Market Overview
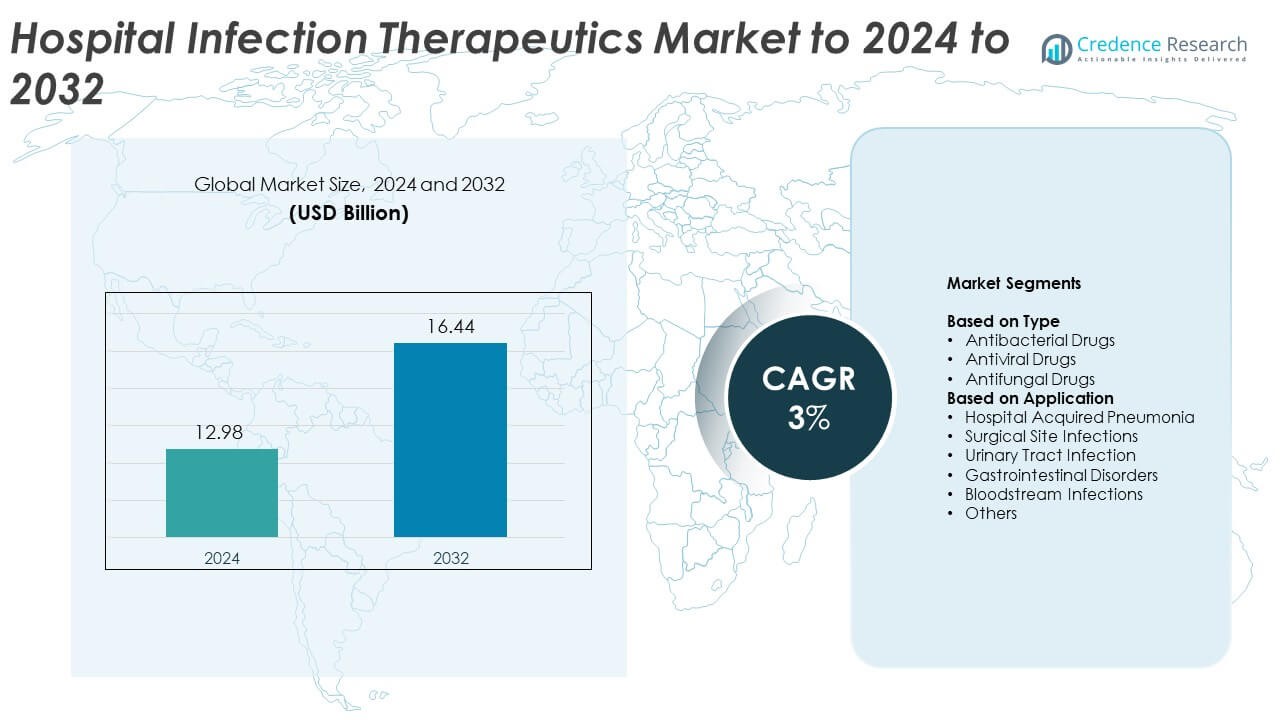
Hospital Infection Therapeutics Market size was valued at USD 12.98 Billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 16.44 Billion by 2032, at a CAGR of 3% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Hospital Infection Therapeutics Market Size 2024 |
USD 12.98 Billion |
| Hospital Infection Therapeutics Market, CAGR |
3% |
| Hospital Infection Therapeutics Market Size 2032 |
USD 16.44 Billion |
The Hospital Infection Therapeutics Market features key players such as Pfizer Inc., Sanofi, Actavis, Hikma Pharmaceuticals PLC, Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb Company, GlaxoSmithKline, and Johnson & Johnson Services. These companies strengthen their positions through advanced antibacterial, antiviral, and antifungal portfolios that target high-burden infections across ICU, surgical, and emergency care settings. North America led the market in 2024 with around 37% share, supported by strong diagnostic adoption and high treatment demand. Europe followed with roughly 29% share, driven by strict stewardship regulations. Asia Pacific held close to 24% share and emerged as the fastest-growing region due to expanding hospital capacity and rising infection rates.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Insights
- The Hospital Infection Therapeutics Market reached USD 12.98 Billion in 2024 and is projected to hit USD 16.44 Billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 3%.
- Rising hospital acquired infections and growing ICU admissions drive strong demand for antibacterial, antiviral, and antifungal drugs, with antibacterial therapies holding about 64% share in 2024.
- Key trends include expanding use of targeted therapies, rapid diagnostics, and combination regimens to address resistant pathogens and improve treatment precision.
- Competition remains strong as leading manufacturers invest in advanced formulations, clinical trials, and global supply capacity to strengthen their presence in high-burden infection categories.
- North America led the market with around 37% share in 2024, followed by Europe at nearly 29% and Asia Pacific at about 24%, while hospital acquired pneumonia remained the dominant application segment with nearly 34% share.
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Type
Antibacterial drugs held the dominant share in 2024 with about 64% of the Hospital Infection Therapeutics Market. Hospitals used these medicines widely to treat resistant pathogens linked to pneumonia, bloodstream infections, and surgical site infections. Demand grew due to rising antimicrobial resistance, which pushed hospitals to rely on advanced broad-spectrum and targeted antibacterial options. Antiviral and antifungal drugs expanded at a steady pace as healthcare systems faced higher viral and fungal infection risks among ICU patients, transplant cases, and individuals with compromised immunity.
- For instance, Pfizer reports a hospital anti-infective portfolio of more than 80 antimicrobial agents covering bacterial, fungal and parasitic infections worldwide.
By Application
Hospital acquired pneumonia led the application segment in 2024 with nearly 34% share. Cases increased due to long ICU stays, ventilator use, and high-risk elderly populations. Hospitals focused on strong antibacterial and antiviral regimens to reduce morbidity linked to severe respiratory infections. Surgical site infections and urinary tract infections also showed strong therapeutic demand as healthcare systems adopted faster diagnostics and improved stewardship programs. Bloodstream infections gained attention because of rising multidrug-resistant organisms, which encouraged use of targeted antibacterial therapies.
- For instance, Gilead Sciences states that Veklury and generic remdesivir have reached more than 14 million COVID-19 patients globally, including over 8 million in low- and lower-middle-income countries, many treated in hospital settings.
Key Growth Drivers
Rising Hospital Acquired Infection Burden
Growing hospital acquired infections increased demand for advanced antibacterial, antiviral, and antifungal therapies. High ICU occupancy, invasive procedures, and aging patients pushed infection rates higher across major health systems. Rising multidrug-resistant organisms also increased dependence on new and effective therapeutic options. Hospitals expanded stewardship programs, which supported timely treatment decisions and boosted adoption of broad-spectrum and targeted drugs designed to reduce complications linked to pneumonia, bloodstream infections, and urinary tract infections.
- For instance, bioMérieux highlights major health body estimates that antibiotic-resistant infections already caused about 1.27 million deaths directly in 2019
Expansion of Critical Care and Surgical Procedures
Growth in critical care admissions brought higher exposure to ventilators, catheters, and invasive monitoring tools. Increased surgical volumes in orthopedic, cardiac, and transplant procedures raised the risk of postoperative infections and strengthened demand for rapid therapeutic action. Hospitals focused on lowering infection-related readmissions, which encouraged wider use of proven drug classes. Higher patient turnover increased the need for stronger treatment protocols, driving steady consumption of antibacterial, antiviral, and antifungal medicines.
- For instance, Stryker’s Sustainability Solutions division serves roughly 3,500 United States hospitals and, in 2023, helped customers divert more than 5 million pounds of medical waste from landfills through device reprocessing programs.
Rise in Immunocompromised Patient Population
More patients with weakened immunity created a stronger need for reliable infection therapeutics. Individuals undergoing chemotherapy, organ transplants, and long-term steroid therapy required aggressive treatment strategies against viral, bacterial, and fungal threats. Frequent exposure to hospital environments increased infection chances, which pushed hospitals to adopt advanced therapies. Increased awareness among clinicians supported faster treatment initiation, strengthening overall demand for specialized therapeutics used to reduce infection severity.
Key Trends and Opportunities
Advances in Precision and Targeted Therapies
Growth in molecular diagnostics supported faster identification of hospital pathogens and resistance patterns. This improvement allowed doctors to choose targeted therapies that improved patient outcomes and reduced unnecessary drug use. Pharmaceutical firms increased research into narrow-spectrum drugs that focus on specific organisms. Adoption of these precise treatment options created strong opportunities for companies that develop next-generation antimicrobials aligned with resistance control goals.
- For instance, Roche Diagnostics notes that 29 billion tests were delivered to customers worldwide in 2023, many on molecular platforms that support pathogen identification and resistance profiling for targeted hospital treatment decisions
Adoption of Combination Therapeutic Strategies
Hospitals expanded use of combination drugs to manage tough infections caused by resistant bacteria, fungi, and viruses. These strategies helped reduce treatment failure and lowered mortality risk, especially in high-risk ICU settings. Growth in clinical trials for dual-action therapies offered fresh pathways for innovation. Healthcare systems supported this shift as combination regimens improved recovery rates and reduced relapse chances, opening long-term opportunities for drug developers.
- For instance, Merck reports more than 1,600 clinical trials evaluating Keytruda across multiple tumor types and treatment settings, with many protocols testing combination regimens that reflect complex therapy strategies used for high-risk inpatients.
Growth in Preventive and Stewardship-Linked Therapies
Hospitals strengthened infection control through preventive therapeutic practices linked to stewardship programs. Increased screening and early antimicrobial use helped control outbreaks linked to pneumonia and bloodstream infections. Companies focused on preventive drug formulations saw rising interest as hospitals looked for ways to reduce antibiotic misuse and avoid resistance escalation. This trend created market opportunities for products aligned with early intervention models.
Key Challenges
Rising Antimicrobial Resistance Levels
Growing resistance across bacterial, viral, and fungal pathogens made treatment difficult and increased the need for stronger drug options. Hospitals faced limited effectiveness of long-used therapies, which pushed care teams to depend on newer and often costly medicines. Resistance also prolonged recovery times, increased ICU stays, and raised mortality risk. These issues placed pressure on healthcare budgets and challenged drug developers to innovate continuously.
High Treatment Costs and Limited Drug Accessibility
Advanced hospital infection therapeutics carry high costs that strain budgets for many healthcare systems, especially in low-resource regions. Newer antibacterial and antifungal drugs often require complex manufacturing, which increases pricing and limits availability. Hospitals struggled to provide equal access to these advanced therapies, which affected patient outcomes in high-burden areas. Slow reimbursement approvals also reduced adoption and created barriers for widespread clinical use.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America held the largest share of the Hospital Infection Therapeutics Market in 2024 with around 37%. Strong healthcare spending, high ICU admissions, and widespread use of invasive procedures supported strong therapeutic demand. Hospitals adopted advanced antibacterial, antiviral, and antifungal drugs to manage rising multidrug-resistant infections. The region benefited from early access to new therapies and strong diagnostic capabilities, which improved treatment precision. Growth in immunocompromised patients and higher surgical volumes further increased the need for effective therapeutics across major hospital networks.
Europe
Europe accounted for nearly 29% share of the Hospital Infection Therapeutics Market in 2024. The region faced substantial hospital infection burdens linked to aging populations, long-term care facilities, and high surgical loads. Strong regulations encouraged stewardship practices that guided responsible therapeutic use while supporting advanced treatment options. Hospitals adopted targeted drugs for pneumonia, bloodstream infections, and urinary tract infections. Growing antimicrobial resistance and increased ICU utilization strengthened demand for next-generation antibacterial, antiviral, and antifungal medicines across Western and Central European healthcare systems.
Asia Pacific
Asia Pacific captured about 24% share of the Hospital Infection Therapeutics Market in 2024. Rapid hospital expansion, rising surgery volumes, and growing critical-care admissions increased therapeutic consumption across major countries. Higher infection rates in overcrowded healthcare settings supported strong demand for broad-spectrum and targeted drugs. Many nations faced significant antimicrobial resistance challenges, driving adoption of advanced therapies. The large patient base and improving diagnostic access created strong growth potential, making the region one of the fastest-expanding markets in global hospital infection management.
Latin America
Latin America held around 6% share of the Hospital Infection Therapeutics Market in 2024. Hospitals faced rising infection cases tied to limited infection-control infrastructure and increasing surgical workloads. Growing adoption of advanced antibacterial and antifungal drugs supported treatment improvements, though access varied across countries. Resistance issues increased pressure on healthcare systems to upgrade diagnostics and therapeutic options. Expansion of public health programs and rising awareness among clinicians supported gradual market growth despite resource constraints in several regions.
Middle East and Africa
The Middle East and Africa accounted for nearly 4% share of the Hospital Infection Therapeutics Market in 2024. The region experienced rising hospital infections due to growing surgical procedures, limited stewardship programs, and lower diagnostic availability in several areas. Demand increased for reliable antibacterial, antiviral, and antifungal medicines as healthcare systems worked to reduce infection complications. Investments in tertiary hospitals and improvements in laboratory capacity strengthened treatment capabilities. However, cost barriers and uneven drug accessibility limited rapid growth, keeping market expansion moderate across many countries.
Market Segmentations:
By Type
- Antibacterial Drugs
- Antiviral Drugs
- Antifungal Drugs
By Application
- Hospital Acquired Pneumonia
- Surgical Site Infections
- Urinary Tract Infection
- Gastrointestinal Disorders
- Bloodstream Infections
- Others
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
The Hospital Infection Therapeutics Market is shaped by major players such as Pfizer Inc., Sanofi, Actavis, Hikma Pharmaceuticals PLC, Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb Company, GlaxoSmithKline, and Johnson & Johnson Services. These companies compete through broad antibacterial, antiviral, and antifungal portfolios designed to address complex hospital acquired infections across ICUs, surgical units, and emergency care settings. Their strategies focus on expanding targeted therapies that improve pathogen-specific outcomes and reduce treatment failures linked to rising antimicrobial resistance. Strong investment in clinical trials strengthens product pipelines and supports faster launch of next-generation therapeutics. Many firms collaborate with hospitals and research institutions to accelerate drug development and refinement of stewardship models. Expanded manufacturing capabilities ensure stable global supply, while digital tools support precision-based prescribing in high-risk cases. Continuous innovation in molecular mechanisms, combination regimens, and formulation advancements helps maintain competitive differentiation and supports long-term market growth.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
- Pfizer Inc.
- Sanofi (France)
- Actavis (U.S.)
- Hikma Pharmaceuticals PLC
- Bayer (Germany)
- Bristol Myers Squibb Company (U.S.)
- GlaxoSmithKline (GSK)
- Johnson & Johnson Services (U.S.)
Recent Developments
- In 2023, GlaxoSmithKline (GSK) Entered a licence agreement with SCYNEXis for the antifungal Brexafemme.
- In 2023, Hikma Pharmaceuticals PLC Launched Cefazolin for Injection for various bacterial infections.
- In 2022, Pfizer entered a definitive agreement to acquire ReViral, a scientific-degree biopharmaceutical organization centered on growing antiviral therapeutics for the breathing syncytial virus (RSV).
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Type, Application and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- Demand for advanced antibacterial, antiviral, and antifungal drugs will rise with growing hospital infection cases.
- Adoption of precision therapies will increase as rapid diagnostics become more accessible.
- Hospitals will expand combination treatment use to manage resistant pathogens more effectively.
- Growth in ICUs and surgical procedures will drive steady therapeutic consumption.
- New drug development will accelerate as resistance challenges intensify globally.
- Preventive and stewardship-linked therapies will gain wider acceptance in hospital networks.
- Emerging markets will show faster adoption as healthcare infrastructure improves.
- Immunocompromised patient growth will push demand for targeted infection therapeutics.
- Digital decision-support tools will improve treatment accuracy and reduce misuse of drugs.
- Partnerships between hospitals and pharmaceutical firms will strengthen innovation and market expansion.




