Market Overview
The global Listeria monocytogenes infections treatment market was valued at USD 4,738.86 million in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 6,948.29 million by 2032, expanding at a CAGR of 4.9% during the forecast period (2025–2032).
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Listeria Monocytogenes Infections Treatment Market Size 2024 |
USD 4,738.86 million |
| Listeria Monocytogenes Infections Treatment Market , CAGR |
4.9% |
| Listeria Monocytogenes Infections Treatment Market Size 2032 |
USD 6,948.29 million |
The Listeria monocytogenes infections treatment market is shaped by the presence of leading pharmaceutical manufacturers that supply first-line and adjunct antimicrobial therapies across global healthcare settings. Companies such as Pfizer Inc., Novartis AG, Merck & Co., GlaxoSmithKline plc, Sanofi, Teva Pharmaceutical Industries, and Baxter International maintain strong market positions through extensive antibiotic portfolios, broad hospital reach, and established distribution networks. North America leads the global market with a share of approximately 38–40%, supported by advanced clinical diagnostics and stringent food safety surveillance systems. Europe follows with 30–32%, driven by robust regulatory frameworks and high diagnostic accuracy across major countries.
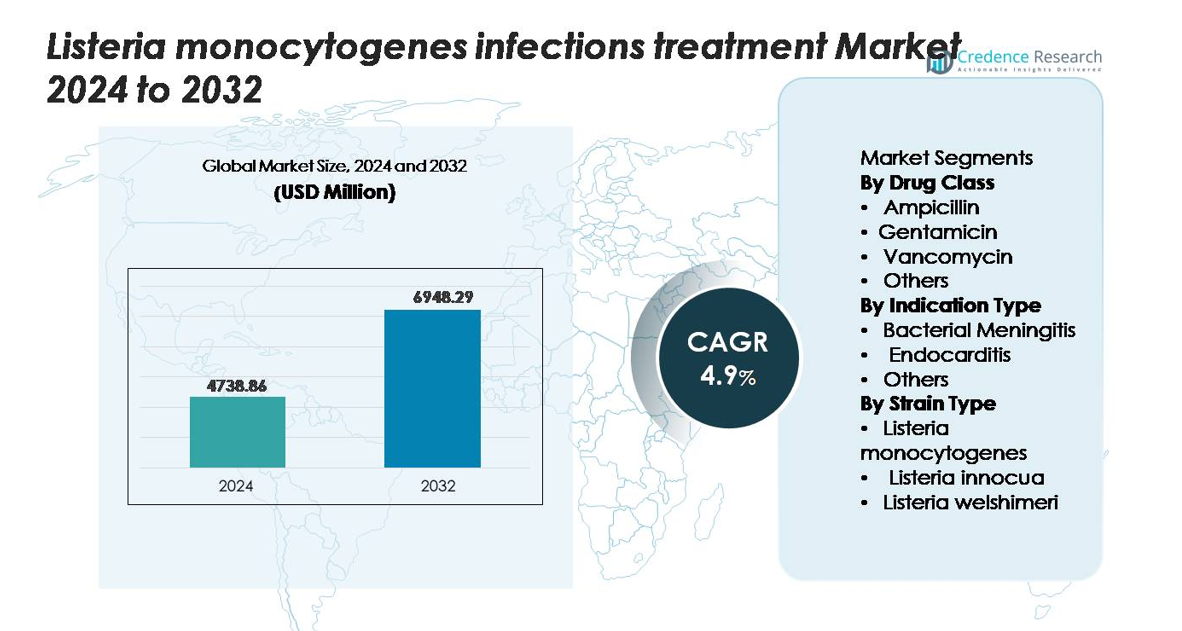
Market Insights
- The global Listeria monocytogenes infections treatment market was valued at USD 4,738.86 million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 6,948.29 million by 2032, registering a CAGR of 4.9% during the forecast period.
- Market growth is driven by rising incidence of foodborne listeriosis, high vulnerability among elderly and immunocompromised patients, and expanding adoption of rapid molecular diagnostics that support early, targeted antimicrobial therapy.
- Key trends include stronger surveillance systems, increasing investment in genomic tracing, and rising adoption of standardized treatment protocols, with Ampicillin remaining the dominant drug class owing to its role as the first-line therapeutic.
- The competitive landscape is shaped by major players such as Pfizer, Novartis, Merck, GSK, and Sanofi, supported by robust antibiotic portfolios and strong presence in hospital and retail pharmacy networks.
- Regionally, North America leads with 38–40%, followed by Europe at 30–32% and Asia-Pacific at 20–22%, while bacterial meningitis remains the largest indication segment globally.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Drug Class
Ampicillin remains the dominant drug class in the Listeria monocytogenes infection treatment market due to its status as the first-line therapy and its strong bactericidal activity against intracellular Listeria species. Its extensive clinical adoption, favorable safety profile, and compatibility with combination regimens drive its leadership. Gentamicin follows as a key adjunct therapy, especially in severe CNS infections, where dual coverage improves treatment outcomes. Vancomycin and other agents serve as alternatives for patients with intolerance or resistance risks. Growing clinical preference for evidence-backed regimens continues to reinforce Ampicillin’s commanding market position.
- For instance, Pfizer manufactures Ampicillin for Injection USP in precise unit doses of 250 mg, 500 mg, 1 g, and 2 g per vial, designed for IV or IM administration, while the company’s labeling documents peak serum concentrations reaching 52 µg/mL following a 2 g IV dose administered over 10 minutes.
By Indication Type
Bacterial meningitis represents the leading indication segment, supported by the high severity of Listeria-related CNS infections and the urgent need for rapid antimicrobial intervention. This segment benefits from established treatment protocols, strong physician awareness, and higher hospitalization rates. Endocarditis forms the second-largest segment due to rising diagnosis accuracy and improved survival rates with combination antimicrobial therapy. Other indications including septicemia and pregnancy-associated listeriosis remain essential but comparatively smaller contributors to market growth. The dominance of bacterial meningitis is reinforced by its clinical complexity, reliance on advanced therapeutics, and consistent demand for prolonged treatment durations.
- For instance, Bristol-Myers Squibb’s Penbritin (Ampicillin) demonstrated effective cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) penetration with measured CSF concentrations reaching 1.2–5.0 µg/mL during meningitis, while Pfizer’s Gentamicin Injection USP achieves peak plasma levels of 5–10 µg/mL when administered at standard dosing intervals values that support synergistic bactericidal activity in severe Listeria meningitis and endocarditis cases.
By Strain Type
Listeria monocytogenes accounts for the largest share of the strain-based segmentation, driven by its role as the primary pathogenic species responsible for the majority of invasive human infections. Its higher virulence, broader environmental presence, and strong association with foodborne outbreaks reinforce its dominance. Listeria innocua and Listeria welshimeri hold secondary positions, largely due to their limited pathogenicity and minimal clinical relevance, though occasional atypical infections contribute to niche demand. As global surveillance improves and food safety regulations tighten, the clinical and therapeutic emphasis on Listeria monocytogenes continues to shape market priorities.
Key Growth Drivers
Rising Incidence of Foodborne Listeriosis and Increasing Vulnerable Populations
The growing global burden of foodborne listeriosis significantly drives the demand for effective treatment options. Listeria poses severe risks to pregnant women, neonates, immunocompromised patients, and the elderly, resulting in higher hospitalization and mortality rates compared to other foodborne pathogens. Increased consumption of ready-to-eat foods, minimally processed products, and refrigerated packaged meals has expanded exposure pathways, making outbreaks more frequent and impactful. Expanding healthcare awareness and improved diagnostic workflows also contribute to a higher detection rate of invasive infections, prompting timely therapeutic intervention. Public health authorities and regulatory agencies are strengthening food safety surveillance programs, leading to quicker identification of contaminated products and improving case reporting. As awareness of the pathogen’s severity rises across medical and food production ecosystems, the need for reliable antimicrobial regimens continues to grow, reinforcing market expansion for first-line therapies and supportive care solutions.
- For instance, bioMérieux’s VIDAS® Listeria monocytogenes II (LMO2) assay delivers automated immunoassay detection. After a required sample enrichment process, which typically takes 25 to 48 hours, the automated assay provides a final result in approximately 70 minutes.
Advancements in Diagnostic Technologies Enabling Faster Clinical Decision-Making
The market benefits substantially from rapid advancements in diagnostic platforms designed to identify Listeria infections in earlier stages. Traditional culture-based identification methods often delay treatment initiation, especially in central nervous system infections where timely intervention is critical. Modern molecular diagnostics, including multiplex PCR assays, next-generation sequencing, and automated microbial identification systems, significantly shorten turnaround times and enhance pathogen detection accuracy. Hospitals widely adopt automated blood culture platforms and rapid antigen testing tools, improving the ability to differentiate Listeria species from other gram-positive rods. Early diagnosis allows clinicians to begin targeted antimicrobial therapy sooner, reducing complications and improving survival outcomes. As more healthcare settings embrace point-of-care diagnostics and integrated laboratory automation, demand for specific therapeutic regimens aligned with rapid detection continues to rise. This technological evolution strengthens the overall treatment pathway and supports broader uptake of standardized clinical protocols.
- For instance, the BioFire® FilmArray® Gastrointestinal Panel by bioMérieux identifies 22 pathogens, none of which is Listeria monocytogenes, with a clinically validated runtime of approximately 60 minutes.
Expansion of Hospital Infrastructure and Strengthening of Critical Care Capabilities
Global improvements in healthcare infrastructure especially in emerging markets are fueling the growth of Listeria monocytogenes infection treatments. Hospitals are expanding intensive care units, enhancing infectious disease departments, and investing in antimicrobial stewardship programs, all of which support more accurate management of severe listeriosis cases. The rising availability of neurologists, cardiologists, and infectious disease specialists further contributes to better clinical outcomes in complex conditions such as meningitis and endocarditis. Improved access to broad-spectrum antibiotics, combination therapies, and continuous monitoring systems enhances patient management, particularly in high-risk groups requiring prolonged inpatient care. Strengthened supply chains and better distribution networks ensure timely availability of essential antibiotics across hospital and retail pharmacies. As developing regions accelerate healthcare modernization, the adoption rate of evidence-based treatment protocols increases, reinforcing the demand for standardized Listeria infection therapies across diverse care settings.
Key Trends & Opportunities
Growing Focus on Antimicrobial Resistance Monitoring and Precision Therapeutics
A major opportunity lies in the global shift toward antimicrobial resistance (AMR) surveillance and precision-based antimicrobial prescribing. Although Listeria monocytogenes currently shows limited resistance to first-line drugs such as ampicillin, emerging research highlights isolated resistance patterns in non-monocytogenes strains and environmental isolates. This encourages healthcare systems to adopt genomic surveillance tools and real-time sequencing programs that support better tracking of resistance evolution. Manufacturers are exploring next-generation antibiotics, novel synergistic combinations, and pathogen-specific inhibitors to strengthen the therapeutic landscape. Opportunities also emerge in diagnostics integrated with antimicrobial susceptibility testing, enabling clinicians to select optimal therapies quickly. This precision-focused approach enhances treatment outcomes, reduces unnecessary antibiotic use, and fosters innovation in targeted drug development. As global AMR programs gain momentum, investment in Listeria-focused research and advanced therapeutics is expected to rise significantly.
- For instance, Illumina’s MiSeq™ system enables whole-genome sequencing of Listeria isolates with read lengths of 2 × 300 base pairs and a demonstrated output of up to 15 gigabases per run, allowing detailed detection of AMR-associated genes such as aac(6′)-I, fosX, and ermC.
Increasing Integration of Food Safety Technologies and Predictive Contamination Modeling
Strengthening food safety systems presents a major opportunity for reducing listeriosis rates and expanding market demand for preventive healthcare solutions. Food manufacturers increasingly adopt predictive modeling software, environmental monitoring sensors, and automated hygiene management platforms to reduce contamination risks across production lines. Cold-chain optimization, temperature-tracking IoT systems, and smart packaging technologies further reduce bacterial survival and improve product safety. Regulatory agencies encourage widespread adoption of hazard analysis models, genomic tracing tools, and centralized outbreak databases. These advancements enhance early detection and minimize large-scale recalls. As predictive technologies become standard in high-risk food categories such as dairy, meat, seafood, and ready-to-eat products the industry relies more heavily on robust clinical protocols and improved surveillance systems. This ecosystem creates new opportunities for diagnostic companies, infection monitoring platforms, and advanced therapeutic developers to integrate with food safety networks and strengthen preventive strategies.
- For instance, Neogen Corporation’s Listeria Right Now™ system applies loop-mediated isothermal amplification to detect Listeria species in environmental samples. The workflow does not need an enrichment step and produces results in under an hour. This approach supports rapid sanitation checks in food and processing sites.
Key Challenges
Limited Treatment Options and Dependence on Narrow-Spectrum Antibiotics
The Listeria treatment landscape faces constraints due to its heavy reliance on a small number of effective antibiotics, primarily ampicillin and gentamicin. The limited diversity of clinically proven therapies raises concerns about potential emergence of resistance and reduces the flexibility of treatment protocols in patients with allergies or contraindications. Alternative agents such as trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole or vancomycin are used selectively but lack the same evidence strength for severe invasive infections. The absence of dedicated Listeria-targeted drug development pipelines further intensifies the challenge. Pharmaceutical investment remains low due to the pathogen’s relatively narrow patient population compared to broader infectious diseases. This restricted therapeutic arsenal places pressure on clinicians and healthcare systems to maintain strict diagnostic accuracy, stewardship practices, and surveillance efforts to prevent resistance development and preserve treatment efficacy.
Challenges in Early Detection Due to Nonspecific Symptoms and Slow Culture Growth
Early diagnosis of listeriosis remains difficult because initial clinical symptoms such as fever, fatigue, or gastrointestinal distress closely resemble those of many other infections. This nonspecific presentation often delays clinical suspicion and prolongs the time before confirmatory testing is performed. Traditional culture-based detection methods require extended incubation periods, slowing clinical decision-making in severe cases like meningitis or septicemia. Although molecular diagnostics offer faster results, their availability is inconsistent across low-resource settings due to cost and infrastructure constraints. These diagnostic hurdles lead to delayed treatment initiation, increasing complications and mortality risk. Inadequate surveillance capacity further limits timely outbreak response. Addressing these challenges requires broader adoption of rapid diagnostic technologies, better training for clinicians, and enhanced laboratory infrastructure to ensure early and accurate identification of Listeria infections across diverse healthcare environments.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America holds the largest market share of approximately 38–40%, driven by strong clinical awareness, advanced diagnostic infrastructure, and stringent food safety regulations. The U.S. leads due to high testing volumes, robust hospital capacity, and frequent monitoring of ready-to-eat food products. CDC-led surveillance and rapid recall mechanisms support early identification of outbreaks, increasing demand for standardized antimicrobial therapies. High prevalence among elderly and immunocompromised populations, combined with broad access to first-line antibiotics, sustains the region’s dominant position. Canada contributes through strong laboratory networks and consistent investment in foodborne pathogen prevention programs.
Europe
Europe accounts for 30–32% of the global market, supported by comprehensive EU-wide surveillance systems and rigorous food safety protocols. Countries such as Germany, France, and the U.K. generate substantial therapeutic demand due to consistent reporting of invasive listeriosis and advanced laboratory capabilities. EFSA-led molecular tracing and outbreak investigation initiatives enhance clinical responsiveness, strengthening treatment uptake. The region’s aging population and high consumption of chilled and ready-to-eat foods elevate infection risks. Strong healthcare infrastructure, widespread diagnostic access, and harmonized clinical guidelines collectively reinforce Europe’s position as the second-largest regional market.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific holds 20–22% of the global market, emerging as the fastest-growing region due to rapid improvements in diagnostic capacity, rising foodborne infection awareness, and expanding healthcare access. China, Japan, South Korea, and Australia lead regional demand as they modernize food processing systems and strengthen cold-chain compliance. Increased consumption of packaged foods and growing recognition of listeriosis in high-risk populations drive market expansion. Government-led disease surveillance programs and investments in hospital infrastructure support higher treatment adoption. Although the market share trails behind North America and Europe, Asia-Pacific’s accelerating laboratory modernization positions it for strong long-term growth.
Latin America
Latin America represents 6–7% of the market, supported by improving food safety regulations, increased monitoring of dairy and meat processing facilities, and rising clinical recognition of listeriosis. Brazil, Mexico, and Argentina lead due to expanding hospital networks and better access to diagnostic services. Growth is moderated by inconsistent testing capabilities and varying regulatory enforcement across countries. Nevertheless, increasing investment in public health laboratories and adoption of international food safety standards are improving case detection. As private healthcare providers expand infectious disease management services, the region gradually strengthens its contribution to treatment demand.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region accounts for 3–4% of the global market, limited by low diagnostic penetration and restricted clinical awareness in several countries. GCC nations contribute the largest share within the region due to stronger hospital infrastructure, higher importation of processed foods, and growing implementation of food safety frameworks. South Africa leads sub-Saharan demand with more developed surveillance systems and broader access to first-line therapies. While the region remains small in overall market contribution, ongoing healthcare modernization, improved laboratory networks, and rising foodborne disease monitoring support gradual market expansion.
Market Segmentations:
By Drug Class
- Ampicillin
- Gentamicin
- Vancomycin
- Others
By Indication Type
- Bacterial Meningitis
- Endocarditis
- Others
By Strain Type
- Listeria monocytogenes
- Listeria innocua
- Listeria welshimeri
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape of the Listeria monocytogenes infections treatment market is characterized by the strong presence of multinational pharmaceutical companies that supply essential antimicrobial therapies used as first-line and adjunct treatments. Leading players such as Pfizer Inc., Merck & Co., Novartis AG, Sanofi, Teva Pharmaceutical Industries, Baxter International, and GlaxoSmithKline plc maintain a dominant position through extensive antibiotic portfolios, established global distribution networks, and consistent supply to hospital and retail pharmacy channels. These companies focus on ensuring availability of critical agents like ampicillin, gentamicin, and alternative broad-spectrum antibiotics used in severe or resistant cases. Ongoing investments in infectious disease research, improved manufacturing capacity, and compliance with stringent regulatory standards further reinforce their market strength. Collaboration with public health agencies and participation in antimicrobial stewardship initiatives enhance clinical trust and adoption. While competition remains stable, emphasis on rapid diagnostics, treatment optimization, and monitoring of emerging resistance patterns continues to shape competitive differentiation.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
- Pfizer Inc.
- GSK plc
- Abbott Laboratories
- AstraZeneca
- Hikma Pharmaceuticals
- Aurobindo Pharma
- Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd.
- Sandoz (formerly Novartis division)
- Cipla Ltd.
- Lupin Limited
Recent Developments
- In September 2024, the United States Food and Drug Administration and the United States Department of Agriculture have granted GRAS (Generally Recognized as Safe) status to INNEO, Innodal biotechnology flagship product, a food processing aid made to eliminate Listeria monocytogenes.
- In August 2024, Sun Pharmaceutical launched a novel antibiotic (tedizolid phosphate, brand name “STARIZO”) in India for acute bacterial skin and skin-structure infections.
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Drug class, Indication type, Strain type and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- The market will continue expanding as global foodborne infection rates rise and vulnerable populations increase.
- Adoption of rapid molecular diagnostics will accelerate early detection and improve treatment outcomes.
- Hospitals will rely more on standardized antimicrobial protocols to manage severe CNS and bloodstream infections.
- Advancements in genomic surveillance will strengthen outbreak tracing and resistance monitoring.
- Pharmaceutical companies will expand production of essential antibiotics to ensure stable supply chains.
- Integration of food safety analytics and predictive contamination models will reduce outbreak severity and drive preventive care demand.
- Emerging markets will see faster growth due to improved healthcare infrastructure and laboratory modernization.
- Treatment optimization will focus on combination therapies for high-risk patients with severe complications.
- Increased regulatory scrutiny will enhance clinical compliance and elevate treatment quality across regions.
- Continued investment in infectious disease preparedness will reinforce market stability and long-term demand.




