Market Overview
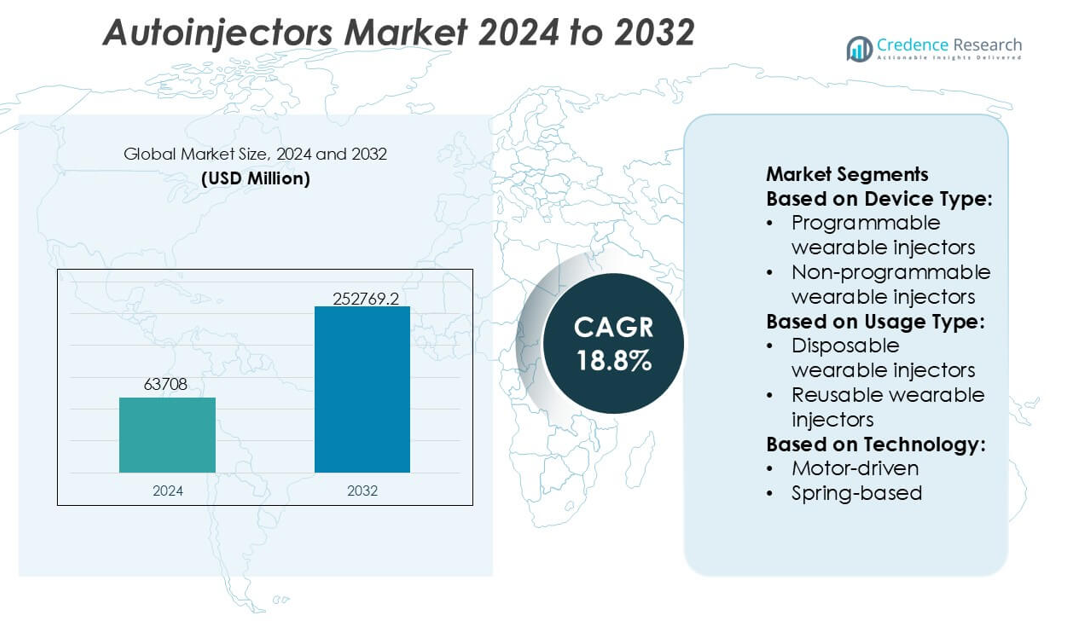
Autoinjectors Market size was valued USD 63708 million in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 252769.2 million by 2032, at a CAGR of 18.8% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Autoinjectors Market Size 2024 |
USD 63708 million |
| Autoinjectors Market, CAGR |
18.8% |
| Autoinjectors Market Size 2032 |
USD 252769.2 million |
The Autoinjectors Market is shaped by a concentrated group of pharmaceutical innovators and specialized device manufacturers that focus on developing safe, ergonomic, and technologically advanced drug-delivery systems for biologics and chronic disease therapies. These companies strengthen their market position by integrating smart connectivity features, enhancing compatibility with high-viscosity formulations, and expanding large-volume wearable platforms to support rising self-administration needs. Strategic partnerships between drug developers and device engineers further accelerate adoption across autoimmune, metabolic, and oncology indications. North America leads the market with an exact 39% share, driven by strong biologics usage, mature regulatory frameworks, and high patient preference for home-based treatment models.
Market Insights
- The Autoinjectors Market reached USD 63,708 million in 2024 and is projected to hit USD 252,769.2 million by 2032 with a CAGR of 18.8%, reflecting strong demand for self-administration and biologic delivery systems.
- Rising uptake of biologics across autoimmune and metabolic diseases drives market expansion, supported by increased preference for patient-friendly injection platforms and large-volume wearable devices.
- Smart, connected autoinjectors and programmable wearables emerge as key trends, enhancing adherence monitoring and compatibility with high-viscosity formulations.
- Market growth faces restraints due to high device manufacturing complexity, stringent regulatory expectations, and limited affordability in emerging regions.
- North America leads with 39% share, while programmable wearable injectors dominate product segments with around 58% share, reinforcing the market’s shift toward advanced, digitally integrated drug-delivery solutions.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Device Type
Programmable wearable injectors dominate the Autoinjectors Market with an estimated 58% share, driven by their ability to deliver precise, adjustable dosing for biologics and chronic disease therapies. Their integrated sensors, microprocessors, and connectivity features enhance adherence monitoring, making them preferred for conditions requiring titration or variable dose regimens. Non-programmable wearable injectors maintain steady demand for their simpler design, cost efficiency, and suitability for fixed-dose applications, particularly in oncology and autoimmune disease treatments. The shift toward personalized dosing and smart drug-delivery ecosystems continues to strengthen programmable device adoption.
- For instance, Ypsomed’s YpsoDose platform incorporates a micro-pump system capable of delivering up to 10 mL of high-viscosity formulations with a dosing precision of ±0.05 mL, supported by an embedded connectivity module that transmits real-time injection logs to clinical dashboards.
By Usage Type
Disposable wearable injectors lead this segment with nearly 63% market share, supported by their single-use sterility, reduced contamination risk, and growing integration with high-viscosity biologic formulations. Rising self-administration trends and patient preference for low-maintenance solutions accelerate adoption across home-care settings. Reusable wearable injectors gain traction in long-term therapy environments where sustainability and lower total cost of ownership matter. However, the need for periodic cleaning and cartridge replacement limits their uptake. Increasing regulatory focus on sharps safety and infection control further reinforces the dominant position of disposable systems.
- For instance, Pfizer’s Imitrex STATdose autoinjector employs a spring-actuated mechanism that delivers a 6 mg subcutaneous dose of sumatriptan in approximately 0.5 seconds, using a sealed, single-use drug cartridge to ensure sterility and eliminate post-procedure handling.
By Technology
-based mechanisms represent the dominant technology with about 46% share, driven by their mechanical simplicity, reliability, and low manufacturing cost. They support consistent force generation for injecting biologics with varied viscosities, making them widely preferred across therapeutic categories. Motor-driven injectors expand steadily due to controlled delivery rates and compatibility with wearable formats, while expanding battery and rotary pump technologies gain adoption in advanced, programmable systems requiring precision flow control. Growing biologics pipelines and demand for painless, automated, and quieter injection systems continue to push innovation across emerging technology categories.
Key Growth Drivers
Rising Adoption of Biologics and Self-Administration Therapies
The expanding use of biologics for autoimmune, metabolic, and oncology conditions drives strong demand for autoinjectors that simplify self-administration. Patients increasingly prefer home-based treatment models that reduce clinic visits and improve adherence. Pharmaceutical companies integrate autoinjectors with high-viscosity biologics to ensure controlled, reliable delivery. The shift toward chronic disease management and personalized dosing further accelerates adoption. As injectable biologic pipelines grow rapidly, autoinjectors emerge as essential delivery platforms that enhance safety, accuracy, and patient comfort.
- For instance, Amgen’s SureClick autoinjector is engineered to deliver a 140 mg dose of evolocumab in approximately 9 seconds using a pre-calibrated spring-driven system, and its later-generation Pushtronex device supports a 3.5 mL on-body infusion over 5 minutes, enabling administration of high-volume biologic formulations with consistent flow control.
Growing Focus on Patient-Centric and Connected Drug Delivery Devices
Healthcare systems emphasize technologies that improve user experience, reduce administration errors, and support remote monitoring. Autoinjectors equipped with sensors, dose-tracking functions, and wireless communication strengthen adherence programs and enable real-time data sharing with clinicians. Their ergonomic designs assist patients with limited dexterity, strengthening their role in long-term therapy. The broader movement toward digital therapeutics and smart drug-delivery ecosystems reinforces continuous investment in connected autoinjector platforms, supporting adoption across high-burden disease areas.
- For instance, Mylan’s epinephrine autoinjector platform uses a 0.3 mg premeasured dose delivered through a spring-activated system calibrated to achieve needle penetration in under 0.15 seconds, and its digital training module logs up to 500 simulated-use events to support accuracy and reduce user error.
Favorable Regulatory Support and Increasing Preference for Home Healthcare
Regulatory bodies encourage safe self-injection practices through clearer guidance on combination-product design, human-factor engineering, and device reliability. Healthcare providers also promote home-care treatment models to reduce costs and expand access for patients with chronic diseases. Autoinjectors align well with this shift by offering consistent dosing and reduced training needs. As payers support outpatient care and telehealth monitoring, manufacturers gain opportunities to develop compliant, user-friendly autoinjector solutions tailored to diverse therapeutic requirements.
Key Trends & Opportunities
Expansion of Wearable and Programmable Injection Platforms
The market benefits from rapid advancements in wearable injectors capable of delivering large-volume biologics over extended periods. Programmable systems allowing variable flow rates and injection profiles present strong opportunities in oncology, immunology, and metabolic disorders. Their integration with digital adherence platforms enhances engagement and supports precision medicine. As biologic formulations become more complex, pharmaceutical companies increasingly collaborate with device developers to create customized wearable platforms that improve therapeutic outcomes and patient comfort.
- For instance, AbbVie’s on-body injector used for risankizumab administration delivers a 3 mL dose in approximately 5 seconds through a motor-regulated mechanism, and its integrated analytics module records each activation event with a timestamp accurate to within 0.1 seconds to support clinician monitoring.
Sustainability and Eco-Efficient Device Development
Rising attention to environmental impact drives opportunities for recyclable materials, reduced-plastic housings, and modular reusable injection mechanisms. Manufacturers explore eco-efficient design strategies that maintain safety while minimizing medical waste. Regulatory encouragement for greener healthcare products supports this transition, creating room for innovative reusable components and low-waste packaging formats. Companies that invest in sustainable engineering can differentiate their portfolios and appeal to environmentally conscious healthcare providers and patients.
- For instance, Teva Pharmaceutical reported the elimination of 1,700 metric tons of packaging material through design optimization initiatives, and the company applied these reductions to injection-device secondary packaging by redesigning carton structures with a validated material reduction of 4.2 grams per unit to lower overall environmental load.
Growing Integration of AI and Data-Enabled Features
Autoinjectors increasingly incorporate data analytics, predictive maintenance alerts, and AI-driven adherence insights. These features help clinicians monitor patient behavior, optimize dosage intervals, and reduce risks of therapy discontinuation. Opportunities emerge for cloud-integrated therapy management systems that link autoinjectors with electronic health records. As digital health reimbursement expands, manufacturers can leverage AI-enabled innovations to enhance value propositions for both patients and care providers.
Key Challenges
High Manufacturing Complexity and Compliance Requirements
Autoinjector development requires adherence to stringent combination-product guidelines, biocompatibility standards, and rigorous mechanical testing. Manufacturers must ensure consistent performance with biologics of varying viscosities, making engineering and validation processes complex and costly. Delays in regulatory approval and the need for extensive human-factor studies increase development timelines. These challenges raise barriers for new entrants and limit rapid commercialization, especially in markets with evolving regulatory frameworks.
Cost Sensitivity and Limited Access in Developing Regions
Although autoinjectors offer superior usability, their higher price compared to traditional syringes restricts adoption in cost-sensitive markets. Limited reimbursement, inconsistent insurance coverage, and lower awareness of self-administration devices further constrain demand. Healthcare systems in emerging regions prioritize essential treatments, making advanced injection technologies less accessible. Manufacturers must balance affordability with innovation to expand penetration and address unmet needs in resource-limited settings.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America leads the Autoinjectors Market with an approximate 39% share, supported by strong biologics consumption, widespread self-administration practices, and advanced healthcare infrastructure. High adoption of programmable and wearable injectors strengthens regional growth as providers prioritize remote care and adherence-focused solutions. Robust regulatory guidance for combination products encourages innovation and rapid commercialization of next-generation drug-device platforms. Pharmaceutical companies actively collaborate with device developers to integrate digital monitoring features. Rising prevalence of autoimmune and metabolic disorders further accelerates demand, reinforcing North America’s dominant position in both disposable and connected autoinjector categories.
Europe
Europe holds nearly 31% of the market, driven by increasing uptake of biologics, well-established reimbursement frameworks, and strong patient preference for at-home treatment models. Demand rises for ergonomic and sustainable autoinjector designs as regional policies emphasize safety, environmental stewardship, and user-friendly device engineering. Countries such as Germany, France, and the U.K. lead adoption due to their mature clinical infrastructure and extensive chronic disease management programs. Manufacturers benefit from supportive regulatory alignment under MDR, enabling faster introduction of advanced wearable and smart injection systems that address complex dosing needs across autoimmune and oncology treatments.
Asia Pacific
Asia Pacific captures around 22% market share, reflecting rapid healthcare modernization, biologics expansion, and growing awareness of self-injection benefits. Rising incidence of diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, and cancer increases demand for cost-effective autoinjectors suited for large patient populations. Countries such as China, Japan, South Korea, and India accelerate investments in localized manufacturing, improving device accessibility and reducing import dependency. The region shows strong interest in disposable injectors due to safety and affordability, while premium segments experience traction with connected and programmable platforms. Expanding private healthcare coverage continues to support long-term market growth.
Latin America
Latin America accounts for nearly 5% of the market, driven by incremental adoption of self-administration devices in Brazil, Mexico, and Argentina. Growing burden of chronic diseases and increasing procurement of biologics gradually strengthen market penetration. However, cost constraints and limited reimbursement systems slow adoption of advanced technologies such as wearable injectors. Local healthcare initiatives promoting home-based treatment and training programs for self-administration improve patient readiness. As pharmaceutical distributors expand partnerships with global device manufacturers, access to standardized autoinjectors improves, supporting gradual segment expansion across mid-income populations.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region holds approximately 3% share, reflecting early-stage adoption influenced by rising chronic disease prevalence and improving specialty care infrastructure. Wealthier GCC countries lead demand due to higher biologics usage and investments in modern drug delivery technologies. Affordability challenges and limited awareness constrain uptake in lower-income African markets, where traditional injection methods remain prevalent. Gradual expansion of private healthcare networks and increased biologics availability create long-term growth opportunities. Training initiatives for patient self-administration and regulatory improvements are expected to enhance future adoption of both disposable and reusable autoinjector systems.
Market Segmentations:
By Device Type:
- Programmable wearable injectors
- Non-programmable wearable injectors
By Usage Type:
- Disposable wearable injectors
- Reusable wearable injectors
By Technology:
- Motor-driven
- Spring-based
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape of the Autoinjectors Market players such as Ypsomed, Pfizer, Inc., Amgen, Mylan N.V., AbbVie, Inc., Teva Pharmaceutical, SHL Medical AG, Owen Mumford, Biogen Idec, and Eli Lilly. the Autoinjectors Market is defined by strong collaboration between pharmaceutical manufacturers and specialized device engineering companies that focus on developing patient-centric, reliable, and compliant drug-delivery platforms. Companies expand their portfolios by integrating advanced mechanical, spring-based, and motor-driven technologies to support high-viscosity biologics and self-administration therapies. The market sees increasing investment in connected and programmable systems designed to improve adherence and enable remote monitoring. Competitors emphasize ergonomic design, safety features, and large-volume delivery capabilities to meet evolving clinical needs. Continuous regulatory alignment and growing biologics pipelines further intensify competition, driving sustained innovation across device formats.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
- Ypsomed
- Pfizer, Inc.
- Amgen
- Mylan N.V.
- AbbVie, Inc.
- Teva Pharmaceutical
- SHL Medical AG
- Owen Mumford
- Biogen Idec
- Eli Lilly
Recent Developments
- In August 2024, LTS (LOHMANN Therapie-Systeme AG) and Grand River Aseptic Manufacturing (GRAM) formed a strategic alliance for sterile fill-finish of drug containers for LTS’ innovative Sorrel™ wearable injector devices, combining GRAM’s manufacturing expertise with LTS’ advanced drug delivery tech to streamline getting complex treatments from lab to patient.
- In April 2024, Contract development manufacturing organization (CDMO) partnered with Ypsomed to invest in technology and infrastructure to propel the YpsoDose patch injector platform to market as a fully integrated solution for the subcutaneous self-administration of large volume injectables.
- In March 2024, Ypsomed reported to de-invest its insulin pen needle and blood sugar monitoring operations to MTD Group to focus on smart pumps and autoinjector development. This shift allows Ypsomed to invest over in expanding its Solothurn site
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Device Type, Usage Type, Technology and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- The market will see rapid adoption of connected and smart autoinjectors that enhance adherence tracking and remote monitoring.
- Demand for wearable large-volume injectors will rise as biologic formulations become more complex and require extended delivery profiles.
- Manufacturers will increasingly invest in sustainable device designs that reduce plastic waste and support reusable components.
- Personalized injection systems with adjustable dosing and patient-specific parameters will gain prominence across chronic disease therapies.
- Regulatory bodies will tighten human-factor and safety requirements, driving higher-quality engineering standards.
- Partnerships between pharma companies and device developers will accelerate innovation in drug–device combination products.
- Emerging markets will expand adoption as awareness of self-administration and biologics increases.
- Miniaturization and ergonomic improvements will make devices easier to use for patients with limited dexterity.
- AI-enabled analytics will support individualized therapy management and predictive adherence insights.
- Production capacity for autoinjectors will scale globally to match rising biologics consumption and home-care treatment models.




