Market Overview
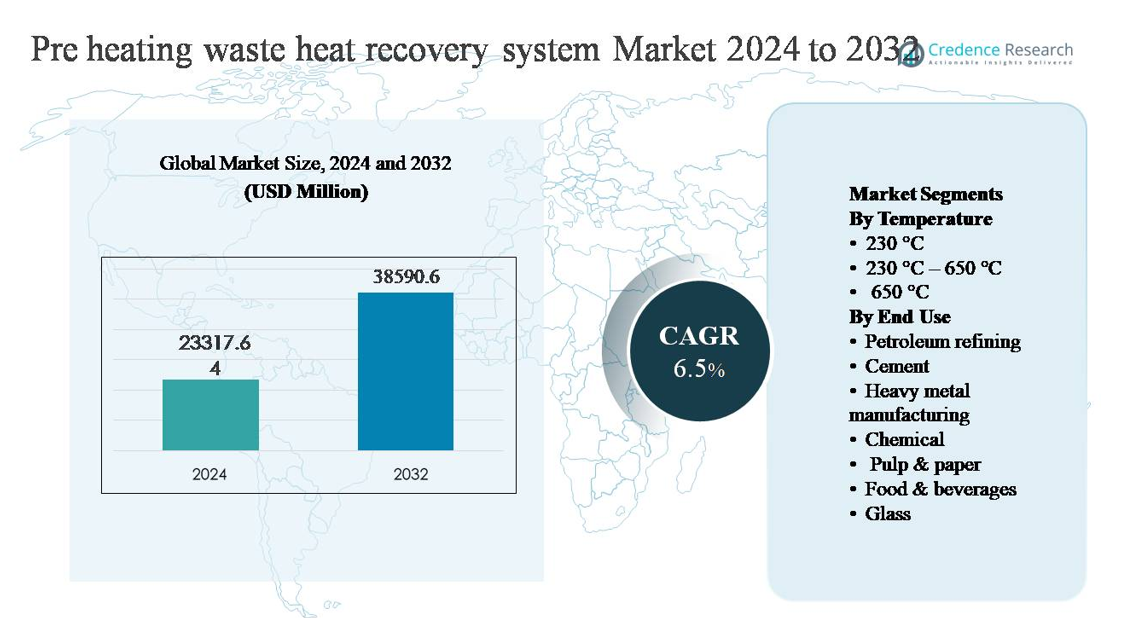
The pre-heating waste heat recovery system market was valued at USD 23,317.64 million in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 38,590.6 million by 2032, expanding at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.5% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Pre-Heating Waste Heat Recovery System Market Size 2024 |
USD 23,317.64 million |
| Pre-Heating Waste Heat Recovery System Market, CAGR |
6.5% |
| Pre-Heating Waste Heat Recovery System Market Size 2032 |
USD 38,590.6 million |
The pre-heating waste heat recovery system market is led by a group of established engineering and thermal solution providers, including General Electric, Dürr Group, Bosch Industriekessel GmbH, EXERGY INTERNATIONAL SRL, Forbes Marshall, Climeon, HRS, Cochran, AURA, and BIHL. These companies compete on system efficiency, high-temperature capability, and project execution across energy-intensive industries such as petroleum refining, cement, metals, and chemicals. Strong EPC experience, advanced heat exchanger design, and lifecycle service support remain key competitive differentiators. Asia Pacific is the leading region, accounting for approximately 42% of the global market share, driven by large-scale industrial capacity in China, India, and Southeast Asia, alongside rising energy efficiency mandates and continuous investments in new and retrofit industrial facilities.
Market Insights
- The pre-heating waste heat recovery system market was valued at USD 23,317.64 million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 38,590.6 million by 2032, expanding at a CAGR of 6.5%, supported by rising deployment across energy-intensive industries and increasing focus on thermal efficiency improvements.
- Market growth is primarily driven by rising industrial energy costs, stricter efficiency mandates, and decarbonization targets, with the 230 °C–650 °C temperature segment holding the dominant share due to its wide applicability across cement, metals, and refining processes.
- Key trends include integration of waste heat recovery with digital process controls, growing adoption in medium-scale industries, and increased preference for modular systems, while petroleum refining remains the largest end-use segment by share.
