Market Overview
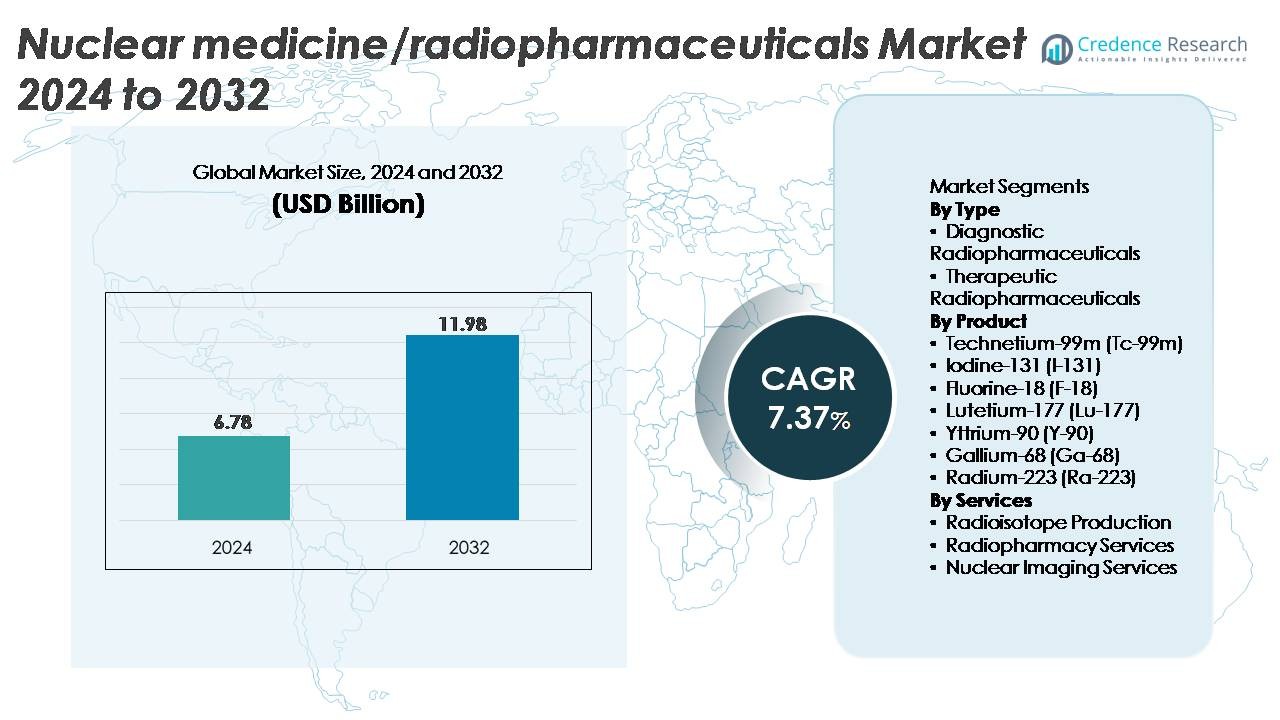
The global nuclear medicine/radiopharmaceuticals market was valued at USD 6.78 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 11.98 billion by 2032, reflecting a CAGR of 7.37% over the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Nuclear Medicine/Radiopharmaceuticals Market Size 2024 |
USD 6.78 Billion |
| Nuclear Medicine/Radiopharmaceuticals Market, CAGR |
7.37% |
| Nuclear Medicine/Radiopharmaceuticals Market Size 2032 |
USD 11.98 Billion |
Major players in the nuclear medicine and radiopharmaceuticals market including NorthStar Medical Radioisotopes, ITM Isotopen Technologien München, Curium Pharma, RadioMedix, Eckert & Ziegler, Jubilant Radiopharma, SHINE Medical Technologies, Isotopia Molecular Imaging, Nordion, and Advanced Accelerator Applications collectively shape the competitive landscape through strong capabilities in isotope production, radioligand therapy development, and global radiopharmacy networks. These companies lead advancements in Lu-177, Ga-68, Ra-223, and Tc-99m supply, strengthening reliability across diagnostic and therapeutic domains. North America remains the leading region with approximately 42% market share, supported by advanced imaging infrastructure, robust radiopharmaceutical manufacturing capacity, and high adoption of precision oncology therapies.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Insights
- The nuclear medicine/radiopharmaceuticals market was valued at USD 6.78 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 11.98 billion by 2032, advancing at a CAGR of 7.37%, supported by rising diagnostic and therapeutic isotope adoption.
- Market growth is driven by expanding use of PET and SPECT procedures, increasing cancer prevalence, and accelerating adoption of Lu-177, Ga-68, and Ra-223–based targeted radionuclide therapies, strengthening demand across diagnostic and therapeutic segments.
- Key trends include the rise of theranostics, rapid commercialization of next-generation isotopes, AI-enabled imaging workflows, and capacity expansion in cyclotron and reactor-based isotope production across global suppliers.
- Competitive activity intensifies as major players scale GMP manufacturing, secure long-term isotope supply agreements, and invest in radioligand therapy pipelines; however, high production costs and global isotope supply vulnerabilities remain significant restraints.
- Regionally, North America leads with ~42% share, followed by Europe at ~30% and Asia Pacific at ~20%; by type, diagnostic radiopharmaceuticals dominate, while F-18 holds the largest product share.
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Type
Diagnostic radiopharmaceuticals represent the dominant sub-segment, accounting for the largest market share due to extensive global utilization in PET and SPECT imaging for oncology, cardiology, and neurology. Widespread clinical dependence on tracer-based imaging, shorter procedure times, and expanding reimbursement coverage sustain their lead. Growth is reinforced by increasing PET-CT installations and rising demand for early cancer detection. Therapeutic radiopharmaceuticals, led by targeted radionuclide therapies, are expanding rapidly as Lu-177 and Ra-223–based therapies demonstrate strong clinical efficacy in metastatic prostate cancer, neuroendocrine tumors, and bone metastases, accelerating adoption across advanced oncology centers.
- For instance, Novartis reported that its Lu-177–DOTATATE therapy in the NETTER-1 trial achieved a median progression-free survival of 28.4 months compared to 8.4 months with high-dose octreotide, while Bayer’s Ra-223 therapy in the ALSYMPCA study reduced the risk of death by 30% across 921 treated metastatic prostate cancer patients, accelerating adoption in advanced oncology centers.
By Product
Fluorine-18 (F-18) remains the dominant isotope, holding the largest share due to its critical use in FDG-PET imaging, superior resolution, and compatibility with high-volume cancer diagnostics. Its widespread cyclotron availability and short half-life support rapid turnover in both hospital and commercial PET centers. Tc-99m follows with strong demand for SPECT cardiology and bone scans, while Ga-68 and Lu-177 are rapidly gaining traction in theranostics for prostate cancer and neuroendocrine tumors. Ra-223 and Y-90 continue expanding in metastatic bone disease and liver-directed therapies, driven by improved clinical outcomes and broadened treatment protocols.
- For instance, GE Healthcare’s PETtrace 800 series cyclotrons are documented to produce up to 16 Ci of F-18 per run, enabling high-capacity FDG output for regional distribution.
By Services
Nuclear imaging services constitute the dominant service sub-segment, supported by rising PET-CT and SPECT-CT procedure volumes and continuous integration of advanced radiotracers into diagnostic workflows. Increasing referrals for oncology staging, cardiac perfusion studies, and neurological assessments strengthens segment leadership. Radiopharmacy services are growing steadily as centralized dose preparation, QC compliance, and just-in-time delivery models expand. Radioisotope production is also advancing, driven by new cyclotron installations and reactor-based isotope capacity upgrades aimed at stabilizing supplies of Tc-99m, Lu-177, and Ga-68 to meet rising theranostic and diagnostic demand.
Key Growth Drivers
Rising Demand for Precision Oncology and Targeted Radionuclide Therapy
The growing shift toward precision oncology significantly accelerates demand for targeted radionuclide therapies that deliver high cytotoxicity with minimal impact on surrounding tissues. Increasing clinical adoption of Lu-177–based radioligand therapies for neuroendocrine tumors and metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer demonstrates strong real-world efficacy, improving survival outcomes and speeding regulatory approvals worldwide. The expansion of theranostics pairing diagnostic imaging tracers with therapeutic isotopes further enhances treatment personalization and expands the patient pool eligible for nuclear medicine interventions. Hospitals and cancer centers increasingly invest in PET-CT and SPECT-CT systems to support individualized therapy planning. Additionally, growing evidence supporting alpha-emitters such as Ra-223 strengthens market momentum by broadening the therapeutic arsenal for resistant and metastatic disease. As clinical trials explore new ligands for breast, colorectal, and glioblastoma indications, radiopharmaceuticals gain traction as frontline and adjunct treatment modalities, driving sustained market acceleration.
- For instance, in the Phase III VISION trial, Novartis’ Lu-177–PSMA-617 demonstrated a median overall survival of 3 months in the treatment arm, compared with 11.3 months in the control arm, across 831 randomized patients
Expansion of PET and SPECT Imaging for Early Disease Detection
The increasing global burden of cancer, cardiovascular disease, and neurological disorders drives rising utilization of PET and SPECT imaging for early and accurate diagnosis. PET imaging using F-18 FDG remains the gold standard for oncology staging due to its superior metabolic sensitivity and ability to detect micro-metastatic lesions that conventional imaging misses. At the same time, Tc-99m-based SPECT continues to dominate cardiac perfusion studies and bone scans, benefiting from large installed device bases and validated clinical pathways. Governments and private healthcare systems are modernizing nuclear imaging infrastructure, adding PET-CT scanners, and adopting Ga-68–based tracers to improve prostate cancer diagnostics. Increased reimbursement support for PET procedures in major markets encourages higher patient throughput. Strategic investments in regional cyclotron networks also improve radiotracer availability, reducing logistical constraints and enabling same-day imaging. Collectively, these advancements reinforce nuclear imaging’s critical role in early detection and treatment planning.
Advancements in Radioisotope Production and Supply Chain Modernization
A major driver of market growth is the modernization of global radioisotope production infrastructure. Many countries are upgrading research reactors and commissioning new cyclotrons to stabilize supply of critical isotopes such as Tc-99m, Lu-177, and F-18. Emerging non-reactor production technologies such as accelerator-driven systems and low-enriched uranium (LEU)–based manufacturing strengthen supply security while meeting non-proliferation standards. These innovations reduce historical dependence on aging reactors and minimize production disruptions. Pharmaceutical companies are also investing in scalable radioligand manufacturing facilities capable of supporting commercial-level therapeutic volumes. Partnerships between isotope suppliers and radiopharmacies improve distribution efficiency, ensuring just-in-time delivery for short-half-life isotopes. As global clinical trials for novel radiotracers expand, production ecosystems become increasingly sophisticated, integrating automated synthesis modules, real-time QC, and GMP-compliant logistics. These supply chain advancements collectively enhance market reliability and enable broader clinical access to high-value diagnostic and therapeutic isotopes.
- For instance, NorthStar Medical Radioisotopes’ FDA-approved RadioGenix® System enables domestic, non-uranium Mo-99 production, helping stabilize Tc-99m supply and reducing reliance on aging research reactors. The company also reports capacity expansions to support multi-curie daily Mo-99 outputs, strengthening U.S. isotope security through LEU-based and accelerator-driven pathways.
Key Trends and Opportunities
Rapid Growth of Theragnostic and Next-Generation Radioligand Platforms
Theranostics has emerged as one of the most transformative trends in nuclear medicine, enabling precise pairing of diagnostic imaging agents with targeted therapeutic isotopes. The success of Ga-68 and Lu-177–based theranostic combinations for prostate and neuroendocrine cancers has paved the way for next-generation radioligands targeting fibroblast activation protein (FAP), CXCR4, HER2, and other tumor-specific receptors. These platforms offer major opportunities for pharmaceutical companies to expand their oncology pipelines with highly selective radiopharmaceuticals. Increasing venture funding and strategic acquisitions indicate strong industry confidence in radioligand innovation. Ongoing advancements in alpha-emitters such as Ac-225 further position theranostics as a high-value oncology frontier. As AI-enabled imaging analytics improve therapy planning and response prediction, the theranostic landscape is expected to evolve rapidly, creating long-term opportunities for developers, manufacturers, and imaging providers.
· For instance, SOFIE’s ⁶⁸Ga-FAPI-46 first-in-human study in 21 patients demonstrated rapid tumor uptake and high lesion-to-background contrast across several solid tumor types, as reported in peer-reviewed findings. Clovis Oncology’s LuMIERE Phase 1 trial confirmed that ¹⁷⁷Lu-FAP-2286 achieved targeted accumulation in FAP-expressing lesions, supporting further development of next-generation theranostic radioligands.
Rising Adoption of Novel Isotopes and AI-Enhanced Imaging Technologies
Opportunities are expanding through the development of novel isotopes with improved targeting specificity, longer half-lives, and enhanced therapeutic efficacy. Isotopes such as Cu-64, Zr-89, and Sc-47 are gaining attention for their versatility across immuno-PET imaging, antibody labeling, and multimodal therapeutic applications. At the same time, AI-enabled imaging platforms significantly improve lesion detection, quantification, and workflow automation. Machine-learning algorithms assist clinicians in distinguishing subtle metabolic abnormalities, reduce interpretation variability, and speed time-to-diagnosis. AI-guided dose optimization and radiotracer scheduling systems enhance operational efficiency in nuclear imaging centers. As radiopharmaceutical research accelerates and health systems digitalize imaging workflows, the integration of new isotopes with machine-learning-driven imaging solutions opens substantial commercial and clinical opportunities.
· For instance, Clarity Pharmaceuticals’ ⁶⁴Cu-SAR-bisPSMA demonstrated high and sustained tumor uptake on next-day imaging in its PROPELLER Phase II study of 30 patients, according to company-reported clinical results. The agent showed clear lesion contrast and supported the use of copper-64 for extended-timepoint PSMA PET imaging.
Key Challenges
Supply Chain Vulnerabilities and Dependence on Limited Production Sources
The nuclear medicine sector continues to face significant supply chain vulnerabilities rooted in limited global production capacity for key isotopes, especially Tc-99m, Lu-177, and I-131. Many production reactors are decades old and prone to outages, creating risks of sudden shortages. The short half-lives of radiotracers demand highly synchronized logistics, increasing the impact of transportation delays, equipment malfunctions, or regulatory bottlenecks. Radioisotope shipping requires strict temperature control, security clearance, and specialized packaging, elevating operational complexity. Emerging markets particularly struggle due to limited regional cyclotrons and high import dependence. These constraints can disrupt imaging schedules, reduce clinical availability, and raise procurement costs, collectively hindering market expansion despite rising demand.
Regulatory Complexity, High Manufacturing Costs, and Skilled Workforce Shortages
Radiopharmaceutical development and commercialization require navigating stringent regulatory frameworks involving radiation safety, GMP compliance, and isotope handling protocols. Approval pathways for new tracers are intensive, requiring dosimetry studies, multi-phase clinical trials, and radiation-exposure assessments. Manufacturing costs are high due to specialized facilities, controlled environments, and continuous QA/QC processes. Many healthcare systems also face shortages of qualified nuclear pharmacists, radiochemists, and medical physicists, limiting operational scalability. Additionally, reimbursement structures in several countries lag behind technological advancement, delaying adoption of innovative tracers. Collectively, these barriers elevate development timelines, restrict market entry, and hinder broader clinical adoption of advanced radiopharmaceutical technologies.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America holds the largest share at approximately 42%, driven by advanced nuclear medicine infrastructure, strong reimbursement frameworks, and high PET-CT and SPECT-CT installation density. The U.S. leads radiopharmaceutical adoption, supported by robust clinical research pipelines in radioligand therapy and expanded cyclotron capacity for F-18 and Ga-68 production. Growth is further fueled by strong FDA activity in approving new tracers and therapeutic isotopes. Canada also contributes through investments in reactor-based isotope production. Strategic collaborations between isotope suppliers, academic centers, and radiopharmacies reinforce the region’s leadership in diagnostic and therapeutic nuclear medicine.
Europe
Europe accounts for around 30% of the global market, supported by established PET and SPECT networks, strong radiopharmaceutical R&D, and widespread adoption of Lu-177 and Ra-223 therapies. Countries such as Germany, France, the U.K., and the Netherlands lead production and clinical use due to long-standing nuclear medicine expertise and regulatory support for radioligand therapy. The region benefits from an advanced reactor ecosystem supplying Tc-99m and therapeutic isotopes to both domestic and export markets. Expansion of theranostics and increased investment in cyclotron facilities continue to strengthen Europe’s competitive positioning.
Asia Pacific
Asia Pacific represents approximately 20% of the market, driven by growing healthcare investments, rising cancer incidence, and rapid expansion of nuclear imaging capacity in China, Japan, South Korea, and India. Increasing installation of PET-CT systems and expanding access to F-18 and Ga-68 tracers strengthen diagnostic utilization. Japan remains a leader in radiopharmaceutical R&D, while China’s accelerated adoption of radioligand therapy boosts demand for Lu-177 and Y-90. National programs supporting domestic isotope production and expanded nuclear medicine training improve regional self-sufficiency and position Asia Pacific for strong long-term growth.
Latin America
Latin America holds nearly 5% of the market, with growth concentrated in Brazil, Mexico, and Argentina. Adoption of PET-CT imaging and FDG-based diagnostics is increasing as governments modernize oncology care infrastructure. However, heavy dependence on imported isotopes and limited radiopharmacy networks constrain wider market penetration. Brazil leads regional production capabilities through research reactor upgrades and expanding cyclotron facilities supporting F-18 supply. As clinical demand for Ga-68 and Lu-177 therapies increases, public–private partnerships and international collaborations play a key role in strengthening regional access to advanced radiopharmaceuticals.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region accounts for approximately 3% of global market share, with growth led by the UAE, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, and Israel. Investments in specialized cancer centers, PET-CT installations, and radiopharmacy facilities are gradually improving access to diagnostic and therapeutic isotopes. Israel remains a technology leader with strong radiopharmaceutical innovation and local production capacity. However, many countries rely on imported isotopes due to limited reactor and cyclotron availability. Continued expansion of nuclear medicine programs and partnerships with global suppliers are expected to enhance regional capability and adoption.
Market Segmentations:
By Type
- Diagnostic Radiopharmaceuticals
- Therapeutic Radiopharmaceuticals
By Product
- Technetium-99m (Tc-99m)
- Iodine-131 (I-131)
- Fluorine-18 (F-18)
- Lutetium-177 (Lu-177)
- Yttrium-90 (Y-90)
- Gallium-68 (Ga-68)
- Radium-223 (Ra-223)
By Services
- Radioisotope Production
- Radiopharmacy Services
- Nuclear Imaging Services
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape of the nuclear medicine and radiopharmaceuticals market is characterized by a mix of established pharmaceutical companies, specialized isotope producers, and rapidly scaling radioligand therapy innovators. Major players such as Novartis, Bayer, Curium, GE HealthCare, and Bracco Imaging maintain strong market positions through diversified diagnostic tracer portfolios, global distribution networks, and leadership in PET and SPECT imaging agents. Novartis continues expanding its radioligand therapy franchise with Lu-177–based therapeutics, while Bayer advances Ra-223 platforms for metastatic prostate cancer. Companies including IBA, NorthStar Medical Radioisotopes, and BWXT Medical strengthen the supply chain through advanced cyclotron systems and non-reactor production technologies to stabilize global isotope availability. Emerging biotech firms are accelerating innovation in next-generation isotopes such as Ac-225 and Ga-68–linked ligands targeting FAP, PSMA, and somatostatin receptors. Strategic collaborations, GMP manufacturing expansions, and long-term supply agreements are key competitive strategies as players work to secure clinical adoption and commercial scale.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
- NorthStar Medical Radioisotopes
- ITM Isotopen Technologien München
- Curium Pharma
- RadioMedix
- Eckert & Ziegler
- Jubilant Radiopharma
- SHINE Medical Technologies
- Isotopia Molecular Imaging
- Nordion
- Advanced Accelerator Applications
Recent Developments
- In November 2025, ITM received U.S. FDA Fast Track Designation for ITM-94 as a diagnostic radiopharmaceutical for clear cell renal cell carcinoma, strengthening its late-stage pipeline in oncology imaging.
- In November 2025, Curium and CapVest completed a recapitalization valuing Curium at about USD 7 billion to accelerate its growth strategy, and earlier that month Curium delivered first commercial PSMA PET diagnostic doses for prostate cancer patients in Czech Republic and Slovakia.
- In November 2024, NorthStar signed an agreement to supply non-carrier-added actinium-225 (Ac-225) to Cellectar Biosciences to support its expanded portfolio of Ac-225–labeled radiopharmaceutical clinical programs, including a Phase 1 pancreatic cancer candidate planned for 2025.
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Type, Product, Services and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- Demand for radioligand therapies will accelerate as more Lu-177 and Ac-225–based agents progress through late-stage clinical trials.
- Theranostics will become a mainstream treatment pathway, expanding beyond prostate and neuroendocrine cancers into breast, colorectal, and glioblastoma applications.
- Novel isotopes such as Cu-64, Zr-89, Sc-47, and FAP-targeted tracers will drive next-generation diagnostic and therapeutic innovation.
- AI-driven imaging analytics will enhance lesion detection, automate workflow processes, and support personalized radiopharmaceutical dosing.
- Global cyclotron and reactor expansions will stabilize isotope supply chains and reduce dependence on legacy production facilities.
- Radiopharmacies will adopt fully automated synthesis and QC systems to improve reliability and regulatory compliance.
- Investment in decentralized production hubs will increase access to short-half-life tracers across emerging markets.
- Regulatory pathways for novel isotopes will streamline as authorities prioritize precision oncology and targeted therapeutics.
- Collaboration between pharma companies, isotope producers, and cancer centers will intensify across theranostic clinical programs.
- Nuclear medicine infrastructure modernization, including new PET-CT and SPECT-CT installations, will expand diagnostic capacity globally.




