Market Overview
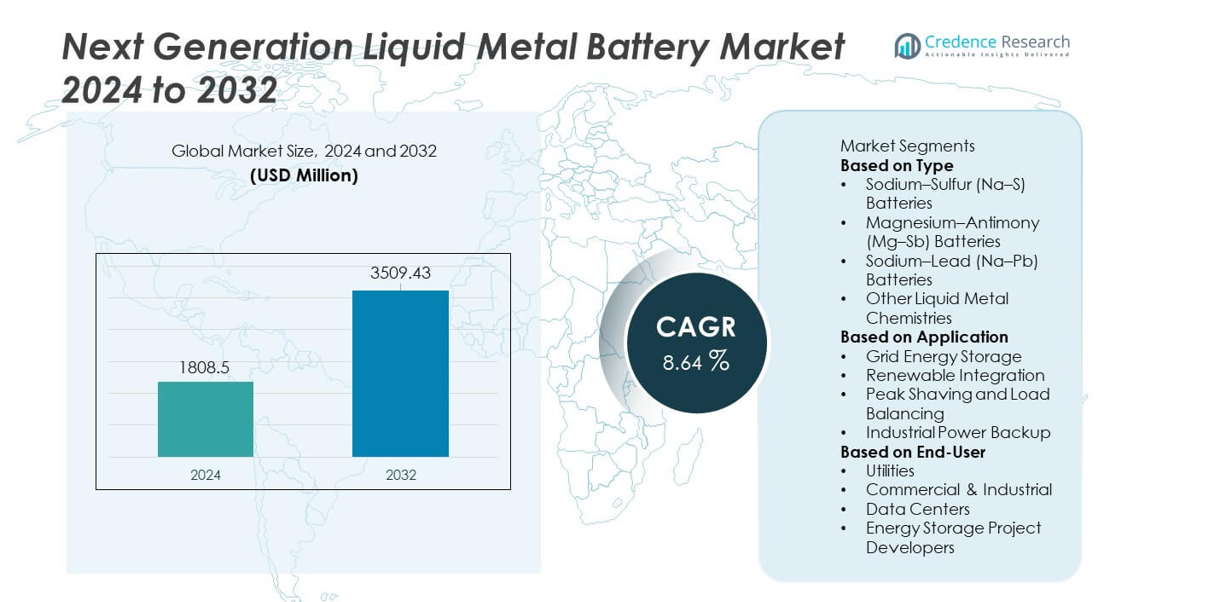
The Next Generation Liquid Metal Battery market reached USD 1,808.5 million in 2024. The market is projected to grow to USD 3,509.43 million by 2032. This growth reflects a CAGR of 8.64% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Next Generation Liquid Metal Battery Size 2024 |
USD 1,808.5 million |
| Next Generation Liquid Metal Battery, CAGR |
8.64% |
| Next Generation Liquid Metal Battery Size 2032 |
USD 3,509.43 million |
Top players in the Next Generation Liquid Metal Battery market include Ambri Inc., Sumitomo Electric Industries, NGK Insulators, EaglePicher Technologies, Liquid Metal Battery Corporation, Japan Metals & Chemicals, Altris AB, GE Research, and Lockheed Martin Energy. These companies focus on advancing high-temperature chemistries, improving alloy stability, and scaling long-duration storage solutions to meet rising demand from utilities and industrial users. North America leads the market with a 38% share, supported by strong grid modernization programs and widespread renewable integration. Europe follows with a 29% share, driven by strict decarbonization targets and large-scale energy transition initiatives that accelerate adoption of advanced liquid metal storage systems.
Market Insights
- The market reached USD 1,808.5 million in 2024 and will reach USD 3,509.43 million by 2032, recording a CAGR of 8.64% during the forecast period.
- Strong demand for long-duration grid storage drives adoption, with the Sodium–Sulfur (Na–S) type segment holding 46% share, supported by high energy density and long cycle life across large utility projects.
- Trends highlight rising integration with renewable plants and hybrid storage systems, while grid energy storage remains the dominant application with a 52% share, driven by increasing renewable penetration and system flexibility needs.
- Competitive activity grows as key companies such as Ambri Inc., Sumitomo Electric Industries, and NGK Insulators scale pilot deployments, expand technology partnerships, and improve high-temperature battery chemistries to enhance reliability.
- North America leads with a 38% share, followed by Europe at 29%, Asia Pacific at 24%, and LAMEA at 9%, reflecting varied grid modernization levels and renewable expansion rates across regions.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Type
Sodium–Sulfur (Na–S) batteries lead the type segment with a 46% market share, supported by high energy density, long cycle life, and strong suitability for large grid storage systems. Magnesium–Antimony (Mg–Sb) batteries gain wider use due to stable thermal performance and lower material cost advantages. Sodium–Lead (Na–Pb) batteries serve medium-temperature applications where lower operational complexity is required. Other liquid metal chemistries grow as research improves alloy behavior and temperature ranges. Rising demand for durable, long-duration solutions strengthens adoption across all chemistries, with Na–S maintaining clear dominance due to proven field performance and large-scale deployment capabilities.
- For instance, Ambri demonstrated a liquid metal system that delivered more than 3,000 charge cycles during controlled testing. The unit maintained stable performance at operating temperatures near 500°C with minimal degradation.
By Application
Grid Energy Storage dominates the application segment with a 52% market share, driven by the need for long-duration storage that supports grid frequency control, peak demand management, and system reliability. Renewable Integration follows as solar and wind projects require stable discharge and thermal-tolerant storage to manage intermittency. Peak Shaving and Load Balancing expand in commercial setups seeking reduced demand charges and smoother energy cycles. Industrial Power Backup adoption rises as heavy industries require high-temperature batteries with extended service life. The strong lead of grid storage reflects rising investments in modern, stable, and scalable energy infrastructure.
- For instance, Sumitomo Electric deployed a Na–S installation with 34 MW output and 245 MWh capacity in Japan. The system supports grid balancing and delivered over 6,000 operational hours in its first evaluation period.
By End-User
Utilities hold the highest share in the end-user segment at 49%, supported by large procurement volumes and strong focus on grid modernization. Commercial & Industrial users adopt liquid metal batteries to improve operational stability and reduce downtime across high-load environments. Data Centers increase adoption due to the need for high-temperature, long-cycle, and reliable backup systems. Energy Storage Project Developers expand deployments as demand rises for long-duration assets across renewable and grid projects. The dominance of utilities reflects structural demand for resilient storage that supports grid flexibility, renewable absorption, and long-term supply stability.
Key Growth Driver
Rising Demand for Long-Duration Grid Storage
Long-duration grid storage needs increase as countries expand renewable capacity and modernize power networks. Liquid metal batteries support multi-hour discharge, stable thermal performance, and strong cycling durability, making them suitable for large utility projects. Grid operators use these systems to balance supply fluctuations, reduce curtailment, and maintain frequency stability. As renewable penetration grows, the need for stable and dispatchable energy storage accelerates. The shift toward flexible grid infrastructure strengthens demand for liquid metal batteries due to their long life span, low degradation rate, and strong reliability in harsh operating conditions.
- For instance, NGK Insulators deployed a sodium-sulfur installation in Abu Dhabi delivering 108 MW output with 648 MWh storage, which is considered the world’s largest virtual battery plant.
Advancements in High-Temperature Battery Chemistry
Advances in battery chemistry strengthen performance, safety, and lifespan across next-generation liquid metal technologies. Research programs improve alloy combinations, melting points, and electrolytic stability, enabling broader operating temperatures and higher throughput. Manufacturers invest in new anode–cathode pairs that reduce material costs and extend cycle life. These improvements support wider industrial adoption and expand use in energy-intensive sectors. Better thermal stability, reduced maintenance needs, and improved tolerance to harsh environments position liquid metal batteries as an attractive choice for large-scale energy storage developers seeking long-term operational value.
- For instance, Ambri engineered a calcium-based cathode paired with an antimony alloy that achieved more than 4,000 charge cycles during controlled testing. The prototype operated at temperatures near 500°C with stable electrochemical efficiency.
Growing Adoption Across Utilities and Industrial Sectors
Utilities and industrial users expand deployment as they seek dependable storage solutions for load balancing, peak demand control, and operational continuity. Liquid metal systems deliver stable output, minimal degradation, and long-term performance suited for heavy-duty applications. Utilities integrate these batteries into grid-side projects to improve resilience and reduce reliance on fossil-based peaking plants. Industrial facilities adopt them to support uninterrupted operations, especially in mining, manufacturing, and processing sectors. Increasing demand for systems that ensure energy reliability, reduce downtime, and support large-scale power needs drives strong market growth.
Key Trend & Opportunity
Integration with Renewable Energy and Hybrid Storage Systems
The integration of renewable plants with hybrid storage systems creates new opportunities for liquid metal batteries. Solar and wind developers seek long-duration storage capable of handling intermittent generation and output smoothing. Combining liquid metal batteries with fast-response technologies, such as supercapacitors or lithium-ion systems, improves overall system efficiency and extends storage windows. This hybrid approach enhances grid stability and reduces renewable curtailment. Increasing renewable project investments support strong growth for liquid metal solutions, as developers prioritize systems with long operational life, high temperature tolerance, and reduced degradation under continuous cycling.
- For instance, Sumitomo Electric integrated a sodium-sulfur system with a wind farm in Northern Japan, operating a 4 MW unit paired with rapid-response inverters. The installation completed more than 6,000 performance hours during hybrid balancing trials.
Expansion of Utility-Scale Storage Projects Worldwide
Utility-scale storage pipelines continue to grow worldwide, creating strong opportunities for large liquid metal battery systems. National grid operators focus on long-duration assets that support transmission stability, regional energy balancing, and disaster resilience. Several countries allocate new funding for multi-hour storage systems, strengthening adoption prospects. Liquid metal batteries provide long deployment life, cost stability, and minimal maintenance requirements, making them attractive for grid planners. As utilities shift toward flexible power systems and phase out traditional peaking plants, demand for scalable thermal-stable batteries rises across major global markets.
- For instance, MIT-affiliated researchers tested a liquid metal prototype with a 1 kWh design that completed more than 4,500 full charge–discharge cycles. The unit sustained operating temperatures above 500°C with stable electrochemical efficiency.
Key Challenge
High Operating Temperatures and System Engineering Complexity
Liquid metal batteries operate at elevated temperatures, creating engineering challenges related to thermal management, material durability, and system insulation. Maintaining stable operating environments requires advanced containment systems and reliable heating mechanisms. These conditions increase system complexity and raise installation requirements for utility and industrial customers. Operators must invest in proper thermal control to prevent inefficiencies during cycling. Although newer chemistries reduce temperature needs, widespread adoption still faces barriers from safety considerations and engineering costs. Addressing these challenges is critical to scaling deployments across diverse applications.
Limited Large-Scale Commercial Deployment and Higher Initial Costs
Early-stage commercialization limits economies of scale and increases initial system costs compared with more established technologies. Many manufacturers operate in pilot or demonstration phases, resulting in higher production expenses, limited supply networks, and slower adoption. Utilities and industries often hesitate to deploy emerging technologies without long-term performance data or cost benchmarks. Financing challenges arise as investors favor mature storage options. These constraints slow market expansion despite strong technical advantages. Scaling production, improving supply chains, and achieving commercial standardization will be essential for broader global adoption.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America leads the market with a 38% share, driven by strong grid modernization programs and rising investments in long-duration energy storage. Utility operators deploy liquid metal batteries to support renewable expansion and stabilize regional power networks. Federal and state-level incentives accelerate large-scale storage adoption, while technology developers in the United States strengthen innovation in high-temperature chemistries. Industrial facilities and data centers also adopt advanced storage systems to reduce outage risks. The region benefits from a mature energy infrastructure, strong policy support, and a robust ecosystem of battery manufacturers and research institutions.
Europe
Europe holds a 29% share, supported by strong climate mandates, energy transition policies, and rapid renewable expansion. Countries prioritize long-duration storage to integrate wind and solar power more efficiently and reduce fossil-based backup generation. Grid operators adopt liquid metal systems to enhance flexibility and maintain stability during peak loads. The region’s industrial base increases adoption for operational reliability and emissions reduction goals. Research programs in Germany, the United Kingdom, and the Nordic countries advance next-generation chemistries. Europe’s focus on decarbonization and clean energy funding strengthens long-term market prospects across utility and industrial segments.
