Market Overview:
Lab Automation for In Vitro Diagnostic Market was valued at USD 5857.6 million in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 9421.01 million by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 6.12% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Lab Automation for In Vitro Diagnostic Market Size 2024 |
USD 5857.6 million |
| Lab Automation for In Vitro Diagnostic Market, CAGR |
6.12% |
| Lab Automation for In Vitro Diagnostic Market Size 2032 |
USD 9421.01 million |
The Lab Automation for In Vitro Diagnostic Market is shaped by major players such as Thermo Fisher Scientific, Agilent Technologies, PerkinElmer Inc., Siemens Healthineers, Becton Dickinson and Company, Beckman Coulter, Abbott Laboratories, Danaher Corporation, bioMérieux SA, and Roche Diagnostics. These companies lead through advanced automated workstations, robotics, and integrated software that support faster, more accurate testing. Strong portfolios in molecular, clinical, and high-throughput diagnostics help them maintain wide global adoption. North America remained the leading region in 2024 with 37% market share, driven by advanced healthcare infrastructure, strong investment in automation, and high diagnostic workloads across large laboratory networks.
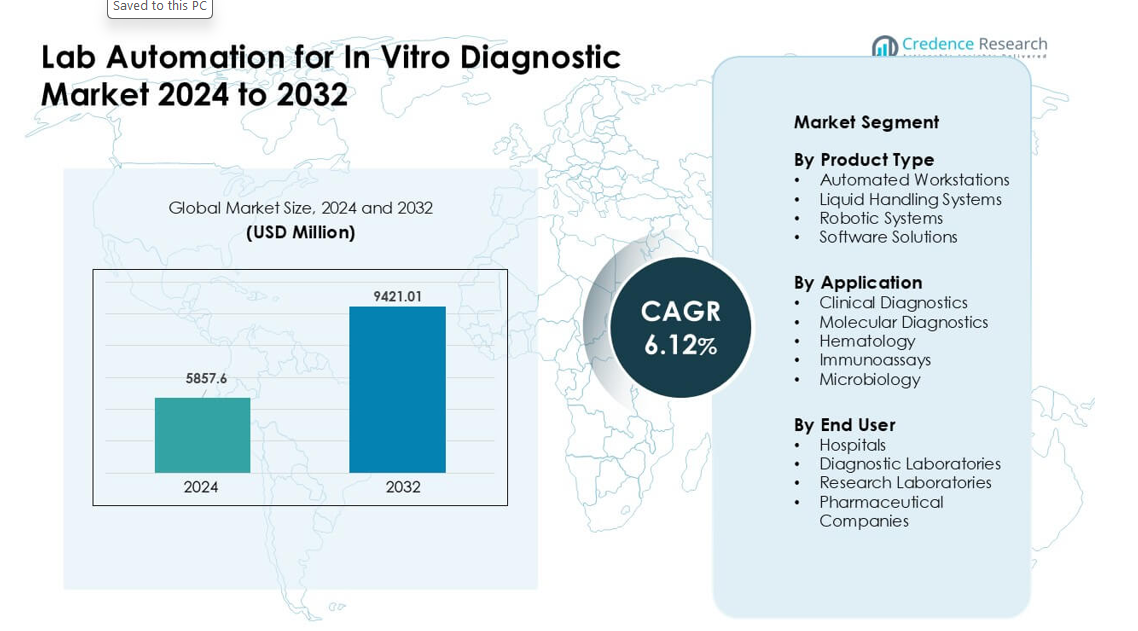
Market Insights:
- The Lab Automation for In Vitro Diagnostic Market reached USD 6 million in 2024 and is projected to hit USD 9421.01 million by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 6.12%.
- Demand rises due to increasing diagnostic volumes, strong adoption of molecular testing, and the push for faster, error-free workflows across high-throughput laboratories.
- Trends include wider use of AI-driven analytics, modular automation platforms, and integrated software tools that improve sample tracking and operational efficiency.
- The market remains competitive, led by Thermo Fisher Scientific, Agilent Technologies, PerkinElmer Inc., Siemens Healthineers, Becton Dickinson and Company, Beckman Coulter, Abbott Laboratories, Danaher Corporation, bioMérieux SA, and Roche Diagnostics.
- North America leads with 37% share, Europe holds 30%, and Asia-Pacific accounts for 25%; automated workstations dominate product type with 42% share, while clinical diagnostics remains the top application with 48%.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Product Type
Automated workstations held the leading share in 2024 with about 42%. Buyers favored these systems due to high throughput, reduced manual errors, and smooth integration with sample prep tools. Many hospitals and labs adopted these units to handle rising diagnostic volumes linked to infectious-disease testing and chronic-care screening. Liquid handling systems and robotic systems grew as labs pushed for faster turnaround time. Software solutions advanced through stronger analytics and real-time monitoring, but automated workstations stayed ahead because they delivered the strongest mix of speed, accuracy, and workflow control.
- For instance, Roche’s cobas® c 703 part of its cobas pro integrated workstation lineup supports up to 2,000 tests per hour with a reagent capacity of 70 positions.
By Application
Clinical diagnostics led the application segment in 2024 with nearly 48% share. Demand increased due to large test volumes across routine panels, infectious disease screens, metabolic tests, and chronic-disease monitoring. Automated platforms helped labs boost accuracy and cut operator workload, which supported rapid adoption. Molecular diagnostics grew fast with higher use of PCR and sequencing, while hematology, immunoassays, and microbiology adopted automation to handle rising sample loads. Clinical diagnostics kept the top spot because hospitals and national labs relied heavily on automated systems to maintain stable turnaround times.
- For instance, Roche’s molecular automation suite cobas 5800 system delivers up to 144 results in an 8‑hour shift, consolidating multiple assays on a single platform, which helps labs efficiently manage routine molecular diagnostics workloads.
By End User
Diagnostic laboratories dominated the end-user segment with around 46% share in 2024. These labs handled heavy daily sample flows, which pushed demand for automated workstations, liquid handling units, and robotics. Automation helped reduce labor strain, improve reproducibility, and maintain compliance with quality standards. Hospitals expanded adoption to support emergency and inpatient testing, while research labs and pharmaceutical companies used automation for assay development and high-volume studies. Diagnostic laboratories remained the leading users because they required consistent, high-throughput performance to support routine and specialized testing needs.
Key Growth Drivers:
Rising Diagnostic Volumes and Need for Faster Turnaround
Global testing volumes continue to rise due to higher chronic-disease prevalence, wider infectious-disease screening, and growing adoption of preventive health programs. Laboratories now process thousands of samples each day, which increases pressure on accuracy and speed. Lab automation supports this need by reducing manual work, lowering error rates, and improving sample traceability. Automated workstations and robotic platforms allow smooth handling of repetitive tasks, which helps labs cut bottlenecks during peak demand. Many hospitals and diagnostic chains also use automation to meet strict reporting timelines mandated by national health systems. These factors place strong emphasis on advanced automated workflows across urban and regional diagnostic centers.
- For instance, the Roche Molecular Work Area built around its cobas® 5800/6800/8800 systems claims to deliver up to 10 million trusted, reproducible results every month worldwide, consolidating high-volume testing without escalating staffing needs.
Expansion of Molecular and High-Complexity Testing
Rapid growth in molecular diagnostics fuels strong automation demand across global laboratories. PCR, sequencing, and advanced pathogen-detection workflows require precise liquid handling, contamination control, and repeatable performance, which automated systems deliver with high reliability. Many labs now adopt automated extraction units, sample prep stations, and integrated robotics to support high-complexity assays at scale. Rising use of genomic profiling in oncology, inherited-disease testing, and antimicrobial resistance studies also pushes labs toward automated instrumentation. Automation enables faster processing of multiplex assays and supports continuous operation. This shift aligns with growing national investments in precision-medicine programs and infectious-disease surveillance, which depend on consistent throughput.
- For instance, using the Roche cobas® 6800 system, a molecular lab can produce up to 576 results in 8 hours (and up to 2,112 in 24 hours), providing high-throughput PCR capability ideal for large-scale molecular diagnostics.
Workforce Shortages and Rising Focus on Operational Efficiency
Many countries face increasing shortages of skilled laboratory technicians, which slows diagnostic workflows and affects service quality. Automation helps laboratories maintain output despite limited staffing by taking over repetitive, labor-intensive tasks. Automated systems also reduce training needs, improve procedural consistency, and support round-the-clock operation without fatigue-related errors. Private labs and hospital networks use automation to cut operational costs while meeting strict accreditation standards. Digital tools such as automated scheduling, QC tracking, and real-time workflow visibility strengthen efficiency further. These benefits make automation a strategic investment for labs seeking stable performance and long-term operational resilience.
Key Trend & Opportunity:
Integration of AI-Driven Analytics and Predictive Workflow Tools
Artificial intelligence plays a growing role in modern diagnostic labs. New platforms combine automation hardware with predictive analytics to optimize batch planning, reagent use, and instrument uptime. AI helps detect processing anomalies early and supports automated QC validation for large sample loads. Software vendors invest in cloud-linked analytics, remote monitoring, and interoperability features that enhance laboratory decision-making. Labs also benefit from automated result interpretation tools for molecular and clinical assays. As data volumes grow, AI-driven automation creates opportunities for real-time reporting, streamlined workflows, and improved clinical insights. This trend supports strong demand for smart, connected automation systems.
- For instance, LabLynx offers an AI‑powered Laboratory Information Management System (LIMS) that provides real‑time anomaly detection, predictive analytics, and intelligent task scheduling helping labs anticipate workload peaks, allocate resources, and minimize bottlenecks before they occur.
Rising Adoption of Modular and Scalable Automation Platforms
Many labs now prefer modular automation units that can scale with patient volume and test complexity. These platforms allow step-by-step expansion, starting from basic liquid handling to full robotic integration. Modular designs reduce upfront costs and help smaller laboratories adopt automation at a manageable pace. Vendors offer plug-and-play units for sample prep, aliquoting, storage management, and plate handling, which increases operational flexibility. This trend aligns with rising demand from mid-sized diagnostic chains in emerging markets. Scalable solutions support broad adoption and create opportunities for long-term upgrades as testing capacity grows.
- For instance, Formulatrix markets its “Rover” and “STACK” automation systems a modular, scalable approach where labs can start with simple plate handling and later scale up by adding robotic arms or additional tracks as throughput demands grow.
Growing Penetration in Emerging Markets
Automation adoption increases across regions such as Asia-Pacific, the Middle East, and Latin America due to expanding healthcare infrastructure and rising test loads. Governments invest in modern laboratory networks, infectious-disease surveillance, and digital health programs, creating strong demand for automated diagnostic platforms. Many private laboratory chains expand rapidly in these regions, adding automated workstations to strengthen service quality and turnaround time. Vendors also localize training, service, and reagent support to win long-term contracts. These developments create large opportunities for high-throughput automation, affordable modular systems, and software-driven workflow tools.
Key Challenge:
High Capital Costs and Limited Budget Flexibility
Many diagnostic laboratories, especially small and mid-sized facilities, struggle with the high initial cost of automated instruments. Expenses related to hardware, installation, software, and maintenance create barriers to adoption. Limited reimbursement rates for diagnostic tests make it harder for labs to justify rapid upgrades. Some emerging-market labs rely on manual workflows due to financial constraints, which slows automation penetration. Vendors attempt to address this challenge through leasing, subscription models, and modular platforms, but cost concerns remain a significant restraint. Budget limitations often delay system replacement cycles and reduce investment in advanced robotics and software.
Integration Complexity and Workflow Compatibility Issues
Integrating new automated systems into existing laboratory workflows often presents technical and operational hurdles. Many labs use legacy LIS platforms, diverse instrument brands, and variable SOPs, which can limit smooth interoperability. Staff must be trained to manage new robotic workflows, recalibrate QC processes, and maintain equipment. Complex laboratory environments also face challenges in physical layout adjustments, contamination control, and sample-tracking upgrades. Any mismatch between instruments and workflow design can reduce efficiency rather than improve it. These integration issues slow adoption and require careful planning, standardization, and vendor coordination to overcome.
Regional Analysis:
North America
North America held the leading share of about 37% in 2024 due to strong diagnostic infrastructure, high adoption of molecular testing, and rapid integration of automated workstations across major labs. Large hospital networks and national reference laboratories used automation to handle rising chronic-disease and infectious-disease test loads. The region benefited from strong spending on precision medicine, advanced sequencing programs, and workforce-efficiency initiatives. Vendors expanded robotics, software platforms, and connected workflow tools to match growing test complexity. These factors kept North America at the forefront of automation adoption.
Europe
Europe accounted for nearly 30% of the market in 2024, driven by strong regulatory support for quality control, structured lab networks, and broad adoption of automated systems in clinical and molecular diagnostics. Many countries expanded national laboratory modernization programs, which increased demand for scalable automation solutions. Reference labs in Germany, the U.K., France, and Nordic countries used robotics to improve accuracy and cut manual workloads. Rising use of molecular assays for cancer, infectious diseases, and antimicrobial resistance strengthened adoption further. Europe remained a key region due to mature healthcare systems and strong compliance standards.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific captured about 25% share in 2024 and remained the fastest-growing region. Large population bases and rising test volumes from chronic and infectious diseases pushed diagnostic centers toward high-throughput automation. Countries such as China, India, Japan, and South Korea invested heavily in laboratory expansion, automated sample handling, and advanced molecular testing platforms. Private diagnostic chains scaled rapidly and adopted automation to support efficiency and affordability. Vendors expanded local manufacturing, service networks, and modular automation solutions. Asia-Pacific’s growth trajectory reflects expanding healthcare access and rising adoption of digital and automated laboratory technologies.
Latin America
Latin America held roughly 5% share in 2024 with steady adoption driven by rising healthcare modernization and wider availability of advanced diagnostic services. Brazil, Mexico, and Argentina led demand as private labs invested in automated workstations and liquid-handling units to improve sample quality and reduce manual errors. Budget constraints slowed full-scale automation, but modular systems and mid-range platforms gained traction. Growing molecular diagnostics adoption, especially in infectious-disease surveillance, supported further uptake. The region’s progress reflects increasing investment in efficiency and standardized testing workflows.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa accounted for about 3% share in 2024, supported by rising investment in healthcare infrastructure and diagnostic capacity. Gulf countries expanded hospital networks and adopted automated platforms to support high-volume testing and infection-control programs. Africa showed slower adoption due to limited budgets, but international partnerships helped introduce automated solutions in major urban labs. Growing demand for molecular diagnostics in disease-surveillance programs drove interest in scalable automation. Despite a smaller base, the region’s development continues to strengthen as healthcare modernization accelerates.
Market Segmentations:
By Product Type
- Automated Workstations
- Liquid Handling Systems
- Robotic Systems
- Software Solutions
By Application
- Clinical Diagnostics
- Molecular Diagnostics
- Hematology
- Immunoassays
- Microbiology
By End User
- Hospitals
- Diagnostic Laboratories
- Research Laboratories
- Pharmaceutical Companies
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape:
The competitive landscape of the Lab Automation for In Vitro Diagnostic Market features strong participation from Thermo Fisher Scientific, Agilent Technologies, PerkinElmer Inc., Siemens Healthineers, Becton Dickinson and Company, Beckman Coulter, Abbott Laboratories, Danaher Corporation, bioMérieux SA, and Roche Diagnostics. These companies strengthen their position through advanced automated workstations, scalable robotics, and integrated software platforms that support high-throughput diagnostics. Many players focus on modular systems that allow laboratories to expand capacity without major workflow disruption. Investments in AI-driven analytics, cloud-connected instruments, and automated QC tools further support market leadership. Strategic collaborations with hospitals, diagnostic chains, and government health programs help expand installed bases. Vendors also compete through improved reliability, lower maintenance designs, and stronger service networks, which address rising demand for accuracy and operational efficiency across global laboratories.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis:
Recent Developments:
- In July 2025, Thermo Fisher Scientific Thermo Fisher debuted LabLink360 (next-generation quality assurance program / QAP software) and the Thermo Scientific™ MAS Omni•CORE™ Max load-and-go quality controls to simplify and automate clinical lab QC and reduce hands-on time announced and showcased at ADLM 2025.
- In March 2025, Beckman Coulter announced FDA 510(k) clearance for the DxC 500i Clinical Analyzer, an integrated clinical chemistry and immunoassay system that boosts high-throughput testing and automation for core IVD labs. The platform is designed to help labs of all sizes reduce manual steps and handle growing test volumes more efficiently.
- In June 2024, Roche launched the cobas c 703 and cobas ISE neo analytical units for the cobas pro integrated solutions platform, delivering higher testing capacity and increased automation. These analyzers are designed to improve core-lab workflows, throughput, and efficiency in routine in vitro diagnostics.
Report Coverage:
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Product Type, Application, End-User and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook:
- Demand for high-throughput automated systems will rise as diagnostic volumes grow.
- AI and machine learning tools will strengthen workflow accuracy and predictive maintenance.
- Modular automation platforms will expand adoption among mid-sized and budget-limited laboratories.
- Integrated robotics will streamline complex molecular and genomic testing workflows.
- Cloud-connected instruments will support remote monitoring and real-time performance tracking.
- Automated quality control tools will reduce manual intervention and enhance result reliability.
- Emerging markets will accelerate adoption as healthcare infrastructure improves.
- Vendors will invest in compact systems designed for decentralized and point-of-care labs.
- Collaboration between automation providers and diagnostic chains will grow to enable large-scale workflow upgrades.
- Sustainability-focused designs will gain traction as labs seek energy-efficient and low-waste automation solutions.




