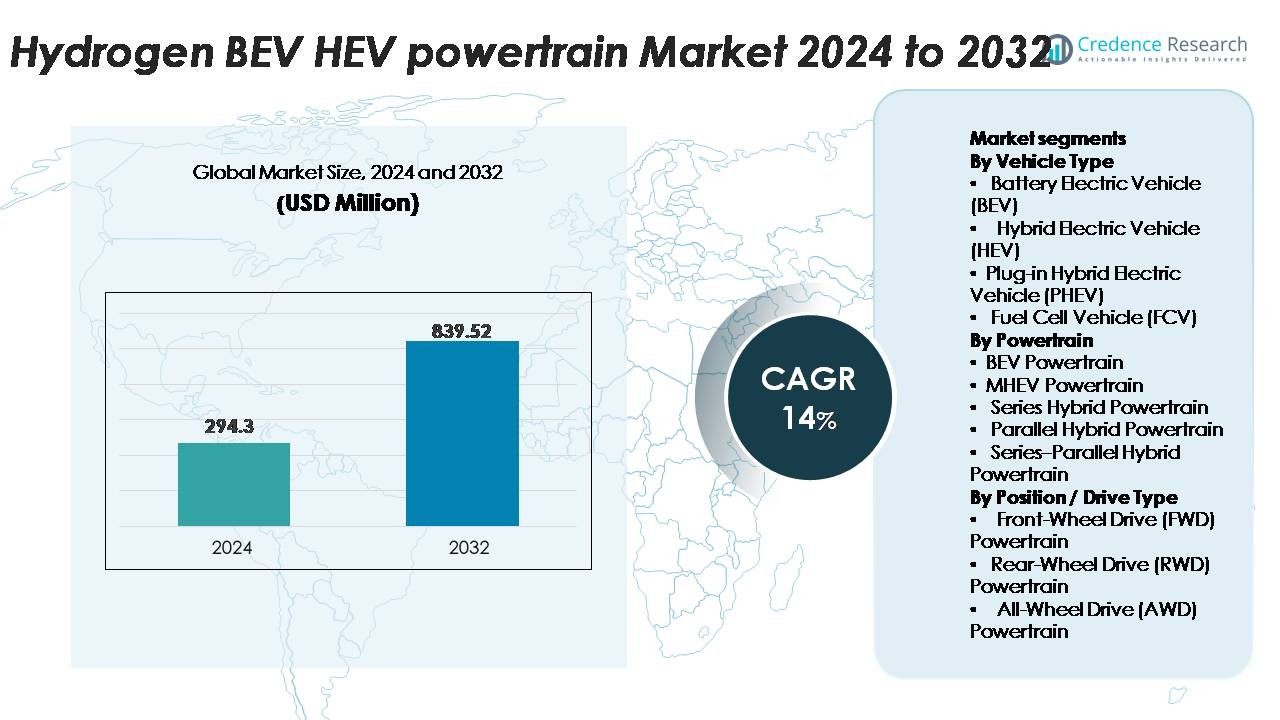
The global Hydrogen BEV–HEV Powertrain Market was valued at USD 294.3 million in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 839.52 million by 2032, registering a CAGR of 14% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Hydrogen BEV–HEV Powertrain Market Size 2024 |
USD 294.3 Million |
| Hydrogen BEV–HEV Powertrain Market, CAGR |
14% |
| Hydrogen BEV–HEV Powertrain Market Size 2032 |
USD 839.52 Million |
The hydrogen BEV–HEV powertrain market is shaped by strong participation from global leaders such as ZF Friedrichshafen, Bosch, Continental AG, BorgWarner, Mitsubishi Electric, Denso Corporation, Cummins Inc., Ballard Power Systems, Magna International, Hitachi, BAE Systems, Knorr-Bremse, Aisin Seiki, FEV, JATCO, Punch Powertrain, Magneti Marelli, and The Voith Group, all advancing integrated electric-hydrogen propulsion technologies. These companies focus on high-efficiency e-motors, advanced inverters, durable fuel-cell stacks, and modular hybrid architectures to support commercial and passenger applications. Europe leads the market with approximately 32% share, driven by strict emission regulations and rapid hydrogen-refueling infrastructure expansion, followed by Asia-Pacific at 30% and North America at 28%, each supported by national hydrogen strategies and strong OEM–energy sector partnerships.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Insights:
- The hydrogen BEV–HEV powertrain market was valued at USD 294.3 million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 839.52 million by 2032, registering a 14% CAGR, supported by accelerating clean-mobility commitments across major automotive regions.
