Market Overview
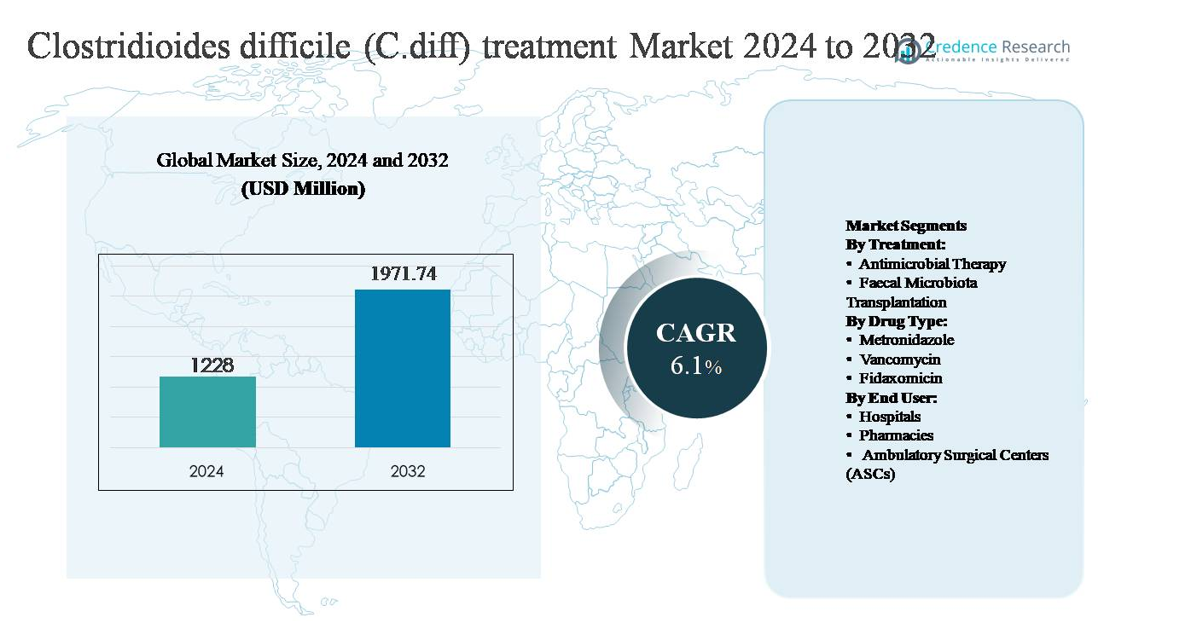
The global Clostridioides difficile (C. diff) treatment market was valued at USD 1,228 million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 1,971.74 million by 2032, expanding at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.1% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
Clostridioides difficile (C. diff) Treatment Market Size 2024
|
USD 1,228 million |
| Clostridioides difficile (C. diff) Treatment Market, CAGR |
6.1% |
| Clostridioides difficile (C. diff) Treatment MarketSize 2032 |
USD 1,971.74 million |
The Clostridioides difficile (C. diff) treatment market is led by a combination of global pharmaceutical, biotechnology, and diagnostics companies that compete on therapeutic efficacy, recurrence prevention, and clinical adoption. Major players such as Pfizer, Novartis AG, Roche AG, Sanofi S.A., Merck & Co., AstraZeneca Plc, Baxter International Inc., Actelion Pharmaceuticals, Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Summit Therapeutics, Trinity Biotech, and Alere, Inc. maintain strong positions through established drug portfolios, diagnostic capabilities, and ongoing clinical development. These companies benefit from deep hospital relationships and alignment with evolving treatment guidelines. North America is the leading region, accounting for approximately 42% of the global market, driven by high CDI incidence, advanced diagnostics, strong reimbursement frameworks, and early adoption of targeted and microbiome-based therapies.
Market Insights
- The global Clostridioides difficile (C. diff) treatment market was valued at USD 1,228 million in 2024 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.1% through 2032.
- Market growth is primarily driven by rising hospital-acquired infections, extensive antibiotic use, and an aging patient population, with antimicrobial therapy remaining the dominant treatment segment, accounting for over 65% market share due to its first-line clinical use and guideline support.
- Key market trends include the growing preference for targeted therapies such as fidaxomicin and the expanding role of microbiome-based treatments for recurrent infections, reflecting a shift toward recurrence prevention and long-term disease management.
- The competitive landscape features strong participation from global pharmaceutical and diagnostics companies competing on efficacy, recurrence reduction, and hospital penetration, while emerging players focus on microbiome innovation to differentiate offerings.
- Regionally, North America leads with 42% share, followed by Europe at 30%, Asia Pacific at 17%, and the remainder split between Latin America and Middle East & Africa, supported by improving diagnostics and infection control initiatives.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Treatment:
The treatment landscape for Clostridioides difficile infection is dominated by antimicrobial therapy, which accounts for the largest market share due to its established role as first-line treatment across mild, moderate, and severe infections. Standardized clinical guidelines, broad physician familiarity, and rapid symptom control continue to reinforce its dominance. However, faecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) is gaining momentum, particularly for recurrent and refractory cases, driven by strong clinical evidence demonstrating lower recurrence rates. Expanding regulatory clarity, standardized formulations, and increasing acceptance of microbiome-based therapies are supporting gradual uptake of FMT as a complementary treatment option.
- For instance, Merck & Co.’s fidaxomicin was validated in Phase III trials enrolling more than 1,100 patients, demonstrating durable clinical response with a fixed 200 mg twice-daily oral dosing regimen over 10 days, which reinforced physician confidence in targeted antibiotic therapy.
By Drug Type:
Among drug types, vancomycin represents the dominant sub-segment, supported by its proven efficacy, strong safety profile, and guideline-backed use for initial and recurrent C. diff infections. Its widespread hospital adoption and availability in oral formulations reinforce its leading position. Metronidazole, once a mainstay therapy, has seen declining usage due to lower efficacy in severe cases, though it remains relevant in resource-constrained settings. Fidaxomicin is the fastest-growing sub-segment, driven by its targeted mechanism, reduced recurrence rates, and increasing preference in high-risk patient populations despite higher treatment costs.
- For instance, generic oral vancomycin capsules are administered at a standardized dose of 125 mg four times daily for 10 days, a regimen supported by decades of hospital use and inclusion in multiple international treatment protocols for Clostridioides difficile infection.
By End User:
Hospitals constitute the dominant end-user segment, capturing the majority of market demand due to the high prevalence of C. diff infections in inpatient settings, particularly among elderly and immunocompromised patients. The need for rapid diagnosis, isolation protocols, and immediate initiation of therapy supports hospital-based treatment dominance. Pharmacies play a growing role in outpatient management and post-discharge therapy continuity, while ambulatory surgical centers (ASCs) represent a smaller but expanding segment as infection control awareness improves and early-stage cases increasingly shift toward outpatient treatment pathways.
Key Growth Drivers
Rising Incidence of Hospital-Acquired Infections
The increasing prevalence of Clostridioides difficile infections (CDI) in hospital and long-term care settings remains a primary growth driver for the treatment market. High antibiotic utilization, prolonged hospital stays, invasive procedures, and an aging inpatient population significantly elevate CDI risk. Elderly patients and those with comorbidities are particularly vulnerable, leading to higher diagnosis rates and sustained demand for effective therapies. Enhanced surveillance, mandatory infection reporting, and improved diagnostic capabilities have further increased case identification. As healthcare systems prioritize reducing hospital-acquired infections, timely treatment of CDI has become integral to patient safety initiatives, directly supporting consistent demand for antimicrobial therapies and advanced recurrence-prevention solutions.
- For instance, Cepheid’s GeneXpert® C. diff molecular diagnostic system delivers PCR-based results in approximately 45 minutes, enabling rapid isolation and treatment decisions in acute-care hospitals.
Shift Toward Guideline-Preferred and Targeted Therapies
Clinical guideline updates increasingly favor targeted therapies with improved efficacy and lower recurrence rates, driving treatment adoption. Vancomycin and fidaxomicin have replaced older broad-spectrum antibiotics in many treatment protocols, particularly for moderate-to-severe and recurrent infections. This shift is supported by growing clinical evidence, physician awareness, and payer recognition of long-term cost savings from reduced recurrence and rehospitalization. Hospitals and clinicians are prioritizing therapies that align with antimicrobial stewardship goals, reinforcing the transition toward more effective, pathogen-specific treatment options and sustaining market expansion.
- For instance, Ferring Pharmaceuticals’ microbiota-based therapy RBX2660 completed controlled clinical studies with more than 800 treated and control subjects, using a single standardized enema-based dose designed to restore gut microbiome diversity, providing a quantified, protocol-driven alternative for patients with multiple documented recurrences.
Growing Burden of Recurrent C. diff Infections
Recurrent CDI represents a significant clinical and economic burden, acting as a strong catalyst for market growth. A substantial proportion of patients experience relapse after initial treatment, necessitating repeated therapy and prolonged care. This challenge has accelerated adoption of advanced treatment strategies, including fidaxomicin and microbiome-based approaches. Healthcare providers increasingly focus on preventing recurrence rather than solely treating acute episodes, driving demand for therapies with durable clinical outcomes. The emphasis on long-term disease management continues to support innovation and sustained investment in this treatment space.
Key Trends & Opportunities
Expansion of Microbiome-Based Therapies
Microbiome restoration therapies, including standardized fecal microbiota transplantation and live biotherapeutic products, represent a key growth opportunity in CDI treatment. These approaches directly address dysbiosis, the root cause of recurrent infections, and have demonstrated strong efficacy in reducing relapse rates. Increasing regulatory clarity, improved manufacturing controls, and growing clinician confidence are accelerating adoption. As these therapies transition from niche interventions to structured clinical options, they present significant opportunities for differentiation and long-term market expansion.
- For instance, Seres Therapeutics’ oral microbiome therapy SER-109 (Vowst™) consists of purified Firmicutes spores administered as four capsules daily for three consecutive days, delivering billions of viable spores per treatment course, and was supported by randomized clinical studies involving over 300 patients with documented recurrent CDI.
Integration of Antimicrobial Stewardship Programs
The global push toward antimicrobial stewardship is reshaping CDI treatment practices. Hospitals are actively minimizing unnecessary antibiotic exposure while optimizing therapy selection for confirmed infections. This trend supports increased use of targeted agents and shorter, evidence-based treatment durations. Pharmaceutical developers and healthcare providers benefit from this shift, as stewardship-aligned therapies gain preference. The integration of stewardship principles creates opportunities for products that demonstrate both clinical effectiveness and reduced resistance risk.
- For instance, Actelion Pharmaceuticals, which operates within the Johnson & Johnson group, now primarily focuses on treatments for pulmonary hypertension (PAH), utilizing existing, approved therapies.
Improved Diagnostics and Early Intervention
Advancements in molecular diagnostics are enabling faster and more accurate identification of CDI, supporting earlier treatment initiation. Rapid testing reduces delays in therapy, improves patient outcomes, and limits transmission within healthcare facilities. Earlier diagnosis expands the treated patient pool and supports timely use of guideline-recommended therapies. This trend enhances overall treatment uptake and reinforces the value proposition of effective, fast-acting CDI treatments.
Key Challenges
High Cost of Advanced Therapies
The cost burden associated with newer CDI treatments remains a significant challenge, particularly for fidaxomicin and microbiome-based therapies. Despite demonstrated clinical benefits, higher upfront costs can limit adoption in cost-sensitive healthcare systems and emerging markets. Budget constraints and reimbursement variability often lead providers to favor lower-cost alternatives, even when recurrence risk is higher. Balancing cost-effectiveness with clinical superiority continues to be a critical barrier to broader penetration of advanced treatment options.
Complexity of Recurrence Management and Patient Compliance
Managing recurrent CDI is clinically complex and resource-intensive. Patients often require prolonged or repeated treatment courses, strict adherence, and close monitoring, which can be challenging in outpatient settings. Non-compliance, comorbidities, and delayed follow-up increase the risk of treatment failure. Additionally, variability in treatment protocols across institutions can lead to inconsistent outcomes. These factors complicate disease management and place operational strain on healthcare providers, limiting optimal therapy utilization despite growing clinical need.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America holds the largest share of the Clostridioides difficile treatment market, accounting for approximately 42% of global revenue. The region’s dominance is driven by high incidence rates of hospital-acquired infections, extensive antibiotic usage, and a rapidly aging population. Strong adherence to clinical guidelines, widespread adoption of fidaxomicin and vancomycin, and early uptake of microbiome-based therapies further support growth. Advanced diagnostic infrastructure and favorable reimbursement frameworks in the United States and Canada enable timely diagnosis and treatment, reinforcing sustained demand across hospital and outpatient care settings.
Europe
Europe represents around 30% of the global C. diff treatment market, supported by well-established healthcare systems and strong infection surveillance programs. Countries such as Germany, the UK, and France report significant CDI prevalence, particularly among elderly populations in hospitals and long-term care facilities. Increasing alignment with updated treatment guidelines and antimicrobial stewardship initiatives is driving adoption of targeted therapies. Additionally, growing acceptance of fecal microbiota transplantation for recurrent infections and supportive regulatory environments contribute to stable market expansion across Western and Northern Europe.
Asia Pacific
Asia Pacific accounts for approximately 17% of the global market and is the fastest-growing regional segment. Rising hospitalization rates, expanding access to diagnostics, and improving awareness of C. diff infections are key growth drivers. Large patient populations in China, India, and Japan contribute to increasing treatment demand, particularly for antimicrobial therapies. While cost sensitivity limits uptake of premium treatments, improving healthcare infrastructure and government investments in infection control are supporting gradual adoption of advanced therapies, positioning the region for strong long-term growth.
Latin America
Latin America holds about 6% of the global C. diff treatment market, driven by increasing recognition of hospital-acquired infections and expanding diagnostic capabilities. Brazil and Mexico are the primary contributors due to higher hospitalization volumes and improving access to antimicrobial therapies. However, limited reimbursement coverage and budget constraints continue to favor lower-cost treatment options. Despite these challenges, rising healthcare spending, improving infection control protocols, and gradual guideline adoption are supporting steady market development across the region.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region accounts for approximately 5% of global market share, reflecting lower diagnosis rates and limited access to advanced therapies. Growth is primarily concentrated in the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries, where improving hospital infrastructure and infection surveillance programs are increasing CDI detection. In contrast, much of Africa remains underpenetrated due to limited diagnostic capacity and constrained healthcare budgets. Ongoing investments in healthcare modernization and infection prevention initiatives are expected to gradually improve treatment uptake over the forecast period.
Market Segmentations:
By Treatment:
- Antimicrobial Therapy
- Faecal Microbiota Transplantation
By Drug Type:
- Metronidazole
- Vancomycin
- Fidaxomicin
By End User:
- Hospitals
- Pharmacies
- Ambulatory Surgical Centers (ASCs)
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape of the Clostridioides difficile (C. diff) treatment market is characterized by a mix of established pharmaceutical companies and emerging biotechnology players focused on reducing infection recurrence and improving patient outcomes. Market leaders compete primarily on clinical efficacy, recurrence prevention, and alignment with evolving treatment guidelines. Companies with strong portfolios in targeted antibiotics maintain an advantage through broad hospital adoption and well-established distribution networks. At the same time, innovative players developing microbiome-based therapies are reshaping competition by addressing the underlying cause of recurrent infections rather than symptomatic control alone. Strategic initiatives such as clinical trial expansions, regulatory approvals, and partnerships with healthcare institutions are central to competitive positioning. Firms are also investing in real-world evidence generation and post-marketing studies to support reimbursement and guideline inclusion. Overall, competition is intensifying as innovation shifts the market from traditional antibiotic therapy toward differentiated, outcome-driven treatment solutions.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
- Pfizer, Inc.
- Novartis AG
- Roche AG
- Sanofi S.A.
- Merck & Co.
- AstraZeneca Plc
- Baxter International Inc.
- Actelion Pharmaceuticals
- Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.
- Summit Therapeutics
Recent Developments
- In March 2024, Thermo Fisher Scientific continued expansion and clinical deployment of its microbiology and molecular diagnostics portfolio supporting C. difficile detection and treatment decision-making. Its Applied Biosystems™ real-time PCR platforms and Oxoid™ C. difficile selective media remained widely used in hospital laboratories, enabling toxin gene detection and culture confirmation within standardized laboratory workflows. These diagnostic systems support antimicrobial stewardship by enabling rapid confirmation of CDI prior to initiating targeted therapies such as fidaxomicin or vancomycin.
- In January 2024, Merck continued post-approval clinical and real-world evidence generation for fidaxomicin (Dificid®) following its earlier acquisition of Cubist Pharmaceuticals. Fidaxomicin remains positioned as a guideline-preferred, narrow-spectrum macrolide antibiotic targeting C. difficile, with the approved regimen consisting of 200 mg orally twice daily for 10 days. Ongoing activities in 2024 focused on stewardship-aligned utilization studies and hospital protocol integration rather than new clinical trial initiations.
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Treatment, Drug type, End-User and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- Treatment strategies will increasingly prioritize recurrence prevention over acute symptom control.
- Targeted antibiotics will continue to replace broad-spectrum therapies in first-line treatment.
- Microbiome-based therapies will gain wider clinical acceptance for recurrent infections.
- Clinical guidelines will further evolve to favor therapies with durable outcomes.
- Hospitals will remain the primary treatment setting due to high inpatient infection rates.
- Antimicrobial stewardship programs will shape therapy selection and usage patterns.
- Early and accurate diagnostic testing will support faster treatment initiation.
- Combination and sequential treatment approaches will emerge for high-risk patients.
- Cost-effectiveness evidence will play a greater role in reimbursement decisions.
- Innovation will focus on patient-specific and precision-based treatment pathways.




