Market Overview
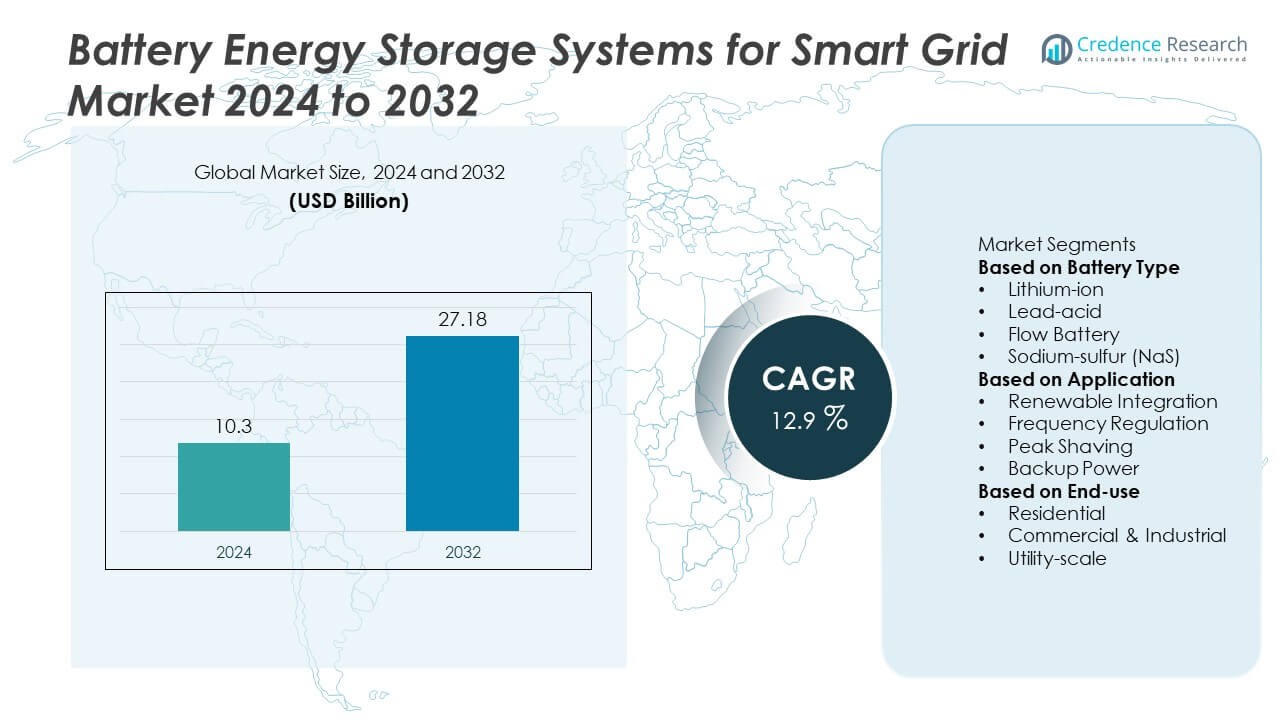
The Battery Energy Storage Systems for Smart Grid market was valued at USD 10.3 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 27.18 billion by 2032, registering a CAGR of 12.9% over the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Battery Energy Storage Systems for Smart Grid Market Size 2024 |
USD 10.3 Billion |
| Battery Energy Storage Systems for Smart Grid Market, CAGR |
12.9% |
| Battery Energy Storage Systems for Smart Grid Market Size 2032 |
USD 27.18 Billion |
Top players in the Battery Energy Storage Systems for Smart Grid market include Tesla, LG Energy Solution, Samsung SDI, Panasonic, Fluence Energy, BYD, Hitachi Energy, Siemens Energy, ABB, and NEC Energy Solutions. These companies lead through strong manufacturing capacity, advanced lithium-ion technologies, and large utility-scale deployments. North America holds the 38% market share, driven by strong policy support and rapid renewable integration. Europe follows with a 29% share, supported by strict decarbonization targets and widespread grid upgrades. Asia Pacific accounts for 25%, led by large-scale installations in China, India, Japan, and South Korea. These regions shape global competitiveness through continuous investment and technology leadership.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Insights
- The market reached USD 10.3 billion in 2024 and will grow at a CAGR of 12.9%.
- Strong renewable integration needs drive demand, with renewable applications holding a 54% segment share.
- Lithium-ion batteries lead with a 72% share as projects favor high efficiency and long cycle life.
- Competition intensifies as Tesla, Fluence, LG Energy Solution, and BYD expand global deployments.
- North America leads with a 38% share, followed by Europe at 29% and Asia Pacific at 25%, supported by large utility-scale installations holding a 68% segment share.
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Battery Type
Lithium-ion batteries lead this segment with a 72% market share, driven by strong energy density, long cycle life, and falling production costs. Their rapid response time supports grid stability and renewable integration, making them the preferred choice for smart grid projects. Lead-acid systems hold a smaller share due to shorter lifespan, while flow batteries gain attention for long-duration storage. Sodium-sulfur (NaS) units serve high-temperature, utility-scale needs but remain niche. The dominance of lithium-ion continues as utilities prioritize efficient performance, strong safety improvements, and scalability for modern grid modernization programs.
- For instance, Tesla deployed a 182.5-MW lithium-ion system at Moss Landing, and CATL delivered a 100-MWh lithium-ion installation in Fujian using cells rated at 3000 charge cycles, showing strong performance in real grid operations.
By Application
Renewable integration dominates the application segment with a 54% market share, supported by rising solar and wind deployments that require stable storage to manage variability. Grid operators use these systems to smooth output, reduce curtailment, and enhance reliability. Frequency regulation follows as grids adopt fast-responding storage to balance real-time fluctuations. Peak shaving applications gain traction across commercial sites seeking lower demand charges. Backup power remains vital for sensitive facilities. Growth in renewable projects, supportive policies, and the need for flexible grid operations strengthen the leading position of renewable integration within smart grid deployments.
- For instance, Fluence and its investors and partners, such as Bayernwerk and Zukunftsenergie Nordostbayern GmbH, have inaugurated a 100 MW/200 MWh battery system for the Wunsiedel grid project in Germany, one of the largest in continental Europe.
By End-use
Utility-scale installations hold the dominant position with a 68% market share, driven by large storage projects that support transmission stability, renewable smoothing, and energy shifting. Utilities deploy high-capacity systems to manage grid congestion, defer infrastructure upgrades, and improve reliability. Commercial and industrial users adopt storage for peak demand management and resilience during outages. Residential adoption grows with rooftop solar, smart meters, and government incentives. The strong lead of utility-scale storage reflects rising investments in grid modernization, large renewable farms, and long-duration solutions that enable strategic control over energy supply and system flexibility.
Key Growth Drivers
Rising Renewable Energy Integration
Growing renewable installations strengthen the need for reliable storage that can manage variable generation. Battery systems help stabilize output, reduce curtailment, and support real-time balancing as solar and wind capacity expands. Utilities deploy large-scale systems to store surplus power and release it during peak demand. Policy incentives, grid modernization programs, and national clean-energy targets further drive adoption. The shift toward low-carbon grids accelerates investment in advanced storage that improves flexibility, enhances reliability, and supports long-term energy planning across diverse regions.
- For instance, Plus Power developed the 185-MW Kapolei Energy Storage Project, a facility in Hawaii using Tesla Megapack batteries with controllers capable of responding in under 250 milliseconds.
Increasing Demand for Grid Stability and Resilience
Modern grids face rising stress due to high peak loads, extreme weather, and distributed energy resources. Battery energy storage offers rapid response and firming capabilities that help operators maintain voltage, frequency, and power quality. Utilities use these systems to reduce outage risks, support black start operations, and enhance overall resilience. Aging transmission infrastructure also increases the need for strategic storage deployment. As reliability becomes a key priority, batteries play a central role in improving system performance and supporting stable, uninterrupted energy supply for urban and industrial zones.
- For instance, Hitachi Energy supplied a 20-MW virtual inertia system in Scotland capable of delivering 5,000 megawatt-seconds of inertia, and ABB deployed a 10-MW battery grid-stabilization unit in Anchorage with inverters supporting a 40-millisecond response time during frequency dips.
