Market Overview
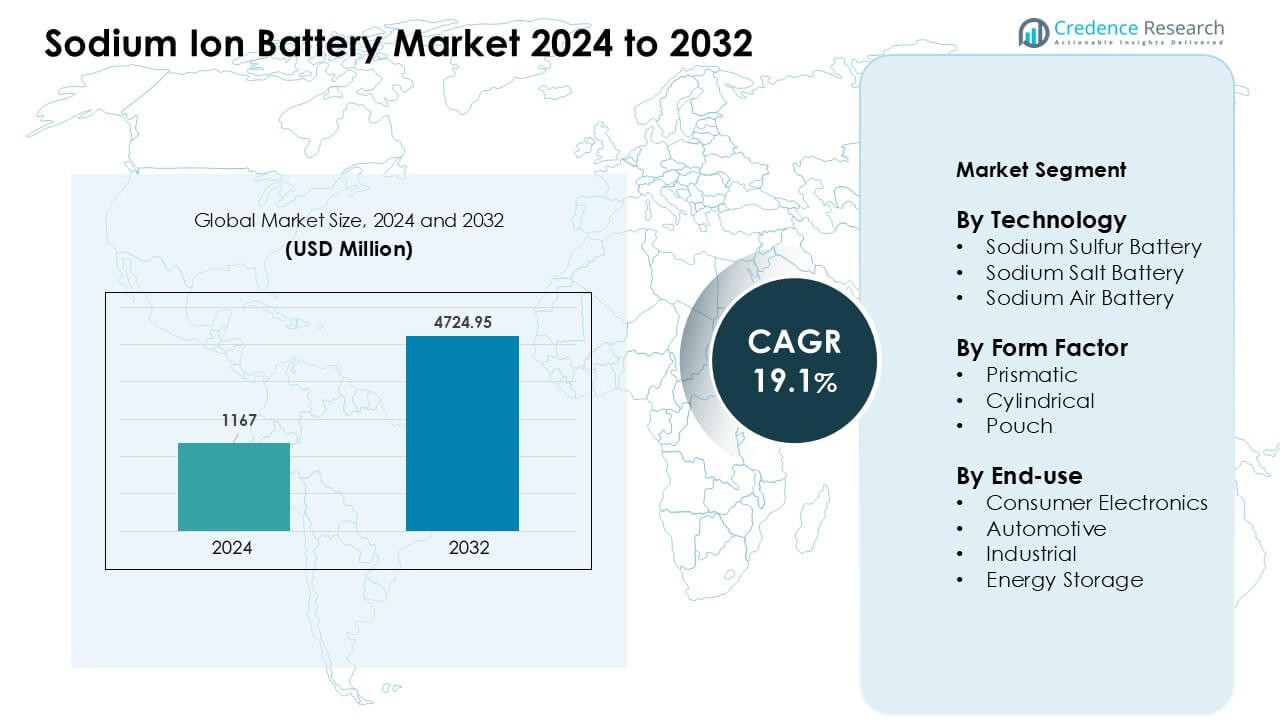
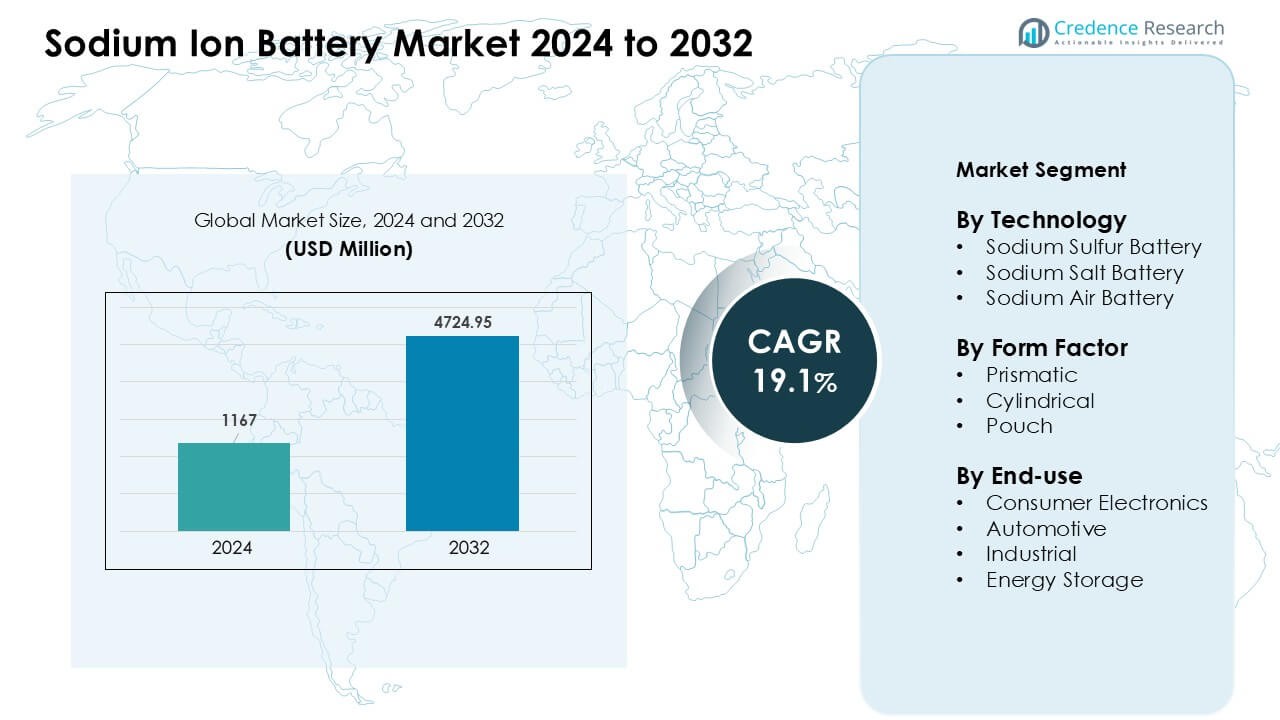
Sodium Ion Battery Market was valued at USD 1167 million in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 4724.95 million by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 19.1 % during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Sodium Ion Battery Market Size 2024 |
USD 1167 Million |
| Sodium Ion Battery Market, CAGR |
19.1 % |
| Sodium Ion Battery Market Size 2032 |
USD 4724.95 Million |
The Sodium Ion Battery Market is shaped by key players such as Natron Energy, Tiamat Energy, Faradion Limited, AMTE Power, Aquion Energy, Contemporary Amperex Technology, Hina Battery Technology, Jiangsu Zhongna Energy Technology, Li-FUN Technology, and Ben’an Energy Technology. These companies expanded sodium ion technology through safer chemistries, improved cycle life, and cost-efficient designs suited for grid storage and entry-level mobility. Asia-Pacific emerged as the leading region in 2024 with about 36% share, driven by strong manufacturing capacity, rapid renewable integration, and large pilot deployments across China and other regional markets.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Insights
- The Sodium Ion Battery Market was valued at USD 1167 million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 4724.95 million by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 19.1%.
- Strong demand for low-cost and thermally stable storage systems drove adoption, with sodium sulfur technology holding about 46% share due to high energy density and long-duration performance.
- Advancements in Prussian blue cathodes, rising EV pilots, and wider renewable integration shaped market trends, while prismatic cells led the form factor segment with nearly 52% share.
- Competitive activity grew as firms such as Natron Energy, Faradion Limited, Tiamat Energy, AMTE Power, and major Chinese manufacturers expanded production capacity and technology partnerships.
- Asia-Pacific dominated regional demand with roughly 36% share in 2024, supported by strong manufacturing and large-scale deployments, while North America and Europe increased adoption through grid modernization and sustainability targets.
 Market Segmentation Analysis:
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Technology
Sodium sulfur batteries held the dominant share in 2024 with about 46% of the Sodium Ion Battery Market. These systems gained strong traction due to high energy density, long cycle life, and strong thermal stability that suits grid storage projects. Many utilities selected sodium sulfur designs for peak-shaving and load-leveling needs, which raised large-scale deployment. Sodium salt batteries expanded as safer choices for mid-range storage, while sodium air batteries stayed in early development. Growing focus on sustainable materials strengthened demand across major demonstration sites.
