Market Overview
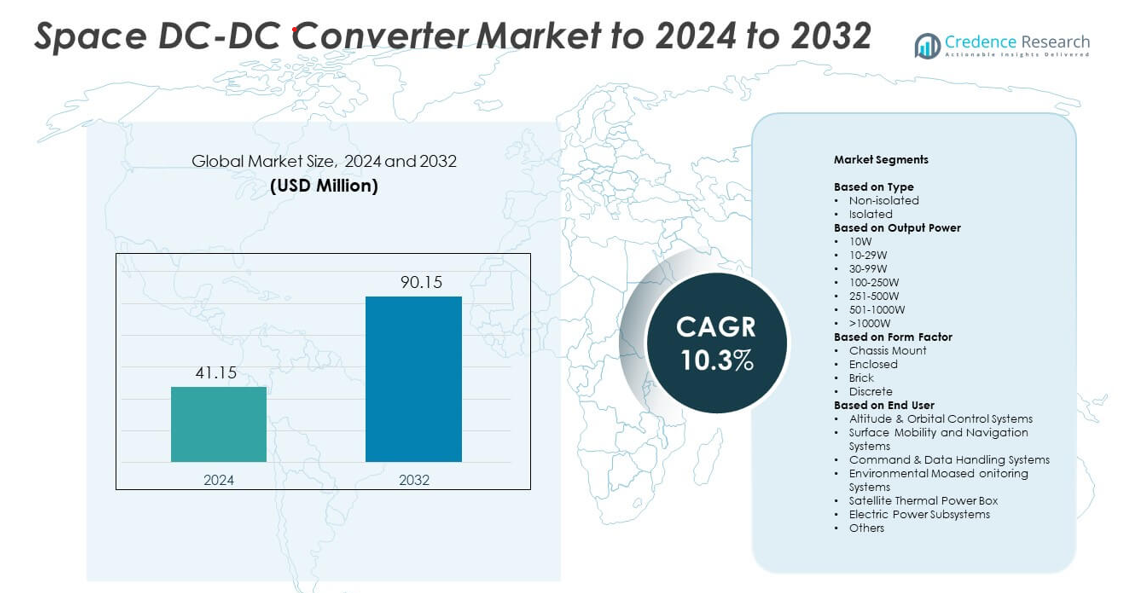
Space DC-DC Converter Market size was valued at USD 41.15 million in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 90.15 million by 2032, at a CAGR of 10.3% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Space DC-DC Converter Market Size 2024 |
USD 41.15 million |
| Space DC-DC Converter Market, CAGR |
10.3% |
| Space DC-DC Converter Market Size 2032 |
USD 90.15 million |
The Space DC-DC Converter Market is shaped by major players including Modular Devices Inc., Infineon Technologies AG, Astronics Corporation, Renesas Electronics Corporation, Crane Co., STMicroelectronics, EPC Space, Advanced Energy Industries Inc., Microsemi Corporation, and Airbus Group SE. These companies drive competitiveness through radiation-hardened designs, high-efficiency power modules, and compact form factors suited for modern satellite platforms. North America emerged as the leading region in 2024 with about 39% share, supported by strong satellite production, defense investment, and a mature space electronics ecosystem. Europe and Asia Pacific followed with notable growth driven by expanding commercial and governmental space programs.
Market Insights
- The Space DC-DC Converter Market reached USD 41.15 million in 2024 and is projected to hit USD 90.15 million by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 10.3%.
- Growth is driven by rising satellite constellations, higher demand for radiation-tolerant power modules, and expanding use of electric propulsion systems across commercial and defense missions.
- Key trends include miniaturized high-density converters, modular power architectures, and wider adoption of advanced semiconductor materials for improved efficiency and thermal control.
- Competition strengthens as major players enhance reliability, reduce converter size, and expand rad-hard product lines tailored for small satellites and high-power payloads.
- North America led the market with about 39% share, followed by Europe at nearly 27% and Asia Pacific at around 23%, while isolated converters dominated by type with roughly 63% share in 2024.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Type
The isolated segment led the Space DC-DC Converter Market in 2024 with about 63% share. Engineers favored isolated converters due to strong protection from voltage spikes, improved noise immunity, and better suitability for radiation-prone satellite environments. These converters support stable power delivery for payloads, propulsion modules, and communication systems. Demand also rose from growing deployment of small satellites and deep-space missions that require high reliability. Non-isolated converters grew at a steady pace as operators adopted compact solutions for low-power electronics and avionics boards.
- For instance, VPT’s SVR Series isolated DC-DC converters are qualified to MIL-PRF-38534 Class K and withstand total ionizing doses up to 100 krad(Si), as documented in VPT’s radiation test reports (2019).
By Output Power
The 30–99W segment dominated this category in 2024 with around 34% share, supported by wide use in satellite payload electronics, telemetry systems, and power regulation modules. This range offers a balance between efficiency, compact size, and thermal stability, which suits large constellations and commercial space missions. Higher-power ranges such as 100–250W and 251–500W gained traction due to rising demand for electric propulsion units and high-load communication hardware. Lower-power options, including 10W units, remained essential for sensors and onboard computing systems.
- For instance, Crane Aerospace & Electronics’ Interpoint hMOR DC-DC converters provide up to 120 watts output power. They accept 15 to 50 volt inputs and operate from −55°C to +125°C.
By Form Factor
Brick-type converters held the leading position in 2024 with nearly 47% share. Their modular structure, strong thermal handling, and radiation-tolerant design made them a preferred choice for bus power systems and high-density satellite platforms. Brick converters also reduce integration time, which supports rapid spacecraft production cycles. Chassis-mount and enclosed formats saw rising uptake in large spacecraft and defense platforms that need rugged housing. Discrete converters remained important for custom power layouts in scientific payloads and specialized mission architectures.
Key Growth Drivers
Rising Satellite Constellation Deployments
Growing production of commercial and government satellite constellations drives strong demand for space-qualified DC-DC converters. Constellations need reliable power regulation for payloads, communication units, and propulsion modules. Expanding programs in Earth observation, broadband connectivity, and navigation increase converter volumes across power classes. Low-Earth orbit platforms also push demand for radiation-tolerant and high-efficiency designs, supporting sustained market growth.
- For instance, SpaceX’s Starlink program had launched 10,663 satellites by 8 December 2025. Of these, 7,867 were listed as operational in public launch statistics.
Advances in Radiation-Hardened Power Electronics
Progress in radiation-hardened semiconductors and improved shielding methods boosts adoption across deep-space and defense missions. These improvements help converters handle extreme temperature swings, ionizing radiation, and voltage instability. Better reliability reduces mission risk and supports longer orbital lifetimes. As agencies and operators seek higher performance with reduced power losses, converter manufacturers benefit from rising investment in advanced rad-hard technologies.
- For instance, Texas Instruments offers several individual space-grade components and reference designs which use these components to build space power systems. Individual products like the TPS7H4011-SP (a 12-A DC/DC converter) are characterized to sustain a total ionizing dose (TID) of 100 krad(Si) and remain immune to destructive single-event effects (SEL, SEB, and SEGR) up to a 75 MeV·cm²/mg linear energy transfer (LET) at 125 °C, ensuring their functionality in harsh space radiation environments.
Growth in Electrification of Spacecraft Systems
Modern spacecraft integrate more electric propulsion units, high-power payloads, and digital subsystems. This shift increases the number of regulated power stages required onboard. DC-DC converters help maintain stable power distribution for sensors, processors, and communication hardware. Higher load demands in next-generation satellites encourage use of efficient, compact, and thermally robust converter architectures, fueling consistent market expansion.
Key Trends & Opportunities
Miniaturization and High-Density Converter Designs
Manufacturers develop smaller, lighter, and higher-density converter modules to match the needs of small satellites and CubeSats. These spacecraft require compact components that deliver high efficiency in limited space. Advanced packaging, gallium nitride devices, and improved thermal solutions create strong opportunities. This trend aligns with rapid growth in commercial space missions seeking reduced launch mass and flexible power architectures.
- For instance, Teledyne e2v HiRel’s TDG650E30BEP GaN transistor is rated 650 volts and 30 amps. It is packaged in a 7.1 by 8.5 by 0.56 millimetre GaNPX device.
Expansion of Modular and Standardized Power Platforms
There is a rising shift toward modular converter formats that support faster spacecraft integration and reduced development cycles. Standardized brick and enclosed designs allow operators to scale systems across multiple missions with minimal redesign. This trend strengthens procurement efficiency and accelerates production of satellite fleets. It also expands opportunities for suppliers offering radiation-tolerant modules built around common form factors.
- For instance, Vicor’s BCM6123 bus converter is housed in a ChiP (Converter housed in a Package) with standard dimensions of 63.34 by 22.80 by 7.21 millimetres (or 2.494 x 0.898 x 0.284 inches).
Key Challenges
Stringent Space Qualification and Testing Requirements
Space-grade DC-DC converters must pass exhaustive testing for radiation tolerance, vibration, thermal cycling, and long-term reliability. These requirements increase development time and cost for manufacturers. Smaller players face difficulty entering the market due to high certification barriers. Lengthy qualification cycles can delay spacecraft programs, creating challenges for suppliers competing in fast-moving commercial segments.
Thermal Management and Power Efficiency Constraints
Converters must maintain stable performance under harsh thermal conditions while supporting rising power demands. Limited surface area in compact spacecraft restricts heat dissipation, increasing design complexity. High efficiency is essential to avoid excess thermal load and power loss. Meeting these constraints while maintaining radiation tolerance remains a major challenge for engineering teams developing next-generation converter systems.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America held the leading position in the Space DC-DC Converter Market in 2024 with about 39% share. Growth came from strong satellite production, defense modernization, and expanding commercial launch activity. The region benefits from advanced power electronics research and high investment from aerospace firms. Rising procurement of small satellites and continued funding for deep-space missions support steady converter demand. Increasing use of electric propulsion and high-power payloads further strengthens adoption across government and private programs.
Europe
Europe accounted for nearly 27% share in 2024, driven by active participation in scientific missions, Earth observation programs, and commercial satellite networks. The region’s investment in radiation-hardened components and standardized power module development supports converter adoption across multiple platform types. Growth is reinforced by strong contributions from national space agencies and collaborative missions under the European Space Agency. Increasing deployment of navigation and communication satellites also boosts demand for high-efficiency DC-DC converters.
Asia Pacific
Asia Pacific captured roughly 23% share in 2024 and continues to expand due to rising satellite manufacturing and government-backed space programs. Countries invest heavily in Earth observation, broadband constellations, and lunar exploration missions, which drives converter demand across diverse power classes. Growth is further supported by rapid development in commercial launch services and rising participation from private space companies. The region’s emphasis on miniaturized spacecraft and cost-efficient platforms strengthens adoption of compact converter designs.
Latin America
Latin America held around 6% share in 2024, supported by gradual expansion in national satellite programs and increased collaboration with global space agencies. The region invests in communication satellites, remote-sensing missions, and capacity-building initiatives that require reliable spacecraft power systems. Growing interest in space technology education and regional launch infrastructure development contributes to future market potential. Demand remains moderate but is expected to rise as countries adopt more advanced payloads and diversify into small satellite platforms.
Middle East and Africa
Middle East and Africa accounted for nearly 5% share in 2024, driven by mission needs in communication, defense monitoring, and environmental observation. Investments in national space agencies and satellite ground infrastructure support steady demand for power conversion systems. The region seeks stronger technological partnerships to improve capability in spacecraft design and subsystem integration. As countries pursue space programs for security and commercial use, adoption of radiation-tolerant and high-efficiency DC-DC converters is expected to rise gradually.
Market Segmentations:
By Type
By Output Power
- 10W
- 10-29W
- 30-99W
- 100-250W
- 251-500W
- 501-1000W
- >1000W
By Form Factor
- Chassis Mount
- Enclosed
- Brick
- Discrete
By End User
- Altitude & Orbital Control Systems
- Surface Mobility and Navigation Systems
- Command & Data Handling Systems
- Environmental Monitoring Systems
- Satellite Thermal Power Box
- Electric Power Subsystems
- Others
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
The Space DC-DC Converter Market features leading companies such as Modular Devices Inc., Infineon Technologies AG, Astronics Corporation, Renesas Electronics Corporation, Crane Co., STMicroelectronics, EPC Space, Advanced Energy Industries Inc., Microsemi Corporation, and Airbus Group SE. These companies compete through advancements in radiation-hardened designs, high-efficiency architectures, and compact converter formats tailored for modern spacecraft. Manufacturers focus on improving thermal stability, enhancing reliability, and supporting higher power densities to meet mission demands. The market also shows strong emphasis on modular platforms that reduce integration time for satellite builders. Increasing adoption of electric propulsion, high-data-rate payloads, and large satellite constellations reinforces demand for robust converter solutions. Continuous investments in semiconductor innovation and qualification testing further strengthen the competitive environment.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
Recent Developments
- In 2025, EPC Space launched the EPCS4001 radiation-hardened DC-DC buck converter controller, designed to be paired with EPC Space’s existing GaN power stages to enable high-efficiency DC-DC converters in space applications, improving power density and switching performance.
- In 2023, Advanced Energy introduced ultra-miniature, programmable high-voltage precision DC-DC converters designed for applications where space and weight are critical, expanding its high-voltage converter portfolio for demanding electronics.
- In 2023, Infineon completed the sale of its HiRel DC-DC converter business to Micross Components, while continuing to supply key semiconductor devices for high-reliability and space power solutions
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Type, Output Power, Form Factor, End User and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- The market will grow as satellite constellations expand across commercial and government programs.
- Demand for radiation-hardened converters will rise with more deep-space and defense missions.
- Miniaturized power modules will gain adoption in small satellites and CubeSats.
- High-efficiency converter designs will support electric propulsion and high-power payloads.
- Modular and standardized converter platforms will speed spacecraft integration.
- Advanced semiconductor materials will improve thermal management and reliability.
- Converter suppliers will benefit from increasing private-sector investment in space technology.
- Autonomous spacecraft systems will require more stable and distributed power regulation.
- Global collaboration will expand opportunities for multi-mission converter development.
- Lifecycle-focused designs will support longer mission durations and reduced maintenance needs.




