Market Overview
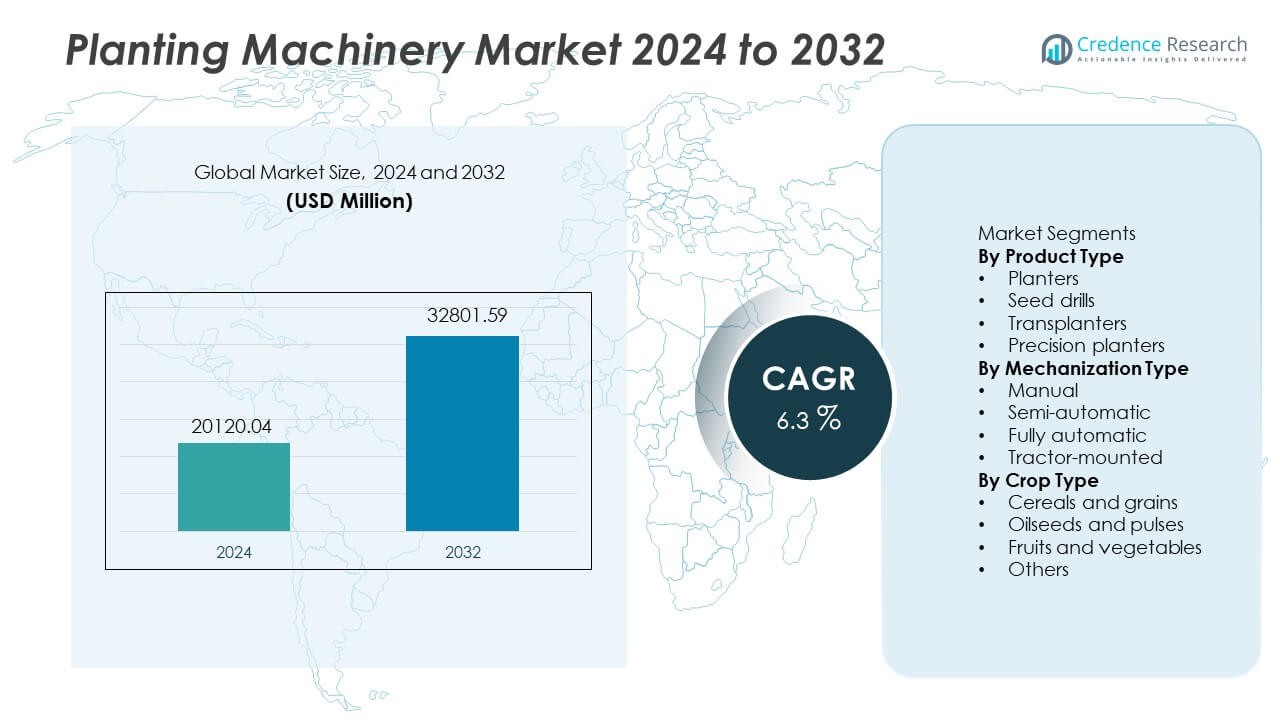
The Planting Machinery Market was valued at USD 20,120.04 million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 32,801.59 million by 2032, registering a CAGR of 6.3% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Planting Machinery Market Size 2024 |
USD 20,120.04 Million |
| Planting Machinery Market, CAGR |
6.3% |
| Planting Machinery Market Size 2032 |
USD 32,801.59 Million |
John Deere, CNH Industrial, AGCO Corporation, Kubota Corporation, CLAAS, Mahindra & Mahindra, Kverneland Group, Great Plains Manufacturing, Yanmar, and Amazone are leading companies in the Planting Machinery market and continue to develop precision planting platforms, advanced metering systems, and digitally monitored equipment to improve field efficiency and seed placement accuracy. These players focus on tractor-mounted and fully automatic planting solutions to support large commercial farms across key agricultural regions. Asia Pacific remains the dominant region with a 33% share due to extensive cereal and rice cultivation, strong government mechanization programs, and wider adoption of high-capacity planting systems across China, India, and Southeast Asia.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Insights
- The Planting Machinery market reached USD 20,120.04 million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 32,801.59 million by 2032 at a CAGR of 6.3.
- Expansion of commercial farming, rising labour shortages, and higher focus on yield improvement drive market adoption, while planters hold a 41% share because they support large cereal and grain cultivation.
- Key trends include precision planting, GPS guidance, automated seed metering, and connected machinery that support sustainable planting and optimize crop output with reduced field labour.
- Competition strengthens as John Deere, CNH Industrial, AGCO, and Kubota deploy precision platforms, fully automatic planters, and localized manufacturing to increase global reach and after-sales support.
- Asia Pacific leads regional demand with a 33% share, followed by North America at 31% and Europe at 28%, while tractor-mounted machinery holds a 54% share due to strong usage in medium and large farms across key producing regions.
 Market Segmentation Analysis:
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Product Type
Planters hold a 41% share of the product segment and remain the dominant machinery due to widespread adoption across commercial farms involved in cereals and row crop cultivation. These machines increase seed placement accuracy, reduce manual labour, and deliver faster field coverage. Seed drills grow as emerging markets adopt mechanized seeding for wheat and pulses. Transplanters gain importance in horticulture and rice farming, while precision planters expand usage in high-value farming due to controlled spacing and digital metering. Planters maintain leadership due to larger farming acreage and rising demand for productivity-enhancing solutions across major agricultural regions.
- For instance, John Deere’s ExactEmerge planter supports high-speed seeding at up to 16 km per hour and uses BrushBelt delivery that places seeds with an accuracy tested across more than 25 different field trials in North America and Europe.
By Mechanization Type
Tractor-mounted machines account for a 54% share of the mechanization segment driven by strong use in medium to large-scale farming, especially for cereals and oilseeds. Tractor-mounted platforms integrate easily with existing farm equipment and deliver high field efficiency. Fully automatic systems expand due to precision planting and reduction of labour dependency. Semi-automatic systems remain relevant for mid-sized farms, while manual tools continue in smallholder agriculture across developing countries. Tractor-mounted machinery dominates as farmers seek higher productivity and consistent planting performance across varied soil conditions.
- For instance, CNH Industrial’s Precision Disk 500T attaches directly to tractors and covers a wide working width in one pass, while Kubota’s tractor-mounted rice transplanters place seedlings efficiently, which was confirmed in various field testing publications.
By Crop Type
Cereals and grains command a 59% share of the crop segment because global wheat, corn, and rice cultivation require high-capacity planting machinery and timely sowing cycles. Increasing food demand and population growth promote mechanization in cereal-producing regions, especially in Asia and Africa. Oilseeds and pulses expand through growing soybean production and rising demand for plant-based protein crops. Fruits and vegetables adopt precision machinery for controlled planting in horticulture. Cereals remain dominant due to large cultivation areas, government support for staple crops, and continuous adoption of mechanized planting systems.
Key Growth Drivers
Rising Mechanization and Declining Farm Labour Availability
Growing labour shortages and higher rural wages push farms to shift from manual planting to mechanized equipment that supports faster field operations and higher productivity. Farmers adopt planters and transplanters to ensure uniform sowing and reduced time pressure during peak seasons. Commercial agriculture grows in developing countries as governments invest in modernization programs, credit access, and equipment subsidies. Mechanization becomes essential for larger farms focused on higher output and improved crop uniformity.
- For instance, Mahindra & Mahindra’s MP461 rice transplanter helps cover a significant area each day and reduces manual labor steps by using a wide feeder belt system and an H-fork and push rod double-action planting arrangement, ensuring uniform planting of paddy saplings.
Increasing Demand for Higher Crop Yields
Global food demand continues to rise due to population growth and expanding consumption of cereals and oilseeds. Precision planters and automated machinery provide better seed spacing, deeper placement, and improved soil contact that boost germination and yield performance. Improved planting efficiency reduces crop losses and increases seed utilization efficiency across large plantations. Farmers adopt modern machinery to achieve large-scale output and enhance return on investment through higher crop productivity.
- For instance, CLAAS precision sowing units can contribute to an increased yield in maize trials conducted by the German Agricultural Society (DLG), supported by electronic depth control and seed drop monitoring across multiple rows.
Government Initiatives Supporting Modern Agriculture
Many countries offer subsidy programs, low-interest loans, and agricultural technology missions to encourage purchase of planting machinery. Governments promote farm mechanization for staple crops under food security programs and sustainability frameworks. Policies support adoption of planting systems for rice, wheat, and oilseeds to reduce dependency on manual planting. These initiatives expand technology penetration across rural agriculture and drive long-term modernization.
Key Trends and Opportunities
Expansion of Precision Agriculture and Digital Equipment
Planters and precision machinery equipped with GPS, IoT sensors, and variable rate controls support accurate seed placement and real-time field monitoring. Digital systems improve decision making, reduce input waste, and support automated sowing. Farmers adopt smart platforms for analysing soil data, optimizing seed depth, and tracking crop growth patterns. These systems open opportunities for advanced machinery sales and digital service platforms for large farms.
- For instance, John Deere’s StarFire RTK guidance delivers pass-to-pass accuracy and supports variable-rate seed control. The system provides highly accurate and repeatable corrections, allowing for tighter guidance, less overlap, and improved efficiency.
Growth in Controlled Farming and High-Value Crops
Rising adoption of horticulture and greenhouse farming increases use of transplanters and precision planters for fruits and vegetables. Farmers shift to high-value crops to improve farm income and reduce reliance on staple cereals. Controlled environment agriculture uses automated systems for seed placement and plant spacing. These trends unlock opportunities for specialized machinery designed for horticulture and intensive farming models.
- For instance, Kubota’s NSPU-68C rice transplanter efficiently places many seedlings across multiple rows and has been used in various field tests for uniform spacing and general operational evaluation.
Key Challenges
High Initial Cost and Limited Smallholder Access
Planting machinery requires high capital investment, especially fully automatic and precision systems, which limits use by small farmers. Financing challenges, high maintenance cost, and parts replacement expenses create adoption barriers in developing regions. Lack of affordable financing reduces purchase ability for small farms. These constraints slow adoption of advanced machinery.
Limited Training and Operational Skills
Advanced planting systems require technical knowledge to adjust seed spacing, calibrate meters, and maintain sensors. Limited training infrastructure and technical support in rural regions restricts efficient usage. Farmers who lack operational skills face breakdown risks and underutilization of machinery, reducing expected returns and slowing market penetration across developing agricultural zones.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America holds a 31% share of the Planting Machinery market supported by large commercial farms, advanced mechanization, and continuous investment in precision planting. The United States leads due to high adoption of GPS-enabled planters and strong focus on large cereal production. Canada expands mechanized planting in grains and oilseeds through modern agriculture programs. Farmers adopt automated machinery to reduce labour and increase planting efficiency. Rising demand for variable rate systems and real-time monitoring strengthens regional adoption. Continuous upgrades to planting systems and strong dealer networks drive further market expansion across major farming states.
Europe
Europe accounts for a 28% share driven by sustainable farming policies, advanced agricultural technology, and strong demand for precision planters. Germany, France, and Italy invest in automated planting systems to improve crop output and comply with sustainability targets. EU regulations encourage lower seed wastage, soil protection, and efficient planting models. Farmers use digital technologies and connected machinery for real-time planting control. Growth in oilseed production supports modern planters, while investments in smart farming drive mechanization. Continuous research and equipment innovation support long-term market adoption.
Asia Pacific
Asia Pacific holds a 33% share due to extensive cereal and rice cultivation across China, India, and Southeast Asia. Governments offer subsidies, credit programs, and farm modernization incentives to support mechanized planting. Rice, wheat, and corn farming across large fields requires high-capacity planting machinery. Rising labour shortages and increasing food security concerns drive adoption of automated planters. Local manufacturers strengthen supply of cost-efficient machines across regional markets. Growing commercial agriculture, especially in China and India, supports long-term market expansion across rural Asia.
Latin America
Latin America holds a 5% share supported by growing soybean and corn cultivation across Brazil and Argentina. Commercial farms adopt precision planters and tractor-mounted equipment to improve planting quality and reduce manual labour. Export-oriented agriculture encourages investment in high-capacity planting machinery. Mechanization grows as governments provide financing for farm upgrades. Farmers adopt automated machines to achieve higher productivity in large farmlands. Regional agribusiness strategies support wider uptake of planting systems in export-focused crops. Rising soil management awareness influences machinery selection across farming regions.
Middle East and Africa
The Middle East and Africa represent a 3% share driven by gradual mechanization and expanding food security programs. Farming in arid and semi-arid areas requires advanced machinery for cereals and grain cultivation. Government initiatives encourage mechanization to reduce import dependence on staple crops. International partnerships and equipment imports support exposure to advanced planting machinery. Labour shortages and increasing cost of manual farming increase adoption of automated systems. Water management concerns drive interest in precision planting solutions that maximize crop productivity across challenging climates.
Market Segmentations:
By Product Type
- Planters
- Seed drills
- Transplanters
- Precision planters
By Mechanization Type
- Manual
- Semi-automatic
- Fully automatic
- Tractor-mounted
By Crop Type
- Cereals and grains
- Oilseeds and pulses
- Fruits and vegetables
- Others
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
John Deere, CNH Industrial, AGCO Corporation, Kubota Corporation, CLAAS, Mahindra & Mahindra, Kverneland Group, Great Plains Manufacturing, Yanmar, and Amazone lead the Planting Machinery market and continue to expand portfolios across planters, transplanters, and precision seeding systems. These companies focus on precision agriculture solutions such as GPS guidance, seed metering, and real-time data tracking that support higher planting accuracy and reduced input wastage. Manufacturers expand regional presence through dealership networks and localized production facilities to serve large farming zones in Asia and North America. Investments in fully automatic planters and advanced sensors strengthen product competitiveness. Companies also collaborate with agritech firms to develop digital platforms that support smart planting decisions and predictive maintenance. Competition increases as regional manufacturers introduce cost-effective machinery tailored for small and mid-sized farms.
Key Player Analysis
- John Deere
- CNH Industrial
- AGCO Corporation
- Kubota Corporation
- CLAAS
- Mahindra & Mahindra
- Kverneland Group
- Great Plains Manufacturing
- Yanmar
- Amazone
Recent Developments
- In November 2025, CNH Industrial highlighted advances in farming innovations – robotics, automation and AI at its “2025 Tech Day,” underlining push toward smart agriculture.
- In September 2025, CNH Industrial, under its New Holland brand, announced plans to build a new and larger tractor manufacturing plant in India.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Product Type, Mechanization Type, Crop Type and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- Precision planters will expand with GPS and real-time soil monitoring.
- Fully automatic systems will gain adoption among large commercial farms.
- Transplanters will grow in horticulture and protected agriculture settings.
- Digital platforms will guide seed depth, spacing, and planting decisions.
- Variable rate planting will improve seed utilization and yield performance.
- Sensor-based systems will support sustainable farming and soil care.
- Government subsidies will continue supporting modernization in developing regions.
- Localized manufacturing will strengthen machinery access in rural markets.
- Robotics and autonomous planters will emerge in advanced farm operations.
- Data-driven planting models will support predictable output and reduced planting risk.

 Market Segmentation Analysis:
Market Segmentation Analysis:

