Market Overview
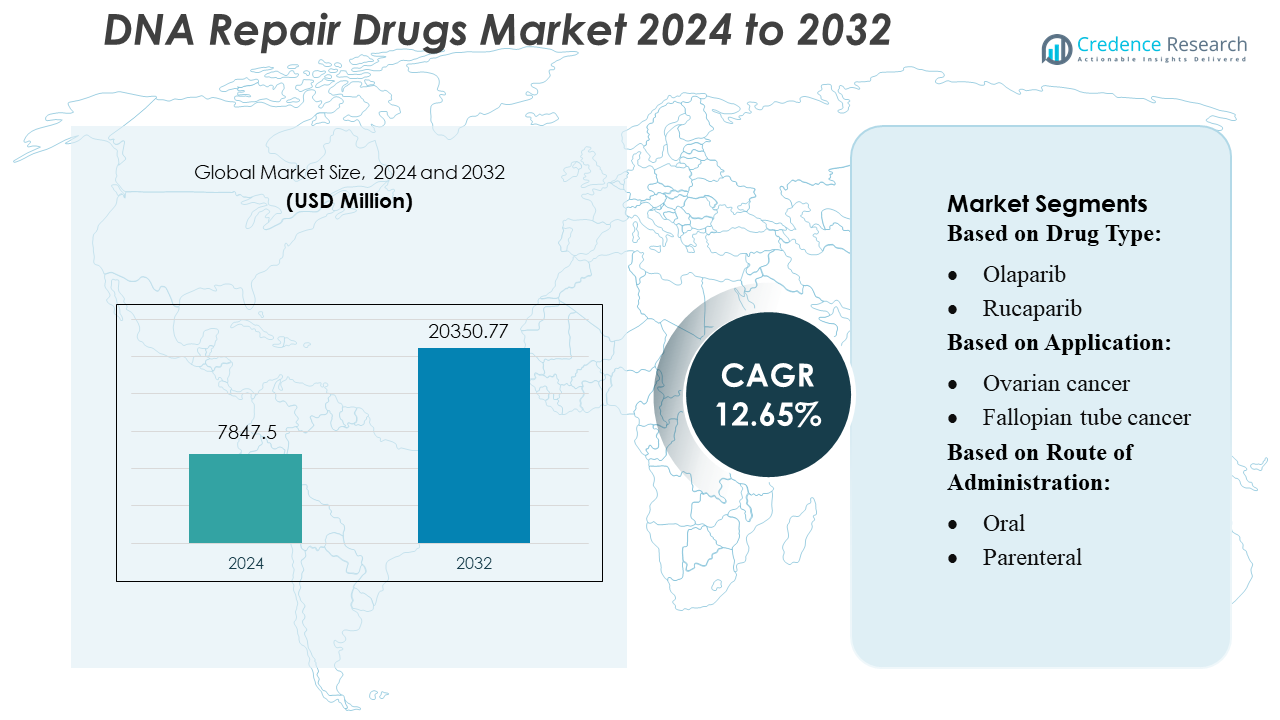
DNA Repair Drugs Market size was valued USD 7847.5 million in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 20350.77 million by 2032, at a CAGR of 12.65% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| DNA Repair Drugs Market Size 2024 |
USD 7847.5 Million |
| DNA Repair Drugs Market, CAGR |
12.65% |
| DNA Repair Drugs Market Size 2032 |
USD 20350.77 Million |
The DNA repair drugs market is shaped by strong participation from leading pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies, including FoRx Therapeutics, Merck KGaA, Artios Pharma Limited, GlaxoSmithKline plc., Clovis Oncology Inc., Breakpoint Therapeutics, Luciole Pharmaceuticals, AbbVie, Johnson & Johnson, and AstraZeneca Plc. These players compete through advancements in PARP inhibitors, expansion into next-generation DDR targets, and strategic collaborations aimed at strengthening clinical pipelines. North America remains the leading region in this market, holding 42% of the global share, supported by advanced oncology infrastructure, high genomic testing rates, and rapid adoption of targeted therapies across multiple cancer types.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Market Insights
- The DNA Repair Drugs Market was valued at USD 7,847.5 million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 20,350.77 million by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 12.65%, driven by rising cancer incidence and increasing adoption of precision oncology.
- Market growth accelerates due to expanding use of PARP inhibitors, wider BRCA/HRD genetic testing, and strong clinical evidence supporting targeted maintenance therapies across ovarian, breast, prostate, and pancreatic cancers.
- Key players, including FoRx Therapeutics, Merck KGaA, Artios Pharma Limited, GlaxoSmithKline plc., and AstraZeneca Plc., strengthen competition through DDR pipeline expansion, combination-therapy development, and strategic R&D collaborations.