- Market growth is driven by rising demand for zero-emission transportation, expansion of hydrogen corridors, and increasing adoption in commercial fleets requiring long range, fast refueling, and high load capacity. BEV powertrains remain the largest segment, while FWD architectures dominate due to cost efficiency and compact packaging.
- Key trends include the advancement of fuel-cell durability, high-voltage e-drive integration, predictive energy-management software, and modular hybrid platforms enabling scalability across passenger and heavy-duty vehicles.
- Competition intensifies as global players such as Bosch, ZF, Continental, BorgWarner, Denso, Cummins, and Ballard invest in next-generation motors, inverters, and hydrogen storage systems, although high system costs and limited refueling infrastructure continue to restrain widespread adoption.
- Regionally, Europe leads with 32%, followed by Asia-Pacific at 30% and North America at 28%, creating concentrated growth clusters supported by policy incentives and strategic OEM–energy partnerships.
 Market Segmentation Analysis:
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Vehicle Type (BEV, HEV, PHEV, FCV)
Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) represent the dominant sub-segment, supported by rapid scaling of high-energy-density batteries, declining pack costs, and strong regulatory momentum for zero-emission fleets. BEVs hold the largest market share due to their simpler drivetrain architecture and accelerated adoption across passenger and light commercial categories. Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs) continue to expand in regions with range-anxiety concerns, while Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs) gain traction in transitional markets. Fuel Cell Vehicles (FCVs) remain niche but grow steadily in heavy-duty mobility segments as hydrogen refueling infrastructure expands.
- For instance, Panasonic’s latest lithium-ion battery cells reach energy densities of 272 Wh/kg, enabling longer-range BEVs with compact architectures.
By Powertrain (BEV, MHEV, Series, Parallel, Series–Parallel)
BEV powertrains account for the largest share owing to their higher energy conversion efficiency, reduced mechanical complexity, and rapid electrification of urban mobility fleets. Mild Hybrid Electric Vehicle (MHEV) systems show strong growth as automakers integrate 48V architectures to meet fuel-efficiency regulations without major platform redesigns. Series hybrid powertrains gain relevance in buses and delivery vehicles, whereas parallel and series–parallel configurations remain widely deployed for performance optimization in passenger hybrids. The dominance of BEV powertrains is driven by cost reductions in battery modules and increasing OEM commitments to full-electric lineups.
- For instance, the single rear motor in some Tesla Model 3 variants achieves peak efficiencies around 97% to 98%, supported by its advanced internal permanent magnet synchronous reluctance motor (IPM SynRM) design.
By Position / Drive Type (FWD, RWD, AWD)
Front-Wheel Drive (FWD) powertrains lead the market due to their compact packaging, lower production cost, and suitability for mass-market electric and hybrid vehicle platforms. FWD configurations deliver efficient space utilization, making them the preferred layout for urban BEVs and compact HEVs. Rear-Wheel Drive (RWD) systems grow in performance-oriented EVs, benefiting from improved weight distribution and traction. All-Wheel Drive (AWD) powertrains expand in premium BEVs with dual-motor setups, offering enhanced torque vectoring and stability. However, FWD remains the dominant sub-segment due to its affordability and widespread OEM deployment.
KEY GROWTH DRIVERS
Rapid Expansion of Zero-Emission Mobility Policies and Hydrogen Infrastructure
Government-led decarbonization programs strongly accelerate adoption of hydrogen BEV–HEV powertrains. Nations across Europe, North America, and Asia are deploying large-scale hydrogen refueling stations, supporting fuel cell integration into passenger cars, buses, and heavy-duty trucks. Policy incentives—such as tax credits, purchase rebates, and carbon-neutral mobility mandates—encourage automakers to electrify product lines using hybridized hydrogen systems. Fleet operators increasingly prioritize low-emission options to meet ESG requirements, reducing long-term operating risks associated with diesel restrictions. International collaborations between energy suppliers, refueling network developers, and OEMs enhance production capacity for green hydrogen, further supporting cost reduction and scalability. As hydrogen infrastructure becomes more robust, OEMs accelerate investments in hybrid-electric and battery-driven powertrains integrated with hydrogen energy storage, expanding the market’s long-term growth potential.
· For instance, Japan’s nationwide hydrogen program has expanded its network to more than 160 operational hydrogen stations, while Germany’s H2 MOBILITY consortium has deployed over 100 public refueling sites capable of dispensing hydrogen at 700-bar pressure (though this number is currently undergoing a planned reduction to approximately 48 stations by the end of 2025 as the focus shifts to larger commercial vehicle hubs).
Advancements in Battery Efficiency, Fuel-Cell Durability, and Powertrain Integration
Technical progress in high-capacity batteries, lightweight fuel-cell stacks, and high-voltage power electronics significantly strengthens adoption of hydrogen-linked BEV–HEV powertrains. Automakers increasingly deploy energy-dense battery modules that extend electric-only range, enabling efficient hybridization with fuel-cell systems for long-distance travel. Improvements in fuel-cell membrane durability, thermal management, and catalyst performance enhance lifecycle reliability, lowering maintenance burdens. Powertrain suppliers also optimize e-motor torque density, regenerative braking efficiency, and compact inverter solutions to improve overall drive efficiency. Integration of hydrogen storage cylinders with modular hybrid architectures allows flexible vehicle designs across SUVs, sedans, commercial vans, and heavy-duty applications. Such synergistic advancements among battery systems, hydrogen fuel cells, and electric drivetrains directly boost operational efficiency and reduce barriers to commercial deployment.
· For instance, CATL’s Qilin battery (using NMC chemistry) achieves 255 Wh/kg at the pack level due to its highly integrated Cell-to-Pack (CTP) 3.0 technology, primarily designed for high-end Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) to offer ultra-long ranges.
Growing Adoption in Commercial Fleets and Long-Haul Transportation
Hydrogen BEV–HEV systems gain major traction in commercial logistics as operators seek cleaner solutions with extended range, fast refueling, and high payload capacity. Heavy-duty trucks, transit buses, and regional delivery fleets increasingly adopt fuel-cell hybrid configurations to meet stringent emissions regulations and reduce dependency on diesel. Hydrogen-backed hybrids offer advantages such as shorter refueling cycles compared to battery-only solutions, enhancing fleet uptime and route continuity. Large commercial operators favor hydrogen vehicles for predictable refueling patterns and reduced range-related disruptions. Industrial sectors—such as mining, ports, airports, and last-mile logistics—deploy hydrogen-electric drivelines to improve operational sustainability. As commercial volumes scale, component economies of scale lower unit prices for power electronics, electric motors, and fuel-cell stacks, reinforcing long-term market momentum.
KEY TRENDS & OPPORTUNITIES
Rising Integration of Software-Defined Powertrains and Predictive Energy Management
A major trend shaping the hydrogen BEV–HEV powertrain market is the shift toward software-defined architectures that optimize energy flow between batteries, motors, and fuel cells. Predictive energy management systems analyze driving conditions, load profiles, and route topographies to balance battery usage and hydrogen consumption in real time. OEMs deploy advanced control algorithms, over-the-air updates, and AI-driven diagnostic systems to increase powertrain efficiency and reduce degradation. Digital twins enable simulation-based optimization of hydrogen hybrid drivelines across diverse operating environments. As vehicles become increasingly connected, cloud-linked power management platforms allow continuous performance upgrades, unlocking new opportunities for aftermarket optimization, fleet analytics services, and predictive maintenance ecosystems.
- FOR instance, Toyota’s fuel-cell system, including its Power Control Unit (PCU) and associated ECUs, processes a significant number of sensor inputs in real-time to precisely manage and balance the fuel cell stack load and battery output under varying conditions.
Expansion of Green Hydrogen Production and Cross-Sector Energy Collaboration
The growing shift toward green hydrogen produced using renewable energy presents significant opportunities for hydrogen-electric hybrid powertrains. Energy companies, electrolyzer manufacturers, and automakers collaborate to expand production capacity, secure long-term supply contracts, and establish renewable hydrogen corridors. Industrial hubs, logistics parks, and mobility clusters adopt integrated hydrogen ecosystems that support both mobility and industrial applications. Large-scale investment in solar, wind, and hydro-based hydrogen production lowers future cost curves, enabling wider commercial vehicle deployment. Cross-sector partnerships accelerate infrastructure rollout and standardization of refueling interfaces, helping hydrogen hybrids transition from niche use to mainstream fleets.
- For instance, Air Liquide operates a 20 MW PEM electrolyzer in Bécancour, Canada, producing up to 8.2 tons of green hydrogen per day for mobility and industrial users.
Increasing Platform Sharing and Modular Powertrain Architectures
Automakers are moving toward modular electric-hydrogen platforms that reduce development time and manufacturing complexity. Shared architectures allow multiple vehicle types—including SUVs, vans, and heavy-duty trucks—to integrate the same motors, inverters, hydrogen tanks, or fuel-cell stacks. This modularity lowers production costs and accelerates the rollout of hydrogen hybrid models across markets. Suppliers benefit from scalable component manufacturing, while OEMs improve configurability for region-specific regulatory or performance requirements. These flexible architectures also support future upgrades in battery chemistry, hydrogen storage density, and power electronics without full platform redesigns, creating long-term innovation opportunities.
KEY CHALLENGES:
High Cost of Fuel-Cell Systems, Batteries, and Hydrogen Storage Components
A major challenge for hydrogen BEV–HEV powertrains is the high cost associated with fuel-cell stacks, high-pressure storage tanks, and advanced battery packs. Platinum-based catalysts, carbon-fiber-wrapped tanks, and high-voltage inverters collectively raise vehicle production costs compared to conventional EVs. Limited large-scale manufacturing further prevents the economies of scale needed for cost reduction. Hydrogen fuel pricing, driven by production and transportation expenses, also remains higher than conventional fuels, slowing early adoption among cost-sensitive markets. The combined capital and operating expenditure makes it difficult for OEMs to offer competitive price points, particularly in passenger vehicle segments.
Limited Hydrogen Refueling Infrastructure and Regional Deployment Imbalances
Insufficient hydrogen refueling stations remain one of the most significant barriers to widespread deployment. Infrastructure is heavily concentrated in select markets such as Japan, South Korea, Germany, and California, creating regional adoption disparities. Commercial fleets require dense station networks to ensure reliable operation, but many regions lack investment-ready business models for hydrogen distribution. Long permitting cycles, land availability constraints, and high station construction costs further slow rollout. Without robust infrastructure expansion, hydrogen BEV–HEV adoption remains restricted to corridors with established refueling support, delaying mass-market penetration.
Regional Analysis:
North America
North America holds around 28% of the market, driven by strong adoption of hydrogen-electric systems in commercial fleets, buses, and long-haul trucks. The U.S. leads deployment through state-level incentives in California and emerging hydrogen corridors across the West Coast and Midwest. Federal decarbonization mandates, tax credits for clean mobility, and substantial investments in green hydrogen production reinforce demand. Canada accelerates adoption through its national hydrogen strategy focused on heavy-duty transportation. Growing OEM–energy partnerships and pilot deployments in logistics hubs support the region’s solid infrastructure expansion and continued leadership in hydrogen-electric hybrid technologies.
Europe
Europe dominates the global market with approximately 32% share, supported by stringent CO₂ reduction targets, rapid hydrogen infrastructure rollout, and strong government-backed decarbonization programs. Germany, France, the Netherlands, and the Nordics lead adoption across buses, municipal fleets, and long-range mobility applications. The EU’s hydrogen roadmap and funding mechanisms under Fit-for-55 and REPowerEU accelerate development of hydrogen corridors and multi-modal refueling ecosystems. Major OEMs integrate hydrogen-electric hybrid platforms into commercial vehicle portfolios, while large-scale green hydrogen projects enhance supply stability. Europe’s regulatory pressure and advanced mobility ecosystems secure its position as the leading regional market.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific accounts for roughly 30% of the market, driven by aggressive national hydrogen strategies in Japan, South Korea, and China. Japan leads commercial deployment of fuel-cell hybrid vehicles and refueling stations, while South Korea scales hydrogen-electric buses and heavy-duty trucks. China accelerates adoption through provincial subsidies and large pilot zones integrating hydrogen-based BEV–HEV platforms into logistics and public transport. Rapid urbanization and large commercial fleet sizes further strengthen demand. Expanding electrolyzer capacity and strategic partnerships between OEMs and energy suppliers improve ecosystem maturity, positioning Asia-Pacific as a high-growth region approaching parity with Europe.
Latin America
Latin America captures around 5% of the market as early-stage hydrogen mobility initiatives gain momentum in Chile, Brazil, and Argentina. Chile’s national green hydrogen strategy promotes adoption in mining fleets and high-load mobility applications. Brazil expands pilot projects for hydrogen-electric buses within major urban centers, supported by renewable energy capabilities. Limited refueling infrastructure and high vehicle costs remain constraints, but rising interest from logistics operators and industrial sectors creates a foundation for long-term growth. International partnerships and renewable hydrogen export projects are expected to accelerate regional adoption of hydrogen BEV–HEV technologies.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region holds nearly 5% of the market, driven primarily by large-scale green hydrogen initiatives in Saudi Arabia, the UAE, and South Africa. Mega-projects such as NEOM’s hydrogen hub create strong potential for future deployment of hydrogen-electric hybrid vehicles, particularly in logistics, construction, and industrial transport. Early adoption focuses on buses and heavy-duty fleets supporting smart city and sustainability programs. Limited infrastructure and high technology import costs delay mass-market penetration, but accelerating investment in hydrogen production and demonstration fleets strengthens future market prospects.
Market Segmentations:
By Vehicle Type
- Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV)
- Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV)
- Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV)
- Fuel Cell Vehicle (FCV)
By Powertrain
- BEV Powertrain
- MHEV Powertrain
- Series Hybrid Powertrain
- Parallel Hybrid Powertrain
- Series–Parallel Hybrid Powertrain
By Position / Drive Type
- Front-Wheel Drive (FWD) Powertrain
- Rear-Wheel Drive (RWD) Powertrain
- All-Wheel Drive (AWD) Powertrain
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape:
The competitive landscape of the hydrogen BEV–HEV powertrain market is characterized by active participation from global automakers, powertrain integrators, and hydrogen technology specialists accelerating development across battery-electric, hybrid-electric, and fuel-cell platforms. Leading OEMs focus on expanding hydrogen-electric portfolios for commercial fleets, long-haul trucks, and advanced passenger vehicles, while suppliers enhance e-motor efficiency, high-pressure hydrogen storage, and next-generation fuel-cell stacks. Strategic partnerships between automotive manufacturers and energy companies support large-scale deployment of hydrogen corridors and refueling ecosystems. Companies are investing heavily in modular powertrain designs, software-defined energy management, and improved catalyst durability to reduce system cost and extend component life. Collaborations with hydrogen producers, infrastructure developers, and mobility service operators further strengthen value-chain integration. Continuous advancements in lightweight materials, high-voltage inverters, and integrated hybrid control units enable improved performance and operating range, positioning competitive players to scale adoption across emerging mobility applications.
Key Player Analysis:
- ZF Friedrichshafen
- Magneti Marelli S.p.A.
- Punch Powertrain Nanjing Co. Ltd.
- Bosch
- BorgWarner Inc.
- BAE Systems plc
- Knorr-Bremse Group
- Continental AG
- Ballard Power Systems
- Mitsubishi Electric
Recent Developments:
- In 2025, the Bosch fuel-cell power module team received the 2025 “German Future Prize” for their work on a hydrogen-powered module capable of enabling zero-emission heavy-duty transport. The module delivers a competitive driving range and supports large-scale deployment.
- In 2023, Bosch has moved aggressively into hydrogen fuel-cell powertrains: it began volume production of its Fuel-Cell Power Module (FCPM) in 2023, aimed at commercial trucks and long-haul heavy vehicles.
- In February 2022, BorgWarner Inc. has advanced its hydrogen-combustion offering: the company secured a production contract to supply a full hydrogen injection system (injectors, fuel rail, ECU, and integration) for a European off-road equipment manufacturer. This system allows existing internal-combustion engines to run on hydrogen with minimal redesign, presenting a near-term pathway for decarbonizing off-road and commercial machinery.
Report Coverage:
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Vehicle type, Powertrain, Position/Drive type and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook:
- Hydrogen BEV–HEV powertrains will gain strong adoption as governments intensify zero-emission mobility mandates and accelerate hydrogen-refueling infrastructure expansion.
- Commercial fleets, especially buses and long-haul trucks, will increasingly transition toward hydrogen-electric hybrids for extended range and high operational uptime.
- Fuel-cell stacks will become more efficient and durable as new membrane materials and catalyst technologies reduce degradation and maintenance requirements.
- Battery–fuel-cell hybrid architectures will mature, enabling optimized energy management and improved drive-cycle efficiency across diverse vehicle segments.
- Green hydrogen production capacity will expand significantly, lowering fuel costs and strengthening long-term market viability.
- Software-defined powertrains will enhance vehicle performance through predictive energy management, real-time diagnostics, and over-the-air optimization.
- Modular and scalable hydrogen-electric platforms will support multi-vehicle integration, reducing development time and improving manufacturing flexibility.
- Strategic alliances between OEMs, energy companies, and infrastructure developers will accelerate ecosystem readiness.
- Advancements in lightweight hydrogen storage systems will increase onboard capacity and extend driving range.
- Regional adoption will broaden beyond Europe and Asia-Pacific as new hydrogen mobility corridors emerge in North America, the Middle East, and Latin America.

 Market Segmentation Analysis:
Market Segmentation Analysis:

