Market Overview
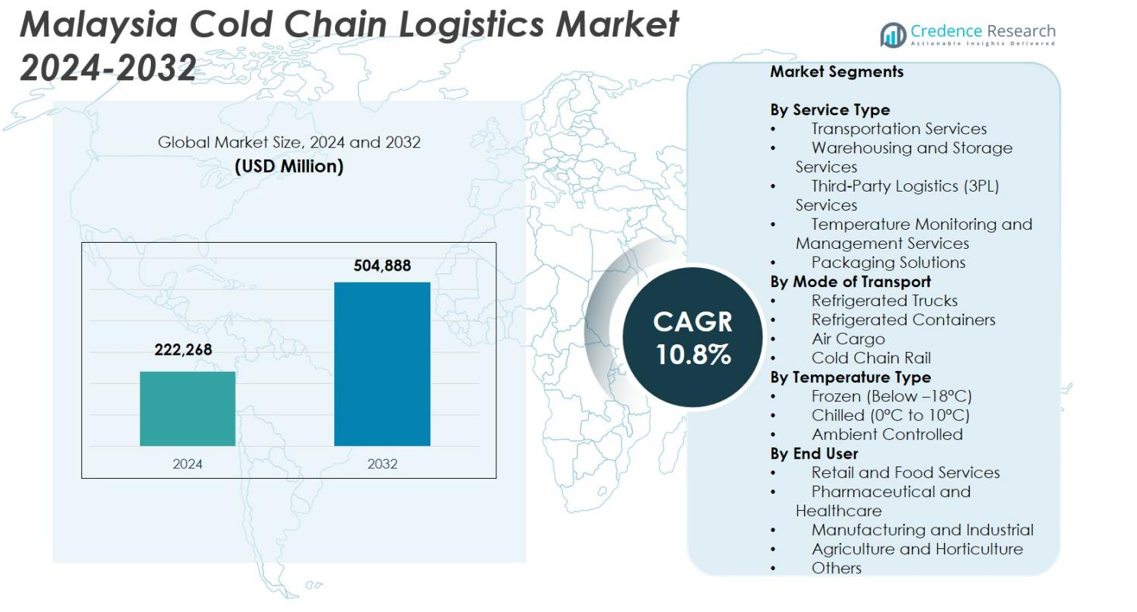
Malaysia Cold Chain Logistics Market size was valued at USD 222,268 million in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 504,888 million by 2032, expanding at a CAGR of 10.8% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Malaysia Cold Chain Logistics Market Size 2024 |
USD 222,268 million |
| Malaysia Cold Chain Logistics Market, CAGR |
10.8% |
| Malaysia Cold Chain Logistics Market Size 2032 |
USD 504,888 million |
Malaysia Cold Chain Logistics Market is shaped by a group of established service providers offering advanced temperature-controlled storage, transportation, and monitoring capabilities. Key players such as Cold Room Malaysia (CRM Logistics Solutions), Tiong Nam Logistics Holdings, SK Cold Chain Solutions, KGW Logistics (Malaysia), Integrated Cold Chain Logistics (ICCL), Frio Logistics, IGLO Malaysia Sdn Bhd, NL Cold Chain Network, PKT Logistics Group Sdn Bhd, and TASCO Cold Chain continue to expand their operational footprints through new cold warehouses, IoT-enabled fleets, and 3PL partnerships. Regionally, the Central Region leads the market with 41.6% share, driven by strong infrastructure, dense industrial activity, and proximity to major ports, positioning it as Malaysia’s primary hub for cold chain operations.
Market Insights
- The Malaysia Cold Chain Logistics Market was valued at USD 222,268 million in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 504,888 million by 2032, expanding at a CAGR of 10.8%.
- Rising demand for frozen and chilled food, pharmaceutical distribution, and e-commerce grocery delivery continues to drive strong adoption of transportation services, which dominated the market with 46.2% share in 2024.
- Key trends include rapid investments in automated cold rooms, IoT-based fleet monitoring, halal-compliant cold handling, and multimodal refrigerated transport supporting efficiency and regulatory compliance.
- Major players such as Cold Room Malaysia, Tiong Nam Logistics Holdings, SK Cold Chain Solutions, KGW Logistics, ICCL, Frio Logistics, and others are expanding infrastructure and service capabilities to strengthen their market position.
- Regionally, the Central Region led with 41.6% share, followed by the Northern Region at 22.4%, Southern Region at 19.3%, and East Malaysia at 16.7%, reflecting varying industrial bases and logistics capacities across the country.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Segmentation Analysis
By Service Type
The Malaysia Cold Chain Logistics Market is dominated by transportation services, accounting for 42.6% of the total market share in 2024, driven by rising demand for efficient last-mile refrigerated delivery across food, pharmaceutical, and e-commerce sectors. The segment benefits from increasing investments in fleet expansion, GPS-enabled refrigerated trucks, and compliance with food safety regulations. Warehousing and storage services are also growing steadily as businesses require large-scale temperature-controlled facilities to manage surging frozen imports. Third-party logistics providers increasingly support integrated cold chain solutions, while temperature monitoring and packaging solutions expand due to stricter quality and traceability standards.
- For instance , DHL Supply Chain Malaysia expanded its temperature-controlled fleet by adding new multi-compartment refrigerated trucks equipped with real-time telematics to improve pharma-grade delivery accuracy.
By Mode of Transport
Refrigerated trucks lead this category with a 55.3% share in 2024, reflecting their essential role in short-haul and intercity distribution of perishable goods across Malaysia’s well-developed road infrastructure. Their dominance is boosted by rapid growth in hypermarkets, online grocery delivery, and pharmaceutical distribution, which require flexible and frequent shipments. Refrigerated containers follow, supported by Malaysia’s thriving seafood export sector, while air cargo expands due to rising vaccine and biopharma shipments. Cold chain rail transport remains minimal but shows long-term potential as Malaysia explores rail-based logistics modernization.
- For instance , DHL opened a “dual-certified” cold-chain facility at its airport-free-zone hub in Kuala Lumpur offering both 15–25 °C and 2–8 °C storage. This enables them to handle a mix of ambient-sensitive and chilled/frozen pharma cargos.
By Temperature Type
The frozen segment holds the largest share at 48.9% in 2024, supported by strong demand for frozen meat, seafood, ready-to-eat meals, and rising consumer preference for long-shelf-life products. Increased imports of frozen foods and expanding quick-service restaurant chains intensify the need for deep-freeze logistics. The chilled segment also grows rapidly with its critical role in dairy, fresh produce, bakery items, and pharmaceuticals, requiring tight temperature control between 0°C and 10°C. Ambient-controlled logistics supports specialty goods and temperature-sensitive packaged foods, driven by enhanced supply-chain automation and monitoring technologies.
Key Growth Drivers
Expansion of the Food, Beverage, and Frozen Processed Goods Sector
The rapid growth of Malaysia’s food and beverage sector, especially frozen and processed food categories, acts as a major catalyst for cold chain logistics expansion. Increasing consumer inclination toward ready-to-cook and frozen meals, driven by urbanization and rising dual-income households, elevates the demand for reliable temperature-controlled logistics. The surge in imports of frozen meat, seafood, and dairy products further strengthens this need. Quick-service restaurant chains, supermarket expansions, and the growth of online grocery platforms require frequent short-haul distribution supported by advanced refrigerated transportation systems. Food safety regulations and Halal certification standards also push companies to maintain strict cold chain integrity, boosting investments in cold rooms, deep-freeze warehouses, and advanced reefer trucks. As Malaysia integrates more global food supply chains, cold chain capacity becomes essential for quality preservation and expanding export competitiveness.
- For instance , Nestlé Malaysia expanded its frozen food portfolio under the Harvest Gourmet and Nestlé Professional lines, prompting upgrades to its cold storage and handling processes to maintain strict temperature integrity.
Strong Growth of the Pharmaceutical and Healthcare Supply Chain
Malaysia’s pharmaceutical and healthcare sector significantly drives cold chain logistics adoption, especially with the rise of temperature-sensitive biologics, vaccines, biosimilars, and specialty drugs. The increasing prevalence of chronic diseases and rising healthcare spending require dependable cold chain pathways to maintain drug efficacy and meet Good Distribution Practice (GDP) standards. Malaysia’s expanding biopharmaceutical manufacturing base and clinical trial activities also intensify the need for highly regulated storage and transport solutions. Additionally, the post-pandemic environment has heightened awareness regarding temperature compliance, traceability, and quality assurance in medicine distribution. Investments in specialized cold chain facilities, insulated packaging, IoT-enabled refrigeration systems, and real-time monitoring platforms continue to accelerate. As healthcare delivery models shift toward home-based care and digital health services, demand for efficient and scalable last-mile cold chain infrastructure grows rapidly.
- For instance , Pharmaniaga enhanced its central warehouse capabilities with upgraded cold rooms and validated temperature-controlled storage to support national immunization and specialty drug distribution.
Rising E-commerce Penetration and Modern Retail Expansion
Malaysia’s fast-growing e-commerce landscape significantly accelerates demand for cold chain logistics, especially within online grocery, meal-kit delivery, and fresh produce segments. Consumers increasingly prefer doorstep delivery of frozen foods, dairy products, seafood, and ready-to-eat meals, requiring companies to enhance last-mile temperature-controlled capabilities. Major retail chains and hypermarkets are expanding omni-channel operations, which depend heavily on cold rooms, refrigerated trucks, and automated sorting systems to ensure product freshness. Government-led digitalization initiatives and investments in smart logistics infrastructure further support this growth. Cloud-based cold chain management systems, real-time temperature tracking, and predictive analytics enhance operational efficiency and reduce spoilage. As consumer expectations for delivery speed and freshness rise, logistics providers continue to invest in multi-compartment reefer vehicles, micro-fulfillment centers, and optimized urban distribution hubs, driving strong and sustained market expansion.
Key Trends & Opportunities
Adoption of Advanced Monitoring, Automation, and IoT Technologies
Technological transformation is reshaping Malaysia’s cold chain logistics landscape, creating major opportunities for innovation and performance improvement. IoT-enabled sensors, telematics, RFID tags, and GPS-integrated reefer systems allow real-time visibility over temperature, humidity, and equipment performance, significantly reducing risks of spoilage. Automation in cold storage facilities such as robotic palletizers, automated retrieval systems, and AI-driven demand forecasting enhances throughput and minimizes operational errors. Predictive maintenance and digital twin models further optimize fleet reliability and energy use. As businesses seek greater supply chain transparency and compliance, demand for integrated cold chain software platforms grows rapidly. This trend opens avenues for technology vendors, logistics providers, and data analytics companies to introduce advanced digital solutions tailored to food, pharmaceutical, and retail applications. Widespread adoption of such technologies improves traceability, reduces operational costs, and elevates service quality, creating strong opportunities for market differentiation.
- For instance , Tiong Nam Logistics enhanced its temperature-controlled fleet by integrating GPS telematics and real-time reefer monitoring solutions to improve shipment traceability and reduce cold-chain breaches.
Expansion of Regional Trade and Growth of Halal-certified Cold Chain Capabilities
Malaysia’s position as a regional logistics hub and leading Halal food producer presents substantial opportunities in cold chain development. Growing exports of Halal-certified frozen foods, seafood, and processed goods require high-quality cold chain systems that comply with stringent global standards. The government’s commitment to strengthening Malaysia’s Halal ecosystem, including certification enhancements and infrastructure investments, further boosts demand for specialized cold chain facilities. In addition, Malaysia’s integration into ASEAN trade networks and rising cross-border e-commerce widen the scope for regional cold chain services. Ports such as Port Klang and Tanjung Pelepas are expanding reefer container capacity, supporting both imports and exports. Foreign investment in cold storage and refrigerated transportation also increases as multinational companies leverage Malaysia as a strategic distribution hub. Collectively, these developments create robust opportunities for logistics players to expand capacity, upgrade technology, and capture growing regional trade flows.
- For instance , the Halal Development Corporation (HDC) advanced its Halal Integrated Platform (HIP) to digitalize certification processes and strengthen compliance monitoring across Halal supply chains.breaches.
Key Challenges
High Capital Investment and Rising Operating Costs
Cold chain logistics operations in Malaysia face significant challenges due to high capital and operational expenses. Establishing and maintaining temperature-controlled warehouses, deep-freeze facilities, and refrigerated truck fleets require substantial upfront investment, limiting participation for small and mid-sized logistics providers. Persistent increases in electricity tariffs, fuel prices, and cooling-system maintenance further elevate operating costs. Many older facilities also lack energy-efficient technologies, resulting in higher wastage and reduced profitability. Additionally, investment cycles for upgrading equipment, adopting digital monitoring tools, and ensuring regulatory compliance place continuous financial pressure on companies. These cost burdens hinder scalability and can create disparities in service quality across the industry, making cost optimization and energy efficiency critical strategic priorities.
Infrastructure Gaps, Skills Shortages, and Temperature Compliance Risks
Although Malaysia’s logistics ecosystem is well-developed, cold chain infrastructure still faces gaps, particularly in rural areas and East Malaysia, where accessibility and distribution networks remain limited. Inconsistent road quality, limited cold storage capacity, and insufficient reefer transport availability can disrupt temperature integrity. The industry also faces a shortage of skilled professionals trained in cold chain handling, temperature monitoring, and pharmaceutical-grade logistics. Human errors in handling, loading, or monitoring conditions significantly increase risks of spoilage and compliance violations. Moreover, extreme weather conditions, equipment malfunctions, and inadequate contingency planning may compromise temperature-sensitive goods. These challenges make workforce development, infrastructure expansion, and stricter process standardization essential to safeguarding product quality and reducing operational disruptions.
Regional Analysis
Central Region
The Central Region held the dominant position with 41.6% market share in 2024, driven by its concentration of manufacturing hubs, major retail chains, pharmaceutical distributors, and advanced logistics infrastructure. Selangor’s extensive network of cold warehouses, proximity to Port Klang, and strong presence of 3PL operators reinforce its leadership in temperature-controlled distribution. Rapid growth in e-commerce grocery delivery and rising demand for high-quality cold storage among food processors also fuel expansion. Continuous investments in automated cold rooms, IoT-enabled fleet monitoring, and compliance-driven pharmaceutical logistics further strengthen the region’s strategic role as Malaysia’s cold chain backbone.
Northern Region
The Northern Region captured 22.4% market share, supported by Penang’s strong electronics, pharmaceutical, and food-processing sectors that rely heavily on temperature-controlled logistics. The region benefits from robust export activity via Port of Penang and an expanding ecosystem of refrigerated warehouses serving seafood, poultry, and high-value perishables. Growth in industrial parks, increasing pharmaceutical contract manufacturing, and the rise of fresh grocery distribution networks are strengthening demand for reliable cold chain services. Investments in cross-border logistics with Thailand and improved last-mile delivery capabilities continue to accelerate adoption of advanced temperature monitoring and efficient refrigerated transportation.
Southern Region
The Southern Region accounted for 19.3% market share, driven by Johor’s growing industrial base, proximity to Singapore, and expanding agrifood production clusters. Demand for frozen and chilled logistics is rising rapidly due to seafood processing, poultry exports, and expanding FMCG distribution centers. Cross-border trade with Singapore boosts the need for high-precision refrigerated trucking and real-time temperature validation. Infrastructure modernization, including new cold warehouses and enhanced port connectivity in Johor, is attracting 3PL service providers. Increasing investments in halal cold chain certification and fresh produce distribution hubs further strengthen the region’s cold chain capabilities.
East Malaysia
East Malaysia held 16.7% market share, supported by the region’s seafood, livestock, and tropical fruit industries, which require efficient cold chain networks to maintain product integrity. Although infrastructure is comparatively less developed, rising demand for frozen foods, growing retail expansion, and greater pharmaceutical distribution activity drive steady market growth. Investments in modern cold rooms, improved port-based refrigerated handling, and enhanced inter-island logistics capabilities are reducing supply chain gaps. Government initiatives to strengthen rural cold chain infrastructure and support agriculture exports are further encouraging adoption of temperature-controlled transportation and storage solutions in Sabah and Sarawak.
Market Segmentations
By Service Type
- Transportation Services
- Warehousing and Storage Services
- Third-Party Logistics (3PL) Services
- Temperature Monitoring and Management Services
- Packaging Solutions
By Mode of Transport
- Refrigerated Trucks
- Refrigerated Containers
- Air Cargo
- Cold Chain Rail
By Temperature Type
- Frozen (Below –18°C)
- Chilled (0°C to 10°C)
- Ambient Controlled
By End User
- Retail and Food Services
- Pharmaceutical and Healthcare
- Manufacturing and Industrial
- Agriculture and Horticulture
- Others
By Geography
- Central Region
- Northern Region
- Southern Region
- East Malaysia
Competitive Landscape
The Malaysia Cold Chain Logistics Market features a diverse and expanding competitive landscape, driven by rising demand for temperature-controlled storage, transportation, and value-added services across food, pharmaceuticals, retail, and e-commerce sectors. Key players including Cold Room Malaysia (CRM Logistics Solutions), Tiong Nam Logistics Holdings, SK Cold Chain Solutions, KGW Logistics (Malaysia), Integrated Cold Chain Logistics (ICCL), Frio Logistics, IGLO Malaysia Sdn Bhd, NL Cold Chain Network, PKT Logistics Group Sdn Bhd, and TASCO Cold Chain are strengthening their market presence through capacity expansions, automation, and digital monitoring technologies. Many companies are investing in advanced cold rooms, multi-temperature distribution centers, and IoT-enabled fleet tracking systems to enhance efficiency and regulatory compliance. Strategic partnerships with manufacturers, retailers, and pharmaceutical firms are supporting integrated supply chain solutions, while increased focus on halal-certified cold chain handling creates new differentiation opportunities. Continuous innovation, sustainability initiatives, and service diversification are shaping competitive dynamics across Malaysia’s rapidly evolving cold chain ecosystem.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
- TASCO Cold Chain
- IGLO Malaysia Sdn Bhd
- NL Cold Chain Network
- Tiong Nam Logistics Holdings
- SK Cold Chain Solutions
- Integrated Cold Chain Logistics (ICCL)
- Frio Logistics
- KGW Logistics (Malaysia)
- PKT Logistics Group Sdn Bhd
- Cold Room Malaysia (CRM Logistics Solutions)
Recent Developments
- In September 2025, Nichirei Corporation signed a share purchase agreement to acquire ICCL Group a cold-chain logistics operator in Malaysia
- In August 2025, DHL Global Forwarding opened Malaysia’s first dual-certified pharma cold chain facility at Kuala Lumpur International Airport (KLIA).
- In January 2025, YCH Group entered into a strategic partnership with Sime Darby Property Berhad to explore industrial and logistics infrastructure development in Malaysia with potential cold-chain implications
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Service Type, Mode of Transport, Temperature Type, End-User and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- The market will experience strong expansion driven by rising demand for frozen, chilled, and temperature-sensitive products across industries.
- Adoption of IoT-enabled monitoring systems will accelerate to improve visibility, compliance, and real-time temperature control.
- Investments in automated cold storage facilities and multi-temperature warehouses will increase nationwide.
- Growth in pharmaceutical manufacturing and vaccine distribution will elevate the need for precision cold chain services.
- E-commerce grocery and fresh food delivery will significantly boost last-mile refrigerated transport demand.
- Multimodal cold chain networks, including road–sea–air integration, will strengthen operational efficiency.
- Halal-certified cold chain solutions will gain prominence as Malaysia expands its export footprint.
- Renewable and energy-efficient refrigeration technologies will see higher adoption to reduce operating costs.
- Partnerships between 3PL providers and food, retail, and pharmaceutical companies will deepen to support integrated logistics.
- Regional infrastructure upgrades will reduce logistics gaps, enhancing capacity in East Malaysia and cross-border hubs.