- High drug costs, treatment resistance, and limited diagnostic access in emerging economies restrain broader adoption, slowing penetration despite strong therapeutic demand.
- North America leads with 42% market share, while oral formulations dominate with nearly 80% share; ovarian cancer remains the largest application segment, supported by strong clinical adoption and frontline therapy approvals.
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Drug Type
Olaparib leads the DNA repair drugs market, accounting for an estimated 42–45% share, driven by its broad regulatory approvals across BRCA-mutated ovarian, breast, pancreatic, and prostate cancers. Its strong clinical evidence, including improved progression-free survival in multiple Phase III trials, strengthens adoption across oncology clinics. Niraparib follows due to its advantage as the only PARP inhibitor approved for both BRCA-mutated and non-mutated ovarian cancers. Rucaparib and Talazoparib show moderate uptake, while other drug types occupy a smaller niche driven by pipeline diversity and combination-therapy trials.
- For instance, FoRx Therapeutics is targeting a distinct DDR vulnerability via FORX-428, a PARG inhibitor with an IC₅₀ of < 1 nM in biochemical assays and < 4 nM in cell-based assays, based on its own preclinical profiling.
By Application
Ovarian cancer remains the dominant application segment, holding over 50% market share, supported by high treatment demand and strong clinical validation of PARP inhibitors as maintenance therapy post-platinum chemotherapy. The segment’s growth is driven by rising early genetic testing, expanded frontline therapy approvals, and improved survival outcomes in recurrent disease. Breast cancer forms the second-largest segment, supported by approvals in HER2-negative BRCA-mutated patients. Fallopian tube and peritoneal cancers contribute steadily, while other applications grow as PARP inhibitors advance into prostate, pancreatic, and solid-tumor combination regimens.
- For instance, FoRx Therapeutics is targeting a distinct DDR vulnerability via FORX-428, a PARG inhibitor with an IC₅₀ of < 1 nM in biochemical assays and < 4 nM in cell-based assays, based on its own preclinical profiling.
By Route of Administration
The oral route dominates with nearly 80% share, driven by the fact that leading PARP inhibitors—Olaparib, Rucaparib, Niraparib, and Talazoparib—are all available as oral formulations, offering superior patient convenience and adherence compared to clinic-based therapies. The rising preference for at-home cancer management, reduced hospital visits, and favorable pharmacokinetic profiles further accelerate adoption. The parenteral segment remains comparatively small and is driven mainly by emerging combination treatments evaluated in intravenous immunotherapy and targeted-therapy regimens under clinical development.
Key Growth Drivers
- Rising Prevalence of BRCA-Mutated and HRD-Positive Cancers
The increasing global incidence of BRCA1/BRCA2 mutations and homologous recombination deficiency (HRD) across ovarian, breast, prostate, and pancreatic cancers strongly drives demand for DNA repair drugs. Wider adoption of genomic profiling enables earlier detection of gene mutations, making targeted therapies such as PARP inhibitors the preferred treatment option. As precision oncology expands, more patients qualify for mutation-specific therapies, accelerating clinical uptake and market penetration. This growing diagnostic integration significantly boosts the overall demand for DNA repair–focused therapeutics.
- For instance, Artios Pharma Limited has demonstrated clear proof of concept in this area: its ATR inhibitor alnodesertib (ART0380), in combination with low-dose irinotecan, achieved a 50% confirmed overall response rate (cORR) in ATM-negative solid tumor patients in its Phase 1/2a STELLA trial.
- Expansion of Regulatory Approvals for PARP Inhibitors
Regulatory agencies continue to broaden indications for DNA repair drugs, particularly PARP inhibitors, across multiple cancer types and treatment lines. Approvals for frontline maintenance therapy, metastatic settings, and recurrent disease enhance clinical utility and increase patient access. Accelerated approvals supported by strong Phase III trial outcomes further strengthen market growth. Additionally, companion diagnostic approvals streamline patient selection, improving treatment outcomes and boosting confidence among oncologists. This continuous regulatory momentum supports sustained expansion of the DNA repair drugs market.
- For instance, GlaxoSmithKline plc. has secured multiple global approvals for its PARP inhibitor niraparib, supported by strong late-stage data. In the PRIMA Phase III trial, niraparib achieved a median progression-free survival of 21.9 months in HRD-positive advanced ovarian cancer patients compared with 10.4 months for standard therapy.
- Growing Adoption of Combination Therapies
Combination regimens involving PARP inhibitors with immunotherapies, angiogenesis inhibitors, and DNA-damaging chemotherapies create new clinical opportunities and drive market expansion. These synergistic approaches aim to overcome resistance mechanisms and improve long-term patient survival. Ongoing trials exploring PARP–PD-1/PD-L1 combinations and PARP–ATR inhibitor combinations broaden therapeutic scope across solid tumors. As combination therapies demonstrate promising efficacy in previously unresponsive patients, pharmaceutical companies invest heavily in joint development programs, accelerating innovation and expanding the treatment landscape.
Key Trends & Opportunities
- Increasing Focus on Next-Generation DNA Repair Targets
Beyond PARP inhibition, industry players are shifting focus toward next-generation DNA repair pathways such as ATR, ATM, DNA-PK, and polymerase theta. These emerging targets offer significant opportunities to overcome resistance and treat tumors with diverse genetic profiles. Multiple early-stage pipelines show encouraging safety and efficacy signals, presenting long-term growth potential. As understanding of synthetic lethality deepens, developers aim to create multi-target inhibitors and dual-mechanism drugs, opening new segments within precision oncology and expanding revenue possibilities.
- For instance, ARIEL2, genomic sequencing of 491 tumor samples identified distinct resistance-associated alterations, including RAD51 upregulation and BRCA reversion mutations, observed in 32 analyzed cases, underscoring why next-generation pathways must be targeted.
- Rising Demand for Personalized and Biomarker-Driven Therapies
Advancements in genomic sequencing and tumor profiling enhance the ability to match patients with highly targeted DNA repair therapies. Increased availability of cost-effective next-generation sequencing (NGS) promotes broader biomarker testing, expanding the eligible patient pool. Precision oncology initiatives from hospitals and government agencies further support biomarker-driven prescribing patterns. This trend creates opportunities for drug–diagnostic partnerships, companion test development, and personalized treatment algorithms, ultimately improving treatment outcomes and driving market growth.
- For instance, Breakpoint Therapeutics—a company dedicated to DNA damage response drug development—was launched with a €30 million Series A financing round, enabling the build-out of high-throughput genomic screening platforms that evaluate DDR pathway vulnerabilities across more than 200 engineered cellular models.
- Untapped Potential in Emerging Markets
Emerging economies in Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East present substantial growth opportunities due to improving cancer diagnosis infrastructure and rising awareness of genetic testing. As healthcare systems modernize, patient access to targeted therapies increases, supported by expanding reimbursement policies and oncology investments. Growing oncology clinical trial activity in these regions also accelerates drug adoption. Pharmaceutical companies are actively strengthening regional distribution networks and partnerships, creating long-term expansion opportunities across underpenetrated markets.
Key Challenges
- High Treatment Costs and Limited Reimbursement Coverage
The premium pricing of PARP inhibitors and other DNA repair drugs poses a significant barrier, particularly in developing markets with limited insurance coverage. High out-of-pocket expenses restrict patient accessibility, reducing optimal utilization despite clinical benefits. Reimbursement policies remain inconsistent across regions, and stringent cost-effectiveness evaluations by payers delay market entry in many countries. These financial barriers hinder widespread adoption and limit the overall growth potential of the DNA repair drugs market.
- Development of Drug Resistance in Long-Term Therapy
The emergence of acquired resistance to PARP inhibitors presents a critical clinical challenge, reducing long-term treatment efficacy. Tumor cells adapt through restoration of homologous recombination pathways, drug efflux mechanisms, or mutations that undermine therapeutic response. This resistance complicates treatment strategies, requiring alternative regimens, combination therapy approaches, or next-generation inhibitors. Addressing resistance demands substantial research investment, extended clinical trial timelines, and innovative mechanism-based drug design, creating operational and scientific challenges for developers.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America holds the largest share of the DNA repair drugs market, accounting for around 40–42%, driven by strong adoption of PARP inhibitors, extensive genomic testing coverage, and a high prevalence of BRCA-mutated cancers. The region benefits from advanced oncology infrastructure, favorable reimbursement frameworks, and rapid integration of companion diagnostics that support personalized treatment. The presence of major pharmaceutical companies and ongoing clinical trials further accelerate innovation. Increasing patient awareness and early cancer screening rates continue to strengthen market growth, solidifying North America’s position as the leading regional contributor.
Europe
Europe represents the second-largest regional market with approximately 28–30% share, supported by widespread utilization of targeted therapies, strong national cancer control programs, and broad access to genomic profiling. Countries such as Germany, the U.K., and France drive market expansion through favorable reimbursement for PARP inhibitors and structured clinical pathways for BRCA and HRD testing. The region also benefits from active clinical research networks and accelerated regulatory approvals from the EMA. Rising adoption of maintenance therapy in ovarian and breast cancers continues to strengthen Europe’s overall market presence.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region and accounts for around 20–22% share, driven by improving cancer diagnosis rates, increasing investment in precision oncology, and expanding patient access to targeted therapies. Countries such as China, Japan, South Korea, and Australia show strong uptake due to the growing availability of BRCA testing and rapid approval of PARP inhibitors. Rising healthcare expenditure, supportive government initiatives, and expanding clinical trial participation contribute to accelerated market penetration. The region’s large patient population and underdiagnosed BRCA mutation base create significant long-term growth potential.
Latin America
Latin America holds approximately 5–6% share, with growth influenced by gradual improvements in genetic testing accessibility and expanding adoption of targeted therapies in major markets such as Brazil, Mexico, and Argentina. While reimbursement challenges persist, increasing private healthcare spending and oncology-focused investments support moderate demand. The introduction of cost-effective diagnostic platforms and participation in international clinical research programs help drive awareness and early mutation detection. As regulatory frameworks evolve and more targeted therapies become accessible, the region continues to show steady but emerging growth potential.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region accounts for around 3–4% share, driven by rising cancer incidence and improving access to advanced therapies in Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries. Wealthier markets such as the UAE, Saudi Arabia, and Qatar exhibit growing adoption of genomic testing and targeted oncology treatments due to strong healthcare modernization initiatives. However, limited diagnostic infrastructure and affordability issues restrict broader uptake across Africa. International collaborations and oncology center expansions are gradually improving access, supporting incremental growth in DNA repair drug utilization across the region.
Market Segmentations:
By Drug Type:
By Application:
- Ovarian cancer
- Fallopian tube cancer
By Route of Administration:
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape of the DNA repair drugs market features a mix of established pharmaceutical leaders and emerging biotechnology innovators, including FoRx Therapeutics, Merck KGaA, Artios Pharma Limited, GlaxoSmithKline plc., Clovis Oncology Inc., Breakpoint Therapeutics, Luciole Pharmaceuticals, AbbVie, Johnson & Johnson, and AstraZeneca Plc. The DNA repair drugs market is defined by rapid innovation, expanding clinical pipelines, and increasing investment in next-generation DNA damage response (DDR) therapies. Companies actively pursue advancements in PARP, ATR, ATM, and DNA-PK inhibition to strengthen their oncology portfolios and address unmet needs in solid tumors. Strategic collaborations, licensing agreements, and biomarker-driven clinical development serve as key competitive strategies, enabling faster entry into high-value cancer segments. Market participants focus heavily on combination-therapy research to overcome resistance and extend patient survival. Growing emphasis on precision oncology, companion diagnostics, and scalable manufacturing capabilities further intensifies competition across global markets.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
Recent Developments
- In October 2025, Mabwell presented data from a Phase I/II study of its B7-H3 antibody-drug conjugate (ADC), 7MW3711, at the European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) Congress. The results showed that the ADC produced tumor regression (partial and complete responses) in patients with B7-H3-positive solid tumors, including esophageal and lung cancers.
- In January 2025, Senaparib Approved by NMPA for 1L Maintenance Therapy in Ovarian Cancer. Impact Therapeutics received Chinese marketing authorization for senaparib as maintenance therapy for advanced ovarian cancer.
- In June 2023, AstraZeneca introduced IMJUDO® (tremelimumab) in the UAE, pioneering cancer treatment in the Middle East. The groundbreaking medication heralds a new era in cancer therapy, offering hope to patients and positioning the UAE at the forefront of medical innovation in the region.
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Drug Type, Application, Route of Administration and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- The market will expand as genomic testing becomes routine in oncology and identifies more patients eligible for DNA repair–targeted therapies.
- PARP inhibitors will maintain strong momentum while next-generation DDR targets such as ATR, ATM, and DNA-PK gain commercial relevance.
- Combination therapies integrating PARP inhibitors with immunotherapy and targeted agents will shape future treatment standards.
- Earlier-line approvals across multiple tumor types will significantly broaden clinical use.
- Advances in synthetic lethality research will drive the development of more selective and durable DNA repair inhibitors.
- Resistance-mitigation strategies will influence innovation, leading to improved second-generation therapies.
- Precision oncology adoption will increase demand for companion diagnostics and biomarker-driven treatments.
- Emerging markets will contribute faster growth due to expanding cancer infrastructure and improved diagnostic access.
- Digital health integration will support real-world evidence generation and optimize treatment outcomes.
- Strong pipeline investments and collaborative research programs will accelerate diversification of the DNA repair drug landscape.




