Market Overview:
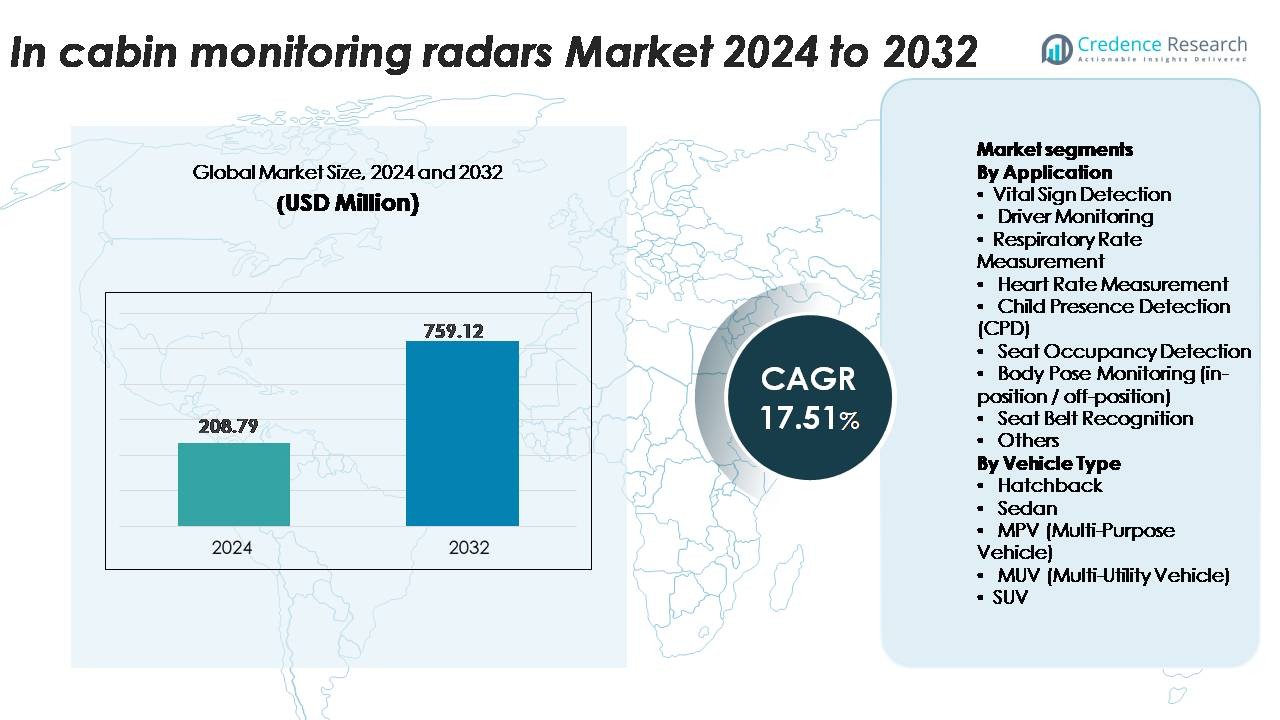
The global In-Cabin Monitoring Radars Market was valued at USD 208.79 million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 759.12 million by 2032, reflecting a robust CAGR of 17.51% over the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| In-Cabin Monitoring Radars Market Size 2024 |
USD 208.79 Million |
| In-Cabin Monitoring Radars Market, CAGR |
17.51% |
| In-Cabin Monitoring Radars Market Size 2032 |
USD 759.12 Million |
The in-cabin monitoring radars market is shaped by a highly competitive group of technology leaders, including Vayyar Imaging Ltd., Continental Corporation, microwave sensors GmbH, LG Innotek, Bitsensing, Infineon Technologies, NOVELIC, Aptiv, Texas Instruments, Smart Radar System Inc., VALEO, InnoSenT GmbH, HARMAN International, and Idneo Company. These players advance mmWave radar architectures, AI-driven micro-motion analytics, and full-cabin occupancy detection solutions adopted across global OEM platforms. Regionally, Asia-Pacific leads the market with a 34% share, driven by large-scale vehicle production and rapid regulatory adoption. North America follows with 32%, supported by strict CPD and DMS requirements, while Europe holds 28%, propelled by Euro NCAP mandates and strong premium-vehicle integration.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Insights:
- The global in-cabin monitoring radars market reached USD 208.79 million in 2024 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 17.51% through 2032, supported by increasing adoption of occupant-aware safety technologies across mass-market and premium vehicles.
- Strong market drivers include regulatory momentum for Child Presence Detection (CPD), advanced Driver Monitoring Systems, and rising integration of radar-based vital-sign tracking in next-generation cockpit platforms, especially in EVs and connected vehicles.
- Key trends involve accelerated adoption of 60/79 GHz mmWave radar, AI-enhanced signal processing, and the shift toward full-cabin radar sensing that enables occupancy mapping, posture classification, and adaptive safety personalization.
- Competitive dynamics intensify as players such as Vayyar, Continental, Valeo, Aptiv, Infineon, Bitsensing, and LG Innotek expand radar portfolios, while restraints include high system cost, cabin-specific calibration complexity, and multi-occupant interference challenges.
- Regionally, APAC leads with 34%, followed by North America at 32% and Europe at 28%, while segment-wise Child Presence Detection captures the highest share at 27%, driven by regulatory mandates and OEM safety prioritization.
 Market Segmentation Analysis:
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Application
The application landscape of in-cabin monitoring radars is led by Child Presence Detection (CPD), which captures the largest market share due to tightening global safety mandates that require radar-based sensing for unattended child alerts. Automakers increasingly prefer mmWave radar for its ability to detect micro-movements behind seats, inside footwells, and even through blankets, strengthening CPD adoption. Vital sign detection—covering respiratory and heart-rate measurements—continues to accelerate as OEMs build occupant-health monitoring into premium models. Additional use cases such as seat-occupancy detection, body-pose tracking, and seat-belt recognition support broader integration into ADAS-linked cabin safety architectures.
- For instance, Vayyar’s automotive-grade 4D imaging radar integrates 48 transmit and 48 receive antennas (96 RF channels) with a 4 GHz bandwidth, enabling sub-5 cm range resolution and detection of breathing motions as small as 5 mm even when an infant is covered by a fabric layer.
By Vehicle Type
Within vehicle categories, SUVs dominate the deployment of in-cabin monitoring radars, accounting for the highest market share, driven by their strong penetration in family-oriented segments where CPD, seat-occupancy detection, and full-cabin radar coverage are critical. SUVs also offer larger interior volumes, enabling multi-zone sensing and advanced multi-occupant analytics. Sedans follow closely, benefiting from integration of radar-enhanced driver-monitoring systems in mid-range and premium trims. Hatchbacks and MPVs/MUVs adopt radar solutions more gradually, primarily in regions enforcing CPD compliance and interior safety regulations, while electrified variants further encourage radar adoption to support intelligent cabin features.
- For instance, Vayyar’s in-cabin 4D imaging radar—integrating 48 TX and 48 RX antennas (96 RF channels) with a detection range of up to 5 m—was validated by OEMs specifically for three-row SUV configurations, enabling simultaneous tracking of up to eight occupants across all seating zones.
Key Growth Drivers
Increasing Regulatory Pressure for Occupant Safety and Mandatory CPD Implementation
Growing global emphasis on reducing in-vehicle fatalities and unattended child deaths significantly accelerates the adoption of radar-based in-cabin monitoring. Safety agencies in Europe, North America, and parts of Asia are pushing regulatory mandates requiring Child Presence Detection (CPD) capabilities in new vehicles. Radar sensors—particularly 60 GHz and 79 GHz bands—enable precise detection of micro-movements such as respiration, making them well-suited for life-critical applications. Automakers increasingly integrate radar modules to comply with Euro NCAP protocols and U.S. automotive safety legislation, which reward vehicles equipped with robust CPD functionality. The need for non-line-of-sight sensing also drives radar preference over camera-only systems. As safety ratings become a core consumer decision factor, OEMs deploy radars to enhance cabin protection systems, including vital-sign monitoring, seat-belt validation, and occupant localization. This regulatory tailwind strongly boosts radar penetration across mass-market and premium segments.
- For instance, Vayyar Imaging’s automotive-grade 4D radar-on-chip integrates 48 transmitters and 48 receivers, generating over 2,000 virtual channels—a configuration that enables high-resolution respiration detection through blankets and obstructions.
Rising Demand for Advanced Driver Monitoring and Cognitive State Assessment
The shift toward intelligent assistance and semi-autonomous driving increases vehicle dependence on accurate driver-state monitoring. Radars complement camera-based Driver Monitoring Systems (DMS) by enabling non-intrusive assessment of fatigue, drowsiness, and micro-motions correlated with cognitive load. Their independence from lighting conditions makes them valuable for nighttime monitoring and adverse weather. Increasing adoption of Level-2+ and Level-3 automation frameworks requires continuous assessment of driver readiness for takeover, amplifying the need for multimodal sensing architectures. Radar-based respiration and heart-rate measurement further enhance DMS accuracy by providing physiological indicators unavailable through vision sensors alone. As OEMs target reduced false-positive alerts and more reliable behavioral analytics, they incorporate short-range radar modules beneath dashboards, steering columns, and seat structures. These capabilities directly support regulatory and NCAP pathways that incentivize robust drowsiness detection, deepening radar integration across future vehicle platforms.
- For instance, Vayyar’s 4D in-cabin radar platform utilizes a high-resolution 48-antenna MIMO array to generate rich, data-dense 4D point clouds, enabling real-time monitoring through materials like seat fabric and blankets. The technology can monitor vital signs like pulse and respiration to support driver fatigue and Occupant Status Monitoring systems.
Expansion of Connected, Software-Defined Vehicle Platforms and Sensor Fusion Models
Automakers are transitioning toward centralized computing and software-defined architectures, making cabin-level sensing a critical data stream for occupant-aware intelligence. Radar sensors provide high-granularity motion data that complements cameras, infrared, and ultrasonic sensors within fusion-based occupant monitoring suites. As OEMs and Tier-1 suppliers pursue advanced algorithms for body-pose monitoring, in-position/off-position classification, and seat-occupancy optimization, radar inputs strengthen predictive modeling and contextual decision-making. Over-the-air (OTA) updates enable continuous enhancement of radar-based features, including improved sensitivity, zone mapping, and health-monitoring analytics. This trend aligns with the growing demand for personalized cabin experiences—climate control adjustments, seat posture correction, targeted airbag deployment, and adaptive infotainment interactions. Radar’s ability to function through fabrics and interior obstructions positions it as an indispensable sensing modality within modern cockpit systems, accelerating its integration in both internal-combustion and rapidly expanding EV platforms.
Key Trend and Opportunities:
Growth of Multi-Function Radar Platforms Supporting Full-Cabin Awareness
A major trend is the evolution from single-purpose radar modules to holistic full-cabin monitoring platforms. Manufacturers now develop radars capable of simultaneously executing CPD, seat occupancy detection, posture identification, and vital-sign measurement through a unified system. Advances in MIMO radar, mmWave SOC integration, and intelligent beamforming unlock higher spatial resolution and micro-motion tracking. OEMs increasingly shift toward consolidated radar boards to reduce BOM cost, wiring complexity, and system weight. This opens opportunities for Tier-1 suppliers to deliver modular radar architectures that support scalable feature unlocks via software. As occupant-centric intelligence grows in relevance for premium comfort and safety differentiation, full-cabin radar platforms become a core innovation avenue for the next generation of smart cockpits.
- For instance, Vayyar’s latest in-cabin 4D imaging radar integrates a 48-antenna MIMO array (24 transmit, 24 receive) capable of generating over 1,200 virtual channels for high-density point-cloud mapping across the entire cabin.
Integration of AI-Driven Signal Processing and Predictive Cabin Analytics
AI and machine learning integration represents a key opportunity for vendors developing radar-based in-cabin monitoring. Deep neural networks improve radar imaging resolution, classify occupant types more accurately, and reduce false alarms in child detection systems. Predictive analytics built on micro-motion patterns, respiration variability, and seating posture enable applications such as early fatigue prediction, wellness monitoring, and adaptive restraint deployment. Companies investing in radar-AI fusion algorithms gain competitive advantage by enhancing system reliability under diverse cabin environments, including clutter, reflective surfaces, and multi-occupant scenarios. As OEMs prioritize occupant-aware personalization and safety intelligence, the demand for advanced AI-powered radar processing pipelines grows substantially.
- For instance, In-cabin radar platform uses an embedded neural network capable of processing over 2 million RF signals per second, enabling real-time occupant classification with respiration-rate accuracy within ±0.3 breaths per minute.
Rising Opportunities in Premium EVs and Software-Defined Luxury Segments
Electric vehicles and luxury OEMs increasingly adopt radar-based cabin sensing to differentiate through safety, comfort, and automation readiness. EV manufacturers incorporate radar-enabled CPD and vital-sign monitoring to align with sustainability-driven brand positioning and high-tech user expectations. Premium brands prioritize features such as adaptive airbag tuning, occupant localization for personalized climate zones, and real-time health monitoring. Radar’s ability to provide continuous, privacy-preserving sensing without camera-related concerns makes it attractive for EV platforms deploying minimalist interior designs. As high-end OEMs shift toward subscription-based feature unlocks, radar hardware becomes a pivotal enabler of monetizable software experiences, opening substantial long-term revenue opportunities for Tier-1 suppliers and semiconductor companies.
Key Challenges:
High System Cost and Integration Complexity Across Vehicle Platforms
Cost remains the primary barrier to mass-market adoption of radar-based in-cabin monitoring. Multi-antenna radar systems, high-power mmWave chipsets, and advanced signal-processing units significantly raise hardware expenses compared to conventional ultrasonic or camera-only systems. Integrating radars within headliners, dashboards, and seat structures requires precise calibration, optimized mounting, and robust thermal and electromagnetic isolation. Vehicle platforms vary significantly in cabin geometry, material reflectivity, and RF propagation behavior, complicating standardization. OEMs face additional cost burdens in software development, sensor fusion calibration, and post-production validation. As regulators expand CPD and DMS compliance requirements globally, manufacturers must balance performance with affordability, challenging suppliers to design highly integrated, low-cost radar modules compatible with diverse vehicle classes.
Technical Limitations and Signal Interference in Multi-Occupant Scenarios
Although radar excels at micro-motion detection, significant technical challenges arise in multi-occupant cabins, cluttered environments, and complex seating arrangements. RF reflections from metallic components, seat frames, and interior trims can cause signal distortion or misclassification in posture and occupancy detection. Distinguishing between closely spaced occupants—such as infants held by adults requires highly advanced algorithms and signal-processing capabilities. Environmental factors like loose objects, blankets, or dense clothing can obscure micro-motion signatures, affecting vital-sign accuracy. Ensuring consistent performance across diverse cabin designs and vehicle materials requires extensive testing and adaptive AI-based correction models. These limitations slow regulatory approval and real-world deployment, positioning advanced algorithmic refinement as a critical challenge for radar technology providers.
Regional Analysis:
North America
North America maintains the largest share of the in-cabin monitoring radars market at approximately 32%, driven by stringent regulatory focus on Child Presence Detection (CPD), advanced Driver Monitoring Systems (DMS), and rapid adoption of Level-2+/Level-3 ADAS platforms. The U.S. leads deployments due to strong NCAP influence, safety-driven consumer preferences, and premium OEM adoption. Technology readiness, semiconductor leadership, and active innovation by Tier-1 suppliers accelerate radar integration across mass-market and luxury vehicles. Increasing EV penetration and subscription-based cockpit software further strengthen demand, positioning North America as the most mature early-adoption region.
Europe
Europe holds around 28% of the global market, supported by stringent Euro NCAP requirements that mandate CPD and encourage advanced in-cabin safety sensing. The region’s strong luxury and premium automotive base led by Germany, France, and Sweden—drives significant radar integration to enhance occupant safety intelligence. Adoption is further fueled by the region’s leadership in automation frameworks and multimodal in-cabin monitoring research. The shift toward software-defined vehicles, combined with the EV boom in Western Europe, boosts radar use for occupant localization, vital-sign sensing, and adaptive airbag deployment, making Europe a high-growth and regulation-driven market.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific commands the largest regional share at roughly 34%, driven by rapid automotive production expansion, rising safety adoption across Chinese and Korean OEMs, and strong government support for intelligent mobility systems. China leads the region with aggressive implementation of CPD and DMS in mid-range vehicles. Japan and South Korea advance radar-AI innovations through their electronics and semiconductor ecosystems. Growing EV penetration, high-volume vehicle manufacturing, and competitive pricing accelerate radar adoption across A-segment and B-segment vehicles. APAC’s cost-efficient supply chain and strong domestic Tier-1 ecosystem position it as the highest-volume growth engine for cabin radar systems.
Latin America
Latin America accounts for about 3% of global demand, limited by slower regulatory enforcement and lower penetration of advanced safety features in mainstream vehicle segments. Adoption is concentrated in Brazil and Mexico, where premium and mid-tier models increasingly integrate radar-based CPD and occupancy detection to meet evolving safety norms. While cost sensitivity restrains mass-market uptake, rising imports of global OEM platforms, expanding EV presence, and growing interest in occupant-aware safety systems gradually support market development. Partnerships between global Tier-1 suppliers and regional OEM assembly plants continue to introduce radar features on select higher-end vehicle lines.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region holds approximately 3% of the market, characterized by gradual adoption of advanced in-cabin sensing in premium and imported vehicle models. GCC countries drive demand through higher luxury vehicle sales and growing regulatory interest in child safety systems. Radar-based CPD and cabin-health monitoring are increasingly promoted in family and SUV segments. However, limited local automotive manufacturing and high price sensitivity across African markets restrict broad adoption. Ongoing smart mobility initiatives in the UAE and Saudi Arabia encourage radar integration in next-generation EVs and connected vehicles, gradually expanding regional opportunities.
Market Segmentations:
By Application
- Vital Sign Detection
- Driver Monitoring
- Respiratory Rate Measurement
- Heart Rate Measurement
- Child Presence Detection (CPD)
- Seat Occupancy Detection
- Body Pose Monitoring (in-position / off-position)
- Seat Belt Recognition
- Others
By Vehicle Type
- Hatchback
- Sedan
- MPV (Multi-Purpose Vehicle)
- MUV (Multi-Utility Vehicle)
- SUV
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape:
The competitive landscape of the in-cabin monitoring radars market features strong participation from leading Tier-1 suppliers, semiconductor manufacturers, and automotive OEMs developing proprietary radar-based occupant safety platforms. Companies such as Bosch, Continental, Valeo, Aptiv, and Denso dominate integration of mmWave radar modules supporting Child Presence Detection (CPD), vital-sign monitoring, and full-cabin occupancy mapping. Semiconductor leaders including Infineon, NXP, and Texas Instruments strengthen the ecosystem with high-resolution 60 GHz and 79 GHz radar chipsets optimized for micro-motion detection and AI-driven signal processing. Emerging firms such as Vayyar, Arbe Robotics, Smart Radar System, and Xandar Kardian differentiate through ultra-wideband imaging, 4D radar capabilities, and health-monitoring algorithms. Competition intensifies as OEMs shift toward software-defined vehicle architectures, prompting suppliers to deliver scalable radar modules with OTA-upgradable features. Strategic partnerships, NPUs for real-time processing, and radar-AI fusion drive innovation speed, cementing radar as a core technology in next-generation occupant-aware safety systems.
Key Player Analysis:
- Vayyar Imaging Ltd.
- Continental Corporation
- microwave sensors GmbH
- LG Innotek
- Bitsensing, Inc.
- Infineon Technologies
- NOVELIC
- Aptiv
- Texas Instruments
- Smart Radar System Inc.
Recent Developments:
- In September 2024: Vayyar Imaging Ltd. The company laid off dozens of employees as part of a strategic shift to reduce cash burn and refocus on core markets (automotive and smart-home sensing).
- In December 2024, At CES 2025, Continental unveiled a working prototype of its biometric in-cabin monitor (combining radar and display-embedded sensors) that tracks vital health signals of all occupants.
- In January 2023, Vayyar announced a partnership with VinFast to integrate its in-cabin 4D imaging radar into the VF 6 and VF 7 electric SUVs, enabling radar-based Child Presence Detection (CPD) and full-cabin occupancy monitoring.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Report Coverage:
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Application, Vehicle type and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook:
- Radar-based full-cabin awareness will evolve into a standard safety layer across global OEM platforms as regulations expand for CPD and advanced DMS functions.
- Multi-modal sensor fusion combining radar, camera, and infrared inputs will strengthen accuracy in posture detection, micro-motion tracking, and occupant classification.
- mmWave 60/79 GHz radar modules will achieve higher spatial resolution with lower power consumption, improving deployment across compact vehicle interiors.
- AI-driven analytics will enable predictive wellness insights, fatigue forecasting, and adaptive restraint optimization based on real-time physiological data.
- Software-defined vehicle architectures will allow OTA upgrades that unlock new radar-based features without hardware changes.
- EV and premium OEM platforms will increasingly adopt radar for personalized cabin experience, climate zoning, and adaptive comfort functions.
- Cost-optimized radar SoCs will expand penetration into mid-range and entry-level vehicles globally.
- 4D imaging radar will gain traction for multi-occupant mapping and motion differentiation in complex cabin scenarios.
- Global NCAP programs will push higher safety scoring criteria tied to radar-enabled CPD and DMS capabilities.
- Partnerships between semiconductor firms, Tier-1 suppliers, and AI software companies will accelerate the commercialization of next-generation occupant monitoring solutions.

 Market Segmentation Analysis:
Market Segmentation Analysis:

