Market Overview
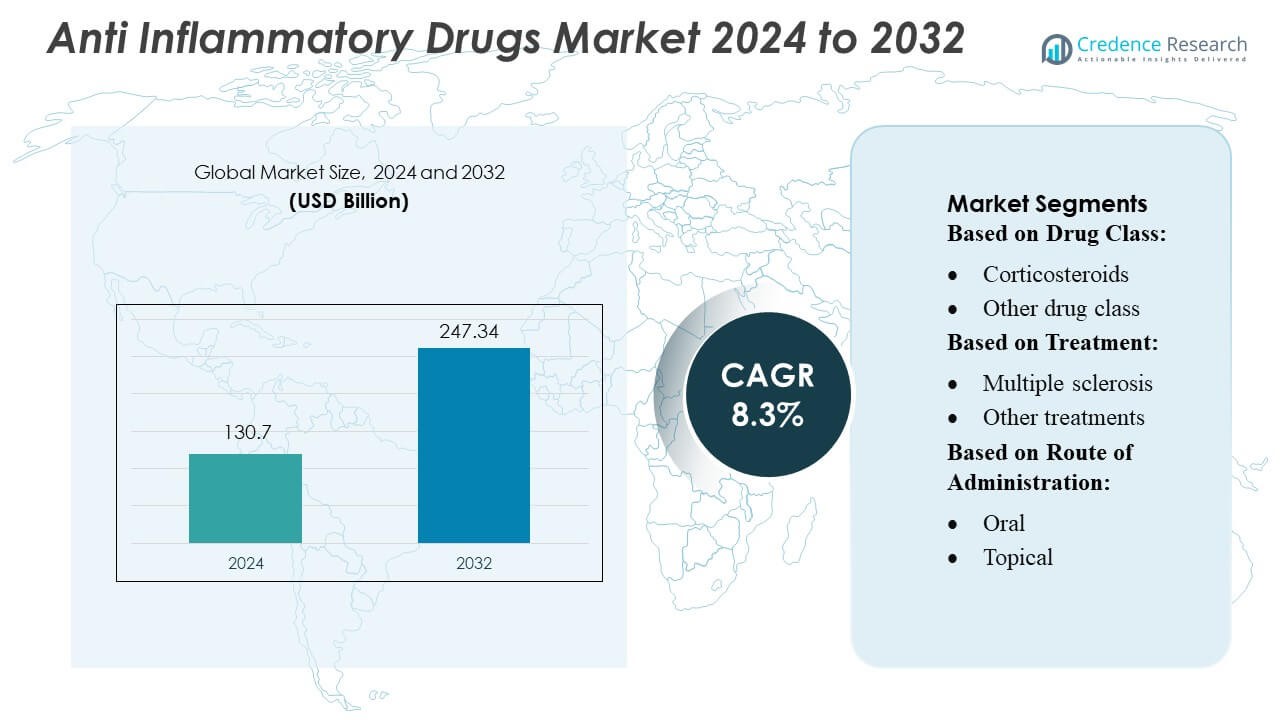
Anti Inflammatory Drugs Market size was valued USD 130.7 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 247.34 billion by 2032, at a CAGR of 8.3% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Anti Inflammatory Drugs Market Size 2024 |
USD 130.7 Billion |
| Anti Inflammatory Drugs Market, CAGR |
8.3% |
| Anti Inflammatory Drugs Market Size 2032 |
USD 247.34 Billion |
The global anti-inflammatory drugs market is dominated by major pharmaceutical firms such as Pfizer, Johnson & Johnson, Novartis, Merck, AbbVie, Amgen, Sanofi, Eli Lilly, Roche, and AstraZeneca, all of which drive innovation across both biologic and small-molecule therapies. North America leads the market, accounting for approximately 44.1% of global share, underpinned by its robust R&D infrastructure, high healthcare spending, and strong adoption of NSAIDs and biologics.
Market Insights
- The market was valued at USD 130.7 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 247.34 billion by 2032 at a CAGR of 8.3%, driven by expanding adoption of biologics and advanced anti-inflammatory therapies.
- Rising prevalence of chronic inflammatory diseases and strong uptake of targeted immunomodulators continue to drive market growth across major therapeutic segments.
- Biologics represent the fastest-growing segment, accounting for a significant share due to higher efficacy in autoimmune and chronic inflammatory conditions.
- Market competition intensifies as global leaders such as Pfizer, Johnson & Johnson, AbbVie, Novartis, and Roche invest in next-generation biologics, biosimilars, and small-molecule innovations.
- North America dominates the market with 44.1% share, supported by high healthcare spending and strong R&D capabilities, while Europe follows closely; meanwhile, the Asia Pacific region shows the fastest growth due to rising disease incidence and expanding pharmaceutical infrastructure.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Drug Class
Anti-inflammatory biologics lead the market with an estimated 45–50% share, driven by their targeted mechanism of action and superior efficacy in chronic autoimmune diseases. Their dominance is reinforced by the expanding use of TNF-α, IL-6, IL-17, and JAK-inhibitor therapies that offer sustained symptom control and reduced relapse rates. In contrast, NSAIDs and corticosteroids maintain stable demand for acute symptom relief but face limitations due to long-term side-effect risks. Growing adoption of next-generation biologics and biosimilars continues to fuel market expansion by improving accessibility and lowering treatment costs.
- For instance, Glenmark Pharmaceuticals strengthened its biologics capabilities through its monoclonal antibody program, including GBR 830, which progressed through Phase 2 trials involving more than 250 patients, and its respiratory portfolio advancement with Ryaltris®, supported by clinical data from over 3,000 participants across multiple global studies.
By Treatment
The arthritis segment holds the largest share—approximately 40% of the overall treatment landscape—supported by high global prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis, and increased prescription of biologics and DMARD-adjacent anti-inflammatory therapies. Rising aging populations, early diagnostic rates, and broader access to chronic disease management programs further sustain segment leadership. IBD and COPD segments demonstrate strong growth momentum due to advancing biologic pipelines, while multiple sclerosis treatments gain traction with improved immunomodulatory options. Other inflammatory conditions contribute steadily through expanded off-label and adjunctive therapy usage.
- For instance, Pfizer’s tofacitinib (XELJANZ) has been studied in over 6,200 rheumatoid arthritis patients globally across its Phase 3 programme, yielding more than 19,400 patient-years of exposure, per company data.
By Route of Administration
Oral administration dominates the market with an estimated 50–55% share, driven by patient convenience, strong adherence rates, and the extensive availability of NSAIDs, corticosteroids, and selective immunomodulators in oral formulations. Demand is reinforced by widening use of chronic maintenance therapies and lower overall treatment costs. Injectable routes continue gaining traction due to the rising adoption of biologics requiring subcutaneous or intravenous delivery, while topical and intranasal formulations retain niche but essential roles in localized and acute inflammatory conditions, offering rapid symptom relief with minimal systemic exposure.
Key Growth Drivers
- Rising Prevalence of Chronic Inflammatory Diseases
The growing burden of chronic inflammatory diseases—including arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, COPD, and multiple sclerosis—continues to drive strong demand for advanced anti-inflammatory therapies. Aging demographics, increased autoimmune disorders, and lifestyle-linked inflammation contribute significantly to rising prescription volumes. Healthcare systems worldwide are adopting long-term management protocols, expanding patient access to biologics and combination therapies. The steady increase in diagnosed cases and treatment-seeking behavior strengthens the market’s foundation and accelerates the need for more effective and durable anti-inflammatory treatment options.
- For instance, Hikma is developing a biosimilar to ustekinumab, BAT2206, through a partnership with Bio-Thera; the molecule, which targets IL-12 and IL-23, is currently in a global Phase III program.
- Expansion of Biologics and Targeted Therapies
Rapid advancements in biologics, biosimilars, and targeted small molecules underpin major market growth. Innovations in TNF-α inhibitors, IL-17/IL-23 blockers, and JAK inhibitors offer superior efficacy and lower relapse rates compared with traditional therapies. Pharmaceutical companies are investing heavily in next-generation immunomodulators capable of precision targeting to minimize systemic adverse effects. As clinical success rates improve and regulatory approvals accelerate, biologics continue to expand their penetration across multiple inflammatory conditions, positioning them as high-value drivers of both revenue growth and therapeutic transformation.
- For instance, Novartis’ Cosentyx® (secukinumab), a fully-human IL-17A inhibitor, demonstrated sustained efficacy over five years in a pivotal extension study involving more than 1,100 patients (PASI 90 maintained in ~66% of participants at Year 4).
- Increased Healthcare Investment and Access to Treatment
Rising healthcare expenditure, government reimbursement support, and expanding insurance coverage amplify patient access to advanced anti-inflammatory drugs. Emerging economies are strengthening chronic disease management programs and upgrading treatment standards, enabling greater uptake of modern therapies. The proliferation of specialty clinics, telemedicine platforms, and digital prescription systems enhances treatment continuity and drug adherence. These improvements, combined with wider availability of biosimilars, reduce cost barriers and support broader market adoption—ultimately driving sustained growth across both developed and developing healthcare ecosystems.
Key Trends & Opportunities
- Growing Adoption of Biosimilars
The expanding biosimilar pipeline presents a significant opportunity to reduce treatment costs and increase affordability, especially for biologic-heavy indications such as arthritis and IBD. As patents for major biologics expire, biosimilars are rapidly gaining regulatory approvals and market penetration. Their comparable clinical efficacy and strong economic value encourage broader physician adoption and patient access. Pharmaceutical manufacturers are increasingly focusing on high-demand biosimilar categories, creating competitive pricing environments that stimulate treatment uptake while supporting long-term market expansion.
- For instance, Lupin’s biosimilar Etanercept (YLB 113) completed a global Phase III trial over 52 weeks involving more than 500 rheumatoid arthritis patients across 11 countries, confirming clinical equivalence with the reference product.
- Advancements in Personalized and Precision Medicine
Precision-based anti-inflammatory therapies are becoming a critical trend as companies develop treatments tailored to genetic, biomarker, and immunologic profiles. Advances in molecular diagnostics, pharmacogenomics, and AI-driven predictive modeling enable more accurate patient stratification and optimized drug response. This shift supports the emergence of targeted small molecules with higher therapeutic specificity and reduced systemic risk. Precision medicine also enhances clinical trial efficiency and accelerates regulatory approvals, offering significant commercial opportunities for manufacturers developing customized immunomodulatory solutions.
- For instance, Bayer and Hurdle recently developed “InflammAge,” a saliva-based DNA methylation biomarker for systemic chronic inflammation, quantifying epigenetic changes in more than 450 CpG sites.
- Shift Toward Novel Delivery Technologies
Innovations in drug delivery—such as extended-release oral systems, self-injectable biologics, transdermal patches, and intranasal formulations—offer new opportunities to improve patient compliance and expand therapeutic applications. These technologies enhance pharmacokinetic control, reduce dosing frequency, and minimize side effects associated with conventional delivery routes. Companies are increasingly investing in user-friendly, home-administered devices to meet rising demand for convenience and decentralized care. This trend strengthens market differentiation and supports the adoption of both biologic and non-biologic anti-inflammatory drugs.
Key Challenges
- High Treatment Costs and Limited Affordability
The high cost of biologics and advanced targeted therapies remains a major barrier to widespread adoption, particularly in low- and middle-income countries. Limited insurance coverage and out-of-pocket payment structures restrict patient access to long-term treatment. While biosimilars help mitigate cost pressures, pricing remains significantly above traditional NSAIDs and corticosteroids. Healthcare systems also face budget constraints in supporting chronic inflammatory disease management. These cost-related challenges hinder treatment continuity and slow market expansion despite the clinical advantages of newer therapies.
- Safety Concerns and Adverse Effects
Anti-inflammatory drugs—particularly NSAIDs, corticosteroids, and certain biologics—continue to face scrutiny due to risks such as gastrointestinal complications, cardiovascular issues, immunosuppression, and long-term organ damage. Regulatory agencies emphasize post-marketing surveillance and safety compliance, increasing the burden on manufacturers. Safety concerns may limit prescribing frequency, restrict long-term use, and affect regulatory approvals for emerging drug classes. As patient awareness grows, demand shifts toward safer alternatives, challenging companies to balance efficacy with improved safety profiles in future product development.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America holds the largest share of the Anti-Inflammatory Drugs Market, accounting for around 38–40%, driven by high prevalence of arthritis, IBD, and respiratory inflammatory disorders. Strong adoption of biologics and JAK inhibitors, coupled with rapid uptake of biosimilars, strengthens regional dominance. Well-established healthcare infrastructure, high per-capita healthcare spending, and widespread insurance coverage accelerate access to advanced therapies. The presence of leading pharmaceutical companies and robust clinical research activity further supports market expansion. Rising demand for targeted immunomodulators and continuous regulatory approvals reinforce the region’s position as the primary revenue contributor.
Europe
Europe represents the second-largest market with approximately 28–30% share, supported by strong public healthcare systems and well-structured reimbursement mechanisms that facilitate access to high-cost biologics. Increasing incidence of chronic inflammatory conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis, ulcerative colitis, and multiple sclerosis, continues to drive drug consumption. The region benefits from an active biosimilar landscape, enabling cost-effective treatment expansion. Regulatory harmonization under the EMA accelerates approvals for innovative therapies. Growing R&D collaborations, aging demographics, and rising adoption of precision-medicine approaches further contribute to Europe’s steady and sustainable growth trajectory in anti-inflammatory therapeutics.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, holding around 20–22% market share, propelled by expanding patient populations, rapid urbanization, and increased diagnosis of inflammatory diseases. Rising healthcare expenditures in countries such as China, India, and Japan drive access to both biologics and cost-effective generics. Government initiatives aimed at improving chronic disease management and insurance penetration further enhance market adoption. Pharmaceutical companies are increasing investments in local manufacturing and clinical research, enabling competitive pricing. The region’s strong growth outlook is supported by biosimilar expansion, improving healthcare infrastructure, and a shift toward advanced immunomodulatory treatment options.
Latin America
Latin America contributes about 6–7% of the global market, with growth driven by increasing awareness of chronic inflammatory conditions and improving access to essential therapies. Brazil and Mexico lead regional demand due to expanding public healthcare coverage and gradual adoption of biologics through government procurement programs. However, cost constraints and uneven reimbursement availability limit broad penetration of advanced anti-inflammatory therapies. Growing availability of generics and biosimilars is helping mitigate affordability challenges. Investments in healthcare modernization and partnerships between multinational pharmaceutical firms and local distributors support incremental growth across the region.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region holds approximately 4–5% market share, characterized by rising incidence of autoimmune and inflammatory diseases alongside improving healthcare capacity in GCC countries. Higher-income markets such as Saudi Arabia and the UAE drive biologic adoption through expanding insurance coverage and investment in specialty clinics. In contrast, lower-income nations experience limited access due to high treatment costs and infrastructure gaps. Increased government spending on healthcare digitization, widening availability of generics, and collaborations with global pharmaceutical companies support gradual market development. Continued economic diversification and healthcare reforms are expected to enhance long-term growth.
Market Segmentations:
By Drug Class:
- Corticosteroids
- Other drug class
By Treatment:
- Multiple sclerosis
- Other treatments
By Route of Administration:
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape of the Anti-Inflammatory Drugs Market is characterized by the presence of major global and regional players, including Glenmark Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, Hikma Pharmaceuticals, Novartis, Lupin, Bayer AG, Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories, Cipla, Johnson & Johnson, and Abbott Laboratories. the Anti-Inflammatory Drugs Market is defined by intensifying innovation, expanding biologics pipelines, and growing investment in advanced immunomodulatory therapies. Companies compete by accelerating research in targeted mechanisms such as TNF-α, IL-17, IL-23, and JAK pathways to achieve higher efficacy with improved safety profiles. Biosimilars continue to reshape pricing dynamics and broaden patient access, particularly in chronic conditions like arthritis and IBD. Firms are also prioritizing lifecycle management strategies, including extended-release formulations, novel delivery systems, and patient-friendly self-injectable devices. Strategic collaborations, regulatory approvals, and expansion into high-growth emerging markets further strengthen competition and diversify therapeutic portfolios.
Key Player Analysis
- Glenmark Pharmaceuticals
- Pfizer
- Hikma Pharmaceuticals
- Novartis
- Lupin
- Bayer AG
- Reddy’s Laboratories
- Cipla
- Johnson & Johnson
- Abbott Laboratories
Recent Developments
- In May 2024, Eisai Co., Ltd. and Biogen Inc. announced that, following the FDA’s Fast Track designation, Eisai had started rolling submission of a Biologics License Application (BLA) to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for lecanemab-irmb (U.S. brand name: LEQEMBI) subcutaneous autoinjector for weekly maintenance dosing.
- In April 2024, Glenmark Pharmaceuticals received final approval from the U.S. Food & Drug Administration (US FDA) for its Acetaminophen and Ibuprofen Tablets, 250 mg/125 mg (OTC). The FDA determined these tablets to be bioequivalent to Advil Dual Action with Acetaminophen Tablets, 250 mg/125 mg (OTC), produced by Haleon US Holdings.
- In February 2024, Hikma Pharmaceuticals PLC (Hikma), a multinational pharmaceutical company, announced the launch of COMBOGESIC IV (acetaminophen and ibuprofen) injection in the U.S. COMBOGESIC IV is an opioid-free, intravenous pain relief medication that combines 1,000 mg of acetaminophen with 300 mg of ibuprofen, a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID).
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Drug Class, Treatment, Route of Administration and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- The market will expand as chronic inflammatory diseases continue to rise globally.
- Companies will accelerate development of biologics and targeted therapies with improved safety profiles.
- Demand for personalized anti-inflammatory treatments will grow with advances in genomic and biomarker research.
- Oral and topical formulations will continue evolving to offer faster onset and longer-lasting relief.
- Biosimilars will gain stronger market penetration as major biologics lose exclusivity.
- Digital health platforms will support better disease monitoring and treatment adherence.
- Research will increasingly focus on non-opioid pain management alternatives.
- Regulatory agencies will encourage development of safer long-term therapies.
- Emerging markets will adopt advanced anti-inflammatory solutions as healthcare access improves.
- Collaborations between biotech firms and pharmaceutical companies will accelerate innovation in novel drug mechanisms.