- For instance, NGK Insulators, Ltd. the most prominent provider of sodium–sulfur (NAS) systems has historically deployed over 720 MW / 5,000 MWh of NAS battery capacity worldwide across more than 250 locations over two decades.
By Form Factor
Prismatic cells led the form factor segment in 2024 with nearly 52% share. Manufacturers preferred prismatic designs because the compact layout, strong mechanical stability, and higher packing efficiency support larger battery modules. Many energy storage firms adopted prismatic formats to improve module uniformity and reduce system integration cost. Cylindrical cells advanced due to rising use in tools and light devices, while pouch cells expanded in pilot automotive programs. Demand rose as producers optimized sodium layouts for better thermal performance during long discharge cycles.
- For instance, LYTH offers a 160 Ah prismatic sodium‑ion cell (model NaCP71173208‑160E3) that delivers 110–150 Wh/kg of energy density with a rated capacity of 160 Ah and supports at least 6,000 cycles at 80% state of health.
By End-use
Energy storage dominated the end-use segment in 2024 with roughly 41% share. Utilities and project developers selected sodium ion systems for long-duration storage due to low material cost, strong safety, and wide thermal tolerance in harsh climates. Grid operators deployed these units in renewable support, frequency control, and microgrid backup, which raised adoption. Consumer electronics showed early growth as firms explored sodium designs for low-cost devices. Automotive interest increased as companies tested sodium packs for entry-level EVs. Industrial users adopted systems for backup and load management.
 Key Growth Drivers
Key Growth Drivers
Rising Demand for Low-Cost Energy Storage
Growing demand for affordable storage pushed strong interest in the Sodium Ion Battery Market. Many utilities and commercial users selected sodium systems because the chemistry uses abundant raw materials, which reduced cost pressure seen in lithium supply chains. The low material price allowed large storage projects to scale without major budget risk. Developers focused on long-duration storage for solar and wind support, which raised adoption in rural and grid-constrained regions. Strong interest from government programs also boosted pilot deployments. The drive for cost-efficient energy security kept sodium ion technology in steady expansion across global markets.
- For instance, according to International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), some manufacturers expect sodium‑ion battery (SIB) cell costs to eventually fall to US$ 40 per kilowatt‑hour (kWh) once production scales up, reflecting the cost advantage of sodium chemistry over traditional lithium‑based cells.
Strong Safety and Thermal Stability Advantages
High safety levels supported faster acceptance in the Sodium Ion Battery Market. Sodium ion systems work safely in wide temperature ranges, which helped grid operators and commercial sites reduce cooling needs. This stability lowered operational cost and reduced fire risks linked to lithium systems. The strong thermal tolerance allowed use in hot climates and remote areas where cooling is limited. Industrial users selected sodium cells for backup power because the chemistry offered predictable performance under stress. These safety benefits helped sodium ion emerge as a trusted option for long-cycle applications and heavy-duty storage sites.
- For instance, sodium-ion batteries (SIBs) are widely considered to have a lower risk of thermal runaway compared to high-energy lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) with certain chemistries (like NMC) due to factors such as lower energy density and the properties of the sodium compounds formed, the specific number provided appears to be from a particular study and not a general rule.
Expanding Renewable Integration Requirements
Growing renewable capacity created major demand for long-duration storage in the Sodium Ion Battery Market. Many solar and wind developers selected sodium systems because they provided stable discharge for several hours at lower cost. The chemistry suited load shifting and frequency support, which improved grid stability during peak demand. National energy targets pushed wider deployment of hybrid systems combining sodium batteries with solar farms and microgrids. This integration helped utilities reduce curtailment losses and improve renewable utilization. Strong support from energy ministries encouraged continuous investment and expansion of pilot-to-commercial-scale sodium ion projects.
Key Trend & Opportunity
Advancements in High-Energy Cathode Materials
New cathode designs created strong opportunities in the Sodium Ion Battery Market. Research groups and battery firms worked on layered oxides and Prussian blue materials that improved energy density and cycle life. These upgrades moved sodium systems closer to mid-range lithium performance levels, which opened access to light mobility and consumer devices. Lower cost also helped producers test new product categories, including backup modules and smart home storage. Firms explored partnerships to commercialize high-capacity cells for grid and industrial tasks. Continued material innovation supported strong growth and wider customer acceptance across new industries.
- For instance, a recent study demonstrated a layered‑oxide sodium cathode (an O3‑type variant) that delivered an energy density of 260 Wh/kg at the electrode level and maintained ~80% capacity retention over 700 cycles in full cells showing substantial progress toward high‑energy, long‑life SIBs.
Growing Use in Entry-Level Electric Vehicles
Automakers showed rising interest in sodium ion packs for low-range EVs, creating new growth paths. Many companies tested sodium cells in city cars, two-wheelers, and small delivery vehicles because the chemistry offered lower cost and stable operation in heat. These traits suited markets in Asia and Europe where short-range mobility demand keeps increasing. Producers focused on improving charge rate and cycle durability to meet automotive standards. Government incentives for budget EVs created more room for sodium-based designs. This shift helped broaden the market’s reach beyond stationary storage and into mass-market transport solutions.
- For instance, CATL a major battery maker has recently developed a sodium-ion battery claimed to reach an energy density of 175 Wh/kg, positioning it close to lower-end lithium batteries and making it a viable candidate for cost-conscious, short-range EVs.
Key Challenge
Lower Energy Density Compared to Lithium Batteries
Energy density remained a major challenge for the Sodium Ion Battery Market. Sodium cells store less energy per unit weight than lithium systems, which limits adoption in high-performance mobility and long-range EVs. Many producers faced engineering limits when attempting to match lithium standards. Lower density increased battery size, which reduced appeal in compact products. Companies invested in next-generation materials, yet commercial results stayed gradual. This performance gap slowed penetration in premium electronics and advanced automotive programs, making sodium ion more suitable for cost-driven segments rather than high-end applications.
Limited Large-Scale Manufacturing Ecosystem
A small manufacturing base slowed growth in the Sodium Ion Battery Market. Few companies operated large sodium cell plants, which restricted supply and raised lead times for major energy projects. Many producers relied on pilot-scale lines that lacked the economies of scale seen in lithium factories. Supply chain gaps in anode materials, separators, and electrolytes created hurdles for mass production. Developers faced delays in qualifying suppliers and meeting long-term procurement needs. This limited ecosystem prevented rapid market expansion and slowed adoption in fast-scaling industries like grid storage and automotive.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America held about 32% share of the Sodium Ion Battery Market in 2024. The region adopted sodium systems for grid modernization, renewable support, and community storage programs. Utilities selected sodium cells for long-duration use because the chemistry offered strong safety and cost benefits. Pilot EV projects accelerated as manufacturers tested sodium packs for short-range fleets. Federal and state initiatives supported storage deployment in rural and high-temperature zones, which increased adoption. Growing interest from data centers and commercial users further strengthened market expansion across the United States and Canada.
Europe
Europe captured nearly 29% share of the Sodium Ion Battery Market in 2024. The region advanced adoption through strict sustainability goals and strong investments in renewable integration. Many countries tested sodium systems for wind and solar balancing due to their safe operation and low resource impact. European automakers explored sodium options for low-cost EVs and urban mobility fleets. The region’s mature research network improved cathode materials and cell design efficiency. Rising need for energy security, coupled with supply diversification away from lithium sources, helped accelerate commercial deployments across major EU countries.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific dominated the Sodium Ion Battery Market in 2024 with about 36% share. China led production with large-scale manufacturing, strong patent activity, and expanding pilot EV programs. The region used sodium systems for residential storage, industrial backup, and renewable microgrids due to favorable cost and strong thermal tolerance. India and Japan increased research efforts to develop prismatic sodium cells for grid support. Growing electricity demand and dense urban development boosted interest in affordable long-duration storage. Strong policy backing and rapid technology scaling kept Asia-Pacific as the fastest-growing regional market.
Latin America
Latin America accounted for nearly 2% share of the Sodium Ion Battery Market in 2024 but showed steady momentum. Countries with expanding solar capacity adopted sodium systems for microgrids and community storage projects. The region valued sodium technology for safe operation in hot climates and remote areas with limited cooling infrastructure. Pilot deployments in commercial buildings and small industries supported early demand. Government energy programs in Brazil, Chile, and Mexico encouraged testing of low-cost alternatives to lithium. Broader renewable goals are expected to strengthen sodium ion adoption across the region.
Middle East & Africa
Middle East & Africa held roughly 1% share of the Sodium Ion Battery Market in 2024. The region explored sodium systems for off-grid sites, desert climate storage, and peak-shaving projects where thermal stability mattered most. Utilities evaluated sodium cells to support solar farms and rural electrification programs. Limited local manufacturing slowed expansion, yet rising interest in cost-effective long-duration storage created new opportunities. Pilot renewable-storage installations in the UAE, Saudi Arabia, and South Africa increased awareness. Growing energy diversification efforts are expected to raise adoption across select markets in the coming years.
Market Segmentations:
By Technology
- Sodium Sulfur Battery
- Sodium Salt Battery
- Sodium Air Battery
By Form Factor
- Prismatic
- Cylindrical
- Pouch
By End-use
- Consumer Electronics
- Automotive
- Industrial
- Energy Storage
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape of the Sodium Ion Battery Market features strong activity from innovators, established cell manufacturers, and emerging large-scale producers. Companies such as Natron Energy, Tiamat Energy, Faradion Limited, AMTE Power, and Aquion Energy advanced sodium ion technology through safer chemistries, faster charge performance, and long-cycle designs aimed at grid and commercial storage. Major Chinese firms including Contemporary Amperex Technology, Hina Battery Technology, Jiangsu Zhongna Energy Technology, Li-FUN Technology, and Ben’an Energy Technology expanded production capacity to supply renewable projects and pilot EV programs. Many players formed partnerships with utilities, microgrid developers, and mobility companies to scale deployment. R&D efforts focused on higher-energy cathodes, improved anodes, and cost-optimized manufacturing, which strengthened competitiveness across global markets.
Key Player Analysis
- Natron Energy, Inc. (U.S.)
- Ben’an Energy Technology (Shanghai) Co., Ltd (China)
- Tiamat Energy (France)
- AMTE Power plc (U.K.)
- Contemporary Amperex Technology (China)
- Aquion Energy (U.S.)
- Li-FUN Technology (China)
- Faradion Limited (U.K.)
- Jiangsu Zhongna Energy Technology (China)
- Hina Battery Technology Co., Ltd (China)
Recent Developments
- In September 2025, Natron Energy, Inc. (U.S.): Natron has ceased operations / shut down, ending its planned large-scale gigafactory expansion after earlier efforts to scale commercial sodium-ion production.
- In October 2024, Faradion Limited became a wholly owned subsidiary of Reliance New Energy after Reliance acquired the remaining minority stake, with the company’s sodium-ion technology earmarked for Reliance’s planned integrated energy-storage gigafactory in Jamnagar, India.
- In January 2024, AMTE Power plc (U.K.): AMTE’s Scottish battery production line and related assets were acquired by LionVolt (Dutch startup) in a transaction reported January 2024; AMTE continues R&D and planning around cell certification and future factory ambitions.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Technology, Form Factor, End-Use and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- Sodium ion batteries will gain wider use in grid-scale storage due to strong cost advantages.
- Advances in cathode materials will raise energy density and improve long-cycle performance.
- Automakers will expand sodium-based trials for entry-level EVs and urban mobility fleets.
- Large Chinese manufacturers will scale production capacity and lower system cost.
- More countries will adopt sodium systems for renewable integration and microgrid backup.
- Prismatic cell formats will remain preferred as companies optimize module efficiency.
- Safety advantages will drive adoption in hot climates and remote industrial sites.
- Partnerships between utilities and battery firms will accelerate commercial deployments.
- Research programs will focus on high-rate charging and improved anode stability.
- Global supply chains will diversify as Europe and North America build new pilot lines.

 Market Segmentation Analysis:
Market Segmentation Analysis: Key Growth Drivers
Key Growth Drivers

