Market Overview
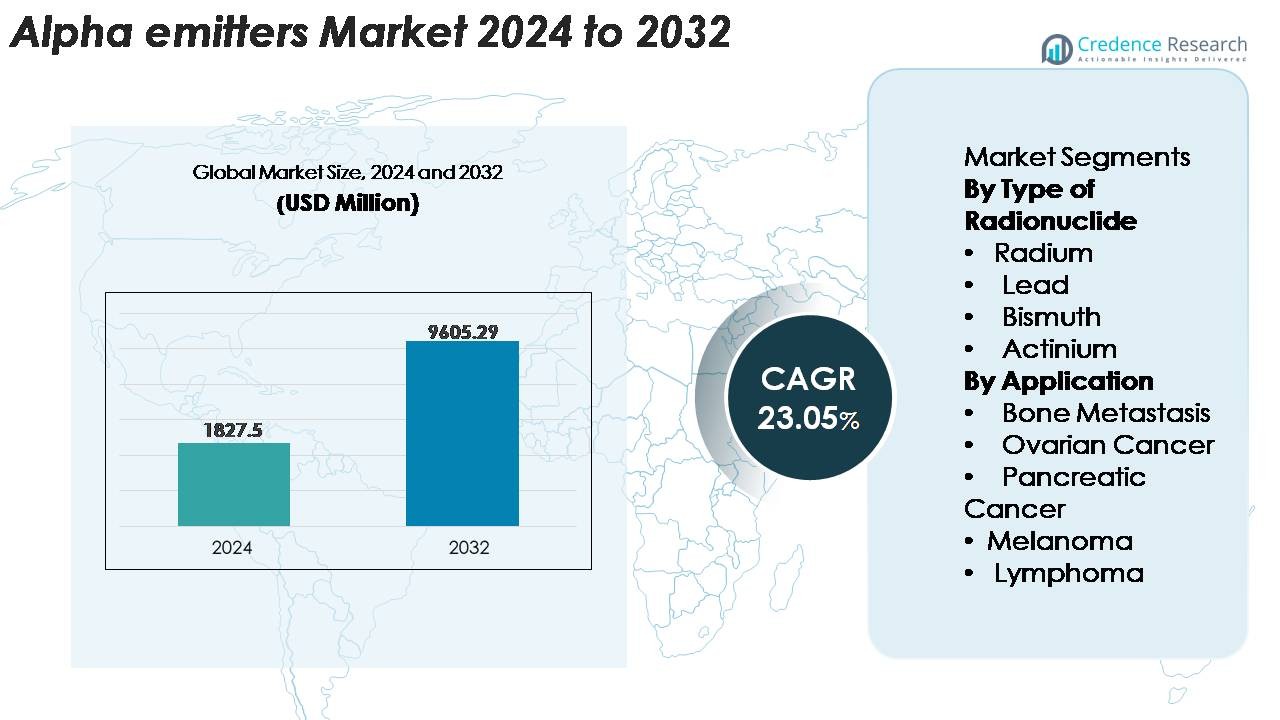
The global Alpha Emitters Market was valued at USD 1,827.5 million in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 9,605.29 million by 2032, registering a CAGR of 23.05% during the forecast period (2025–2032).
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Alpha Emitters Market Size 2024 |
USD 1,827.5 Million |
| Alpha Emitters Market, CAGR |
23.05% |
| Alpha Emitters Market Size 2032 |
USD 9,605.29 Million |
North America leads the alpha emitters market with an estimated 38–40% share, driven by advanced nuclear medicine infrastructure and strong clinical adoption of targeted alpha therapies. The competitive landscape includes innovators such as RadioMedix, Inc., IBA Radiopharma Solutions, Actinium Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Lantheus Medical Imaging, Inc., Alpha Tau Medical, Siemens Healthineers, Fusion Pharmaceuticals, NTP Radioisotopes SOC Ltd., IBA Group, and Bayer AG. These companies focus on expanding Actinium-225 and Lead-212 production, strengthening GMP-compliant radiopharmaceutical pipelines, and accelerating clinical programs in hard-to-treat cancers. Europe and Asia-Pacific follow as fast-growing regions with increasing investment in theranostic oncology platforms.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Insights
- The global alpha emitters market was valued at USD 1,827.5 million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 9,605.29 million by 2032, growing at a 23.05% CAGR during the forecast period.
- Strong market growth is driven by rising adoption of targeted alpha therapy, expanding Actinium-225 and Lead-212 production capacity, and increasing clinical use in prostate, ovarian, pancreatic, and hematologic cancers; Actinium-based radionuclides hold the largest share among types.
- Key trends include rapid expansion of radiotheranostic platforms, increased hospital investment in nuclear medicine infrastructure, and growing pipeline collaborations between radiopharmaceutical developers and isotope suppliers.
- Competitive activity intensifies as players diversify therapeutic candidates and secure long-term isotope access, while challenges include limited alpha isotope availability, complex manufacturing pathways, and strict regulatory handling requirements.
- Regionally, North America leads with 38–40%, followed by Europe at 27–29% and Asia-Pacific at 21–23%, supported by expanding clinical trials and strengthening oncology infrastructure across top-adopting markets.
 Market Segmentation Analysis:
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Type of Radionuclide
Actinium-based alpha emitters represent the dominant radionuclide segment, holding the largest market share due to their high linear energy transfer, short path length, and strong therapeutic index in targeted radiotherapies. Actinium-225’s compatibility with precision-designed monoclonal antibodies and small-molecule ligands strengthens its adoption in late-stage oncology pipelines. Radium isotopes continue to gain traction in skeletal metastasis treatment, while bismuth and lead isotopes expand use in dose-intensified radiopharmaceutical constructs. Growing investment in scalable actinium-225 production technologies further accelerates clinical uptake and supports broader integration across commercial radiotherapeutic programs.
- For instance, the U.S. Department of Energy’s Isotope Program increased annual Ac-225 output to up to 80 millicuries per week using accelerator-driven spallation routes.
By Application
Bone metastasis remains the leading application segment, accounting for the highest adoption of alpha-emitting radiopharmaceuticals due to their superior marrow-sparing properties and ability to deliver localized cytotoxicity to metastatic lesions. High clinical use of targeted alpha therapies in advanced prostate cancer significantly strengthens demand. Applications in ovarian, pancreatic, melanoma, and lymphoma treatments are growing as clinical trials validate enhanced tumoricidal performance in resistant disease profiles. The expansion of precision oncology programs and increasing preference for minimally invasive radiotheranostics further support uptake across emerging therapeutic areas.
- For instance, Bayer’s Xofigo® (radium-223 dichloride) demonstrated a median 3.6-month extension in overall survival in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) during its pivotal ALSYMPCA study, reflecting the strong clinical pull toward bone-targeting alpha therapy.
KEY GROWTH DRIVERS
Rising Adoption of Targeted Alpha Therapy (TAT) for Hard-to-Treat Cancers
Targeted Alpha Therapy is gaining rapid clinical traction as oncologists seek highly potent treatments for metastatic, refractory, and radiation-resistant cancers. Alpha particles provide significantly higher linear energy transfer compared to beta emitters, enabling them to induce double-strand DNA breaks while minimizing collateral damage to healthy tissues. This mechanism delivers meaningful therapeutic advantages in prostate cancer, neuroendocrine tumors, ovarian cancer, and hematologic malignancies. Increasing clinical evaluations of alpha-labeled monoclonal antibodies, peptides, and small molecules strengthens adoption across precision oncology programs. As pharmaceutical companies expand late-stage TAT pipelines, the market benefits from accelerating trial activity, expanding patient access, and strong interest from academic centers exploring alpha-based theranostics for personalized treatment strategies.
- For instance, Actinium Pharmaceuticals’ Iomab-B (targeted iodine-131 conjugate used in conditioning for bone marrow transplant) enabled 100% of evaluable patientsin its SIERRA trial to access a bone marrow transplant (BMT) and achieve engraftment.
Expanding Production Capacities and Technological Advances in Radionuclide Manufacturing
Continuous advancement in alpha-emitter production technologies is a major catalyst for market expansion. Government laboratories, radiopharmaceutical manufacturers, and cyclotron operators are investing in scalable Actinium-225, Lead-212, and Bismuth-213 production pathways to overcome long-standing supply shortages. Innovations in accelerator-based irradiation, thorium-based generator systems, and automated radiochemical processing enable higher purity, greater output, and improved reliability for clinical supply chains. These developments are crucial for supporting commercial-scale therapeutic programs, especially as alpha emitter–based trials increase globally. Standardizing production protocols enhances regulatory confidence, while emerging industrial collaborations strengthen global distribution networks. As manufacturing limitations ease, pharmaceutical developers gain greater freedom to scale investigational products, shorten development timelines, and expand multi-center clinical studies.
· For example, the U.S. Department of Energy’s Isotope Program has documented that its accelerator-based production of Actinium-225 yields about 50 millicuries per batch. These batches are processed on periodic production cycles rather than a continuous weekly schedule, supporting research and clinical demand for alpha-emitting isotopes.
Increasing Preference for Radiotheranostics and Personalized Oncology Care
The shift toward precision medicine is driving strong interest in radiotheranostic models that combine diagnostic imaging with therapeutic alpha emitters. Clinicians increasingly adopt molecular imaging to identify patients who will benefit most from targeted alpha therapy, improving treatment outcomes and reducing unnecessary toxicity. This integrated approach enhances patient selection, optimizes dosing strategies, and supports long-term monitoring of therapeutic response. Healthcare systems also recognize the value of radiotheranostics in reducing overall treatment costs by minimizing ineffective interventions. As the prevalence of advanced cancers rises and molecular biomarkers become more accessible, alpha-based theranostics emerge as an important tool for individualized oncology pathways. Growing hospital investments in nuclear medicine infrastructure further support the broader adoption of alpha-emitting therapeutics.
KEY TRENDS & OPPORTUNITIES
Rapid Clinical Expansion of Actinium-225 and Lead-212 Therapeutic Platforms
A major industry trend is the robust pipeline growth surrounding Actinium-225 and Lead-212 conjugates, driven by their strong therapeutic index and compatibility with next-generation targeting vectors. Pharmaceutical developers are actively pursuing antibody–drug conjugates, peptide-receptor ligands, and small molecules labeled with these radionuclides to address tumors with high unmet need, including pancreatic, ovarian, melanoma, and hematologic cancers. Lead-212’s availability through generator technologies and Actinium-225’s expanding production capacity present strategic opportunities for commercial development. The rising number of combination therapy trials pairing alpha emitters with immunotherapies, PARP inhibitors, and DNA-repair blockers signals significant future market potential. These platforms also encourage partnerships between radiopharmaceutical firms and biotech innovators, energizing cross-industry collaboration.
· For example, Fusion Pharmaceuticals is advancing FPI-2265, an Actinium-225–labeled PSMA-targeted radiotherapy, through its multicenter Phase 2 portion of the AlphaBreak trial, which plans to enroll about 60 patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. The company has confirmed first-patient dosing in this Phase 2 study.
Emerging Use of Alpha Emitters in Early-Stage and Minimal Residual Disease Treatment
A growing opportunity lies in the application of alpha emitters beyond late-stage cancers into earlier disease settings and minimal residual disease (MRD). Their short-path, high-energy profile makes alpha therapies particularly well-suited for eliminating micrometastatic lesions, circulating tumor cells, and residual tumor clusters that remain after surgery or chemotherapy. Early data from clinical studies indicates improved progression-free outcomes when alpha therapies are used as adjuvant or consolidation treatments. This shift has opened a new therapeutic landscape where alpha emitters may serve as frontline or maintenance therapy in select cancers. As oncology protocols evolve toward early intervention, demand for scalable alpha-based regimens is likely to rise significantly.
· For example, Actinium Pharmaceuticals’ Actimab-A, an Actinium-225–labeled CD33-targeting antibody, has shown meaningful clinical activity in relapsed or refractory AML when combined with CLAG-M salvage chemotherapy. In a recently published study, 8 of 12 responders achieved measurable residual disease (MRD) negativity, supporting the potential of alpha therapy in high-risk AML.
Growing Investments in Hospital Nuclear Medicine Infrastructure
Hospitals and cancer centers worldwide are expanding nuclear medicine capabilities to support increasing demand for radiopharmaceutical therapies. Investments include hot labs, shielded radiopharmacies, advanced SPECT/PET systems, and high-precision alpha therapy administration units. These upgrades enable institutions to participate in multi-center clinical trials and offer cutting-edge targeted therapies. Improved infrastructure also enhances patient throughput, reduces waiting times, and improves safety standards for handling alpha-emitting isotopes. As reimbursement systems evolve and nuclear oncology gains mainstream visibility, healthcare providers recognize the strategic value of incorporating alpha emitters into treatment portfolios creating strong opportunities for radiopharmaceutical vendors and service providers.
KEY CHALLENGES
Limited Global Supply and High Production Complexity of Alpha Isotopes
Despite rising demand, global production of key alpha isotopes particularly Actinium-225 and Bismuth-213 remains insufficient to meet clinical and commercial requirements. Production relies heavily on complex accelerator-based processes, long-lived parent isotope generators, and highly specialized radiochemical purification steps. These limitations create bottlenecks for pharmaceutical companies advancing multiple clinical programs. Fragmented supply chains and dependency on government facilities further increase vulnerability to disruptions. High production costs and stringent quality control requirements add pressure to scale economically. Without significant investment in industrial-scale isotope manufacturing, supply constraints may slow market expansion and delay regulatory approval for alpha-based therapeutics.
Regulatory, Safety, and Logistics Barriers in Handling Alpha Emitting Therapeutics
Alpha-emitting radiopharmaceuticals require strict compliance with radiation safety standards, specialized storage, and regulated transportation protocols, creating operational challenges for manufacturers, distributors, and treatment centers. Regulatory frameworks vary significantly across regions, complicating market entry and delaying product approvals. Handling alpha emitters demands advanced shielding, trained personnel, and radiation-controlled environments, which many healthcare facilities still lack. Moreover, ensuring secure cross-border transport of short-half-life isotopes is logistically challenging and cost-intensive. These factors collectively hinder rapid adoption and limit broader accessibility of alpha-based therapies, especially in emerging markets with underdeveloped nuclear medicine infrastructure.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America dominates the alpha emitters market, accounting for roughly 38–40% of global demand due to its strong nuclear medicine infrastructure, extensive radiotheranostic research programs, and high adoption of targeted alpha therapy in advanced oncology. The region benefits from expanding Actinium-225 and Lead-212 production capacities supported by national laboratories, specialty radiopharmacies, and private isotope suppliers. Increasing clinical trials across prostate, ovarian, and hematologic cancers accelerates therapeutic uptake. Favorable reimbursement frameworks, strong academic–industry collaboration, and rapid integration of radiotheranostics in precision oncology further consolidate North America’s lead in commercial and clinical applications.
Europe
Europe holds approximately 27–29% of the market, supported by a well-established regulatory environment for radiopharmaceuticals and strong participation from academic medical centers in clinical research. Countries such as Germany, France, the U.K., and the Netherlands lead in nuclear medicine advancements and maintain robust imaging and therapy capabilities. Growth is reinforced by expanding supply networks for alpha isotopes and rising adoption of targeted radiotherapies in hospital oncology programs. Increasing investments in theranostic infrastructure and the region’s high acceptance of personalized cancer treatment models continue to strengthen Europe’s position in emerging alpha-emitter applications.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific accounts for an estimated 21–23% of the alpha emitters market, driven by rising cancer incidence, expanding nuclear medicine capabilities, and strong government investments in radiopharmaceutical manufacturing. Countries such as Japan, South Korea, China, and Australia lead regional adoption of alpha therapies and participate actively in multi-center clinical trials. Rapid modernization of diagnostic imaging systems and increasing availability of PET/SPECT radiotheranostic platforms fuel demand. Growing private hospital networks and government support for innovation in oncology accelerate uptake, positioning Asia-Pacific as one of the fastest-expanding markets for alpha-based therapeutic development.
