Market Overview
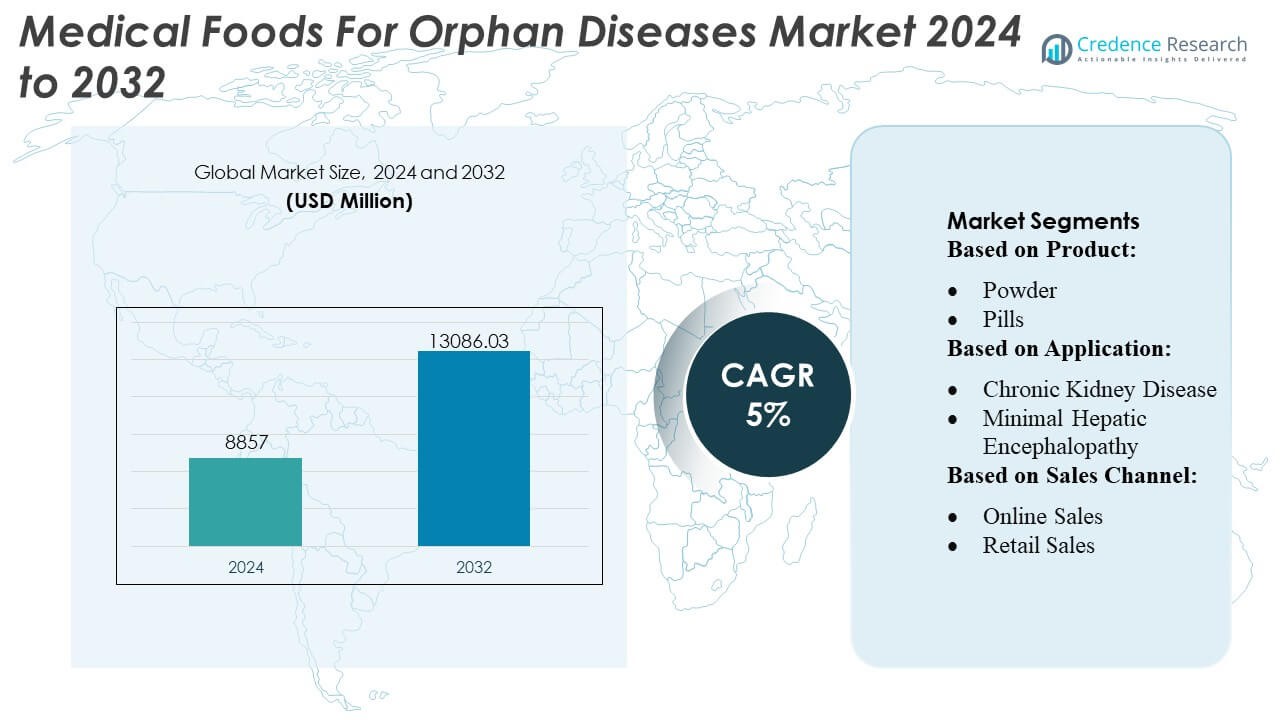
Medical Foods For Orphan Diseases Market size was valued USD 8857 million in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 13086.03 million by 2032, at a CAGR of 5% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Medical Foods For Orphan Diseases Market Size 2024 |
USD 8857 Million |
| Medical Foods For Orphan Diseases Market, CAGR |
5% |
| Medical Foods For Orphan Diseases Market Size 2032 |
USD 13086.03 Million |
The Medical Foods for Orphan Diseases Market features a mix of global nutrition specialists, metabolic therapy innovators, and clinical nutrition manufacturers that compete through targeted formulations, advanced amino-acid blends, and condition-specific products designed for rare metabolic and genetic disorders. Companies strengthen their positions by expanding clinical partnerships, enhancing R&D pipelines, and improving distribution through specialty pharmacies and hospital networks. The market demonstrates strong geographic concentration, with North America leading the industry at an exact 38% share, supported by a well-established rare-disease treatment framework, high diagnostic rates, and broad reimbursement access for specialized medical nutrition.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Insights
- The Medical Foods for Orphan Diseases Market was valued at USD 8,857 million in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 13,086.03 million by 2032, registering a 5% CAGR during the forecast period.
- Strong market drivers include rising diagnosis of rare metabolic disorders and increasing adoption of specialized amino-acid blends and disease-specific formulations, particularly for phenylketonuria and urea cycle disorders, which represent the dominant segment share.
- Key trends include accelerated R&D investment, expansion of clinical validation programs, and broader integration of medical foods into multidisciplinary rare-disease treatment pathways.
- Competitive activity intensifies as global nutrition companies enhance hospital-based distribution, secure partnerships with metabolic clinics, and strengthen specialty-pharmacy channels; however, restraints include stringent regulatory requirements and high formulation development costs.
- Regionally, North America accounts for a 38% market share, supported by strong reimbursement and advanced diagnostic capabilities, while Europe and Asia-Pacific expand through improved newborn screening and growing access to metabolic-care infrastructure.
 Market Segmentation Analysis:
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Product
The powder segment dominates the Medical Foods for Orphan Diseases Market with an estimated 38–40% share, driven by its flexibility in dosing, ease of formulation, and high suitability for metabolic disorders requiring precise nutrient control. Powder-based medical foods support stable amino acid composition, extended shelf life, and improved compliance among pediatric and adult patients with conditions such as PKU, MSUD, or homocystinuria. Pills and liquids gain traction for elderly and dysphagia-prone patients, while the “other” category—gels, bars, and modular supplements—expands gradually as manufacturers introduce condition-specific nutrient blends.
- For instance, Haldor Topsoe A/S reported an h-index of 173, reflecting its scientific leadership in catalysis, and invested nearly DKK 700 million in R&D during 2023 to advance its heterogeneous catalyst technologies.
By Application
Phenylketonuria (PKU) remains the leading application segment, accounting for roughly 24–26% market share, supported by the longstanding clinical necessity for phenylalanine-restricted therapeutic nutrition across all age groups. Rising diagnostic rates, expanded newborn screening programs, and continuous development of improved amino-acid–based formulations reinforce segment leadership. Other high-growth applications include MSUD, homocystinuria, tyrosinemia, and eosinophilic esophagitis, driven by increasing recognition of rare metabolic and immunological disorders. Broader use cases—such as chronic diarrhea, chemotherapy-induced gastrointestinal conditions, cachexia, and wound healing—support diversification of medical foods into supportive and adjunctive therapeutic pathways.
- For instance, Clariant Catalysts’ digital service portal, CLARITY, has been adopted at more than 80 plants worldwide, serving over 380 active users in 28 countries (as of December 2023).
By Sales Channel
Institutional sales lead the market with an estimated 42–44% share, driven by strong procurement volumes from hospitals, specialty clinics, metabolic disorder centers, and long-term care facilities. Clinicians prescribe condition-specific medical foods that require strict nutritional oversight, making institutional channels critical for complex orphan disease management. Retail sales maintain consistent adoption through pharmacies and specialty stores, particularly for chronic metabolic and digestive disorders. Online sales accelerate rapidly as manufacturers expand e-commerce platforms and subscription-based delivery models, improving accessibility for patients requiring continuous nutritional therapy across remote or underserved locations.
Key Growth Drivers
1. Rising Prevalence and Early Diagnosis of Rare Metabolic Disorders
Expanding newborn screening programs and heightened clinical awareness significantly accelerate the diagnosis of orphan metabolic disorders such as PKU, MSUD, and homocystinuria. Earlier detection increases lifetime therapeutic nutrition requirements, strengthening demand for condition-specific medical foods. Healthcare systems increasingly mandate metabolic screening panels, expanding the treated patient base. As precision nutrition becomes integral to managing enzyme deficiencies and amino-acid imbalances, clinicians rely more heavily on tailored medical food formulations, driving sustained adoption across paediatric and adult cohorts.
- For instance, Arkema SA reports that its Siliporite® molecular sieves now offer a service life of 4–5 years when used in highdemand petrochemical separation applications, supporting prolonged catalyst stability.
2. Advancements in Specialized Therapeutic Nutrition Formulations
Continuous innovation in amino-acid–based blends, low-protein food matrices, and hypoallergenic compositions fuels market growth by improving patient outcomes and long-term adherence. Manufacturers enhance palatability, micronutrient stability, and metabolic accuracy, enabling better management of chronic metabolic and immunological disorders. Novel modular nutrition systems allow clinicians to customize therapy by adjusting protein equivalents, caloric density, and micronutrient profiles. These advancements expand therapeutic applicability, support complex care pathways, and position medical foods as an essential component of integrated orphan disease treatment strategies.
- For instance, UOP LLC (Honeywell) recently launched its MTO-600 catalyst formulation, which achieves “up to 10% lower coke yield” and “at least 1% improved methanol consumption” compared to its previous MTO-100 version.
3. Increasing Clinical Integration Across Hospitals and Specialty Centers
Hospitals, metabolic clinics, and rare-disease care networks increasingly incorporate medical foods into standardized treatment protocols, reinforcing clinical legitimacy and expanding adoption. Institutional nutrition teams collaborate with metabolic specialists to design individualized dietary prescriptions for rare genetic, gastrointestinal, and neurological disorders. Reimbursement improvements in select regions further support structured nutritional therapy within healthcare settings. The shift toward multidisciplinary rare-disease management—combining clinical nutrition, pharmacotherapy, and genetic counseling—strengthens reliance on medically supervised food products across both acute and long-term care environments.
Key Trends & Opportunities
1. Expansion of Personalized Nutrition and Precision-Dosing Solutions
The market experiences a strong shift toward personalized nutrition driven by digital tools, metabolic monitoring, and genotype-guided dietary planning. Precision-dosing features—such as portion-controlled powders, individualized amino-acid ratios, and modular nutrient packs—offer opportunities for tailored therapy aligned with patient-specific metabolic thresholds. Manufacturers investing in data-driven platforms and home-based monitoring solutions gain a competitive edge, as clinicians increasingly prioritize nutrition plans synchronized with metabolic markers, growth metrics, and disease-progression profiles.
- For instance, Nebula® bulk metal catalyst—commercialised more than ten years ago—has been deployed across over 60 refineries with more than 130 unit cycles, according to the company’s 2016 announcement.
2. Growing Role of E-Commerce and Direct-to-Patient Distribution Models
Online subscription services and specialized digital pharmacies create new opportunities to reach patients who require consistent access to condition-specific nutritional products. E-commerce platforms reduce supply interruptions, support automated refill cycles, and offer rapid delivery across underserved regions. This shift enhances convenience, especially for patients managing lifelong metabolic restrictions. Manufacturers leveraging omni-channel strategies—combining hospital-based distribution with direct-to-patient fulfillment—can expand market reach, strengthen brand loyalty, and serve geographically dispersed patient populations.
- For instance, Verdium recycled metal saves over 30 metric tons of CO₂ compared to using primary mined metal, representing a carbon footprint reduction of up to 97%.
3. Development of Palatable Low-Protein and Allergen-Controlled Food Categories
Emerging product lines—such as improved low-protein bakery items, ready-to-use meal replacements, and allergen-free formulations—create substantial growth opportunities. These innovations address long-standing compliance issues by offering better taste profiles, diversified textures, and broader culinary options for patients with chronic dietary restrictions. Companies developing sensory-enhanced low-protein staples, fortified beverages, and hypoallergenic blends can capture new demand, particularly among adolescents and adults seeking improved dietary quality and variety within strict medical guidelines.
Key Challenges
1. High Cost and Limited Reimbursement Coverage Across Regions
Medical foods often face inconsistent reimbursement frameworks, limiting patient affordability and long-term therapy adherence. Coverage disparities between regions and payers force many families to bear significant out-of-pocket expenses for lifelong dietary management. The high production cost of specialized formulations—requiring controlled amino-acid synthesis and stringent quality standards—further widens access gaps. These financial constraints challenge market expansion, especially in low- and middle-income markets where rare-disease support mechanisms remain underdeveloped.
2. Restricted Availability and Supply Chain Limitations
The market encounters recurring shortages due to limited manufacturing capacity, dependency on specialized raw materials, and strict regulatory requirements governing production. Many countries lack localized manufacturing, relying heavily on imports that are vulnerable to logistical disruptions. Shelf-life constraints, cold-chain requirements, and the need for batch-tested metabolic accuracy complicate distribution. These limitations restrict timely access for patients requiring uninterrupted nutritional therapy, posing a major barrier to consistent disease management and market scalability.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America holds the largest market share of 38–40%, supported by strong clinical infrastructure, widespread newborn screening programs, and high awareness of metabolic and neurological orphan disorders. The region benefits from well-established reimbursement structures and a strong presence of specialized metabolic centers that integrate medical foods into standard rare-disease care. Growing investments in precision nutrition, advancements in amino-acid–based formulations, and expanding patient advocacy networks further accelerate adoption. Improved distribution networks and rising demand for palatable low-protein and hypoallergenic foods enhance long-term dietary management across pediatric and adult populations.
Europe
Europe captures 31–33% of the global market, driven by robust regulatory frameworks supporting rare-disease nutrition therapy and comprehensive national screening programs. Countries such as Germany, the U.K., France, and the Netherlands demonstrate high adoption of medical foods for metabolic disorders including PKU, MSUD, and tyrosinemia. Strong public healthcare systems and structured reimbursement enhance access, while ongoing clinical research on gastrointestinal and immunological orphan conditions sustains demand. European manufacturers also lead innovations in palatable low-protein bakery products and ready-to-consume dietary solutions, reinforcing the region’s strong influence on product development and clinical uptake.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific accounts for 20–22% of the market, with rapid growth driven by expanding diagnostic capabilities, improved healthcare access, and rising awareness of metabolic disorders across China, Japan, India, and South Korea. Governments increasingly emphasize newborn screening, enabling earlier intervention and continuous nutritional management. The region also experiences strong demand for cost-effective formulations and pediatric-focused medical foods. Growing urbanization, dietary transitions, and better clinical training for metabolic specialists strengthen market penetration. As e-commerce platforms expand access to specialized nutrition products, Asia-Pacific is emerging as a major high-growth region for orphan-disease medical foods.
Latin America
Latin America holds 5–6% market share, influenced by improving healthcare policies and increasing recognition of metabolic and gastrointestinal orphan diseases. Brazil, Mexico, and Argentina lead in adoption due to better diagnostic frameworks and rising specialist availability. However, inconsistent reimbursement and limited local manufacturing restrict widespread access. Healthcare providers increasingly incorporate medical foods into treatment for PKU, chronic diarrhea, cachexia, and post-chemotherapy nutritional support. Growth accelerates as patient advocacy groups expand awareness and governments gradually strengthen newborn screening initiatives, creating opportunities for international manufacturers to broaden regional distribution channels.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region captures 3–4% market share, shaped by gradual improvements in clinical nutrition services and rare-disease diagnostics. Gulf countries, particularly the UAE and Saudi Arabia, invest in specialty metabolic clinics and adopt medical foods for PKU, tyrosinemia, and immunological disorders. Access remains limited across Africa due to supply-chain barriers and high treatment costs. Nevertheless, international partnerships, import-driven availability, and targeted government programs gradually expand adoption. Growing demand for pediatric metabolic nutrition and increased clinical training in tertiary hospitals support a steady but early-stage growth trajectory.
Market Segmentations:
By Product:
By Application:
- Chronic Kidney Disease
- Minimal Hepatic Encephalopathy
By Sales Channel:
- Online Sales
- Retail Sales
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape of the Medical Foods for Orphan Diseases Market features a diverse mix of global pharmaceutical and nutrition-focused players, including Xellia Pharmaceuticals, B. Braun SE, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Mankind Pharma, Merck & Co., Inc., AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Gilead Sciences, Inc., Bayer AG, Sandoz International GmbH, and Pfizer Inc. the Medical Foods for Orphan Diseases Market is shaped by a mix of global pharmaceutical innovators, specialized nutrition companies, and emerging regional manufacturers that focus on developing condition-specific therapeutic formulations. Competition intensifies around advancements in amino-acid–based blends, palatable low-protein foods, hypoallergenic compositions, and modular nutrition systems designed to support precise metabolic control. Companies increasingly invest in clinical trials, sensory enhancement technologies, and age-tailored product formats to strengthen compliance among pediatric and adult patients. Strategic collaborations with metabolic clinics, rare-disease foundations, and digital-health platforms expand clinical reach and improve patient management. Meanwhile, supply chain optimization, expansion of e-commerce channels, and regional manufacturing initiatives support greater availability across underserved markets. Continuous innovation in formulation accuracy, micronutrient stability, and personalized nutrition tools remains essential for maintaining competitive differentiation in this specialized therapeutic nutrition space.
Key Player Analysis
- Xellia Pharmaceuticals
- Braun SE
- Bristol-Myers Squibb
- Mankind Pharma
- Merck & Co., Inc.
- AbbVie
- AstraZeneca
- Gilead Sciences, Inc.
- Bayer AG
- Sandoz International GmbH
- Pfizer Inc.
Recent Developments
- In June 2025, the FDA granted orphan drug designation to rilzabrutinib for sickle cell disease, an oral BTK inhibitor designed to reduce painful vaso-occlusive crises, which are common in this rare condition affecting fewer than 200,000 people in the US.
- In January 2025, Lupin and Avas Pharmaceuticals SRL launched NaMuscla (mexiletine), an orphan drug, for the symptomatic treatment of myotonia in adults with non-dystrophic myotonic disorders in Italy.
- In March 2024, AbbVie acquired Landos Biopharma to strengthen its portfolio of inflammatory and autoimmune disease treatments, particularly with Landos’ lead asset, NX-13. NX-13 is an oral NLRX1 agonist in Phase 2 trials for ulcerative colitis (UC) that aims to provide anti-inflammatory effects and facilitate epithelial repair. The acquisition also includes potential applications for Crohn’s disease, another inflammatory bowel disease.
- In February 2024, AstraZeneca has concluded the acquisition of the US-based clinical-stage biopharmaceutical company Icosavax in deal. AstraZeneca will strenghten its vaccine pipeline with a Phase III-ready candidate for respiratory infections.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Product, Application, Sales Channel and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- The market expands as diagnostic rates for rare metabolic and genetic disorders improve globally.
- Manufacturers prioritize personalized nutrition formulas tailored to patient-specific metabolic pathways.
- Advancements in genomics accelerate development of condition-specific medical foods with higher clinical precision.
- Digital health platforms strengthen patient monitoring and adherence to specialized nutritional regimens.
- Regulatory agencies streamline pathways for medical food approvals supporting faster commercialization.
- Industry participants increase investment in amino-acid-based and lipid-modified formulations to enhance therapeutic efficacy.
- Distribution networks broaden through specialty pharmacies and hospital-integrated nutrition management programs.
- Collaborations between biotech firms and nutrition science companies drive innovation in enzyme-compatible formulations.
- Growing clinical evidence supports expanded use of medical foods as adjunct therapy in orphan disease management.
- Emerging markets adopt specialized nutrition care frameworks, boosting demand for advanced medical food solutions.

 Market Segmentation Analysis:
Market Segmentation Analysis:

