Market Overview
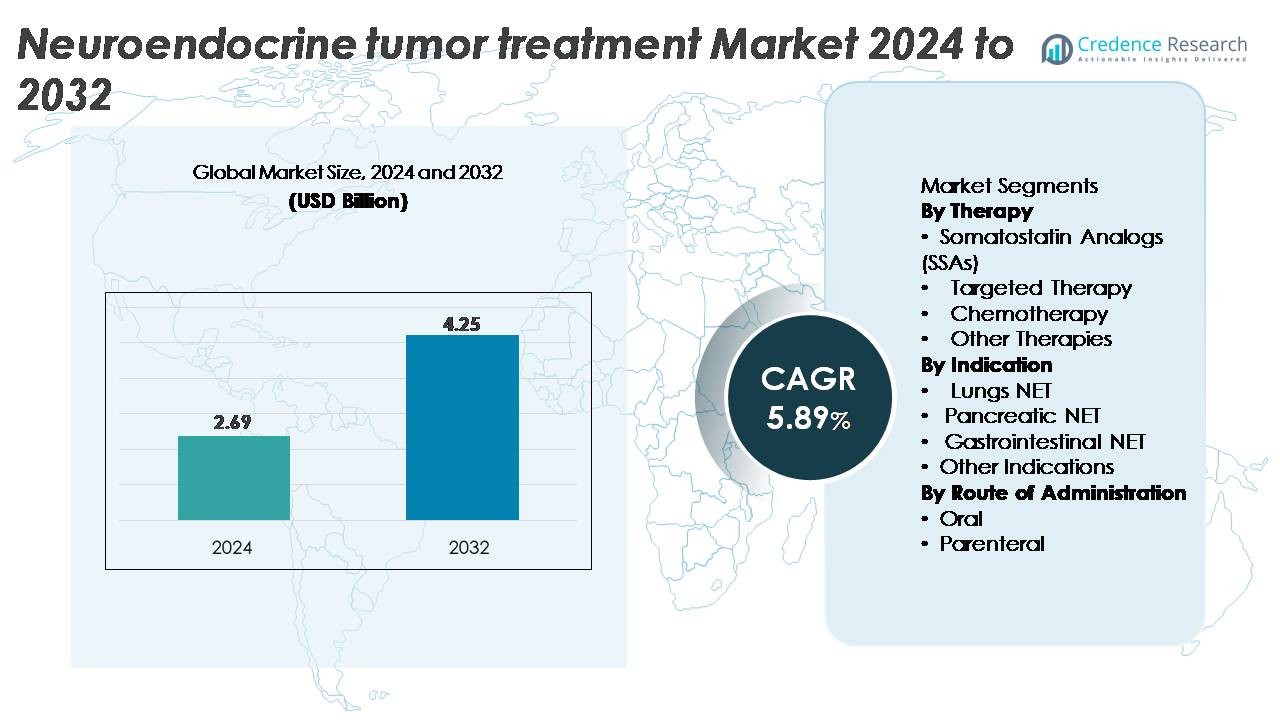
The neuroendocrine tumor (NET) treatment market was valued at USD 2.69 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 4.25 billion by 2032, reflecting a CAGR of 5.89% during the forecast period (2025–2032).
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Neuroendocrine Tumor (NET) Treatment Market Size 2024 |
USD 2.69 Billion |
| Neuroendocrine Tumor (NET) Treatment Market, CAGR |
5.89% |
| Neuroendocrine Tumor (NET) Treatment Market Size 2032 |
USD 4.25 Billion |
The neuroendocrine tumor (NET) treatment market is dominated by leading players such as Novartis AG, Ipsen, F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd., Eli Lilly & Company, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Lantheus Holdings (Progenics), Boehringer Ingelheim, Hutchison MediPharma, Jubilant Life Sciences, and AVEO Pharmaceuticals, each strengthening their portfolios through advancements in somatostatin analogs, targeted therapies, and radioligand treatments. Novartis and Ipsen maintain strong leadership due to extensive SSA and PRRT platforms, while oncology innovators like Roche and BMS expand competitive intensity in targeted biologics. Regionally, North America leads the market with approximately 38% share, driven by advanced diagnostic infrastructure, broad biologics access, and strong radiopharmaceutical adoption.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Insights
- The neuroendocrine tumor (NET) treatment market was valued at USD 2.69 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 4.25 billion by 2032, registering a CAGR of 5.89% during the forecast period.
- Market growth is driven by rising global NET incidence, increasing adoption of somatostatin analogs (SSAs), broader uptake of targeted therapies, and earlier diagnosis enabled by advanced imaging such as SSTR-PET.
- Key trends include accelerating expansion of radioligand therapies (PRRT), increasing use of genomic profiling for personalized treatment, and growing preference for long-acting injectable formulations that improve patient adherence.
- Competitive dynamics are shaped by strong portfolios from Novartis, Ipsen, Roche, Eli Lilly, and Lantheus, with companies intensifying R&D investment in next-generation targeted agents, radiopharmaceuticals, and combination regimens to capture unmet clinical need.
- Regionally, North America leads with ~38% share, followed by Europe at ~32% and Asia-Pacific at ~20%, while by therapy, somatostatin analogs hold the dominant segment share driven by frontline usage across GEP-NETs and lung NETs.
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Therapy
Somatostatin analogs (SSAs) represent the dominant therapy segment, accounting for the largest market share due to their established efficacy in controlling hormone secretion and slowing tumor progression in functional and non-functional NETs. Widely used agents such as octreotide LAR and lanreotide depot remain first-line treatments, supported by strong clinical evidence and broad physician preference. Targeted therapy continues to expand rapidly as drugs like everolimus and sunitinib achieve deeper penetration in pancreatic NETs, while chemotherapy and emerging radionuclide-based options strengthen demand for multimodal treatment strategies.
- For instance, in the CLARINET trial conducted by Ipsen, lanreotide depot achieved a median progression-free survival of 32.8 months in advanced gastroenteropancreatic NETs, demonstrating sustained disease-stabilizing activity.
By Indication
Gastrointestinal NETs hold the dominant market share owing to their higher global prevalence, earlier diagnostic visibility, and broad adoption of SSAs, targeted drugs, and radionuclide therapies. Pancreatic NETs form the second-largest segment, driven by increasing utilization of targeted therapies and improved biomarker-based diagnosis. Lung NETs maintain steady demand as greater awareness and refined imaging techniques enhance case detection. Other indications, including rare or hereditary NETs, continue to grow with advancements in personalized medicine and multi-disciplinary treatment pathways that support earlier intervention and long-term disease management.
- For instance, Novartis’ Lutathera demonstrated a median progression-free survival that was not reached (NR) at the time of the primary analysis of the NETTER-1 trial, versus 8.4 months for the control arm, underscoring its effectiveness in gastrointestinal tumors.
By Route of Administration
Parenteral administration dominates the market, driven by the widespread use of injectable SSAs, targeted biologics, and chemotherapy regimens that require controlled dosing and clinical oversight. Long-acting injectable formulations further reinforce its leadership by enabling sustained therapeutic concentration and convenient monthly dosing. Conversely, the oral segment shows steady growth as targeted therapies, particularly mTOR and tyrosine kinase inhibitors, gain broader adoption for pancreatic and gastrointestinal NETs. Increasing patient preference for home-based treatment and reduced hospital visits continues to support expansion of orally administered regimens.
Key Growth Drivers
Rising Global Incidence and Earlier Diagnostic Adoption
The increasing global incidence of neuroendocrine tumors significantly drives treatment demand as improved imaging modalities, biomarker assays, and screening practices allow earlier diagnosis. High-resolution CT/MRI, SSTR-PET imaging, and chromogranin A profiling are now routinely integrated into diagnostic workflows, enabling detection of low-grade and asymptomatic NETs that were previously underdiagnosed. Earlier identification expands the eligible patient pool for somatostatin analogs, targeted therapies, and radionuclide treatments, reinforcing strong baseline therapy uptake. Growth is also supported by rising awareness among endocrinologists, oncologists, and gastroenterologists, along with expanding multidisciplinary care centers specializing in NET management. As survival rates improve with earlier intervention, long-term maintenance therapies further strengthen recurring treatment revenues and expand the addressable market.
· For instance, NETSPOT® (Ga-68 DOTATATE), developed by Advanced Accelerator Applications (Novartis), is FDA-approved for imaging somatostatin receptor–positive NETs and delivers radiochemical purity above 95%. The tracer supports high-resolution PET scans and helps detect lesions as small as 4–5 mm, improving early NET identification.
Expansion of Targeted Therapies and Precision Medicine Approaches
Advancements in molecular oncology and precision medicine are accelerating demand for targeted NET treatments that deliver higher tumor specificity and improved tolerability compared with conventional chemotherapy. Therapies such as mTOR inhibitors, tyrosine kinase inhibitors, and peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRT) have reshaped treatment algorithms by offering durable responses in progressive or metastatic NETs. Growing availability of genomic profiling supports personalized therapy selection based on tumor genetics, receptor expression, and proliferative index. Increased clinical trial activity around receptor-targeted radionuclides, angiogenesis inhibitors, and next-generation peptide analogs continues to expand the therapeutic arsenal. As precision-based approaches demonstrate improved progression-free survival and quality-of-life benefits, adoption of targeted and biologically guided therapies is expected to remain a strong growth catalyst.
- For instance, Novartis’ everolimus demonstrated a median progression-free survival of 11 months in progressive GI and lung NETs in the RADIANT-4 trial, confirming its durability across non-functional tumors.
Greater Use of Long-Acting Injectables and Combination Regimens
The shift toward long-acting injectable formulations and combination regimens is driving significant growth by improving treatment adherence, reducing dosing burden, and extending therapeutic efficacy. Monthly SSA injections remain the cornerstone of frontline management, offering stable symptom control and tumor-growth suppression. Combination protocols integrating SSAs with targeted therapies, chemotherapy, or PRRT are gaining traction as evidence supports enhanced response rates in progressive NETs. Long-acting formulations also reduce clinic visits, aligning well with patient preference and value-based care models. Enhanced drug delivery technologies, depot formulations, and sustained-release mechanisms are fostering broader utilization across gastroenteropancreatic, lung, and metastatic NET categories. As clinicians increasingly adopt multi-mechanism approaches to manage resistant tumors, demand for flexible combination strategies continues to strengthen market expansion.
Key Trends and Opportunities
Advancements in Radioligand Therapy (RLT) and PRRT Expansion
Radioligand therapy (RLT) represents one of the most transformative trends in NET care, with PRRT gaining widespread acceptance for advanced tumors. The success of radionuclide-labeled somatostatin analogs has created strong momentum for next-generation isotopes and improved receptor-targeting ligands. Expanded use of SSTR-PET imaging optimizes patient selection and enhances treatment precision, supporting broader integration into metastatic and refractory disease management. Rising investment in radiopharmaceutical infrastructure, including isotope production and nuclear medicine facilities, is accelerating accessibility across developed and emerging markets. As clinical trials explore PRRT combinations with SSAs, targeted drugs, and immunotherapies, the pipeline for multi-modality RLT approaches continues to grow, presenting substantial long-term opportunities.
· For instance, ITM Isotope Technologies Munich SE supplies no-carrier-added Lutetium-177 (Lu-177 n.c.a., marketed as EndolucinBeta®) with a certified specific activity of >3,000 GBq/mg and radionuclidic purity of ≥99.9%, which is used globally in PRRT production and supports high-precision dosing for NET radioligand therapies.
Integration of AI, Digital Oncology, and Biomarker-Based Personalization
AI-driven decision support, digital oncology platforms, and biomarker-guided personalization are reshaping NET treatment planning and monitoring. Machine learning tools enhance tumor grading, imaging interpretation, and progression prediction, enabling earlier therapeutic adjustments. Digital tools support remote monitoring of symptoms and biochemical markers, reducing hospital visits and improving continuity of care for chronic NET patients. Meanwhile, biomarker-driven personalization leveraging Ki-67 index, receptor expression profiles, and circulating tumor markers improves therapy selection and response prediction. The convergence of AI with real-world evidence platforms also accelerates post-marketing insights, enabling more effective therapy optimization. This trend opens strong opportunities for pharmaceutical and diagnostic companies to develop integrated treatment ecosystems.
- For instance, GE HealthCare’s Edison platform integrates FDA-cleared AI tools such as AIR Recon DL, which improves MRI image quality by reducing noise and enhancing resolution by up to 40%, supporting clearer visualization for oncology imaging workflows. Edison also streamlines radiology tasks by embedding AI algorithms directly into GE’s imaging systems for faster and more consistent diagnostic review.
Key Challenges
High Treatment Costs and Limited Access to Advanced Therapies
The significant cost burden associated with targeted therapies, long-acting injectables, and radioligand treatments poses a major barrier to widespread adoption, particularly in low- and middle-income regions. Limited reimbursement pathways and regional disparities in nuclear medicine infrastructure restrict access to PRRT and specialty biologics. Many advanced treatments require specialized administration facilities, adding logistical and operational challenges for hospitals and patients. High diagnostic costs associated with advanced imaging modalities further intensify financial pressure. These access limitations slow overall treatment uptake and widen global care disparities, challenging market expansion in resource-constrained settings.
Complex Disease Heterogeneity and Limited Predictive Biomarkers
The biological heterogeneity of neuroendocrine tumors complicates treatment planning, as NETs vary widely by grade, site of origin, proliferative activity, and receptor expression patterns. This variability limits the universal applicability of certain therapies and increases the difficulty of predicting treatment response. While targeted and RLT options are expanding, the absence of robust predictive biomarkers slows precision-based adoption and leads to variable outcomes. Moreover, slow-growing NETs often require long-term monitoring, demanding highly individualized regimens. Clinical complexity also results in delayed diagnosis and inconsistent referral pathways, further challenging standardized treatment implementation across global healthcare systems.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America holds the largest share of the neuroendocrine tumor (NET) treatment market at approximately 38%, supported by advanced diagnostic capabilities, high adoption of somatostatin analogs, and strong penetration of targeted therapies and PRRT. The region benefits from a well-established oncology ecosystem, widespread use of SSTR-PET imaging, and favorable reimbursement for specialty biologics. Academic cancer centers and active clinical research pipelines further drive uptake of novel radionuclide and targeted agents. Growing patient awareness and increasing incidence of GEP-NETs and lung NETs continue to accelerate treatment demand across the U.S. and Canada.Europe accounts for roughly 32% of the global NET treatment market, driven by strong adoption of PRRT across nuclear medicine centers in Germany, the Netherlands, France, and Italy. The region benefits from structured cancer registries, standardized care pathways, and widespread availability of long-acting SSAs. Robust public healthcare systems support patient access to advanced biologics and imaging diagnostics. Increasing clinical trial participation in targeted therapy combinations and radioligand innovations enhances therapeutic diversity. With rising NET prevalence and expanding precision oncology programs, Europe continues to maintain a strong demand profile for both injectable and oral therapies.
Asia-Pacific
The Asia-Pacific region holds about 20% of the NET treatment market, supported by improving diagnostic infrastructure and rising healthcare expenditure in China, Japan, South Korea, and Australia. Growing adoption of SSTR imaging, greater oncologist awareness, and increasing availability of SSAs and targeted drugs contribute to steady expansion. Japan remains a key hub due to mature oncology practices and early uptake of novel biologics. Meanwhile, China shows rapid growth as cancer screening programs expand and tertiary hospitals strengthen nuclear medicine capacity. APAC’s growing patient pool and rapid modernization drive strong long-term treatment demand.
Latin America
Latin America represents approximately 6% of the global market, with growth driven by improvements in cancer diagnostics and rising availability of SSA therapies in Brazil, Mexico, and Argentina. Limited nuclear medicine infrastructure restricts PRRT access, but gradual expansion of public and private oncology networks is improving therapy availability. Increasing training programs for endocrinologists and oncologists are enhancing NET recognition, reducing diagnostic delays. Economic constraints continue to challenge adoption of high-cost targeted therapies; however, strengthening reimbursement models and regional importation of biologics are gradually expanding the treatment landscape.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region accounts for around 4% of the NET treatment market, with demand primarily concentrated in Saudi Arabia, the UAE, and South Africa. Improvements in cancer referral pathways and the establishment of specialized oncology centers have increased access to SSAs and targeted therapies. Limited nuclear medicine capacity restricts widespread PRRT adoption, although Gulf countries are investing in radiopharmaceutical facilities. Rising incidence of gastrointestinal cancers and improved healthcare insurance coverage support gradual treatment uptake. Despite systemic access challenges, MEA continues to exhibit steady demand growth as diagnostic and therapeutic infrastructure evolves.
Market Segmentations:
By Therapy
- Somatostatin Analogs (SSAs)
- Targeted Therapy
- Chemotherapy
- Other Therapies
By Indication
- Lungs NET
- Pancreatic NET
- Gastrointestinal NET
- Other Indications
By Route of Administration
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East
- Africa
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape of the neuroendocrine tumor (NET) treatment market is shaped by a mix of established biopharmaceutical leaders and emerging radiopharmaceutical innovators focused on expanding therapeutic options across somatostatin analogs, targeted therapies, and radioligand treatments. Key players such as Novartis AG, Ipsen Pharma, and Pfizer maintain strong positions through extensive SSA portfolios, targeted oncology pipelines, and global distribution networks. Novartis leads with its broad NET strategy spanning SSAs and radioligand therapy, supported by ongoing clinical expansion of next-generation PRRT candidates. Ipsen strengthens its competitiveness through lifecycle enhancements of long-acting SSAs and active partnerships in molecular diagnostics. Meanwhile, companies like Advanced Accelerator Applications, ITM Isotope Technologies, and Lutathera-focused developers continue to elevate radiopharmaceutical innovation, broadening access to precision treatments. Rising investment in receptor-targeted agents, improved imaging tools, and combination therapy trials intensifies market rivalry, driving continuous R&D activity and product differentiation across key segments.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
- Novartis AG
- Ipsen
- Lantheus Holdings, Inc. (Progenics Pharmaceuticals)
- Hutchison MediPharma Limited (HUTCHMED)
- Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.
- Eli Lilly & Company
Recent Developments
- In July 2025, the company Bristol-Myers Squibb announced a new “hub” to accelerate next-generation cancer therapies and highlighted ongoing work in gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors.
- In January 2024, Novartis AG its radioligand therapy Lutathera® significantly reduced risk of disease progression or death by 72% when used as first-line in advanced gastroenteropancreatic NETs.
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Therapy, Indication, Route of administration and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- Adoption of radioligand therapies is expected to accelerate as next-generation isotopes and improved targeting ligands enter clinical practice.
- Precision medicine will expand as genomic profiling and biomarker-based patient selection become standard in NET treatment pathways.
- Long-acting injectables and sustained-release formulations will gain broader use to enhance adherence and reduce clinic dependency.
- Combination regimens integrating SSAs, targeted therapies, and PRRT will see stronger uptake for managing progressive and metastatic NETs.
- AI-enabled imaging and digital oncology platforms will improve diagnostic accuracy and treatment monitoring.
- Emerging targeted agents focusing on angiogenesis, mTOR pathways, and receptor-specific mechanisms will diversify therapeutic options.
- Expanded nuclear medicine infrastructure will increase access to PRRT in developing regions.
- Growth in multidisciplinary NET centers will streamline diagnosis, treatment coordination, and long-term disease management.
- Increased clinical trial activity will accelerate innovation in novel biologics and personalized radiopharmaceuticals.
- Rising patient awareness and improved referral pathways will support earlier detection and broader therapy adoption.




