Market Overview
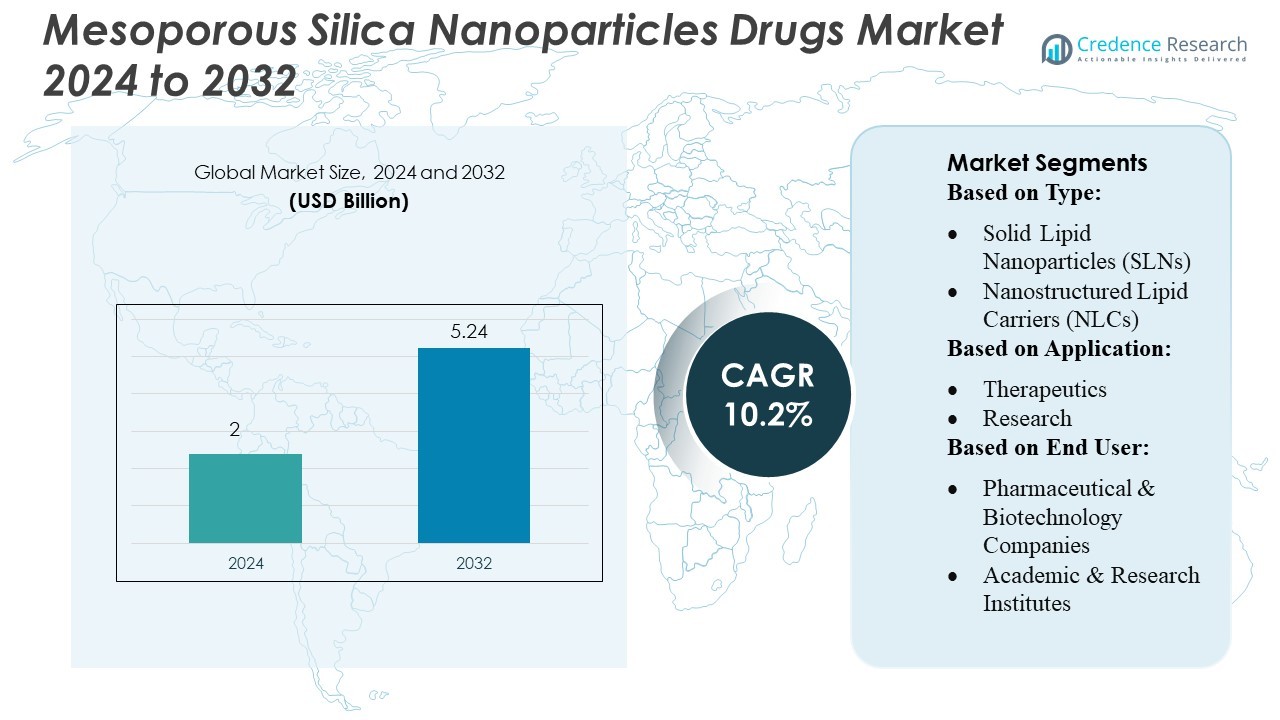
Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Drugs Market size was valued USD 2 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 5.24 billion by 2032, at a CAGR of 10.2% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Drugs Market Size 2024 |
USD 2 Billion |
| Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Drugs Market, CAGR |
10.2% |
| Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Drugs Market Size 2032 |
USD 5.24 Billion |
The Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Drugs Market is shaped by the activities of key players such as ACS Material LLC, Merck KGaA, Glantreo Ltd., MKnano, AGC Chemicals Americas, Inc., Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation, nanoComposix, Inc., Taiyo International, W.R. Grace & Co., and American Elements, all of which focus on advanced material engineering, high-purity MSN production, and functionalized nanocarrier development for pharmaceutical applications. North America leads the global market with an exact 38% share, supported by strong nanomedicine research infrastructure, high investment in drug-delivery innovation, and established collaborations between biotechnology firms and academic institutions.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Insights
- The Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Drugs Market was valued at USD 2 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 5.24 billion by 2032, registering a CAGR of 10.2% during the forecast period.
- Rising demand for targeted and controlled drug-delivery systems, especially in oncology and chronic disease treatments, continues to drive market expansion, with therapeutics holding the dominant application share.
- Technological advancements, along with the involvement of key players focusing on high-purity MSN production and functionalized drug-delivery platforms, strengthen the competitive landscape.
- High production costs, regulatory complexities, and challenges in large-scale MSN synthesis remain key restraints for market penetration across emerging markets.
- North America leads with 38% regional share, supported by strong nanomedicine R&D, while solid lipid nanoparticle-based systems hold the leading segment share, driven by superior stability and high drug-loading efficiency.
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Type
Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLNs) dominate the Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Drugs Market, accounting for an estimated 45–50% share due to their strong stability, scalable manufacturing profile, and enhanced drug-loading efficiency. Their ability to improve the bioavailability of hydrophobic drugs, paired with controlled-release characteristics, drives their broader adoption across pharmaceutical formulations. Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (NLCs) follow, supported by improved payload capacity and lower drug expulsion during storage, while the “Others” category grows gradually as niche nano-platforms advance through early-stage research and development.
- For instance, ACS Material LLC supplies mesoporous silica nanoparticles with a verified BET surface area of up to 800 m²/g and tunable pore diameters ranging from 2 to 50 nm, enabling high drug-loading capacity and consistent diffusion-controlled release performance.
By Application
Therapeutics represent the leading application segment, holding approximately 60% of the market, driven by the rising demand for targeted drug-delivery systems in oncology, infectious diseases, and chronic disorder management. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles offer tunable pore structures that enable high drug loading, sustained release, and reduced systemic toxicity, strengthening their clinical relevance. The research segment continues to expand as universities and biotechnology firms increase investments in nanoscale drug-delivery models, enabling advanced studies in gene delivery, imaging, and combination therapies.
- For instance, Merck KGaA has demonstrated scalable loading of poorly soluble drugs by adsorbing ibuprofen into mesoporous silica particles in a 100 kg batch, stabilizing the molecule in its amorphous form within pores around 2.3–2.7 nm in diameter and achieving a pore volume of approximately 0.98 cm³/g.
By End-user
Pharmaceutical & Biotechnology Companies are the dominant end-user group, capturing nearly 55–60% market share, supported by their extensive drug-development pipelines and growing integration of nano-enabled delivery systems into commercial formulations. Their emphasis on improving therapeutic efficacy and reducing development timelines accelerates the adoption of mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Academic & Research Institutes continue to contribute significantly through innovation-driven studies, while the “Others” category—including CROs and specialized nanotechnology labs—experiences steady growth due to rising outsourcing of preclinical and formulation research.
Key Growth Drivers
- Rising Demand for Targeted Drug Delivery
The demand for targeted and controlled drug-delivery systems is a major driver of the Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles (MSN) Drugs Market. MSNs offer high surface area, tunable pore size, and excellent biocompatibility, enabling precise delivery of therapeutic molecules while minimizing off-target toxicity. Pharmaceutical companies increasingly adopt MSNs for oncology, antimicrobial therapy, and chronic disease management due to their ability to enhance drug bioavailability and therapeutic index. Growing clinical research supporting MSN-mediated delivery further accelerates adoption across advanced drug-development pipelines.
- For instance, Glantreo Ltd. manufactures pharmaceutical-grade mesoporous silica with pore diameters precisely tunable between 2 nm and 30 nm, BET surface areas reaching up to 1,200 m²/g, and particle-size distributions controlled to within ±5 nm, supporting highly predictable drug-loading and release kinetics.
- Expanding R&D Investments in Nanomedicine
Significant growth in nanomedicine R&D activities is strengthening the commercialization potential of mesoporous silica nanoparticles in drug delivery. Academic institutes, biotech startups, and pharmaceutical firms are investing heavily in nanoparticle engineering, surface functionalization, and hybrid nanostructures. These research initiatives enable innovations such as stimuli-responsive release systems and multifunctional therapeutic carriers. Advances in imaging, gene delivery, and combination nano-therapies continue to widen the application scope. Government-backed funding programs for nanotechnology research also enhance translational capabilities, promoting faster evaluation and adoption of MSN-based formulations.
- For instance, MKnano supplies mesoporous silica nanopowders with particle sizes ranging from 50 nm to 200 nm, pore diameters tunable between 2 nm and 15 nm, and surface areas reaching up to 1,000 m²/g, enabling high-capacity drug loading and controlled-release studies in preclinical research.
- Advancements in Material Science and Nano-fabrication
Accelerated progress in material science, synthesis techniques, and scalable nano-fabrication processes is creating favorable conditions for MSN integration into drug-delivery solutions. Improved templating methods, microemulsion techniques, and green synthesis approaches have enhanced particle uniformity, purity, and safety profiles. These advancements support consistent drug loading and controlled-release performance, which are crucial for clinical acceptance. Additionally, improved surface-coating technologies enable targeted delivery and reduced immunogenicity. The ability to tailor MSNs for personalized medicine further positions them as a high-potential platform for next-generation therapeutics.
Key Trends & Opportunities
1. Growth of Stimuli-Responsive and Smart Nanocarriers
A key trend in the MSN drugs market is the rapid development of stimuli-responsive nanocarriers capable of releasing drugs in response to pH, temperature, enzymes, or magnetic fields. Smart MSNs enhance precision therapy and reduce systemic exposure, making them attractive for cancer and inflammatory disease treatment. Opportunities emerge as researchers design multifunctional MSNs that combine diagnostics and therapy, enabling real-time monitoring of drug release. This trend supports the growth of personalized medicine and facilitates entry into new therapeutic segments requiring controlled, on-demand drug administration.
- For instance, AGC’s materials division supplies high-purity porous silica with controlled pore diameters of 6–10 nm, particle-size distributions tailored between 3 µm and 10 µm, and specific surface areas in the 300–800 m²/g range, offering reliable platforms for functionalization and stimuli-responsive release research.
2. Increasing Adoption in Oncology and Immunotherapy
Mesoporous silica nanoparticles are gaining traction in oncology due to their ability to encapsulate chemotherapeutics, nucleic acids, and immunomodulators with high efficiency. Their controlled-release behavior and tumor-targeting potential offer opportunities for combination therapy and reduced toxicity. Additionally, MSNs are being explored for vaccine delivery, antigen presentation, and immune-cell modulation, creating opportunities in emerging immunotherapy markets. As cancer incidence rises globally, pharmaceutical companies increasingly explore MSN-based platforms to develop more effective and safer therapeutic options, strengthening commercialization prospects.
- For instance, Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation’s SYLYSIA® porous silica features BET surface areas ranging from 200 to 800 m²/g, pore volumes up to 1.6 cm³/g, and median particle sizes controllable between 3 µm and 20 µm, supporting high-capacity loading and functionalization for therapeutic applications.
3. Potential for Integration with Biotechnology and Biologics
The integration of MSNs with biologics—including peptides, antibodies, mRNA, and gene-editing tools—presents significant future opportunities. Their porous structure allows stable loading of sensitive biomolecules while protecting them from degradation. This compatibility aligns with the expanding biologics market and the growing need for advanced delivery systems. MSNs engineered for intracellular delivery and improved endosomal escape are particularly promising for gene therapy and regenerative medicine. These emerging capabilities position MSNs as an enabling technology for next-generation biological and nucleic acid-based therapeutics.
Key Challenges
1. Safety, Toxicity, and Regulatory Barriers
One of the major challenges for MSN-based drug products is uncertainty surrounding long-term safety, biocompatibility, and biodegradation profiles. Regulatory agencies require extensive preclinical and clinical data to assess particle distribution, accumulation, and clearance mechanisms. Variability in synthesis methods further complicates standardization, making it difficult to establish universal guidelines. These concerns increase development timelines and cost burdens for manufacturers. Ensuring consistent safety profiles and building clear regulatory frameworks remain essential for broader clinical acceptance and commercialization.
2. Manufacturing Scalability and Quality Control Issues
Scaling up the production of mesoporous silica nanoparticles while maintaining uniform pore structure, particle size, and purity presents significant operational challenges. The need for high-precision synthesis, controlled functionalization, and contamination-free processing complicates mass manufacturing. Establishing robust quality-control protocols becomes difficult due to the complexity of evaluating nanoscale parameters. These challenges can limit cost efficiency and hinder large-scale commercialization. Manufacturers must invest in advanced production technologies and standardized fabrication processes to meet pharmaceutical-grade requirements and support market expansion.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America holds the leading position in the Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Drugs Market with an estimated 35–38% share, supported by strong pharmaceutical R&D activities, well-established nanomedicine research centers, and accelerated clinical adoption of advanced drug-delivery systems. The region benefits from significant investments by biotechnology companies exploring MSN-based therapeutics for oncology, immunology, and targeted delivery applications. Regulatory pathways, although stringent, encourage innovation through structured approvals for nanotechnology-based formulations. The presence of major research institutes, expanding collaborations with nanomaterials developers, and substantial government funding further reinforce North America’s dominance in the market.
Europe
Europe accounts for approximately 28–30% of the market, driven by robust academic research capabilities, high adoption of advanced nanomaterials, and continuous innovation in targeted drug-delivery systems. Countries such as Germany, France, and the U.K. lead due to strong pharmaceutical manufacturing ecosystems and early integration of mesoporous silica nanoparticles in experimental therapeutics. Government-backed nanotechnology initiatives and cross-border research programs accelerate product development cycles across the region. The increasing focus on precision medicine, paired with rising collaborations between universities and biotech firms, supports steady growth in MSN-enabled drug-delivery research and enhances Europe’s competitive presence.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific exhibits the fastest growth trajectory and commands roughly 24–26% of the market, propelled by expanding pharmaceutical production, large patient pools, and increased investments in nanotechnology research infrastructure. China, Japan, India, and South Korea lead in MSN development due to rising industrial capabilities and government support for nanomedicine innovations. Regional manufacturers benefit from cost-efficient production environments, enabling accelerated development of MSN-based formulations. Growing demand for cancer therapeutics and targeted drug-delivery technologies further boosts adoption. Strengthening collaborations between academic institutions and emerging biotech firms position Asia-Pacific as a key contributor to future MSN advancements.
Latin America
Latin America holds an estimated 4–5% market share, with growth influenced by rising interest in nanotechnology research and the gradual modernization of pharmaceutical manufacturing capabilities. Brazil, Mexico, and Argentina lead regional developments due to increasing collaborations between universities and international nanomaterials suppliers. While adoption of MSN-based drug-delivery systems is still in early stages, the region is witnessing increased investment in oncology and chronic disease therapeutics, driving research toward advanced nanocarriers. Improvements in healthcare infrastructure and supportive innovation policies are expected to foster wider integration of mesoporous silica nanoparticles in drug-development activities.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region captures roughly 3–4% of the market, supported by growing healthcare investments and increasing interest in advanced therapeutic technologies. Gulf countries such as the UAE and Saudi Arabia are strengthening biotechnology and pharmaceutical R&D ecosystems, creating opportunities for MSN-based drug-delivery research. Adoption remains gradual due to limited nanotechnology manufacturing capabilities and reliance on imported materials; however, research collaborations with global institutions are expanding. Rising incidence of cancer and chronic diseases, coupled with modernization of medical research facilities, is expected to support steady long-term integration of mesoporous silica nanoparticles across the region.
Market Segmentations:
By Type:
- Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLNs)
- Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (NLCs)
By Application:
By End User:
- Pharmaceutical & Biotechnology Companies
- Academic & Research Institutes
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
The Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Drugs Market features ACS Material LLC, Merck KGaA, Glantreo Ltd., MKnano, AGC Chemicals Americas, Inc., Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation, nanoComposix, Inc., Taiyo International, W.R. Grace & Co., and American Elements. The Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Drugs Market exhibits a competitive landscape driven by advancements in nanomaterial engineering, increasing pharmaceutical adoption of targeted drug-delivery technologies, and expanding research collaborations. Companies within this space focus on improving pore-size control, enhancing biocompatibility, and developing functionalized nanoparticles that support higher drug loading and sustained-release performance. Innovation pipelines continue to prioritize smart nanocarriers, including stimuli-responsive and multifunctional MSN platforms that integrate diagnostics and therapeutics. Partnerships between material suppliers, biotechnology firms, and academic institutions strengthen validation efforts and accelerate the transition from laboratory-scale developments to clinical applications. As demand for precision medicine grows, competition intensifies around scalable manufacturing, regulatory compliance, and the integration of MSNs with biologics and gene-based therapeutics.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
Recent Developments
- In August 2025, Zenara Pharma Private Limited, were approved by the FDA in the United States, as the first FDA-approved generic equivalent of Almatica Pharma’s product. It was granted Competitive Generic Therapy (CGT) designation, which provided 180 days of U.S. marketing exclusivity.
- In June 2025, Advent International announced that it has signed a definitive agreement to invest through primary and secondary transactions to acquire a significant minority stake in Felix Pharmaceuticals.
- In August 2024, Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd. launched STARIZO, an antibacterial treatment to combat Acute Bacterial Skin and Skin Structure Infections caused by drug-resistant bacteria such as MRSA in India. The medication offers the convenience of once-a-day dosing for six days, making it easier for patients than traditional treatments requiring more frequent dosing over longer periods.
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Type, Application, End-User and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- The market will increasingly adopt functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles to support advanced targeted drug-delivery applications.
- Drug developers will prioritize MSN-based carriers for oncology, immunotherapy, and chronic disease therapeutics.
- Regulatory clarity for nanomedicine products will improve, accelerating clinical translation and commercialization.
- Integration of MSNs with biologics, including peptides, antibodies, and nucleic acids, will expand therapeutic applications.
- Stimuli-responsive and smart MSN platforms will gain traction for controlled and on-demand drug release.
- Scalable and cost-efficient manufacturing methods will become a key industry focus to meet rising demand.
- Collaborative research between pharmaceutical companies and academic institutions will intensify to advance MSN-enabled therapies.
- Personalized medicine initiatives will drive the development of patient-specific MSN formulations.
- Hybrid nanocarriers combining MSNs with polymers or lipids will emerge as competitive next-generation delivery platforms.
- Adoption of MSNs in combination therapy and theranostics will strengthen their role in future clinical treatments.