Falling Battery Costs and Advancements in Storage Technologies
Declining lithium-ion production costs and improvements in battery chemistry encourage broader adoption across utility and commercial sectors. Longer cycle life, improved safety features, and faster response times strengthen the value proposition for smart grid applications. Manufacturers innovate with thermal management, enhanced battery management systems, and modular architectures that simplify deployment. Cost-efficient installations attract utilities seeking scalable solutions for long-duration needs. Continuous R&D investment also improves efficiency and enables competitive pricing, accelerating market penetration across developed and emerging regions.
Key Trends & Opportunities
Growth of AI-Enabled Energy Management and Smart Grid Optimization
AI and analytics tools unlock new value by optimizing energy dispatch, forecasting demand, and improving asset performance. Smart grids integrate predictive control systems that enhance operational efficiency and reduce balancing costs. Energy storage operators use AI to monitor battery health, extend lifespan, and minimize downtime. Digital twins, real-time monitoring, and cloud-based platforms create opportunities for intelligent automation. This trend supports greater scalability, reduces operating costs, and enhances system reliability. As digital transformation accelerates, advanced software becomes a major growth avenue for next-generation storage solutions.
- For instance, Siemens Energy deployed an AI-based grid optimization platform that analyzes over 2,000 data points per second, while Wärtsilä’s GEMS software manages more than 3 GW of storage assets using algorithms that cut degradation by 11,000 cycle-equivalent units across controlled fleets.
Expansion of Hybrid Renewable and Storage Projects
Hybrid systems combining solar, wind, and battery storage gain momentum as utilities seek flexible, high-efficiency power solutions. These integrated projects reduce grid dependency, improve capacity utilization, and support steady renewable output. Developers benefit from optimized land use, lower transmission losses, and reduced project costs. Governments support hybrid deployments through auctions, incentives, and flexible interconnection rules. The rise of utility-scale hybrids creates strong opportunities for long-duration storage, advanced power conversion systems, and modular designs that enhance system resilience and performance.
- For instance, NextEra Energy’s subsidiary FPL developed the 409-MW Manatee Energy Storage Center, which was a leading solar-powered battery facility at the time of its 2021 commissioning. The center delivers 900 MWh of energy and is charged by an existing solar farm.
Key Challenges
High Upfront Investment and Limited Financing Options
Despite falling costs, battery storage projects require significant upfront capital, especially at utility scale. Many regions lack favorable financing structures, slowing adoption among smaller utilities and commercial users. Long payback periods and uncertainty in revenue streams create barriers for investors. Limited clarity in market regulations and grid service compensation further complicates project viability. These financial constraints restrict broader deployment and delay grid-wide modernization efforts, particularly in emerging economies with budget limitations.
Regulatory Gaps and Complex Interconnection Requirements
Inconsistent policies and unclear regulatory frameworks hinder rapid integration of storage into grid operations. Interconnection rules vary across regions, creating delays and increasing project complexity. Many markets still treat storage as both generation and load, leading to double charges and operational challenges. Slow permitting processes and limited standardization raise project timelines. These barriers reduce market flexibility and restrict storage participation in critical grid services. Clearer policies, streamlined approvals, and standardized guidelines are needed to unlock full market potential.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America leads the market with a 38% share, supported by strong investments in grid modernization and renewable integration. The United States drives adoption with large utility-scale projects, advanced battery technologies, and favorable federal incentives that promote grid resilience. Growing deployment of solar-plus-storage systems strengthens demand across both residential and commercial sectors. States prioritize storage to manage peak loads, reduce outage risks, and support decarbonization targets. Canada also expands storage to stabilize remote grids and integrate hydropower. Ongoing policy support and rapid technological progress reinforce the region’s leadership in advanced smart grid storage solutions.
Europe
Europe holds a 29% market share, driven by strict carbon reduction targets and rapid renewable expansion across major economies. Countries such as Germany, the UK, and Spain deploy large-scale storage to support rising wind and solar output while improving grid flexibility. Strong regulatory frameworks, capacity market mechanisms, and storage-friendly grid codes accelerate adoption. Demand also grows in residential sectors due to rising rooftop solar and supportive subsidy programs. Utilities prioritize long-duration storage, frequency regulation, and congestion management. Europe’s commitment to clean energy transition continues to push sustained investment in advanced battery energy storage for future grid needs.
Asia Pacific
Asia Pacific accounts for a 25% market share, driven by heavy renewable additions and rising electricity demand across China, India, Japan, and South Korea. China leads regional deployment with strong government mandates and large factory capacities that reduce battery costs. India accelerates storage adoption to stabilize solar-heavy grids and support peak management. Japan focuses on grid reliability and disaster resilience, while South Korea advances energy storage through strong manufacturing capabilities. Growing urbanization, large-scale renewable parks, and supportive policy reforms drive strong momentum, making Asia Pacific one of the fastest-growing regions for smart grid storage integration.
Latin America
Latin America holds a 5% market share, with growth led by expanding solar and wind installations across Brazil, Chile, and Mexico. Grid operators adopt storage to manage intermittency, enhance rural electrification, and reduce dependence on aging infrastructure. Chile leads regional deployment with policy frameworks that support hybrid renewable systems and long-duration storage. Brazil invests in storage to strengthen reliability and support large renewable auctions. Commercial and industrial users adopt systems for backup power and demand management. Although early in adoption, rising renewable potential positions Latin America for steady market expansion.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region captures a 3% market share, supported by large-scale solar projects and rising interest in grid stability solutions. Gulf countries invest in storage to support clean energy targets and smooth output from utility-scale solar farms. The UAE and Saudi Arabia lead deployments with major smart grid programs and pilot energy storage initiatives. In Africa, storage supports rural electrification, microgrids, and backup power for unstable grids. Limited regulatory frameworks and financing challenges slow broader adoption, yet strong renewable expansion and national diversification strategies create long-term growth potential for battery-based smart grid storage.
Market Segmentations:
By Battery Type
- Lithium-ion
- Lead-acid
- Flow Battery
- Sodium-sulfur (NaS)
By Application
- Renewable Integration
- Frequency Regulation
- Peak Shaving
- Backup Power
By End-use
- Residential
- Commercial & Industrial
- Utility-scale
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
Competitive landscape in the Battery Energy Storage Systems for Smart Grid market features major players such as Tesla, LG Energy Solution, Samsung SDI, Panasonic, Fluence Energy, BYD, Hitachi Energy, Siemens Energy, ABB, and NEC Energy Solutions. These companies compete through advancements in lithium-ion technology, enhanced battery management systems, and scalable modular designs that support a wide range of grid applications. Leading manufacturers focus on improving cycle life, thermal stability, and safety to meet rising utility-scale requirements. Partnerships with utilities, renewable developers, and grid operators strengthen market presence and enable deployment of large integrated systems. Vendors also expand global footprints through manufacturing capacity increases and long-term supply contracts. Strong emphasis on R&D, digital optimization tools, and hybrid renewable-storage solutions helps companies deliver high-performance systems that improve grid flexibility and resilience. Growing investment in long-duration technologies further shapes competitive positioning across the industry.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
- Tesla, Inc.
- LG Energy Solution
- Samsung SDI
- Panasonic Holdings Corporation
- Fluence Energy, Inc.
- BYD Company Ltd.
- Hitachi Energy
- Siemens Energy
- ABB Ltd.
- NEC Energy Solutions
Recent Developments
- In September 2025, Samsung SDI debuted its next-generation ESS (energy-storage-system) products at the RE+ 2025 trade show.
- In July 2025, Tesla, Inc. signed a deal with LG Energy Solution for LG ES to supply lithium-iron-phosphate battery cells for Tesla’s storage business in the US.
- In February 2025, BYD Company Ltd. secured contracts totalling 12.5 GWh of grid-scale energy storage with Saudi Electricity Company, marking one of the largest storage deals worldwide.
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Battery Type, Application, End-use and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- Utility-scale storage adoption will rise as grids demand higher flexibility.
- Renewable integration needs will strengthen large projects across major markets.
- Advancements in battery chemistry will improve cycle life and system safety.
- AI-enabled energy management will support smarter grid operations.
- Hybrid renewable-storage plants will expand across solar and wind corridors.
- Falling battery costs will accelerate installations in emerging economies.
- Long-duration storage technologies will gain traction for peak shifting.
- Residential and C&I adoption will grow with demand-side management needs.
- Policy reforms will support storage participation in grid services markets.
- Global manufacturing capacity will expand, reducing supply constraints.