- The competitive landscape features global engineering and thermal solution providers competing on system efficiency, high-temperature capability, retrofit expertise, and lifecycle service support, with differentiation increasingly based on operational reliability and integration capabilities.
- Regionally, Asia Pacific leads with about 42% market share, followed by Europe at ~26% and North America at ~19%, while Latin America and the Middle East & Africa together account for the remaining share, driven by cement, mining, refining, and heavy industrial activity.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Temperature:
The pre-heating waste heat recovery system market, by temperature, is led by the 230 °C–650 °C segment, which accounts for the largest market share, as this range aligns with exhaust and flue gas temperatures across most continuous industrial processes. Industries favor this segment due to its compatibility with recuperators, regenerators, and economizers that deliver high thermal recovery without complex materials. Key drivers include strong energy efficiency gains, manageable corrosion risks, and cost-effective system design. While systems below 230 °C serve low-grade heat recovery, and >650 °C cater to niche high-temperature applications, mid-range systems remain dominant due to scalability and operational reliability.
- For instance, Dürr Group’s ECO NT regenerative thermal oxidizer platforms are engineered to recover waste heat from exhaust streams entering at approximately 300 °C–600 °C, using stainless-steel plate heat exchangers rated for continuous operation at 650 °C and enabling downstream hot-water or thermal-oil outputs up to 4 MW per unit for process pre-heating.
By End Use:
By end use, petroleum refining represents the dominant sub-segment, holding the highest market share owing to energy-intensive operations such as distillation, cracking, and reforming, which generate large volumes of recoverable waste heat. Refiners deploy pre-heating systems to reduce fuel consumption in furnaces and boilers, driving rapid payback. Cement and heavy metal manufacturing follow, supported by kiln and furnace exhaust recovery. Growth across chemical, pulp & paper, glass, and food & beverages is driven by rising energy costs, decarbonization targets, and regulatory pressure to improve overall thermal efficiency.
- For instance,ExxonMobil installed a waste heat recovery system at its Antwerp refinery designed to capture heat and reuse it to preheat crude feed streams, directly reducing furnace firing rates and improving overall energy efficiency.
Key Growth Drivers
Rising Industrial Energy Costs and Efficiency Mandates
Escalating energy prices across fossil fuels and electricity are compelling industrial operators to prioritize energy efficiency investments, positioning pre-heating waste heat recovery systems as a high-impact solution. Energy-intensive sectors such as petroleum refining, cement, metals, and chemicals face sustained pressure to lower operating costs while maintaining throughput. Pre-heating systems directly reduce primary fuel consumption by capturing exhaust heat and reusing it in upstream processes, improving overall thermal efficiency. Regulatory frameworks promoting energy audits and efficiency benchmarks further reinforce adoption, particularly in large continuous-process facilities. As industries seek predictable returns on capital, waste heat recovery offers measurable fuel savings, short payback periods, and reduced dependence on volatile energy markets, making it a strategic investment rather than a discretionary upgrade.
- For instance, Honeywell UOP has documented refinery furnace convection section upgrades in which flue gas streams entering at approximately 420 °C are routed through high-surface-area finned tube banks to preheat crude or process feedstocks by more than 100 °C, directly reducing burner firing rates measured in several megawatts per heater.
Decarbonization Targets and Emissions Reduction Requirements
Industrial decarbonization goals are a major growth driver for pre-heating waste heat recovery systems, as manufacturers pursue lower greenhouse gas emissions without disrupting core production. Recovering waste heat reduces combustion requirements in boilers and furnaces, directly cutting carbon dioxide and nitrogen oxide emissions. Governments and industry bodies increasingly link emissions performance to operating permits, incentives, and long-term competitiveness. Pre-heating systems enable compliance by delivering emissions reduction through efficiency rather than fuel switching, which often requires deeper process changes. For multinational manufacturers with science-based targets, waste heat recovery supports immediate Scope 1 emissions reduction while aligning with corporate sustainability commitments and environmental reporting frameworks.
- For instance, ArcelorMittal has reported the deployment of waste heat recovery units on steel reheating furnaces, where flue-gas heat at temperatures exceeding 500 °C is captured via metallic recuperators to preheat combustion air to above 450 °C, lowering furnace fuel demand while maintaining slab throughput
Expansion of High-Temperature Industrial Capacity
Ongoing expansion of cement plants, metal smelters, glass furnaces, and refinery units is driving demand for pre-heating waste heat recovery systems integrated at the design stage. New facilities increasingly incorporate heat recovery as a standard component to optimize energy balances from commissioning. In emerging economies, rapid industrialization combined with tightening efficiency norms encourages adoption of pre-heating solutions to control long-term operating costs. Retrofitting older plants also contributes to growth, as operators modernize equipment to extend asset life. The ability of pre-heating systems to scale with production capacity and integrate with existing thermal processes makes them a preferred solution during both greenfield and brownfield expansions.
Key Trends & Opportunities
Integration with Advanced Process Control and Digital Monitoring
A key trend shaping the market is the integration of pre-heating waste heat recovery systems with advanced process control and digital monitoring platforms. Real-time temperature, flow, and pressure data enable operators to optimize heat capture and transfer efficiency under variable operating conditions. Predictive analytics improve maintenance planning, reducing downtime and performance degradation. This digitalization trend enhances system reliability and improves return on investment, creating opportunities for suppliers offering smart, sensor-enabled solutions. As industries move toward connected and automated plants, digitally integrated waste heat recovery systems gain preference in capital investment decisions.
- For instance, Valmet’s Industrial Internet platform, applied to recovery boiler heat recovery systems in pulp and paper mills, aggregates temperature and flow data from multiple heat exchangers and applies machine-learning models to predict corrosion and fouling risks in flue-gas heat recovery sections.
Growing Adoption in Medium-Scale and Diverse Industries
Beyond heavy industries, medium-scale sectors such as food & beverages, pulp & paper, and specialty chemicals are increasingly adopting pre-heating waste heat recovery systems. Improvements in modular design and corrosion-resistant materials enable deployment in lower-temperature and process-sensitive environments. This broadens the addressable market and creates opportunities for customized systems tailored to specific production lines. Rising awareness of energy optimization across smaller facilities, combined with stricter environmental standards, supports steady adoption outside traditional heavy industrial users.
- “For instance, Alfa Laval has documented the use of its Compabloc™ welded plate heat exchangers in food and beverage plants to recover waste heat from exhaust streams entering at approximately 180 °C-250 °C, using fully welded stainless-steel plates rated for high pressure and clean-in-place operation.”
Key Challenges
High Capital Investment and Retrofit Complexity
High upfront capital costs remain a significant challenge, particularly for retrofitting existing plants with pre-heating waste heat recovery systems. Installation often requires process downtime, structural modifications, and integration with legacy equipment, increasing project complexity and financial risk. Smaller operators may struggle to justify investment despite long-term savings, especially when production schedules are tight. Engineering challenges related to space constraints and system customization further limit adoption in older facilities, slowing market penetration in retrofit-heavy regions.
Operational Reliability and Material Degradation Risks
Maintaining long-term operational reliability presents another key challenge, especially in high-temperature and corrosive environments. Exhaust streams containing particulates, sulfur compounds, or moisture can cause fouling, corrosion, and thermal stress, reducing system efficiency over time. Selecting appropriate materials and ensuring regular maintenance increases lifecycle costs and technical complexity. Inconsistent performance or unplanned shutdowns may deter risk-averse operators, highlighting the need for robust design, advanced materials, and skilled operation to sustain system effectiveness.
Regional Analysis
Asia Pacific
Asia Pacific dominates the pre-heating waste heat recovery system market, accounting for approximately 42% of global market share. The region’s leadership is driven by extensive industrial capacity in cement, metals, chemicals, and petroleum refining across China, India, Japan, and Southeast Asia. Rapid industrialization, rising energy costs, and government-led efficiency mandates strongly support adoption. New plant construction increasingly integrates waste heat recovery at the design stage, while aging industrial infrastructure fuels retrofit demand. Strong capital expenditure in heavy industries and expanding manufacturing output continue to reinforce Asia Pacific’s position as the primary growth engine for the market.
Europe
Europe holds around 26% of the global market share, supported by stringent energy efficiency regulations and aggressive decarbonization targets. Industries across Germany, France, Italy, and the Nordics actively deploy pre-heating waste heat recovery systems to meet emissions reduction requirements while maintaining industrial competitiveness. High penetration is observed in cement, glass, and chemical manufacturing, where thermal efficiency improvements directly support compliance. The region also benefits from advanced engineering capabilities and strong adoption of digitalized heat recovery solutions. Retrofit projects dominate demand, as European industries modernize legacy plants to extend asset life and reduce carbon intensity.
North America
North America represents approximately 19% of the global pre-heating waste heat recovery system market. Demand is driven by petroleum refining, chemicals, and heavy metal manufacturing in the United States and Canada. Operators increasingly invest in waste heat recovery to offset fuel price volatility and meet internal sustainability goals. While regulatory pressure is moderate compared to Europe, corporate-led efficiency initiatives and ESG commitments play a key role. Retrofit installations are common across mature industrial facilities, while selective greenfield investments integrate pre-heating systems to improve long-term operating economics and reduce energy consumption.
Latin America
Latin America accounts for about 7% of the global market share, with growth centered on Brazil, Mexico, and Chile. The region’s cement, mining, and metals industries generate substantial recoverable waste heat, creating steady demand for pre-heating systems. Rising fuel costs and increasing focus on operational efficiency are key adoption drivers. However, investment pace remains uneven due to capital constraints and economic volatility. As industrial modernization accelerates and energy efficiency programs expand, waste heat recovery adoption is expected to strengthen, particularly in export-oriented and energy-intensive facilities.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region holds roughly 6% of the global market share, driven primarily by petroleum refining, petrochemicals, and metals production. High-temperature industrial processes generate significant waste heat, making pre-heating systems attractive for fuel savings and emissions reduction. Gulf countries lead adoption due to large-scale refining and chemical capacity, while Africa shows emerging demand in cement and metals. Although adoption is constrained by limited retrofit activity in some markets, long-term industrial diversification and energy optimization initiatives support gradual growth across the region.
Market Segmentations:
By Temperature
- 230 °C
- 230 °C – 650 °C
- 650 °C
By End Use
- Petroleum refining
- Cement
- Heavy metal manufacturing
- Chemical
- Pulp & paper
- Food & beverages
- Glass
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape of the pre-heating waste heat recovery system market is characterized by the presence of global engineering firms and specialized thermal solution providers competing on efficiency, customization, and project execution capabilities. Leading players leverage strong expertise in heat exchanger design, materials engineering, and system integration to serve energy-intensive industries such as petroleum refining, cement, metals, and chemicals. Competition increasingly centers on delivering high thermal recovery efficiency, reliable operation in high-temperature and corrosive environments, and seamless integration with existing process infrastructure. Companies with established EPC capabilities and long-term service offerings maintain an advantage by supporting complex retrofit projects and large-scale installations. Strategic focus areas include expanding regional footprints, enhancing digital monitoring capabilities, and developing advanced materials to improve system durability. As industrial customers prioritize energy optimization and emissions reduction, competitive differentiation increasingly depends on proven performance, lifecycle support, and the ability to deliver measurable operational cost savings.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
Recent Developments
- In Sep 10 2025, HRS highlighted its heat exchanger systems’ efficiency for waste heat recovery in wastewater treatment and anaerobic digestion, noting up to ~40 % thermal energy reuse potential in such systems.
- In June 2025, Climeon showcased its ORC industrial waste heat recovery solution at the NEO Group event, demonstrating the value of its HeatPower systems for capturing and converting industrial waste heat into usable energy.
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Temperature, End-Use and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- Adoption will increase as industries prioritize energy efficiency to offset rising fuel and electricity costs.
- Integration of waste heat recovery at the design stage will become standard in new industrial plants.
- Retrofit demand will grow steadily as operators modernize aging facilities to improve thermal performance.
- High-temperature applications will see wider deployment with advances in materials and system durability.
- Digital monitoring and automation will enhance system reliability and optimize heat recovery efficiency.
- Cement, metals, and petroleum refining will remain the primary demand-generating industries.
- Medium-scale industries will increasingly adopt modular and customized pre-heating solutions.
- Decarbonization targets will reinforce long-term investment in waste heat recovery technologies.
- Collaboration between EPC firms and technology providers will strengthen project execution capabilities.
- Emerging economies will drive incremental growth through industrial expansion and efficiency mandates.




