Market Overview
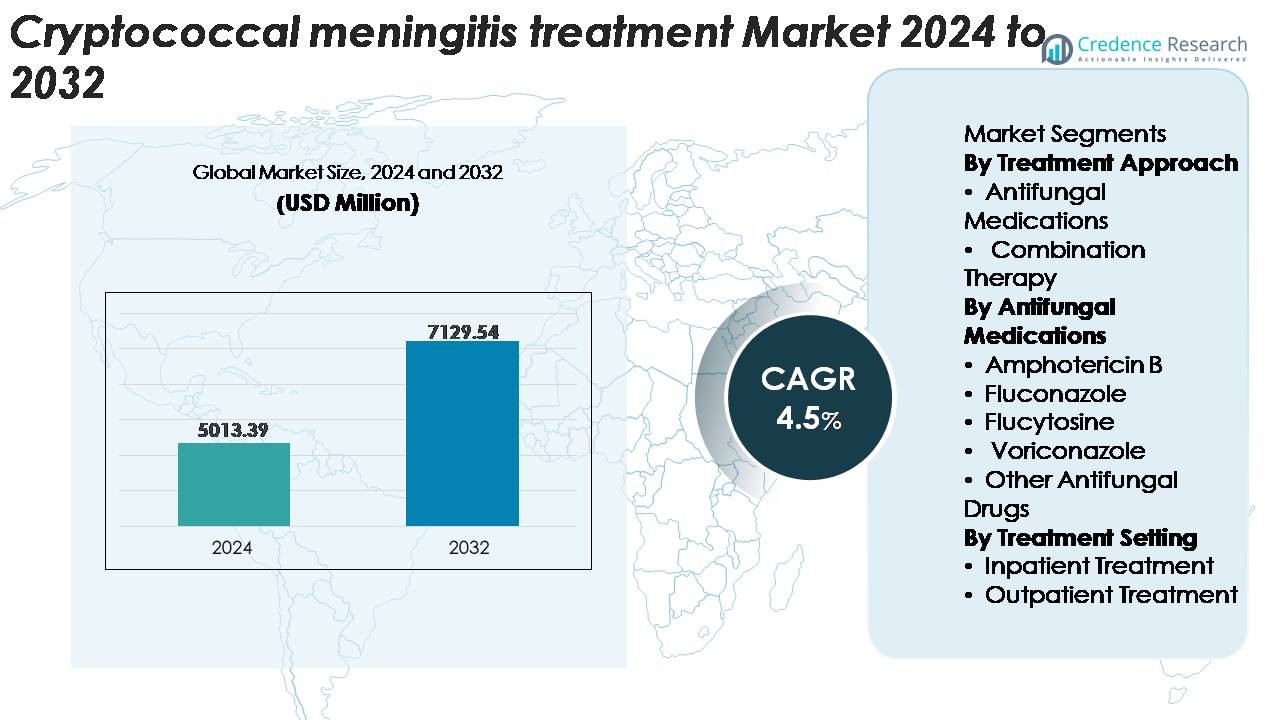
The global cryptococcal meningitis treatment market was valued at USD 5,013.39 million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 7,129.54 million by 2032, expanding at a CAGR of 4.5% during the forecast period (2025–2032).
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Cryptococcal Meningitis Treatment Market Size 2024 |
USD 5,013.39 Million |
| Cryptococcal Meningitis Treatment Market, CAGR |
4.5% |
| Cryptococcal Meningitis Treatment Market Size 2032 |
USD 7,129.54 Million |
The cryptococcal meningitis treatment market is shaped by leading pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies such as Pfizer Inc., Gilead Sciences, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Glenmark Pharmaceuticals, Sanofi, and Sun Pharmaceutical Industries, each contributing to the development, manufacturing, and global distribution of essential antifungals including amphotericin B, fluconazole, and flucytosine. These players compete through advancements in formulation technologies, wider therapy availability, and strategic partnerships that support treatment access in high-burden regions. North America leads the global market with an exact 38% share, driven by superior diagnostic coverage, widespread adoption of guideline-based treatments, and robust infectious disease management infrastructure.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Insights
- The cryptococcal meningitis treatment market was valued at USD 5,013.39 million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 7,129.54 million by 2032, expanding at a CAGR of 4.5% during the forecast period.
- Market growth is driven by rising HIV-associated cryptococcal infections, expanding access to antifungal therapies, and broader adoption of combination treatment protocols that accelerate fungal clearance and reduce relapse rates.
- Key trends include increasing uptake of liposomal amphotericin B, wider implementation of cryptococcal antigen (CrAg) screening, and growing investment in hospital-based induction therapy supported by improving healthcare infrastructure across emerging markets.
- Competitive activity remains strong among major players such as Pfizer, Gilead Sciences, Glenmark, Sun Pharma, and Sanofi, with companies focusing on improved formulations, essential drug supply expansion, and partnerships that strengthen availability in high-burden regions.
- Regionally, North America leads with 38% share, followed by Europe at 27% and Asia-Pacific at 23%, while inpatient treatment dominates the segment mix due to the need for intensive induction therapy and close monitoring during early disease management.
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Treatment Approach
Antifungal medications represent the dominant treatment approach, capturing the largest market share due to their established clinical efficacy, accessibility across healthcare systems, and inclusion in first-line global treatment guidelines. Their strong adoption is driven by the essential role of antifungal monotherapy in early-stage disease management and resource-constrained settings where combination therapy remains cost-intensive. Combination therapy is expanding gradually as clinicians prioritize faster fungal clearance, reduced relapse rates, and improved survival outcomes, particularly in advanced HIV-associated cryptococcal meningitis. However, the high cost and toxicity-monitoring requirements limit its broader penetration.
- For instance, Pfizer’s fluconazole commercialized globally as Diflucan for systemic fungal infections has been validated in clinical studies to achieve typical cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) penetration levels in the range of approximately 30 to 40 µg/mL when administered at a daily dose of 1200 mg.
By Antifungal Medications
Amphotericin B remains the leading antifungal drug segment, holding the highest market share due to its rapid fungicidal activity, strong clinical recommendation for induction therapy, and continued dependence in low- and middle-income countries. Its dominance is reinforced by the availability of both conventional and liposomal formulations, supporting wider therapeutic applicability. Fluconazole maintains substantial usage in consolidation and maintenance therapy, while flucytosine gains traction where access improves. Voriconazole and other agents serve niche roles, primarily in cases of intolerance or resistance, but do not match the market presence of Amphotericin B.
- For instance, Gilead Sciences’ liposomal amphotericin B (AmBisome) has been shown to deliver a markedly improved safety profile, with clinical pharmacokinetic studies reporting a mean peak plasma concentration of 11.5 µg/mL following a 3 mg/kg infusion and documented nephrotoxicity rates significantly lower than conventional amphotericin B; additionally, AmBisome’s single high-dose regimen of 10 mg/kg used in the ACTA trial demonstrated rapid fungal clearance within the first 7 days of treatment.
By Treatment Setting
Inpatient treatment dominates the market, accounting for the largest share because cryptococcal meningitis requires hospitalization for induction therapy, intensive monitoring, management of intracranial pressure, and administration of intravenous antifungals. The complexity of initial treatment and the need for rapid clinical intervention continue to anchor demand in hospital-based settings. Outpatient treatment is gradually increasing as patients transition to oral consolidation and maintenance regimens, supported by expanding healthcare access and improved follow-up infrastructure. However, outpatient care remains secondary, reflecting the criticality and acute nature of early-stage disease management.
Key Growth Drivers
Rising Burden of HIV-Associated Cryptococcal Infections
The increasing global prevalence of advanced HIV infection remains the strongest driver for cryptococcal meningitis treatment demand, particularly in regions with delayed antiretroviral therapy (ART) initiation and high HIV viral load burden. A significant portion of cryptococcal infections occur in individuals with CD4 counts below 100 cells/µL, creating sustained need for rapid diagnostic intervention and aggressive antifungal therapy. Although ART programs continue to expand, gaps in care retention and treatment adherence allow progression to opportunistic fungal infections, reinforcing consistent market demand. Expanded surveillance programs, WHO-led screening initiatives, and government-backed cryptococcal antigen (CrAg) testing campaigns are improving case identification, pushing more patients into formal treatment pathways. In low-income regions, healthcare development programs increasingly incorporate fungal infection management, enhancing access to antifungals and inpatient care. Overall, the persistent epidemiological burden and growing awareness of cryptococcal meningitis prevention and treatment are accelerating the medical and therapeutic uptake.
- For instance, Abbott’s rapid lateral-flow CrAg assay delivers a confirmed analytical sensitivity of 1 ng/mL of cryptococcal polysaccharide antigen, enabling earlier diagnosis in high-risk HIV cohorts and accelerating linkage to antifungal treatment.
Advancements in Antifungal Therapeutics and Formulation Technologies
Advances in antifungal drug development significantly strengthen the treatment landscape, especially the rise of newer formulations of amphotericin B that reduce toxicity while preserving high fungicidal activity. Liposomal and lipid-complex variants are gaining preference due to lower nephrotoxicity and improved clinical tolerability, supporting broader adoption in hospital settings. Additionally, enhanced manufacturing capabilities are increasing production of essential drugs such as flucytosine, addressing historical shortages. Ongoing clinical evaluations of combination regimens and optimized dosing protocols are improving survival outcomes and accelerating fungal clearance, which contributes to higher treatment acceptance. Improvements in drug delivery formats, including prolonged-release formulations and intravenous-to-oral transition therapies, further support continuity of care. These therapeutic innovations, supported by global guideline updates and stronger procurement frameworks, collectively strengthen the treatment market’s long-term expansion.
· For instance, fluconazole (available in both IV and oral formats from various manufacturers, including Pfizer) achieves high cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) penetration, with concentrations typically approximating 20 to 40 µg/mL with a 1200 mg/day regimen. This high bioavailability (around 80% of plasma concentration) enables reliable IV-to-oral transition without loss of therapeutic exposure.
Expansion of Global Access Programs and Healthcare Infrastructure
Growth in international health initiatives targeting opportunistic infections, especially in sub-Saharan Africa and Southeast Asia, is a central growth accelerator. Global health agencies, non-profit procurement alliances, and national infectious disease programs continue to invest in antifungal availability, laboratory infrastructure, and inpatient management capabilities for cryptococcal meningitis. Donor-funded programs increasingly prioritize cryptococcal screening among high-risk HIV populations, enabling early detection and quicker therapeutic intervention. Many countries are upgrading infectious disease wards, enhancing critical care systems, and expanding pharmacy supply chains to maintain reliable access to amphotericin B, fluconazole, and flucytosine. Training programs for clinicians and nurses further promote standardized treatment protocols. As health systems strengthen their readiness to manage complex fungal infections, patient survival rates improve, encouraging sustained reliance on formal treatment structures. These collective infrastructure and access improvements substantially elevate market penetration and long-term treatment demand.
Key Trends & Opportunities
Growing Shift Toward Combination Therapy for Faster Clinical Recovery
A strong trend shaping the market is the increasing preference for combination therapy, particularly amphotericin B paired with flucytosine or fluconazole, driven by evidence demonstrating faster fungal clearance and reduced relapse rates. Updated global treatment guidelines recommend combination regimens as first-line induction therapy, prompting hospitals to adopt more intensive treatment protocols. The trend is further supported by clinical studies confirming improved neurological outcomes and lower mortality with multi-drug approaches. This shift opens opportunities for pharmaceutical companies to optimize dosing, expand production of essential antifungals, and introduce safety-enhanced formulations. As diagnostic testing becomes more widespread, the clinical community increasingly emphasizes early combination therapy, creating avenues for market expansion in both developed and resource-limited healthcare systems.
- For instance, Mylan’s (Viatris) flucytosine achieves therapeutic plasma concentrations of 40–60 µg/mL at a dosing level of 100 mg/kg/day, enabling predictable pharmacodynamics when paired with amphotericin B during induction therapy.
Increasing Investment in Diagnostics, Screening, and Preventive Care
Another emerging opportunity lies in the rapid enhancement of cryptococcal antigen (CrAg) diagnostics and preventive screening programs within HIV treatment ecosystems. Point-of-care CrAg tests and laboratory-based antigen detection systems are being widely adopted due to their ability to detect early fungal infection before symptomatic meningitis develops. This trend supports earlier therapeutic intervention, reducing severe disease progression and improving treatment outcomes. Governments and global health organizations are integrating routine CrAg screening into HIV clinical guidelines, especially for patients with very low CD4 counts. The expansion of preventive fluconazole therapy for CrAg-positive individuals also presents opportunities for drug demand growth. As screening technologies continue to advance and become more cost-effective, early diagnosis and preventive protocols will significantly shape future treatment pathways and improve market penetration.
- For instance, Abbott’s IMMY-approved CrAg Lateral Flow Assay commercialized through its diagnostics channel offers an analytical sensitivity of 1 ng/mL of cryptococcal polysaccharide antigen, enabling detection of early cryptococcal infection even in asymptomatic, high-risk HIV patients.
Key Challenges
Limited Access to Essential Antifungal Drugs in Low-Resource Regions
Despite notable progress, many countries continue to face shortages of critical antifungal drugs such as amphotericin B and flucytosine, significantly limiting treatment effectiveness. High acquisition costs, fragmented supply chains, and inadequate cold-chain storage capabilities restrict availability in several high-burden regions. Conventional amphotericin B requires intensive monitoring and supportive care to manage toxicity, which many under-resourced hospitals cannot consistently provide. Flucytosine shortages remain a persistent challenge due to limited global manufacturers and uneven distribution. These constraints often force reliance on suboptimal monotherapy regimens, leading to poorer patient outcomes. Ensuring sustainable access to quality-assured antifungals remains one of the most pressing barriers to broad market expansion.
Toxicity, Treatment Complexity, and High Mortality Rates
The inherently complex and high-risk nature of cryptococcal meningitis treatment continues to challenge healthcare systems worldwide. Amphotericin B, despite its effectiveness, carries risks of nephrotoxicity, electrolyte imbalance, and infusion-related reactions, requiring skilled clinicians and intensive monitoring. Patients often need prolonged hospitalization for induction therapy and repeated lumbar punctures to manage intracranial pressure, making treatment resource-intensive. Even with appropriate therapy, mortality rates remain high, particularly in patients presenting late or with severe immunosuppression. The combination of clinical complexity, treatment toxicity, and limited supportive care capacity in many regions slows therapeutic adoption and underscores the need for safer, easier-to-administer regimens.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America holds the largest market share at 38%, driven by advanced healthcare infrastructure, strong infectious disease management systems, and widespread access to antifungal medications. High awareness of opportunistic fungal infections among HIV patients and strong diagnostic coverage significantly support early intervention and treatment uptake. The region benefits from continuous clinical research, availability of liposomal amphotericin B, and established guidelines that promote combination therapy. Growing investment in fungal disease surveillance and collaborative initiatives between research institutes and pharmaceutical companies further strengthen market expansion. Overall, North America maintains its lead through strong treatment accessibility and high clinical standards.
Europe
Europe accounts for 27% of the global market, supported by robust hospital networks, high adoption of guideline-based treatment, and increasing use of liposomal antifungal formulations. Countries with strong HIV management programs ensure early cryptococcal screening, improving patient outcomes and supporting higher therapy uptake. Government funding for infectious disease control and continuous improvement in laboratory capacities further enhance diagnostic accuracy. The region also benefits from stringent regulatory oversight that ensures the availability of high-quality antifungal drugs. With rising incidence among immunocompromised populations, Europe continues to strengthen its market position through sustained healthcare investment and clinical standardization.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific holds 23% of the market and represents one of the fastest-growing regions due to its large HIV-infected population, increasing diagnostic awareness, and expanding healthcare access. Countries such as India, Thailand, and China report high cryptococcal disease burden, driving strong demand for antifungal therapy. Government-led HIV programs increasingly integrate cryptococcal antigen testing, supporting earlier treatment initiation. Investments in tertiary care hospitals and improvements in medicine distribution channels further enhance treatment reach. Rising availability of generic antifungals strengthens affordability, while ongoing partnerships with global health organizations continue to address access gaps, positioning Asia-Pacific as a critical growth region.
Latin America
Latin America captures approximately 7% of the market, driven by moderate disease prevalence and gradual improvements in HIV care infrastructure. Brazil, Mexico, and Argentina lead regional demand due to expanding public health programs and better diagnostic penetration in urban hospitals. However, uneven access to amphotericin B and flucytosine across rural settings limits treatment consistency. Increasing regional adoption of cryptococcal screening in HIV clinics enhances early detection, supporting stronger reliance on inpatient treatment pathways. International aid initiatives and training programs for infectious disease professionals continue to strengthen treatment capacity, gradually improving the region’s market share.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region holds 5% of the global market but remains the most high-burden area for cryptococcal meningitis, particularly in sub-Saharan Africa. Despite strong clinical need, limited access to essential antifungal drugs and diagnostic shortages constrain treatment penetration. International health partnerships, including HIV care programs and donor-supported procurement of amphotericin B and fluconazole, are gradually improving availability. Expansion of CrAg screening for high-risk populations and improvements in inpatient care capacity support incremental growth. Continued investment in health infrastructure and treatment access remains essential for increasing the region’s future market share.
Market Segmentations:
By Treatment Approach
- Antifungal Medications
- Combination Therapy
By Antifungal Medications
- Amphotericin B
- Fluconazole
- Flucytosine
- Voriconazole
- Other Antifungal Drugs
By Treatment Setting
- Inpatient Treatment
- Outpatient Treatment
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape of the cryptococcal meningitis treatment market is shaped by a mix of global pharmaceutical leaders and regional manufacturers focused on expanding the availability of essential antifungal therapies. Key companies such as Pfizer Inc., Gilead Sciences, Glenmark Pharmaceuticals, Sun Pharmaceutical Industries, Sanofi, and Bristol-Myers Squibb play central roles through the production of amphotericin B, fluconazole, and other standard antifungal agents. Competition centers on improving treatment safety, enhancing formulation technologies, and strengthening supply reliability, particularly in high-burden regions where access remains inconsistent. Many manufacturers are investing in liposomal and lipid-complex amphotericin B variants to reduce toxicity and expand clinical adoption. Strategic partnerships with global health organizations and procurement programs support broader distribution of critical drugs like flucytosine, historically limited by production constraints. Companies also emphasize compliance with WHO-preferred treatment protocols, ensuring their products align with evolving clinical guidelines. Overall, competition remains driven by efficacy, availability, and innovations that address unmet medical needs.Bottom of Form
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
- Pfizer Inc
- Lupin Ltd
- Novartis AG
- Amplyx Pharmaceuticals
- Glenmark Pharmaceuticals
- Janssen Biotech Inc (Johnson & Johnson)
- Abbott Laboratories
- Sigmapharm Laboratories LLC
- Valeant Pharmaceuticals Inc
- Bristol-Myers Squibb Company
Recent Developments
- In August 2024, a pooled analysis of three clinical trials from Uganda demonstrated that daily liposomal amphotericin B plus flucytosine was noninferior to daily conventional amphotericin B deoxycholate with flucytosine in HIV‑associated cryptococcal meningitis, supporting wider use of liposomal formulations due to better safety.
- In March 2024, a survey of North American infectious-disease physicians revealed that only a minority are using the single high-dose liposomal amphotericin B regimen (AMBITION‑cm), despite its proven noninferiority in trials. Many clinicians cited concerns about applicability to high-resource settings, and the fact that existing guidelines have not yet fully incorporated the newer induction strategy
- In August 2023, researchers at the University of Minnesota published results of the “EnACT” trial showing a new oral lipid‑nanocrystal formulation of amphotericin B for cryptococcal meningitis. This formulation demonstrated strong antifungal activity, good tolerability, and much lower toxicity than traditional IV amphotericin, potentially offering a safer, easier‑to-administer oral therapy.
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Treatment approach, Antifungal medications, Treatment setting and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- The market will see stronger adoption of combination therapy as global guidelines increasingly recommend multi-drug regimens for faster fungal clearance.
- Improved access to liposomal amphotericin B formulations will reduce treatment-related toxicity and expand use in hospital settings.
- Expansion of cryptococcal antigen screening programs will support earlier diagnosis and drive higher treatment initiation rates.
- Growing investment in healthcare infrastructure in Asia-Pacific and Africa will improve inpatient treatment capacity and drug availability.
- Increased production of flucytosine will help address long-standing supply shortages in high-burden countries.
- Pharmaceutical companies will prioritize safer, more tolerable antifungal formulations to improve patient outcomes.
- Partnerships between governments, NGOs, and drug manufacturers will enhance antifungal distribution in low-resource regions.
- Rising HIV awareness and improved ART adherence programs will reduce late-stage disease presentations but maintain stable treatment demand.
- Digital diagnostic tools and point-of-care screening technologies will strengthen early case identification.
- Regulatory support for essential medicine procurement will continue to improve affordability and access to critical antifungals.