Asia Pacific
Asia Pacific accounts for a 24% share, driven by rising power demand, large renewable installations, and strong investments in grid expansion. Countries such as China, Japan, South Korea, and India adopt liquid metal batteries to address intermittency issues and improve storage resilience. Rapid industrialization increases demand for stable backup power across heavy industries and manufacturing hubs. Government programs promoting long-duration storage and energy security further accelerate adoption. Local manufacturers expand pilot deployments and strengthen supply chains. Growing renewable capacity additions and ongoing grid stability challenges position Asia Pacific as one of the fastest-growing regions.
Latin America, Middle East & Africa (LAMEA)
LAMEA holds a 9% share, supported by gradual adoption of renewable energy projects and rising interest in dependable long-duration storage. Middle Eastern countries deploy liquid metal systems to improve grid reliability and support large solar installations. African nations explore these batteries for rural electrification and industrial power stabilization. Latin America increases adoption to support hydropower-dependent grids during seasonal fluctuations. Limited commercial deployments slow growth, but ongoing infrastructure development and clean-energy commitments create strong long-term potential. Expanding government interest in modern grid solutions supports wider adoption across this combined regional group.
Market Segmentations:
By Type
- Sodium–Sulfur (Na–S) Batteries
- Magnesium–Antimony (Mg–Sb) Batteries
- Sodium–Lead (Na–Pb) Batteries
- Other Liquid Metal Chemistries
By Application
- Grid Energy Storage
- Renewable Integration
- Peak Shaving and Load Balancing
- Industrial Power Backup
By End-User
- Utilities
- Commercial & Industrial
- Data Centers
- Energy Storage Project Developers
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape features key players such as Ambri Inc., Sumitomo Electric Industries, NGK Insulators, EaglePicher Technologies, Liquid Metal Battery Corporation, Japan Metals & Chemicals, Altris AB, GE Research, and Lockheed Martin Energy. These companies focus on advancing high-temperature chemistries, improving alloy compositions, and enhancing cycle life to strengthen technology performance. Leading manufacturers expand pilot deployments with utilities and industrial users to validate long-duration operation and reduce system degradation. Strategic partnerships with renewable developers, grid operators, and government agencies accelerate commercialization efforts. Firms invest in scaling production facilities, optimizing thermal management systems, and developing cost-efficient materials to achieve competitive pricing. Ongoing research programs support breakthroughs in anode–cathode combinations, thermal stability, and operational safety. Competitive differentiation grows as companies integrate digital monitoring, predictive diagnostics, and modular designs to serve diverse applications across grid storage, renewable integration, and peak load management.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
- Ambri Inc.
- Sumitomo Electric Industries, Ltd.
- NGK Insulators, Ltd.
- EaglePicher Technologies
- Liquid Metal Battery Corporation
- MIT Energy Initiative–Affiliated Developers
- Japan Metals & Chemicals Co., Ltd.
- Altris AB
- GE Research
- Lockheed Martin Energy
Recent Developments
- In July 2024, Ambri Inc emerged from restructuring after prior financial troubles and confirmed sale of its assets under new ownership.
- In July 2023, Ambri Inc. and Xcel Energy were advancing their collaboration for a 300-kWh utility-scale demonstration project of Ambri’s Liquid Metal™ battery system, with installation expected to begin in early 2024 at SolarTAC in Colorado.
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Type, Application, End-User and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- Demand for long-duration storage will rise as grids expand renewable capacity.
- Utilities will increase adoption to strengthen grid stability and reduce peak-load pressure.
- Advancements in high-temperature chemistries will improve battery life and operational safety.
- Manufacturing scale-up will reduce system costs and support wider commercial deployment.
- Hybrid storage models will gain traction as developers combine liquid metal systems with fast-response technologies.
- Industrial users will adopt these batteries to stabilize operations in energy-intensive sectors.
- Research programs will accelerate new alloy combinations that enhance efficiency and durability.
- Data centers will deploy liquid metal batteries to support resilient and long-cycle backup systems.
- Regional governments will promote deployment through policies supporting long-duration storage.
Global competition will intensify as more companies enter pilot and utility-scale projects.




