Market Overview
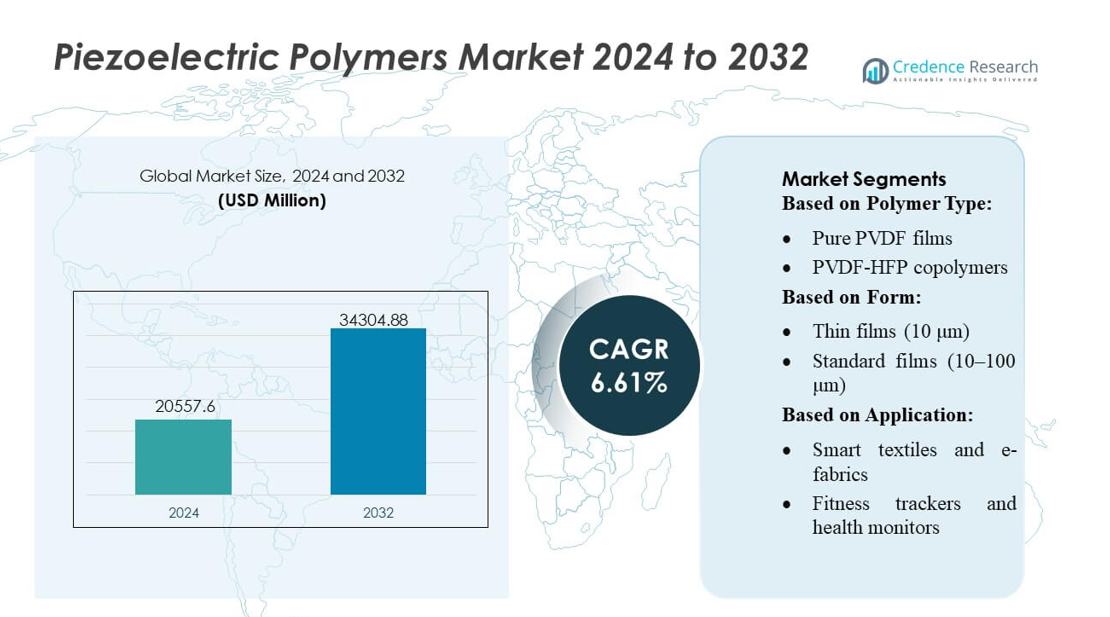
Piezoelectric Polymers Market size was valued USD 20557.6 million in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 34304.88 million by 2032, at a CAGR of 6.61% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Piezoelectric Polymers Market Size 2024 |
USD 20557.6 million |
| Piezoelectric Polymers Market, CAGR |
6.61% |
| Piezoelectric Polymers Market Size 2032 |
USD 34304.88 million |
The Piezoelectric Polymers Market features a diverse competitive ecosystem shaped by material innovators, component manufacturers, and advanced sensor solution providers driving performance improvements in flexibility, electromechanical coupling, and device miniaturization. Companies such as CeramTec, Sparkler Ceramics, CTS Corporation, Noliac A/S, Mad City Labs, Inc., Peizosystem Jena GmbH, Piezomechanik Dr. Lutz Pickelmann GmbH, APC International, Ltd., Harris Corporation, and PI Ceramic GmbH strengthen market progress by expanding high-precision polymer films, thin-film actuators, and next-generation transducer technologies. North America leads the global market with an exact 41 percent share, supported by strong R&D investments, early adoption of flexible sensors, and a robust ecosystem for wearable electronics and medical device integration.
Market Insights
- The Piezoelectric Polymers Market reached USD 20557.6 million in 2024 and is projected to hit USD 34304.88 million by 2032 at a 61% CAGR, driven by strong demand for flexible, lightweight sensing and energy-harvesting components.
- Rising adoption of PVDF and copolymer-based materials enhances electromechanical coupling efficiency, supporting growth in wearable electronics, medical implants, and soft robotics; the sensors segment continues to hold the largest share due to expanding use in health monitoring and industrial automation.
- Competition intensifies as CeramTec, CTS Corporation, PI Ceramic GmbH, Peizosystem Jena GmbH, and Noliac A/S accelerate advancements in thin-film actuators, micro-transducers, and precision polymer films to strengthen product portfolios.
- Market progress faces restraints from material processing limitations, temperature sensitivity, and performance degradation under long-term mechanical stress, affecting adoption in high-load industrial environments.
- North America dominates with an exact 41% regional share, supported by strong R&D activity, rapid integration of flexible sensors in medical devices, and early adoption across aerospace and wearable electronics ecosystems.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Polymer Type
PVDF and basic copolymers maintain the leading position with an estimated over 45% share, driven by their strong electroactive β-phase content, superior mechanical flexibility, and compatibility with large-scale film manufacturing. Pure PVDF films dominate within this category due to their established performance in sensors, energy harvesters, and medical transducers. Rising adoption of P(VDF-TrFE) advanced copolymers, especially thin films and nanofibers, strengthens demand in precision electronics and MEMS. Polymer-ceramic composites such as PVDF-BaTiO₃ and PVDF-ZnO gain momentum for high-output applications, while emerging bio-based and experimental polymers expand niche R&D-driven opportunities.
- For instance, PiezoPaint™ flexible‑substrate piezoelectric patches depositable on fabrics, polymers, PCBs, or paper are specified with film thickness between 100 to 200 µm and usable film dimensions from 1 to 200 mm, enabling integration into wearable substrates and flexible electronics.
By Form
Films and membranes represent the dominant form segment with over 50% market share, supported by extensive usage in flexible sensors, wearable patches, and energy-harvesting layers. Within this group, thin films around 10 μm lead due to their high sensitivity, ease of integration into compact electronics, and compatibility with roll-to-roll processes. Standard and thick films address industrial transducers and structural monitoring systems. Fibers and textiles including electrospun nanofibers, core-spun yarns, and woven fabrics see fast growth from smart textile innovations, while 3D-printed and molded composite structures gain traction for customized piezoelectric architectures in robotics and biomedical devices.
- For instance, Noliac’s multilayer actuator research documents performance envelopes of soft-doped (NCE51) and hard-doped (NCE46) PZT materials over elevated temperatures (up to 200 °C), showing measured variation of free displacement, stiffness and other performance parameters under high-field and high-temperature conditions.
By Application
Wearable electronics hold the largest share at over 40%, propelled by strong adoption in smart textiles, health-monitoring patches, and next-generation e-skin systems. Fitness trackers, smart watches, and flexible IoT devices rely heavily on PVDF-based films for continuous energy harvesting and motion sensing. IoT sensor networks including environmental, industrial, and smart-city infrastructure systems expand demand for durable, lightweight piezoelectric polymers. Medical devices and implants represent a rapidly advancing segment, supported by implantable pacemakers, biosensors, prosthetic feedback systems, and controlled drug-delivery platforms that utilize biocompatible piezoelectric materials for precision operation.
Key Growth Drivers
Expanding Adoption in Wearables and Smart Textiles
The market grows strongly as wearable electronics, smart textiles, and e-skin platforms increasingly integrate flexible piezoelectric polymers for motion sensing, pressure detection, and energy harvesting. Lightweight PVDF and P(VDF-TrFE) films enable self-powered capabilities, enhancing battery life and improving user comfort in fitness trackers, medical patches, and smart clothing. Advancements in low-temperature processing and thin-film deposition further boost adoption across consumer electronics and healthcare. This expanding use-case ecosystem establishes piezoelectric polymers as a preferred material for next-generation personalized and connected devices.
- For instance, Nano‑View®/M Series, which offers sub‑nanometer resolution with closed‑loop control and XYZ motion ranges up to 300 µm per axis under PicoQ® feedback control.
Rising Deployment of IoT and Distributed Sensor Networks
IoT expansion accelerates demand for piezoelectric polymers as industries deploy dense sensor networks for structural monitoring, environmental tracking, and industrial automation. These materials offer mechanical durability, low power consumption, and the ability to generate real-time data from vibrations and pressure variations. Their compatibility with flexible substrates and wireless communication modules supports integration into smart city infrastructure, precision agriculture, and remote monitoring nodes. As energy-efficient IoT systems gain priority, piezoelectric polymer-based self-powered sensors play a central role in reducing maintenance and enabling long-life field operations.
- For instance, Piezosystem Jena GmbH stack‑type actuator offers motion up to 82 µm, with sub‑nanometer resolution, high stiffness up to 210 N/µm, and blocking force up to 850 N under appropriate drive voltage.
Advancements in Medical Devices and Implantable Systems
Medical innovation significantly drives the market as piezoelectric polymers enhance precision sensing, biomechanics monitoring, and controlled drug delivery. PVDF and its copolymers deliver biocompatibility, flexibility, and stable electromechanical response, making them suitable for implantable pacemakers, biosensors, prosthetics, and neural interfaces. Their ability to operate as miniature energy harvesters reduces reliance on frequent battery replacements in implantable systems. Growing demand for minimally invasive devices and personalized treatment technologies strengthens adoption across diagnostics, rehabilitation equipment, and long-term physiological monitoring solutions.
Key Trends & Opportunities
Growth of Advanced Film Architectures and Nanostructured Materials
The market benefits from innovations in nanostructured films, including electrospun nanofibers, ultrathin P(VDF-TrFE) layers, and polymer–ceramic hybrid systems engineered for higher piezoelectric coefficients. These architectures offer improved sensitivity, faster response times, and greater flexibility for emerging applications in robotics, soft actuators, and AI-integrated sensors. Advancements in additive manufacturing and 3D-printed piezoelectric structures open opportunities for custom device geometries and biomedical implants. This trend positions nanostructured polymer platforms as a central enabler of next-generation smart materials and multifunctional electronic components.
- For instance, APC’s proprietary PZT materials (e.g. APC 850, APC 855) show piezoelectric charge constant d₃₃ up to around 630 × 10⁻¹² C/N for certain compositions, enabling strong actuation or sensing performance in high‑power or high‑sensitivity devices.
Increasing Shift Toward Sustainable and Bio-Based Polymers
Environmental priorities create opportunities for bio-based and biodegradable piezoelectric polymers that reduce reliance on fluorinated materials. Research-stage bio-piezoelectric materials derived from cellulose, amino acids, and biopolymers attract attention for wearable healthcare systems, eco-friendly sensors, and transient electronics. Their renewable origin and compatibility with green manufacturing align with regulatory expectations for sustainable electronics. As industries move toward circular material solutions, bio-based piezoelectric polymers present a strategic pathway for companies aiming to differentiate through environmental performance while supporting low-impact device innovation.
- For instance, PICMA® actuators (product series P‑843) deliver a travel range up to 90 µm, a push force capacity around 800 N, and a pull force capacity near 300 N, with sub‑microsecond response time and sub‑nanometer resolution for high‑precision applications.
Integration into Soft Robotics and Human–Machine Interfaces
The rapid development of soft robotics and interactive interfaces drives opportunities for highly flexible, conformable piezoelectric polymers. These materials enable tactile sensing, proprioception, and motion feedback in robotic grippers, prosthetic limbs, and haptic communication systems. Their ability to withstand repeated mechanical deformation without performance loss makes them ideal for artificial skin, rehabilitation robotics, and immersive XR systems. As industries pursue more intuitive human–machine interaction platforms, piezoelectric polymers serve as core functional elements that deliver real-time sensory feedback and adaptive control capabilities.
Key Challenges
Performance Limitations Compared to Ceramic Counterparts
Despite their flexibility advantages, piezoelectric polymers often exhibit lower piezoelectric constants and thermal stability than ceramic materials such as PZT. These limitations restrict use in high-power actuation, high-temperature environments, and heavy industrial applications. Achieving consistent β-phase crystallinity and stable electromechanical output remains a technical challenge during large-scale processing. Manufacturers must balance mechanical flexibility with improved electrical performance, driving ongoing R&D investment into composite structures, advanced copolymers, and optimized fabrication methods to reduce the performance gap with traditional ceramic technologies.
Complex Manufacturing Processes and Cost Pressures
Producing high-quality piezoelectric polymer films, nanofibers, and composite structures requires precise control of crystallization, poling, and material purity, increasing manufacturing complexity and cost. Scaling advanced processes such as electrospinning, atomic-layer deposition, and multilayer lamination poses technical barriers for mass production. Cost-sensitive consumer electronics and IoT applications face challenges in justifying premium material pricing. Without broader process optimization and standardized fabrication routes, manufacturers may struggle to achieve competitive cost-to-performance ratios that support large-volume commercial deployment.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America leads the Piezoelectric Polymers Market with an estimated 34% share, supported by strong R&D capabilities, advanced electronics manufacturing, and early adoption of flexible sensors in wearables and healthcare devices. The region benefits from robust investment in IoT infrastructure, biomedical engineering, and smart textiles, accelerating demand for PVDF-based films and P(VDF-TrFE) copolymers. Growing deployment of piezoelectric polymers in implantable medical devices, industrial monitoring systems, and defense-grade sensing platforms sustains momentum. Extensive collaborations between research institutes and material developers further strengthen innovation pipelines, reinforcing the region’s leadership position.
Europe
Europe holds approximately 29% of the market, driven by strong regulatory support for advanced materials, sustainable electronics, and high-performance sensors. The region’s industrial ecosystem emphasizes automotive safety systems, precision robotics, and wearable healthcare technologies, boosting adoption of piezoelectric polymer films and composites. Demand grows as energy-harvesting components gain relevance in smart infrastructure and Industry 4.0 applications. Leading universities and material research centers advance polymer–ceramic hybrid structures and nanofiber architectures, enhancing performance characteristics. Emphasis on eco-friendly materials and rising interest in biodegradable piezoelectric polymers further expand Europe’s technological and commercial footprint.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific accounts for the fastest growth trajectory and commands roughly 31% market share, supported by large-scale electronics production, expanding IoT device manufacturing, and strong government incentives for advanced materials. China, Japan, and South Korea lead innovation in flexible sensors, e-textiles, and miniaturized actuators, strengthening demand for PVDF and P(VDF-TrFE) thin films. Rapid development of consumer wearables, smart home technologies, and industrial automation accelerates adoption across emerging economies. APAC’s deep manufacturing capacity enables competitive pricing and large-volume output, positioning the region as a global hub for piezoelectric polymer technology development and commercialization.
Latin America
Latin America captures roughly 4% of the market, with steady growth emerging from expanding healthcare modernization, smart agriculture technologies, and early adoption of IoT-based environmental monitoring systems. Countries such as Brazil, Mexico, and Chile increasingly explore piezoelectric polymer sensors for industrial safety, remote monitoring, and wearable health devices. Local manufacturing remains limited, but rising import availability and growing integration of flexible sensors into consumer electronics support demand. Government-led digitalization efforts and partnerships with global electronics suppliers help strengthen technology penetration, gradually improving the region’s position in the overall market landscape.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region accounts for approximately 2% market share, driven by selective adoption in industrial monitoring, oil and gas operations, and smart city infrastructure projects. Countries in the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) invest in IoT and automation systems that incorporate piezoelectric polymer-based sensors for vibration detection and environmental tracking. Healthcare modernization in South Africa and the UAE further supports growth in wearable and diagnostic applications. Limited regional manufacturing capacity restrains broader adoption, yet increasing reliance on imported high-performance materials and pilot projects in smart infrastructure create emerging opportunities.
Market Segmentations:
By Polymer Type:
- Pure PVDF films
- PVDF-HFP copolymers
By Form:
- Thin films (10 μm)
- Standard films (10–100 μm)
By Application:
- Smart textiles and e-fabrics
- Fitness trackers and health monitors
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
The Piezoelectric Polymers Market features a competitive landscape shaped by companies such as CeramTec, Sparkler Ceramics, CTS Corporation, Noliac A/S, Mad City Labs, Inc., Peizosystem Jena GmbH, Piezomechanik Dr. Lutz Pickelmann GmbH, APC International, Ltd., Harris Corporation, and PI Ceramic GmbH. the Piezoelectric Polymers Market is defined by continuous innovation in material engineering, advanced processing technologies, and application-specific product development. Companies prioritize enhancing the piezoelectric response of PVDF-based films, improving β-phase crystallinity, and expanding the use of nanofiber architectures and polymer–ceramic hybrid systems to meet rising performance requirements. Efforts focus on scaling thin-film manufacturing, optimizing poling techniques, and integrating flexible materials into wearables, medical implants, and IoT sensor networks. Market participants strengthen competitiveness through strategic collaborations with electronics manufacturers, medical-technology innovators, and research institutions. Growing emphasis on lightweight, biocompatible, and energy-efficient materials further drives product differentiation and positions the industry for accelerating adoption across smart devices, industrial monitoring systems, and next-generation soft robotics applications.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
- CeramTec
- Sparkler Ceramics
- CTS Corporation
- Noliac A/S
- Mad City Labs, Inc.
- Peizosystem Jena GmbH
- Piezomechanik Dr. Lutz Pickelmann GmbH
- APC International, Ltd.
- Harris Corporation
- PI Ceramic GmbH
Recent Developments
- In September 2025, Daikin declared a five-year deal with ENGIE North America to supply all the businesses of the company with 100% renewable electricity, such as the Daikin Texas Technology Park, where its largest manufacturing facility, together with the North American headquarters, resides. This partnership highlights the use of renewable energy sources by Daikin.
- In June 2025, Queensgate Instruments released a new heavy-duty nanopositioning piezo stage that can handle loads up to 6 kg, extending its high-performance line. This lever-amplified stage, which has a 250 µm travel range, is suitable for applications like semiconductor inspection, white light interferometry, and precision manufacturing due to its sub-nanometer resolution, flexure-guided motion, and direct capacitive sensing.
- In July 2024, 3M made a strategic investment in Ohmium International, a developer of green hydrogen production electrolyzer systems, as part of its efforts to support a transition to a low-carbon economy and potentially decarbonize its own operations
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Polymer Type, Form, Application and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- The market will advance as flexible piezoelectric films gain wider use in wearable health-monitoring devices.
- Manufacturers will expand production of PVDF-based materials to meet rising demand for lightweight energy-harvesting components.
- Researchers will improve polymer alignment techniques to increase sensitivity and extend device longevity.
- Adoption will accelerate in soft robotics due to the need for stretchable and responsive sensing materials.
- Integration of piezoelectric polymers into smart textiles will grow as brands seek ultra-thin, washable sensing layers.
- Automotive suppliers will incorporate these polymers into vibration monitoring and occupant-sensing systems.
- Medical device companies will use next-generation polymers to develop smaller, more accurate implantable sensors.
- Renewable-energy applications will rise as flexible polymer harvesters become more efficient in low-frequency environments.
- Electronics manufacturers will adopt these materials for self-powered switches and compact tactile interfaces.
- Sustainability initiatives will promote bio-based and recyclable piezoelectric polymers, driving material innovation.