Latin America
Latin America represents around 6–7% of the global alpha emitters market, with growth concentrated in Brazil, Mexico, Argentina, and Chile. Adoption is supported by improving nuclear medicine infrastructure, expanding access to PET-CT and SPECT imaging, and rising participation in international clinical collaborations. However, access to alpha isotopes remains limited, creating supply and distribution constraints. Despite these challenges, increasing demand for advanced oncology treatments, greater government focus on cancer care modernization, and emerging public–private partnerships are driving gradual integration of targeted radiopharmaceutical therapies across high-burden cancer populations.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region accounts for approximately 4–5% of the market, with growth led by the UAE, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, and Israel. Investments in specialty nuclear medicine centers, radiopharmacies, and advanced oncology facilities support the introduction of alpha-emitting therapeutic programs. Israel remains a key innovation hub with strong radiopharmaceutical research capabilities. However, limited isotope availability, regulatory complexities, and insufficient infrastructure restrict broader adoption in several countries. Ongoing healthcare modernization initiatives and rising interest in precision oncology are expected to gradually increase the region’s participation in alpha-based therapies.
Market Segmentations:
By Type of Radionuclide
- Radium
- Lead
- Bismuth
- Actinium
By Application
- Bone Metastasis
- Ovarian Cancer
- Pancreatic Cancer
- Melanoma
- Lymphoma
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape of the alpha emitters market is shaped by a mix of radiopharmaceutical developers, isotope producers, nuclear research laboratories, and technology partners advancing targeted alpha therapy pipelines. Companies increasingly focus on scaling Actinium-225, Lead-212, and Bismuth-213 production through accelerator-based systems, thorium generator technologies, and high-purity radiochemical processing capabilities. Strategic collaborations between biotech firms and medical isotope suppliers are accelerating clinical translation of alpha-labeled antibodies, peptides, and small-molecule therapeutics. Market players emphasize GMP-compliant manufacturing, supply chain reliability, and regulatory alignment to support commercial expansion. As clinical trials broaden across prostate, ovarian, pancreatic, and hematologic cancers, competition intensifies around securing long-term radionuclide access and advancing differentiated theranostic platforms. Emerging entrants are targeting production innovation to ease global isotope constraints and strengthen their positioning in the growing radiotheranostics ecosystem.
Key Player Analysis
- RadioMedix, Inc.
- IBA Radiopharma Solutions
- Actinium Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
- Alpha Tau Medical
- Fusion Pharmaceuticals
- NTP Radioisotopes SOC Ltd.
- IBA Group
- Bayer AG
Recent Developments
- In October 2025, Actinium Pharmaceuticals, Inc. revealed new pre-clinical data for its first-in-class antibody radioconjugate ATNM‑400 (Actinium-225 payload) across prostate and lung cancers.
- In June 2025, RadioMedix, Inc. announced a proprietary bench-top ²¹²Pb generator for targeted alpha therapy development.
- In February 2025, IBA Radiopharma Solutions partnered with Framatome to develop a global network of cyclotrons for alpha-emitter isotope ^211At production (astatine-211) and enable scalable supply for oncology applications.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Type of radionuclide, Application and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- The adoption of targeted alpha therapy will accelerate as more late-stage clinical trials demonstrate strong efficacy in hard-to-treat cancers.
- Actinium-225 production capacity will expand significantly through accelerator technologies and global manufacturing partnerships.
- Radiotheranostics will become a mainstream oncology approach, integrating diagnostic imaging with alpha-based precision treatment.
- More pharmaceutical companies will enter the alpha therapy space through collaborations, licensing agreements, and joint development programs.
- Alpha emitters will move beyond late-stage cancers into earlier treatment lines and minimal residual disease applications.
- Hospitals will continue investing in advanced nuclear medicine infrastructure to support safe preparation and administration of alpha therapeutics.
- Lead-212 and Bismuth-213 platforms will gain traction due to generator-based supply models and growing research activity.
- Combination therapies pairing alpha emitters with immunotherapy or DNA-repair inhibitors will expand clinical utility.
- Regulatory frameworks for radiopharmaceuticals will strengthen, improving global harmonization and accelerating approvals.
- Emerging markets will gradually increase adoption as isotope availability, clinical expertise, and oncology infrastructure improve.

 Market Segmentation Analysis:
Market Segmentation Analysis:

